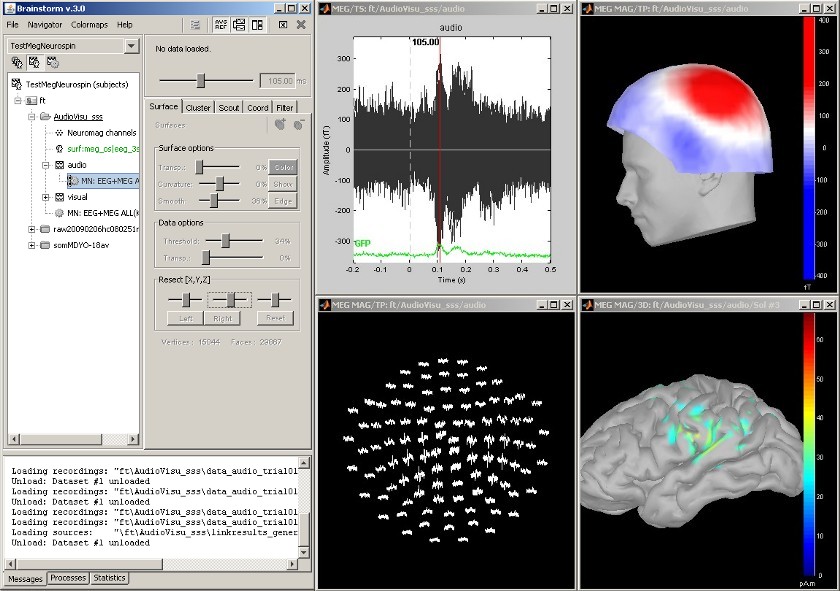
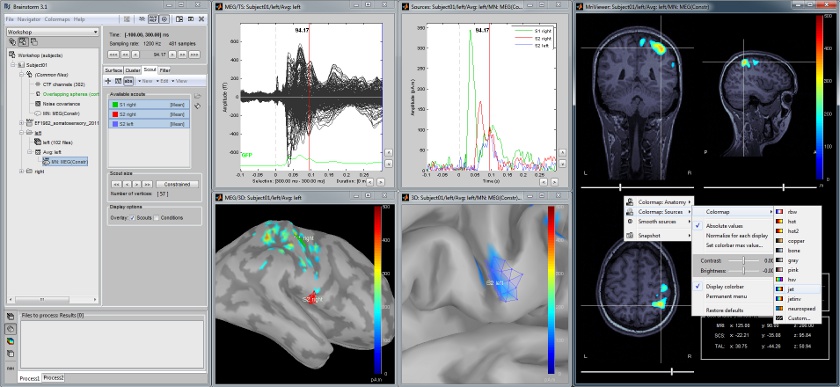
Screenshots
Featuring MEG auditory evoked responses
Acquisition on an Elekta Neuromag Vectorview306, instrument.
Brief description of the following pictures:
- Main Brainstorm window
- Time series of all MEG sensors [-200, 500] ms
- Magnetic field topographty, magnetometers at t=106ms
- Topographical layout of magnetometers time series [-200, 500] ms
- Modeling of cortical currents, obtained from magnetometers, at t=106ms
Keeping your data organized and accessible
The tree in the main Brainstorm window represents the database for the selected study. This database has three levels of definition: Protocol (ie. study, selected in the toolbar), Subject, and Condition. Most of the operations that can be performed on a file are easily accessible from the popup menu revealed by right-clicking over the file.
The first three buttons in the toolbar allows the user to switch between different views of the same database:
- Anatomy: display the MRI and surfaces for each participant in the study
- Functional data (sorted by subject): sensor definitions, MEG and EEG data, source models, statistic and time-frequency maps
- Functional data (sorted by condition): same as above, but sorted in a different way
The following example features a MEG+EEG protocol called "Catching", sorted by conditions. There are two experimental conditions, Catch and NoCatch, and 7 subjects per condition. The popup menu shows all the actions that are available for the recordings of subject cc, condition Catch.
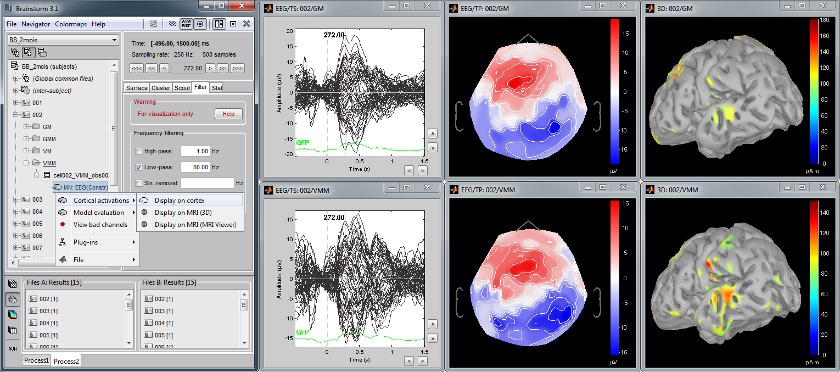
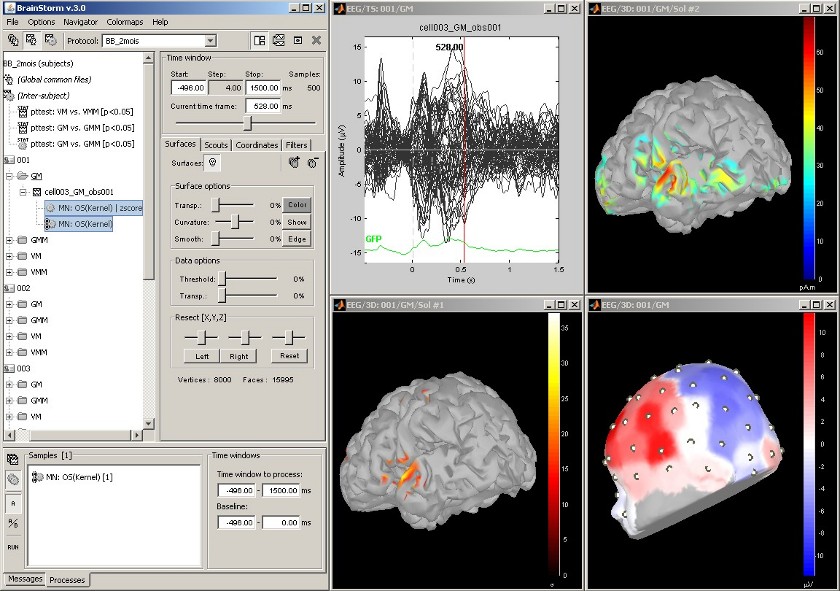
Multiple conditions: Baby auditory EEG responses
Acquisition system: EGI GSN - Baby 64 electrodes
Description:
- One subject: "001"
- Three conditions: "GM", "GMM", "VM"
- Two views: overlaid electrodes time series, and estimated cortical sources at t=376ms
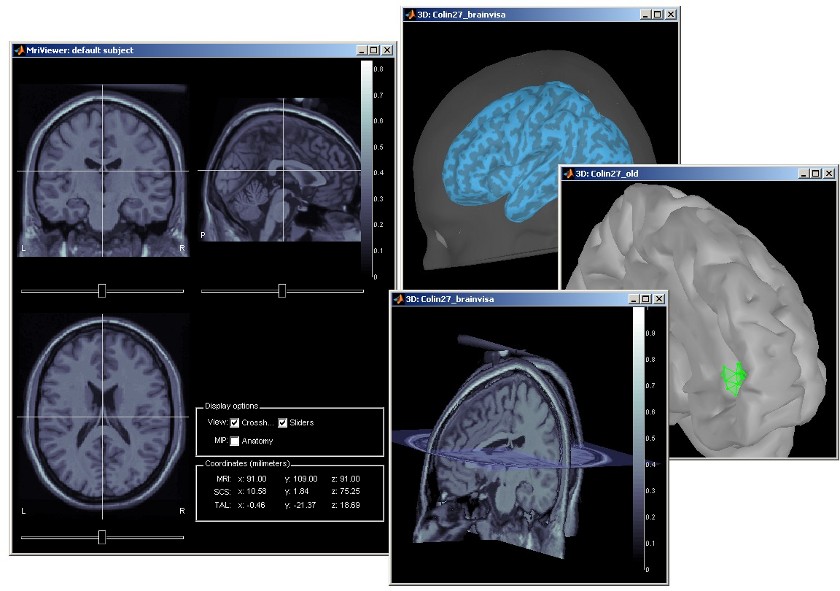
Subject anatomy: MRI and surfaces
Brainstorm features the possibility to model MEG and EEG neural generators either from the individual subject anatomy, or by using a template anatomy (MNI / Colin27) that can be warped to the individual scalp surface. Multiple interactive tools are available to view, register and process the MR images and the corresponding tessellated envelopes. However, tissue segmentation must be performed using another software; multiple options exist today in the academic community (?listed here).
We provide a few examples of the views you can easily obtain with Brainstorm. All the 3D views can be rotated freely with the mouse, zoomed with the wheel, edited with the "Surface panel" and contextual popup menus. The MRI slices can be browsed with a simple mouse operation: right-click and mouse drag.
Channel selection
All the figures displayed by Brainstorm are linked in time. If they feature the same dataset, the sensor selection is also the same for all views. The selection of a channel subset can be easily perfomed by clicking on the corresponding channels in a time series display or a 3D view. Selected channels can be displayed separately, marked as "bad", or deleted.
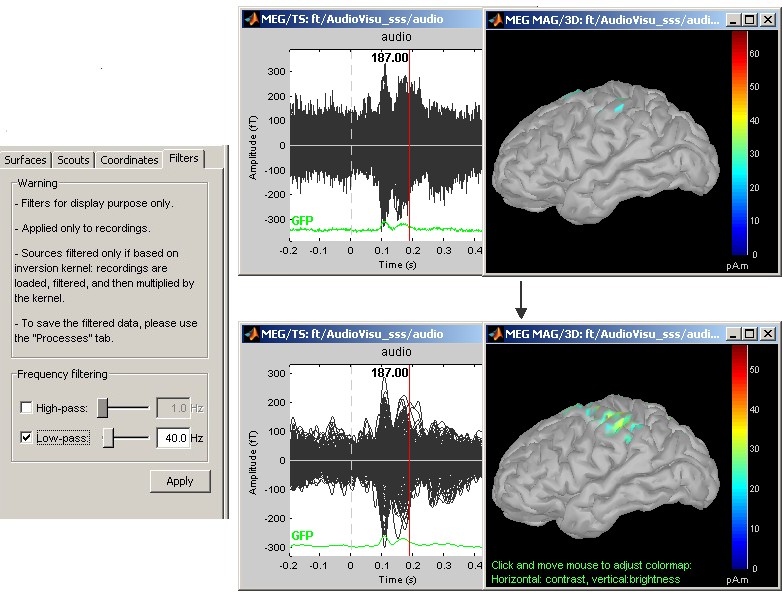
Online bandpass filtering
Recordings and sources: 40Hz low-pass filtering with the "Filters" tab in main Brainstorm window.
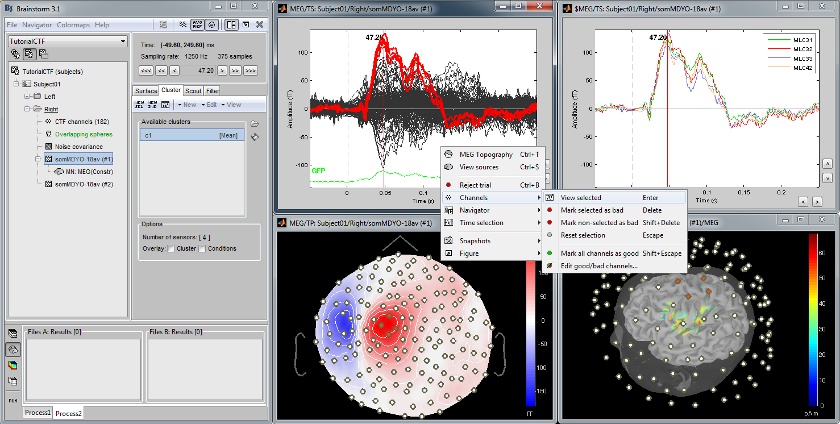
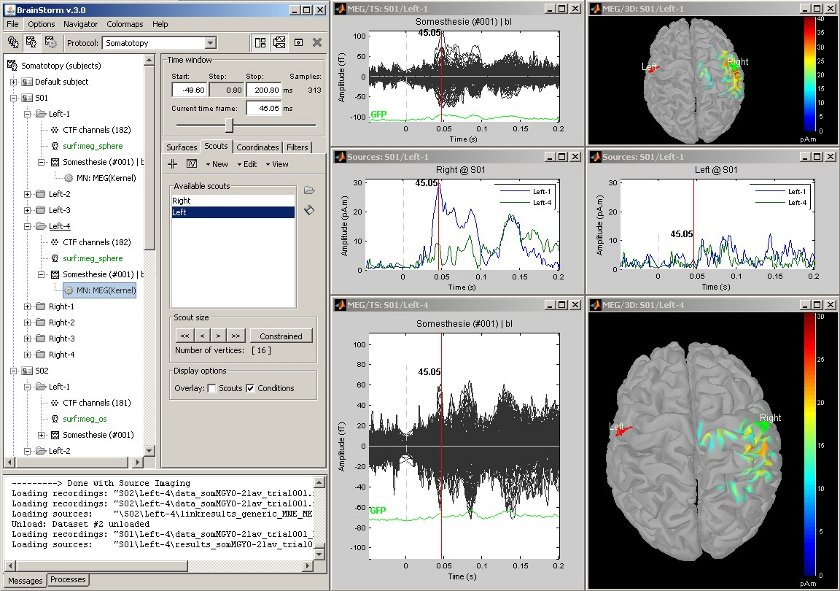
Defining cortical region of interest: Scout
Acquisition system: CTF MEG - 151 sensors
The scouts are subsets of the cortical vertices, defined graphically with the "Scouts" tab. They are useful to extract the time series of a the electrical activity of one or several brain regions.
This example shows the cortical response to an electric stimulation of the left index finger. With the two scouts Left and Right we can observe the electrical activity in the primary somatosensory cortex in both hemispheres.
Scouts: multiple conditions
Acquisition system: CTF MEG - 151 sensors
Same experiment than the previous example, but showing at the same time the responses for condition Left-1 (electric stimulation of the left index) and Left-4 (left ring finger).
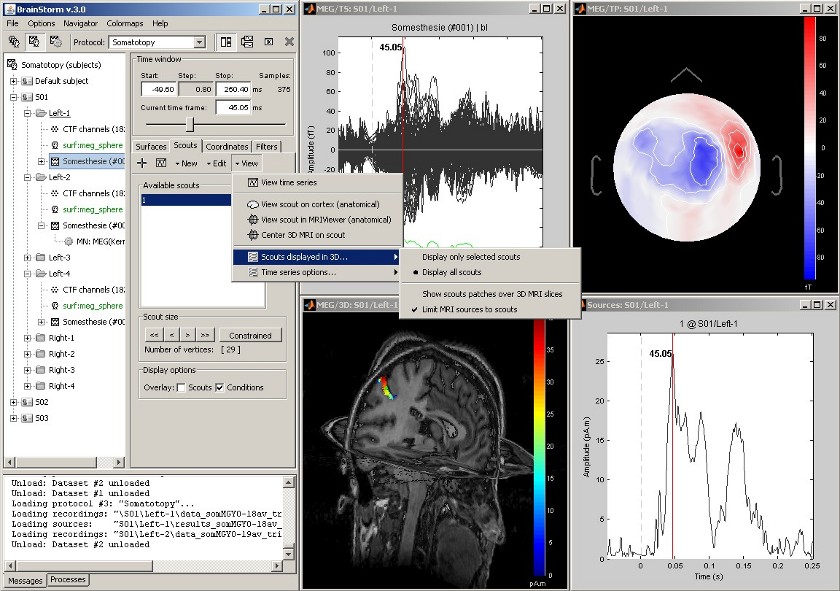
View cortical sources in MRI
Acquisition system: CTF MEG - 151 sensors
Same experiment, with additional display of the scout activity on the 3D MRI slices.
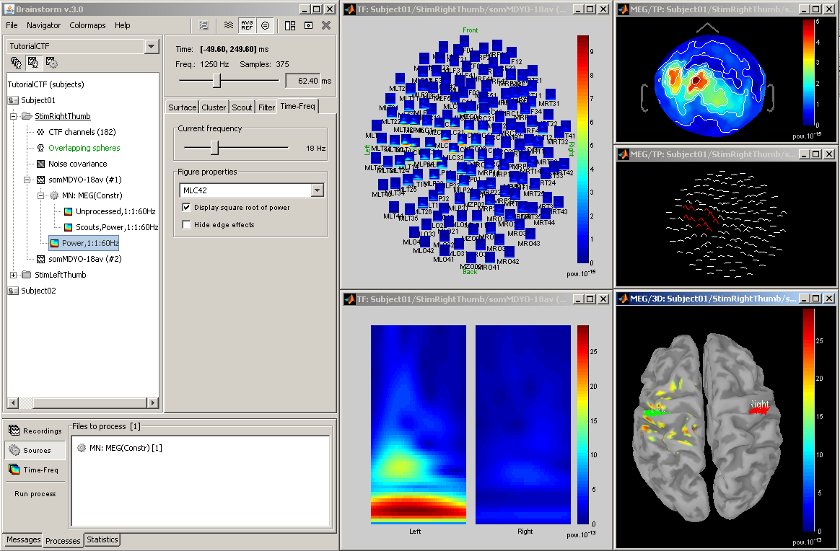
Time-frequency
Acquisition system: CTF MEG - 151 sensors
Time-frequency decompositions at the sensor or the source level, on small regions of interest or in full resolution.
Statistical analysis: z-score
Acquisition system: EGI GSN - Baby 64 electrodes
The "Processes" tab in the main Brainstorm window allows the user to apply several functions to a set of recordings of sources files. Drag and drop files from the database tree to the white box in the "Processes" tab, and click on "Run" to process them.
The function that was applied here is a z-score statistic. The algorithm is the following.
For each channel:
Compute the mean m and the variance v for the baseline
For all the time samples: substract m and divide by v
The top-right figure represents the initial sources estimate, and the bottom-left figure shows the z-score values for those sources.
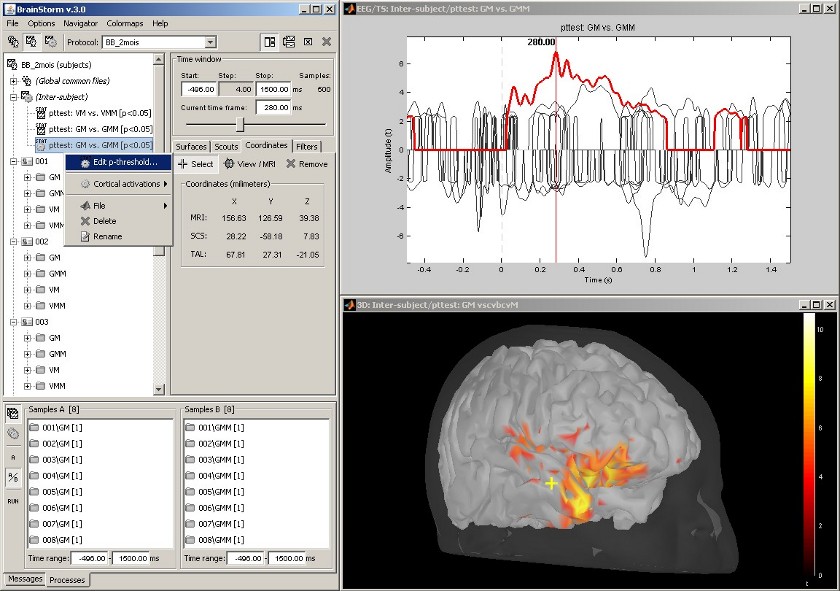
Statistical analysis: t-test
Acquisition system: EGI GSN - Baby 64 electrodes
The "Processes" tab can also be used for computing statistical tests, to evaluate the differences between two experimental conditions.
This example shows the evaluation of the difference between conditions GM and GMM, using the results of many different subjects (paired Student t-test, p<0.05). The top figure represents the significance of the difference at the electrodes level across the time, and the bottom figure the thresholded t-values at the cortical level at 280ms.
This image also illustrates the "Coordinates" tab. It is possible to pick any point from any surface by clicking on it, and immediately get its coordinates in all the coordinates systems used by Brainstorm (MRI, Subject's head and Talairach).