Simulations
Author: Francois Tadel
This tutorial addresses everything that can be called "simulation" in Brainstorm: simulation of simple signals, simulation of full source maps from a few scouts, simulation of MEG/EEG recordings from source maps (real or synthetic). Its goal is to group all the information that was previously spread across multiple tutorials and forum posts, and difficult to access.
Contents
Simulate signals
You have no data in your database. Some process in the Simulate menu can generate signals and save them as new files in the database. Because you start from nothing, the Process1 list needs to be empty. Click on Run and try the following processes.
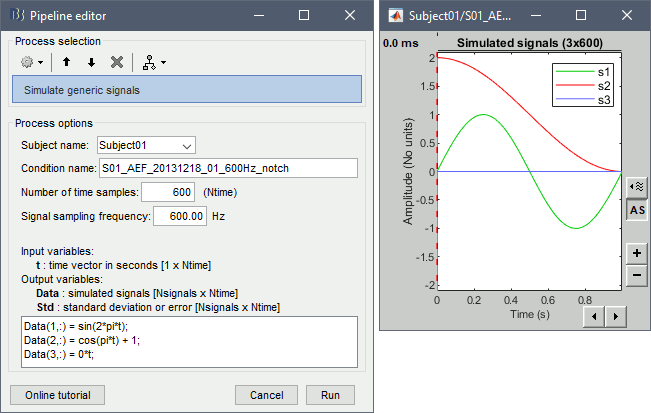
Simulate generic signals
This process allows to define a set of signals with Matlab code and save it in a Brainstorm file. With the text box, you can write a free-form piece of code, which will be evaluated with the function eval(). This code must at least define the variable Data [Nsignals x Ntime], based on in the input time vector t (defined automatically by the process from the number of time points and the sampling frequency). The more rows you add to the Data matrix, the more signals you will have in your file. The example below creates three signals. Another example is available in the tutorial Time-frequency.
Simulate AR signals
https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/Connectivity?Simulated_data_.28AR_model.29
Simulate AR signals Random
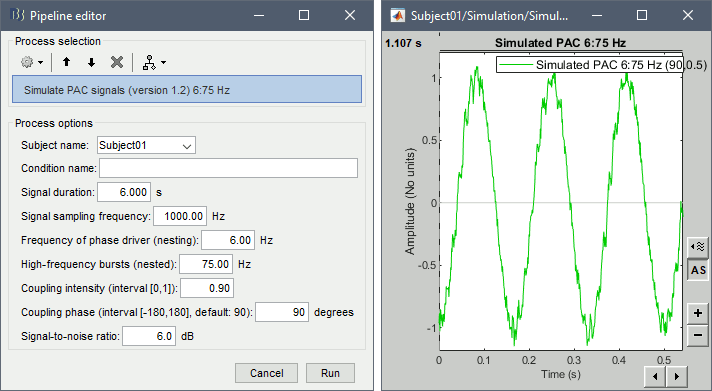
Simulate PAC signals
This process generates synthesized data containing cross-frequency phase-amplitude coupling. It is fully documented in the tutorial Phase-amplitude coupling: Method.
Generate full source maps from scout signals
https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/TutScouts#Scout_toolbar_and_menus
Simulate recordings: Multiply the selected scouts with the forward model. Simulate the scalp data that would be recorded if only the selected cortex region was activated; all the other sources are set to zero. Create a new data file in the database.
If no scout selected: simulate recordings produced by the activity of the entire cortex.
Simulate MEG/EEG recordings from real sources
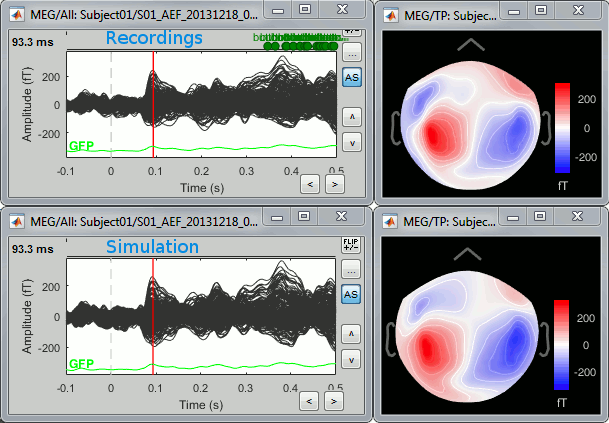
After estimating the sources from real MEG/EEG recordings with the minimum norm method, you can simulate recordings from the model. This is done simply by multiplying the source time series with the forward model:
EEG_sim [Nelec x Ntime] = Forward_model [Nelec x Nsources] * MN_sources [Nsources x Ntime]
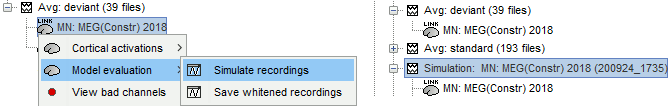
To simulate MEG/EEG recordings from a minimum norm source model: right-click on the source file, then select the menu Model evaluation > Simulate recordings. This can be useful for evaluating the quality of the model. The process is documented in the tutorial Source estimation.
Simulate MEG/EEG recordings from simulated dipoles
These examples are based on the introduction tutorials, but can easily be transposed to any study. The inputs you need to provide to the process depend on the type of orientation constrains
Constrained
Unconstrained
https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/TutVolSource#Volume_scouts
Additional documentation
Articles
A great simulation article was published by Prof. Debener's neuropsychology lab in Oldenburg. It uses Brainstorm to evaluate and improve the design of ear-EEG devices. All the Matlab/Brainstorm scripts used in this study are available on figshare, together with some videos illustrating the simulations that were done.
Meiser A, Tadel F, Debener S, Bleichner MG
The Sensitivity of Ear-EEG: Evaluating the Source-Sensor Relationship Using Forward Modeling
Brain Topography, Aug 2020
Forum discussions
Simulate recordings from sources: http://neuroimage.usc.edu/forums/showthread.php?2563
Simulate recordings from simulated signals: https://neuroimage.usc.edu/forums/t/simulate-scalp-recording/2421/3