EEG and epilepsy
This tutorial introduces some concepts that are specific to the management of EEG recordings in the Brainstorm environment. It also describes a standard pipeline for analyzing epilepsy recordings. It is based on a clinical case from the Epilepsy Centre, at the University Hospital Freiburg, Germany. The anonymized dataset can be downloaded directly from the Brainstorm download page.
License
This tutorial dataset (EEG and MRI data) remains proprietary of the Epilepsy Centre, University Hospital Freiburg, Germany. Its use and transfer outside the Brainstorm tutorial, e.g. for research purposes, is prohibited without written consent from the Epilepsy Centre in Freiburg. For questions please contact A. Schulze-Bonhage, MD, PhD: andreas.schulze-bonhage@uniklinik-freiburg.de
Presentation of the clinical case
This tutorial dataset was acquired in a patient who suffered from focal epilepsy with focal sensory, dyscognitive and secondarily generalized seizures since the age of eight years. He does not have any typical risk factors for epilepsy. The high resolution 3T epilepsy MRI including postprocessing was found to be normal. FDG-PET of the brain did not show any pathological changes in the glucose metabolism. Non-invasive telemetry revealed left fronto-central sharp waves, polyspikes and bursts of beta band activity (max. amplitude FC1, Cz) especially during sleep. The tutorial dataset was acquired during one night of the non-invasive telemetry recording at the Epilepsy Centre Freiburg, Germany.
Afterwards the patient underwent invasive EEG to identify the epileptogenic area and to map functionally important cortex. Details about invasive EEG and source localization from invasive EEG in this patient are reported in Dümpelmann, et al. (2011). Subsequently a left frontal tailored resection was performed. The histological analysis revealed a focal cortical dysplasia type IIB according to the classification of Palmini, et al. (2004). The postsurgical outcome is Engel 1A with a follow-up of 5 years.
The EEG data distributed here was recorded at 1024Hz, using a Neurofile NT digital video-EEG system with 128 channels and a 16-bit A/D converter. The signal was filtered in the recording system with a high-pass filter with a time constant of 1 second and a low-pass filter with a cutoff frequency of 344 Hz. The spikes were marked in the Deltamed Coherence Viewer.
References
Dümpelmann M, Ball T, Schulze-Bonhage A (2011)
sLORETA allows reliable distributed source reconstruction based on subdural strip and grid recordings. Human Brain Mapping.
Palmini A, Najm I, Avanzini G, Babb T, Guerrini R, Foldvary-Schaefer N, Jackson G, Luders HO, Prayson R, Spreafico R, Vinters HV (2004) Terminology and classification of the cortical dysplasias. Neurology, 62:S2-8.
Download and installation
- Requirements: You have already followed all the introduction tutorials and you have a working copy of Brainstorm installed on your computer.
Go to the Download page of this website, and dowload the file: sample_epilepsy.zip
Unzip it in a folder that is not in any of the Brainstorm folders (program folder or database folder)
- Start Brainstorm (Matlab scripts or stand-alone version)
Select the menu File > Create new protocol. Name it "TutorialEpilepsy" and select the options:
"No, use individual anatomy",
"Yes, use one channel file per subject".
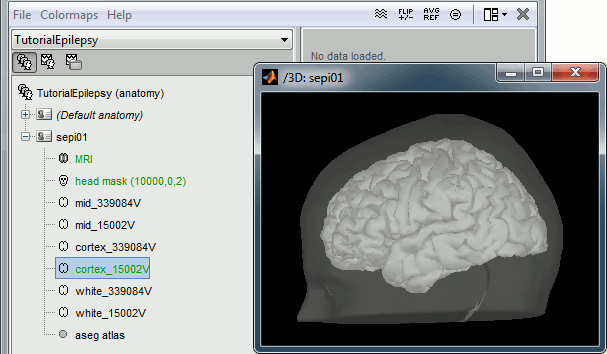
Import the anatomy
Right-click on the TutorialEpilepsy folder > New subject > sepi01
- Leave the default options you set for the protocol
Right-click on the subject node > Import anatomy folder:
Set the file format: "FreeSurfer folder"
Select the folder: sample_epilepsy/anatomy
- Number of vertices of the cortex surface: 15000 (default value)
- Set the 6 required fiducial points (indicated in MRI coordinates):
- NAS: x=135, y=222, z=75
- LPA: x=57, y=118, z=68
- RPA: x=204, y=119, z=76
- AC: x=131, y=145, z=110
- PC: x=130, y=119, z=111
- IH: x=128, y=134, z=170 (anywhere on the midsagittal plane)
Without the individual MRI
If you do not have access to an individual MR scan of the subject (or if its quality is too low to be processed with FreeSurfer), but if you have digitized the head shape of the subject using a tracking system, you have an alternative: deform one of the Brainstorm templates (Colin27 or ICBM152) to match the shape of the subject's head.
For more information, read the following tutorial: Warping default anatomy
Access the recordings
Link the recordings
- Switch to the "functional data" view.
Right-click on the subject folder > Review raw file:
- Select the file format: "EEG: Deltamed Neurofile-Coherence (*.bin)"
Select the file: sample_epilepsy/data/tutorial_EEG.bin
- The new file "Link to raw file" lets you access directly the contents of the EEG recordings
- The channel file "Deltamed channels" in the (Common files) folder contains the name of the channels, but not their positions. We need to overwrite this file and import manually the positions of the electrodes (either a standard cap or accurate positions digitized with a Polhemus device).
Prepare the channel file
Right-click on the subject folder > Import channel file:
- Select the file format: "EEG: ANT Xensor (*.elc)"
Select the file: sample_epilepsy/data/tutorial.elc
- Confirm that you want to overwrite the exising channel file.
- This file contains the default electrodes positions from the ASA software (ANT)
- The recordings contain signals coming from different types of electrodes:
- 29 EEG electrodes
- EOG1, EOG2: Electrooculograms
- EMG, ECG: Electromyogram and electrocardiogram
- SP1, SP2: Sphenoidal electrodes
- RS: Electrode on the right shoulder
- PHO: Photo stimulation channel
- DELR, DELL, QR, QL: Additional
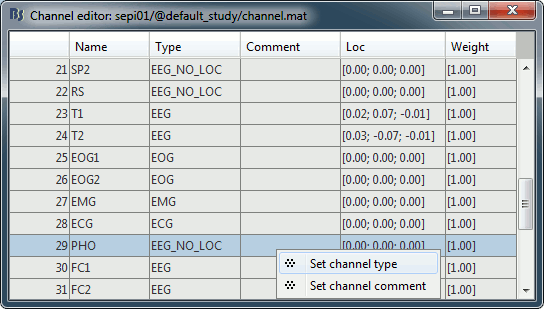
- The file format for the electrodes positions does not describe the type of the channels correctly, therefore all the signals saved in the files are classified as EEG. We need to redefine this manually to get correct groups of sensors, we want to have only real EEG electrodes in the "EEG" category and put everything that we are not going to use a "MISC" category.
Right-click on the channel file > Edit channel file:
- Note that the EOG, EMG and ECG channels already have a different type
- Select all the other non-EEG channels: SP1, SP2, RS, PHO, DELR, DELL, QR, QL
Right-click in the window > Set channel type: type MISC
- Close the figure and accept to save the modifications
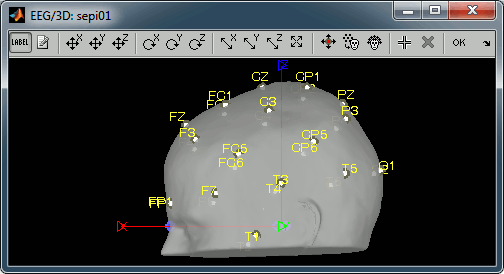
Register electrodes with MRI
- The channel file we imported contains generic electrodes positions, hence it cannot be properly aligned properly with the head surface coming from the MRI. We need to register manually these electrodes positions with the subject anatomy.
Right-click on the channel file > MRI registration > Edit...
- The default positions are already quite good, and the head shape is correct, there not much manual registration to do. You can click on the Label button in the toolbar to show the electrodes names.
- Click on the button "Refine registration with the head points" to find a better registration between the head shape defined by the electrodes and the head surface coming from the MRI.
- Click on the button "Project electrodes on the scalp surfaces", to ensure all the electrodes touche the skin surface.
- Click on "OK" to save the modifications.
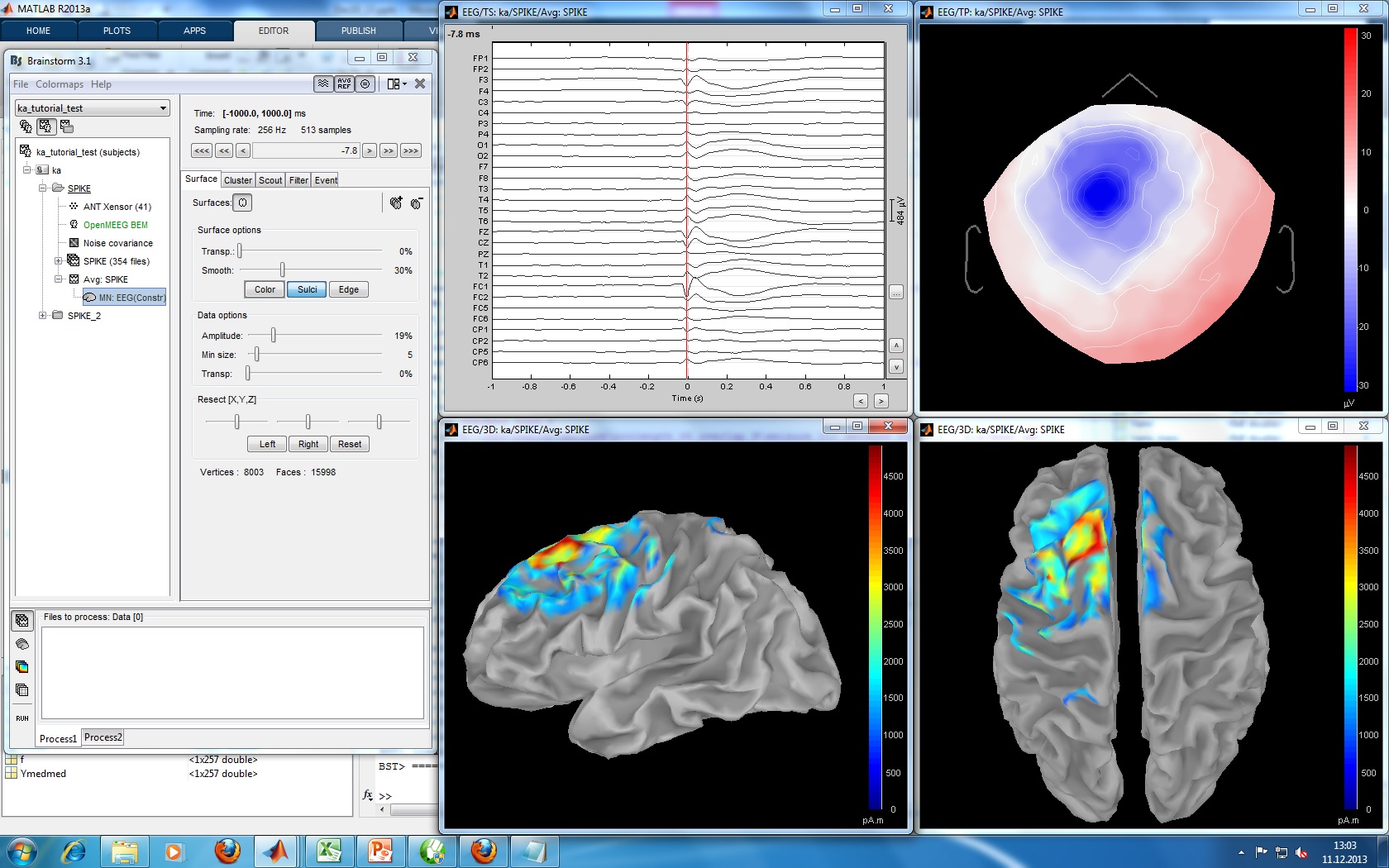
Mark and review spikes
- How was it done initially?
- How would we do it in Brainstorm?
- Import 177 spikes:
[-1, +1] seconds or [-500, +500]ms around the spike events (???)
- Remove DC offset based on the whole trial (-1s to +1s) (???)
- Or maybe we don't need the DC offset removal: In the EEG there should not be DC shift because there is usually a hardware highpass filter at around 0.1 Hz in the EEG amplifier (???)
Source analysis
- Pial surface or white matter envelope (???)
- Compute head model: OpenMEEG or 3-shell sphere (???)
Noise covariance matrix: [-1000, -800] ms from all the imported trials (???)
[-500, -400] ms or [-500, -300] ms for shorter epochs
- Source model: wMNE / sLORETA (???)
- Constrained / Unconstrained orientations (???)
Moving dipoles
Illustrate John/Beth's tools for calculating and displaying dipoles.
Tools to be developed for this tutorial
- Set the time resolution of the display figures in seconds per centimeter (s/cm): the length of the page changes automatically with the size of the window.
Flexible montage interface => Longitudinal bipolar montage (double banana) with e.g. a bipolar mesial ring (Cz-C3-T3-T1-T2-C4-Cz).