Tutorial 16: Average response
Authors: Francois Tadel, Elizabeth Bock, Sylvain Baillet
All the epochs we have imported in the previous tutorial are represented by matrices that have the same size (same number of channels, same number of time points), therefore they can be averaged together by experimental condition. The result is called indifferently "evoked response", "average response", "event-related field" in MEG (ERF) or "event-related potential" in EEG (ERP). It shows the components of the brain signals that are strictly time-locked to the presentation of a stimulus.
Average trials separately
We will now compute the average responses for both the "standard" and "deviant" conditions, for each acquisition run separately. Note that in MEG, it is not recommended to average across acquisition runs which correspond to different head positions (ie. different "channel files"). If the head of the subject moved between two blocks of recordings, one sensor does not record the same part of the brain before and after, therefore the runs cannot be compared directly.
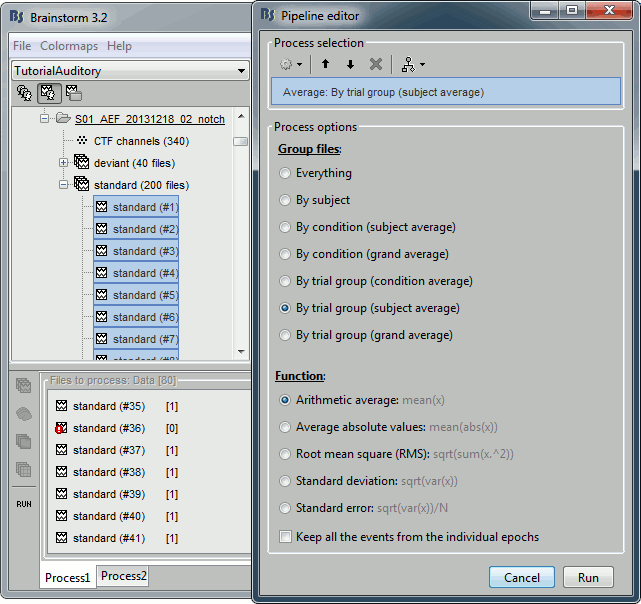
Drag and drop all the "standard" and "deviant" trials for both runs in Process1.
Select the process "Average > Average files".
Select: By trial group (folder average), Arithmetic average, Keep all the event markers
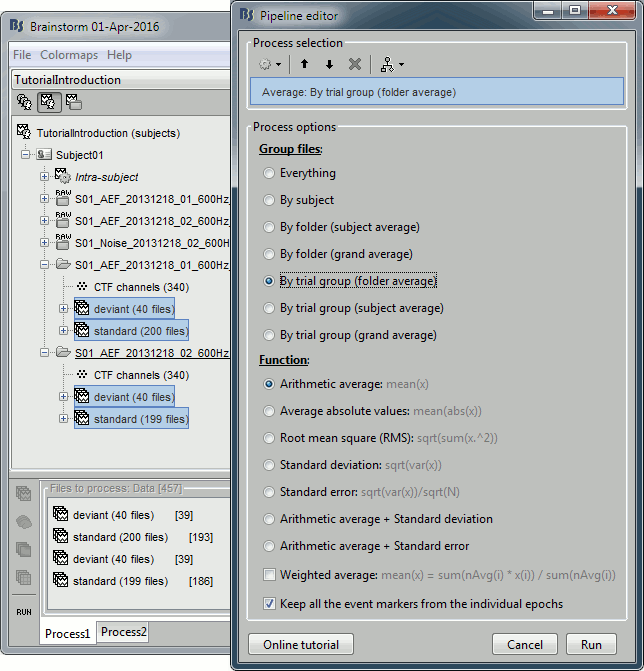
You get two new files for each average:
Process options
Description of all the options of the process:
Averaging across runs + StdErr
I
Doing it for illustration purposes.
- As said previously, it is usually not recommended to average recordings in sensor space across multiple acquisition runs because the subject might have moved between the sessions. Different head positions were recorded for each run, we will reconstruct the sources separately for each each run to take into account those movements.
- However, in the case of event-related studies it makes sense to start our data exploration with an average across runs, just to evaluate the quality of the evoked responses. We have seen that the subject almost didn't move between the two runs, so the error would be minimal. We will compute now an approximate sensor average between runs, and we will run a more formal average in source space later.
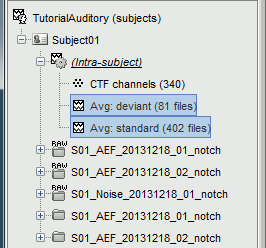
- We have 80 good "deviant" trials that we want to average together.
Select the trial groups "deviant" from both runs in Process1, run process "Average > Average files" Select the option "By trial group (subject average)"
- To compare properly this "deviant" average with the other condition, we need to use the same number of trials in the "standard" condition. We are going to pick 40 "standard" trials from Run01 and 40 from Run02. To make it easy, let's take the 40 first good trials.
Select the 41 first "standard" trials of Run01 + the 41 first "standard" trials of Run02 in Process1. This will sum to 80 selected files, because the Process1 tab ignores the bad trials (trial #37 is bad in Run01, trial #36 is bad in Run02)
Run again process "Average > Average files" > "By trial group (subject average)"
The average for the two conditions "standard" and "deviant" are saved in the folder (intra-subject). The channel file added to this folder is an average of the channel files from Run01 and Run02.
From continuous tutorials:
Averaging
Drag and drop the two lists of trials (or the two condition folders) in the Process1 list, and run the process "Average > Average files", with the option "Average by condition (subject average)". This will group the trials by conditions, and calculate one average per condition and subject. The option "By condition (grand average)" would average each condition for all the subjects together, but as there is only one subject in this case, the result would be same. The other options would generate one average file per subject ("by subject"), one average file per group of trials and per subject ("by trial group"), or only one average no matter what the input is ("everything").
The function to apply is the regular arithmetic average. The option "Keep all the events from the individual epochs" would group all the event markers present in all the epochs and save them in the new averaged file. It can be useful to check the relative position of the artifacts or the subject responses, or quickly detect some unwanted configuration such as a subject who would constantly blink right after a visual stimulus. We don't really need this here, leave this option unselected.
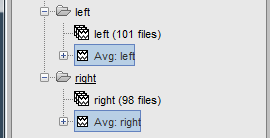
It creates two files: "Avg: left" and "Avg: right".
Double-click on the "Avg: Left" file to display the MEG recordings for this file (or right-click > MEG > display time series). It shows a very typical an clean evoked response, with a very high signal-to-noise ratio.
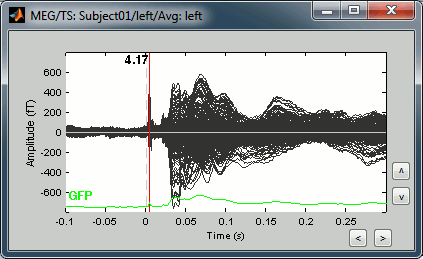
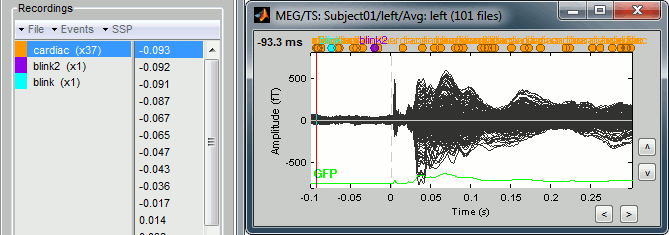
Just for the records, this is how it would look like if we had selected the option "Keep all the events from the individual epochs". The summary of the markers of all the epochs is: 37 heartbeats and 2 blinks.
From auditory
Visual exploration
- Display the two averages, "standard" and "deviant":
Right-click on average > MEG > Display time series
Right-click on average > MISC > Display time series (EEG electrodes Cz and Pz)
Right-click on average > MEG > 2D Sensor cap
In the Filter tab, add a low-pass filter at 100Hz.
Right-click on the 2D topography figures > Snapshot > Time contact sheet.
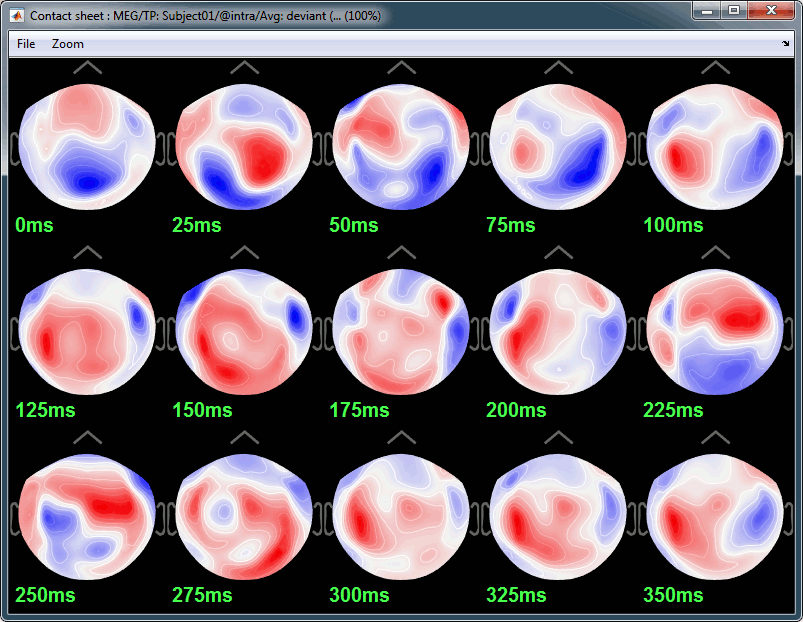
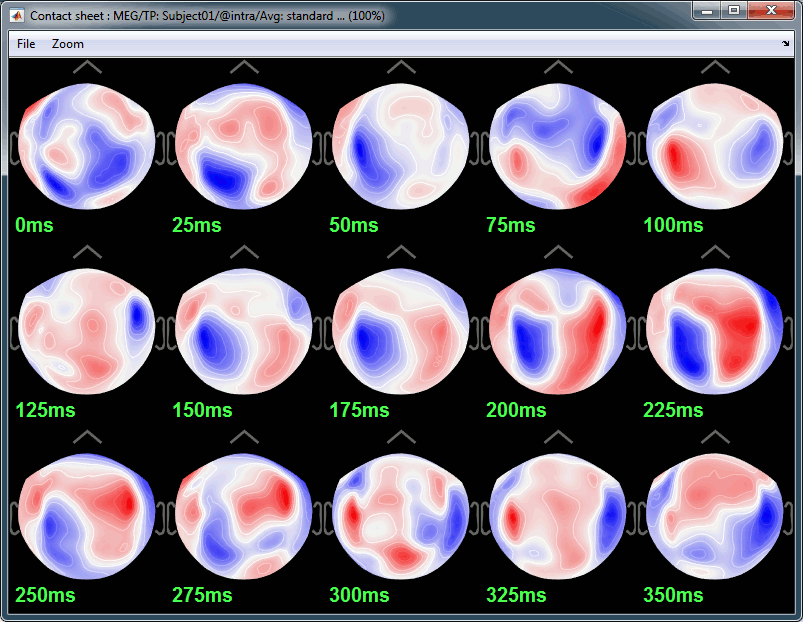
- Here are results for the standard (top) and deviant (bottom) beeps:
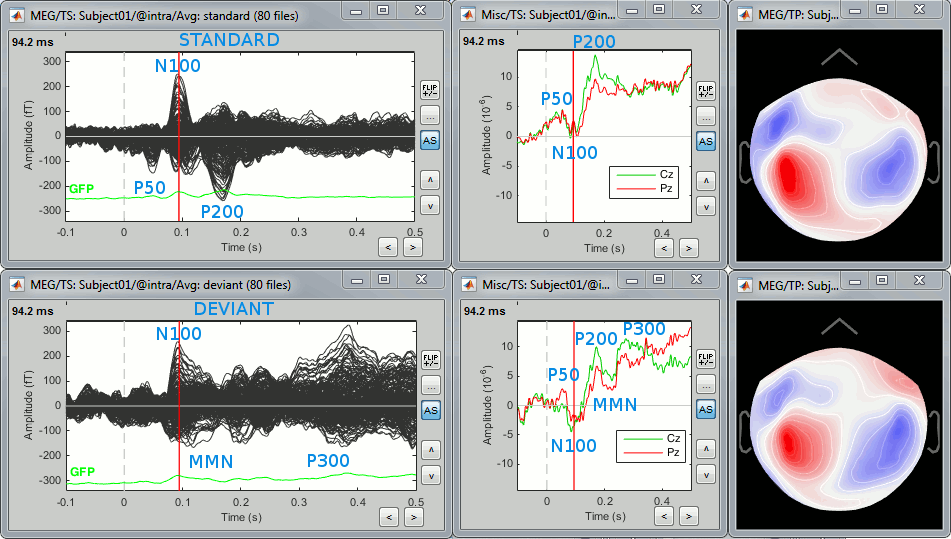
P50: 50ms, bilateral auditory response in both conditions.
N100: 95ms, bilateral auditory response in both conditions.
MMN: 100-200ms, mismatch negativity in the deviant condition only (detection of deviant).
P200: 170ms, in both conditions but much stronger in the standard condition.
P300: 300-400ms, deviant condition only (decision making in preparation of the button press).
Standard (right-click on the topography figure > Snapshot > Time contact sheet) :
Deviant: