MEG current phantom (CTF)
Authors: Francois Tadel, Elizabeth Bock
This tutorial explains how to use some sample recordings from the CTF current phantom to test dipole fitting functions.
Contents
License
The datasets used in this tutorial remain property of their respective authors. Their use and transfer outside the Brainstorm tutorial, e.g. for research purposes, is prohibited without written consent from the authors. If you reference this dataset in your publications, please aknowledge its authors and cite Brainstorm as indicated on the website. For questions, please contact us through the forum.
CTF phantom
Authors: Elizabeth Bock, Francois Tadel and Sylvain Baillet
MEG Lab, McConnell Brain Imaging Center, Montreal Neurological Institute, McGill University, Canada.
Neuromag phantom
Authors: John Mosher
Epilepsy Center, Cleveland Clinic Neurological Institute, Cleveland, OH USA.
4D phantom
Authors: Jean-Michel Badier, Christian Bénar
MEG Lab, Institut des Neurosciences des Sytèmes, Aix-Marseille Université/INSERM 1106, France.
CTF current phantom
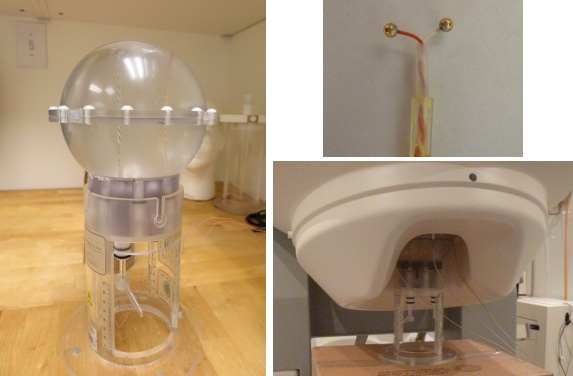
The CTF current dipole phantom is a spherical container filled with a conducting saline solution which contains a current source and sink. This electric dipole is used to simulate brain sources in a conductive medium. The globe has a 130mm inner diameter and small attachment posts to attach the three CTF head localization coils. The position of this dipole can be adjusted within this globe.
The dipole itself is constructed of two gold spheres about 2 mm in diameter, separated by 9.0 mm center to center. The dipole moment can be calculated by the equation m=I.L, where I is the current flow (in Amperes) and L is the length of the dipole (0.009 meters).
The location of the dipole is recorded relative to the center of the sphere (0,0,0)m, where X is positive toward the nasion, Y is positive toward the left ear and Z is positive toward the top of the head (see the CoordinateSystems tutorial for more details).
Reference
VSM/CTF documentation: PN900-0018, Revision 3.2, 23 November 2006. This document can be found with your full CTF installation at /opt/ctf/docs/Phantom.pdf.
Files available for this tutorial
phantom_ctf/ds/phantom_200uA_20150709_01.ds
Current=200uA, Moment=1800nAm, Frequency=7Hz, Location=(0, -18, 49)mm - 03-Jul-2015
This corresponds to a very strong dipole, that could be studied without any averaging.phantom_ctf/ds/phantom_20uA_20150603_03.ds
Current=20uA, Moment=180nAm, Frequency=23Hz, Location=(0, -18, 49)mm - 03-Jun-2015
This is a weaker dipole, closer to the range of amplitudes we can except from the brain. You will not see the dipole activity emerging from the noise without averaging a few cycles together.phantom_ctf/ds/emptyroom_20150709_01.ds
MEG empty room measurements: the phantom is in the MEG helmet but not connected - 09-Jul-2015phantom_ctf/ds/phantom_20160222_01.pos
"Head shape" of the phantom digitized with a Polhemus device using the Brainstorm digitizer.phantom_ctf/fif/phantom_20uA_20150603_03.fif
Dataset 20uA converted to FIF format using MNE utility mne_ctf2fiffphantom_ctf/fif/phantom_200uA_20150709_01.fif
Dataset 200uA converted to FIF format using MNE utility mne_ctf2fiffAll recordings were performed by Elizabeth Bock at the MEG lab at McGill with a CTF MEG system with 275 axial gradiometers.
Download and installation
Requirements: You have followed the introduction tutorials and Brainstorm is installed.
Go to the Download page of this website, and download the file: sample_phantom.zip
- Unzip it in a folder that is not in any of the Brainstorm folders (program folder or database folder)
- Start Brainstorm (Matlab scripts or stand-alone version)
Select the menu File > Create new protocol. Name it "TutorialPhantom" and select the options:
"No, use individual anatomy",
"No, use one channel file per acquisition run (MEG)".
Generate anatomy
In the Matlab command window: type "generate_phantom_ctf".
This creates a new subject PhantomCTF and generates the "anatomy" for this device: one volume and a few surfaces representing the geometry of the phantom.
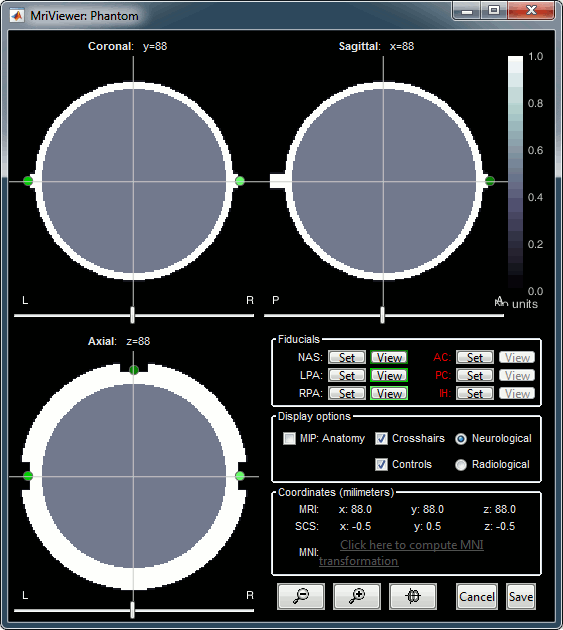
You can display the MRI and surfaces as presented in the introduction tutorials.
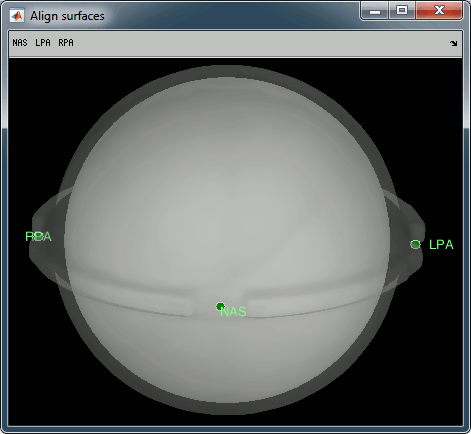
Access the recordings
- Switch to the "functional data" view.
Right-click on the subject folder > Review raw file.
Select the file format: "MEG/EEG: CTF (*.ds)"
Select all the folders in: sample_phantom/phantom_ctf/ds.
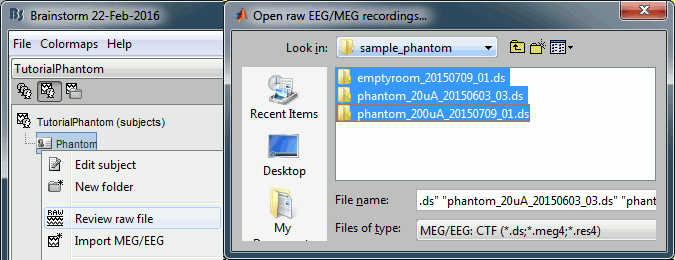
- Each folder corresponds to one dataset:
emptyroom_20150709_01.ds: Phantom inside the MEG helmet, but not plugged in
phantom_20uA_20150603_03.ds: Phantom active, 23Hz, 20uA, [0,-1.8,4.9]cm
phantom_200uA_20150709_01.ds: Phantom active, 7Hz, 200uA, [0,-1.8,4.9]cm
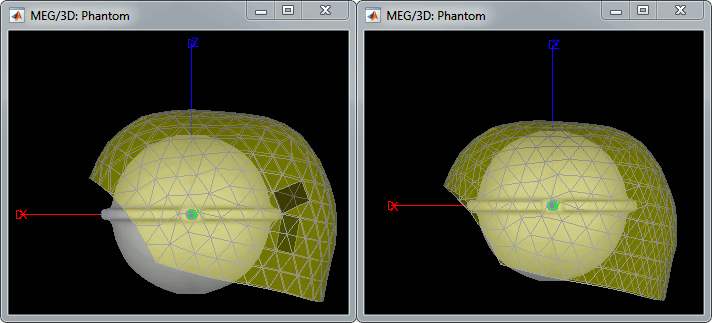
The recordings were acquired on different days, the position of the phantom in the MEG helmet is not the same for the two runs. Left = 20uA, Right = 200uA
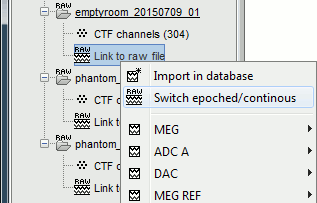
For each of the three runs: right-click on "Link to raw file" > Switch epoched/continuous
Import recordings
Mark events
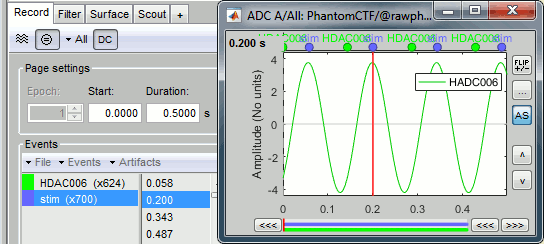
The sinusoidal signal is generated by the CTF hardware on channel HDAC006. While there are some automatic trigger events generated by the system that can be used for importing, we will have a more precise event average if the events are detected again offline.
- In Process1: Select the 20uA and 200uA links, then click on [Run].
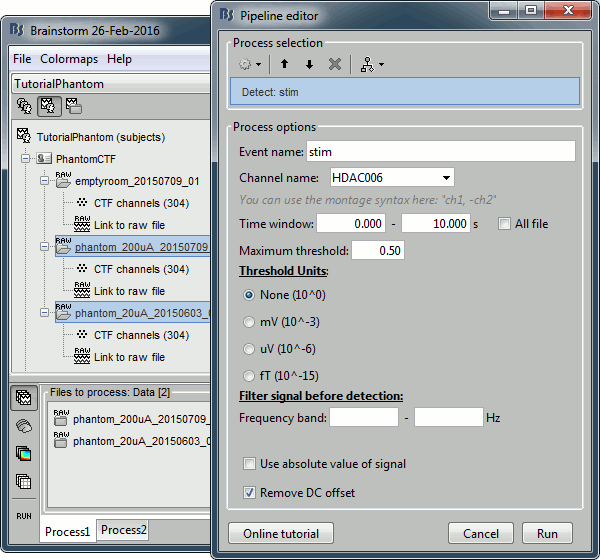
Select process: Events > Detect events above threshold
Event name=stim, Channel name=HDAC006, Time window=[0,10]s, Max thresh=0.5, Units=None, No filter, Uncheck absolute value, Check remove DC.
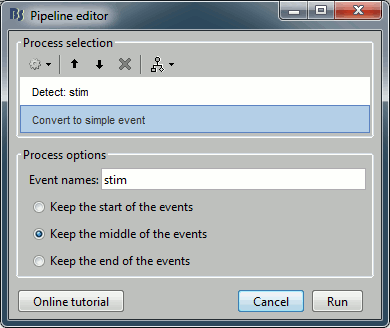
Add the process Events > Convert to simple event:
Event names=stim, Keep the middle of the events.
Import the events
Put the two phantom raw links in the Process1 box, click Run > Import recordings > Import MEG/EEG: Events: Subject name=Phantom, Event names=stim, All file, Epoch time=[-70,70]ms, uncheck Create one condition, check the last three boxes
Add the process Pre-process > Remove DC offset: All file, Sensor types=MEG, check overwrite
Add the process Average > Average files: By trial group (folder average)
Noise covariance
- Using the emptyroom recording
Right-click on the Link to raw file > Noise covariance > Compute from recordings: Baseline=[0,998.3]ms, select Block by block, Full matrix
Right-click on the Noise covariance: MEG > Copy to other folders
Source modeling
Compute head model: for each phantom recording, right-click on the respective channel files > Compute head model: MRI volume, MEG method=Overlapping spheres, Regular grid (isotropic)=2mm
Compute sources: right click the head model > Compute sources [2015] > Dipole modeling, NP performance index
GLSp into Process1, Sources > Dipole scanning: All file
Dipole fitting with FieldTrip
Comparison with other programs
High SNR (200uA)
- CTF dipole fitting: x=-1mm, y=-17mm, z=44mm, goodness of fit=99.95%
- MNE dipole fitting: x=-0.79mm, y=16.82mm, z=43.94mm, goodness of fit=99.9%
Low SNR (20uA)
- CTF dipole fitting: x=-1mm, y=-17mm, z=44mm, goodness of fit=98.38%
- MNE dipole fitting: x=-1.38mm, y=16.31mm, z=44.01mm, goodness of fit=99.1%
Digitized head points
The head points collected with the Brainstorm digitizer are usually copied to the .ds folders and imported automatically when loading the recordings. We decided not to include them in this example because in the case of this current phantom, there is no ambiguity in the definition of the anatomical fiducials. As this refined registration with the .pos files is not part of the standard CTF workflow, not including it will make it easier to compare the workflow and results with other programs.
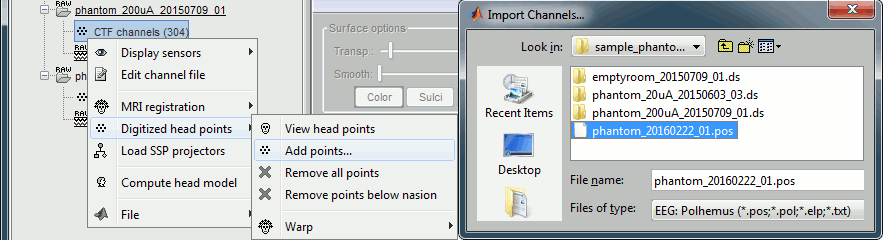
For additional testing purposes, the .pos file for the phantom is included in the sample_phantom.zip package, but you have to add it manually to the recordings. Do not use these points to refine automatically the registration: the fitting algorithm may fail finding the best rotation around the Z axis because the phantom is completely spherical, and the registration is already close to perfection.
Right-click on one of the channel files (20uA or 200uA) > Digitized head points > Add points.
Select the file format: "EEG: Polhemus"
Select file: sample_phantom/phantom_20160222_01.pos
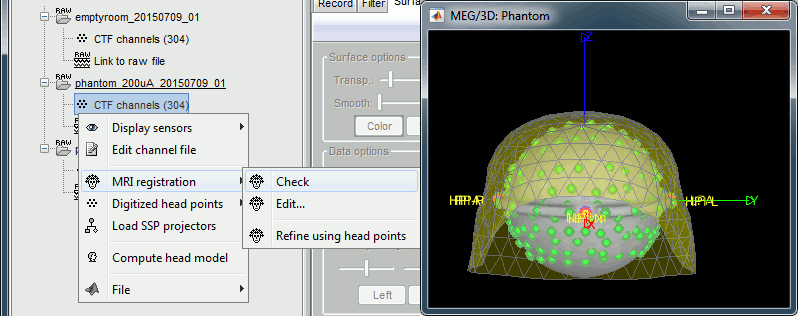
Right-click on the channel file > MRI registration > Check.
Scripting
Generate Matlab script
Available in the Brainstorm distribution: brainstorm3/toolbox/script/tutorial_phantom.mm