DBA tutorial: Compute sources in deep cerebral structures
Authors: Jean-Eudes Le Douget, Francois Tadel, Denis Schwartz, Raymundo Cassani
This tutorial explains step-by-step how to use the DBA (Deep Brain Activity) functionality, useful to assess subcortical source localization.
Warnings: (added in April 2021)
The mixed head models introduced in this tutorial are complicated to handle in terms of data structures, they produce values of different types in the same files, and have shown to cause many interpretation and computation errors among Brainstorm users. For general studies, we recommend using simpler source spaces: surface or volume.
Mixed head models are mostly indicated for individual subject analysis, and not suitable for group analysis when using individual anatomy for all the subjects. We do not have any accurate solution for projecting the individual mixed source space to the template space. use volume head models instead. See tutorials: Volume source estimation, Subjects coregistration.
Import database
This tutorial is based on resting-state recordings for 7 subjects with two conditions: eyes open (YO), eyes closed (YF). We have recorded 20 runs of 15 seconds for each subject and each condition.
The goal is to compute the contrast between the two conditions in the alpha band. The data has already been filtered in the alpha frequency band (7-13Hz) and the default anatomy is used for all the subjects.
Start by downloading the tutorial dataset TutorialDba.zip from the Download page.
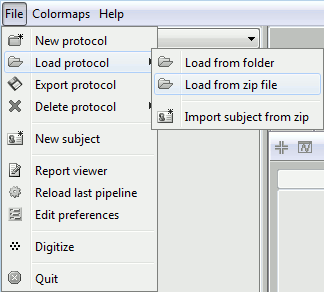
The file is an exported Brainstorm protocol. To load it in your database, use the menu:
File > Load Protocol > Load from zip file.
Select deep structures
The first step consists in creating the surface file that includes the cortex and the deep structures that we want to include in the model. Here, in the default anatomy:
Right-click on "aseg atlas" > Less vertices > 15000 vertices. Use the default resmpling method (Matlab's reducepatch) for now.
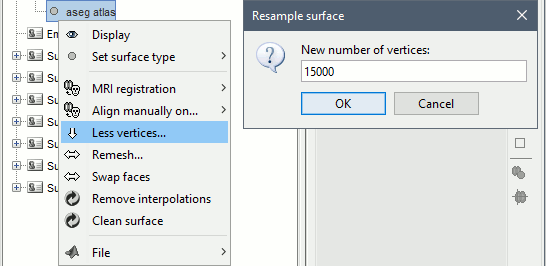
Double-click on "aseg atlas_15018V" (contains the subcortical structures from the FreeSurfer altas). Don't worry if the final number of vertices is slightly different than the one specified.
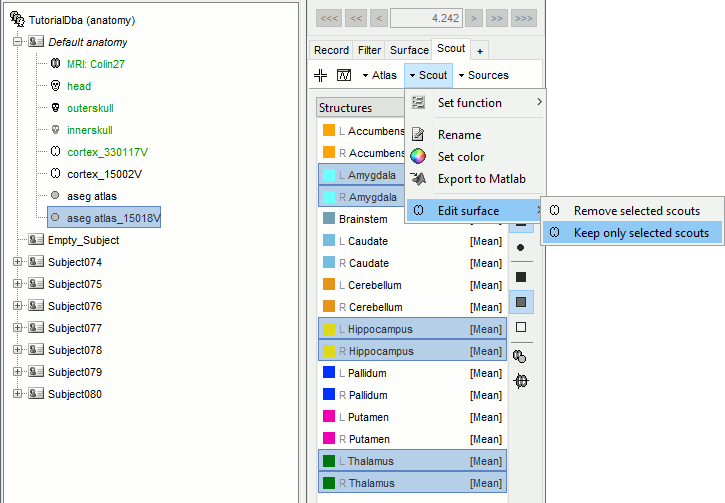
Select the amygdala, the thalamus and the hippocampus, and create a subatlas.
Merge the cortex with the selected structures. Rename the new surface in "cortex_mixed".
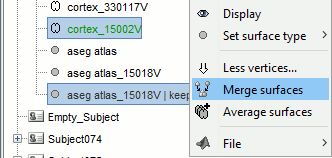
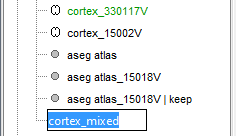
Open the cortex_mixed surface and create a new atlas "Source model options". With Matlab 2015b+, the display looks weird because it limits the number of possible transparent layers to 5. To produce nicer figures, disable the OpenGL renderer (File > Edit preferences). The display will be much slower, but the renderer won't suffer from this limitation.
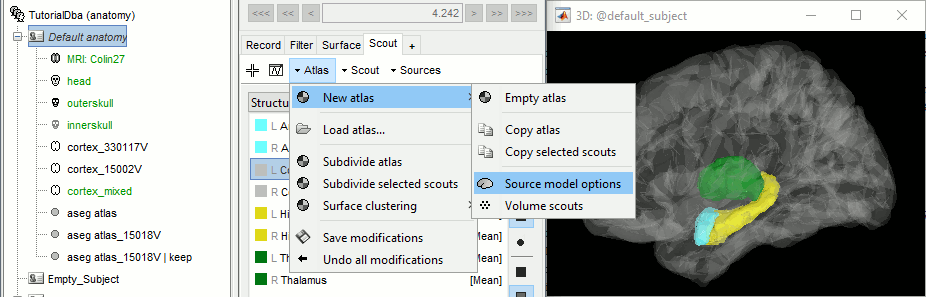
Select all the structures and set modeling options to "Deep brain" for all of them.
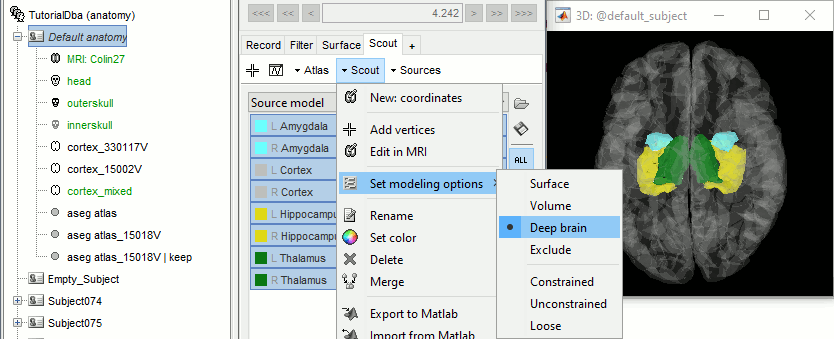
It will automatically set the orientation constraint to "constrained" for the cortex and hippocampus regions, and "unconstrained" for all the other regions. Don't forget to close the window with the new surface so that all these changes can be saved.
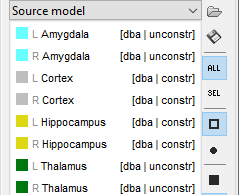
Location and orientation constraints
Two types of constraints can be applied to each anatomical region in the atlas "Source model":
Based on the anatomical observations reported for each subcortical region in the reference articles (next section), the preferred combination of constraints is described below. The reference articles also estimate the number of averaged trials needed to detect responses in some regions.
|
Location
constraint |
Preferred
orientation |
Default orientation
constraint |
Trials (MEG) |
Trials (EEG) |
Cortex |
Surface |
Normal |
Constrained |
- |
- |
Hippocampus |
Surface |
Normal |
Constrained |
21 |
45 |
Cerebellum |
Surface |
Normal |
Unconstrained |
- |
- |
Accumbens |
Volume |
None |
Unconstrained |
- |
- |
Amygdala |
Volume |
None |
Unconstrained |
- |
- |
Brainstem |
Volume |
None |
Unconstrained |
400 (LGN) |
490 (LGN) |
Caudate |
Volume |
None |
Unconstrained |
- |
- |
Putamen |
Volume |
None |
Unconstrained |
34 |
23 |
Pallidum |
Volume |
Y axis |
Constrained |
> 10000 |
> 10000 |
Thalamus |
Volume |
None |
Unconstrained |
3500 |
3700 |
Source estimation
Head model
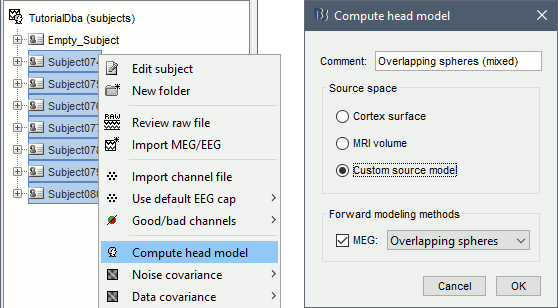
Select all the subjects (except for the empty room recordings) > right-click > Compute head model. Select "Custom source model", and leave the other options to their defaults.
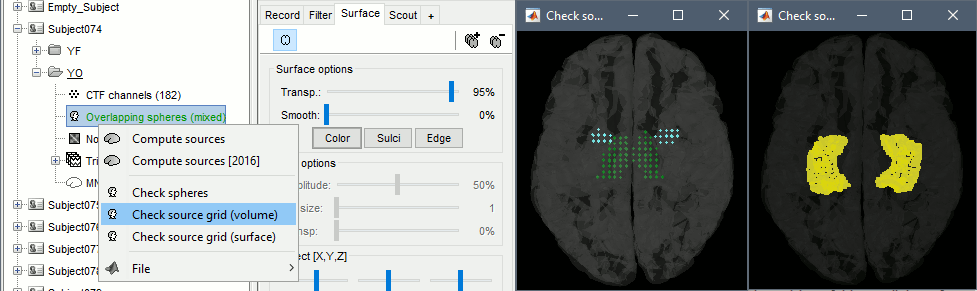
You can explore the source grids that were computed. Right-click on one of the head models > Check source grid (volume) and Check source grid (surface). In the Scout tab, select the atlas "User scouts" to get a clearer view. In panel Surface, increase the transparency of the surface to see the source grids representing the select subcortical regions.
Inverse model
- The noise covariance matrix was estimated from the empty room recordings (Empty_Subject) and copied to all the folders of all the subjects.
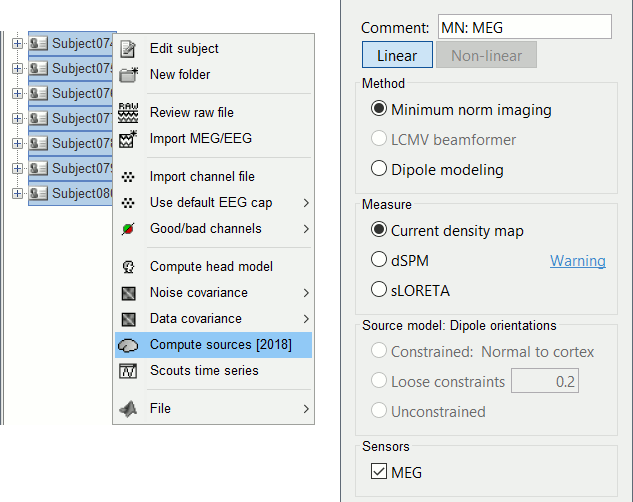
Select all the subjects (except the empty room recordings), right-click > Compute sources.
Select Minimum norm (wMNE) and leave the other options to their default values.
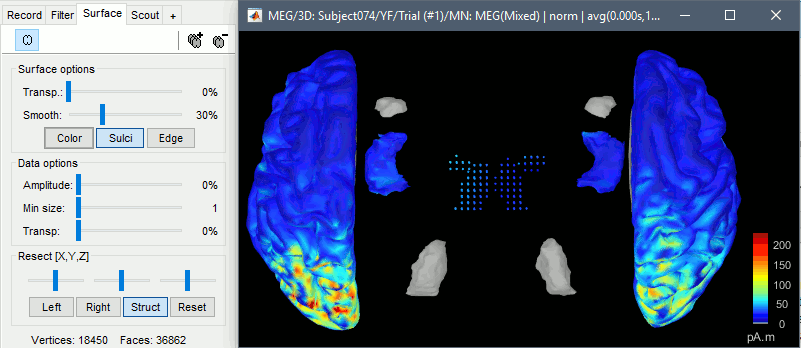
Double-click on the sources for any trial (segment of 15s of rest recordings). Make sure the atlas "User scouts" is selected in the Scout tab, then explore the display options available in the Surface tab. The surface regions (cortex and hippocampus) are represented as surfaces, and the values are directly mapped on the surface. The volume regions (amygdala and thalamus) are represented as grids of dots.
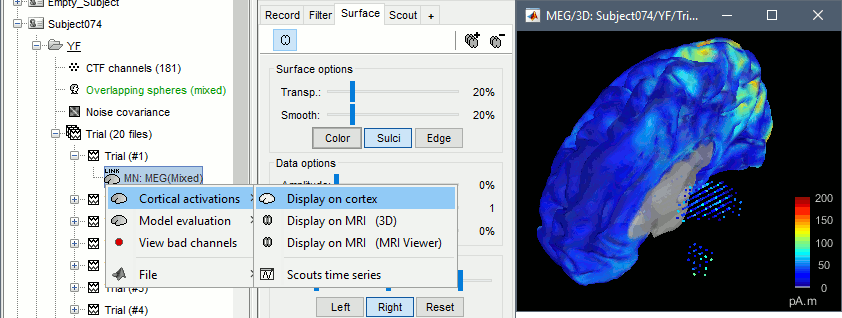
To be able to visualize the activity of the subcortical regions, you can use the button [Struct] at the bottom of the Surface tab. It moves the different structures so you can see them all. The grid points corresponding to the volume regions stay in place, so you can see them (while the corresponding surface is moved).
Compute statistics
We will now design a statistical analysis to assess the eyes-open and eyes-closed contrast. As a reminder, the recordings available in the database have already been filtered in the alpha frequency band (7-13Hz). As a measure of the global of the activity in this frequency band, we will average all the time samples in each block of 15s. Note that this is not the recommended procedure anymore: it would have been better to simply compute a PSD from the sources estimated for the continuous file link, but this option was not available at the time this tutorial was written.
In Process1, select all the subjects (except for Empty_Subject)and select [Process sources].
Run process Average > Average time > Use absolute value, All file.
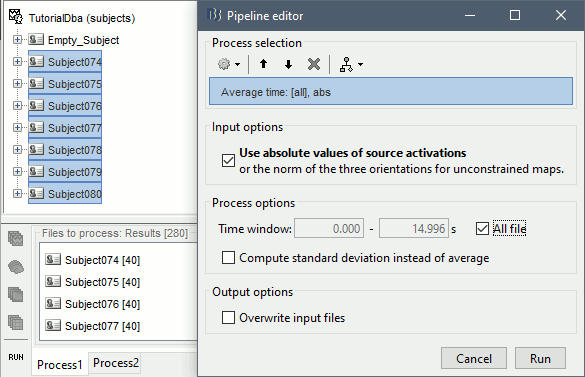
The option Use absolute values of source activations also "flattened" the source maps. The regions that had a few regions with "unconstrained" source orientations, with three values per grid point. These three orientations were grouped into one value by taking the norm along the three axes: sqrt(x2+y2+z2).
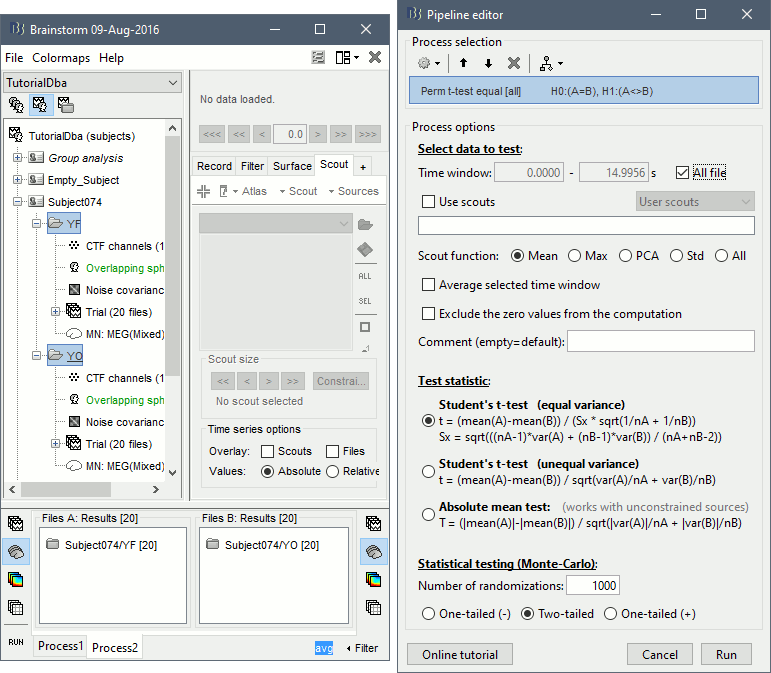
- In Process2, select FilesA=Subject74/YF (eyes closed) and FilesB=Subject74/YO (eyes open). Then enter "avg" in the Filter box, to select only the time averages. You should have 20 files selected on each side.
Run the process Test > Permutation test (independent), as configured as below:
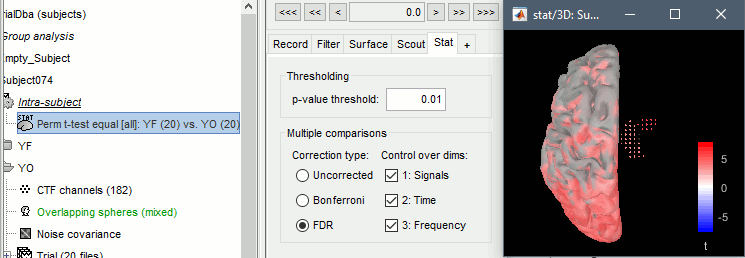
The statistical result can be displayed similarly to the source files, and you can edit the statistical threshold in the Stat tab. Red values indicate that the power in the alpha band is significantly higher in condition YF (eyes closed). As expected, that parieto-occipital regions appear clearly in this contrast.
Volume scouts
Some subcortical structures are modeled as volume source structures (for instance here, the thalamus and the amygdala). It is not possible to display scouts time series for these structures from the "Source model" or "Structures" atlases. It is necessary to create a new atlas, specific to volume scouts. Volume scouts are described in the tutorial Volume source estimation. The only difference here is that you will be able to create them from the grid of points you see in the 3D figures (instead of the MRI slices).
- Double-click on one of the source files (not averaged in time) to open it. From the Surface tab, configure it so you see the grid of points corresponding to the right thalamus (make the surface 100% transparent, or hide the right hemisphere).
In the Scout tab, menu Atlas > New atlas > Volume scouts.
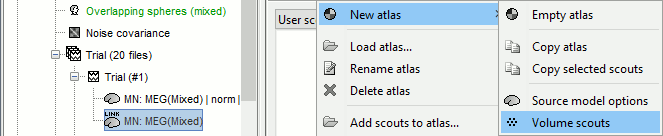
Click on the button [Create scout], click on one of the points of the right thalamus. Then grow it until it includes all the sources in the structure. Rename it to "Thalamus R".
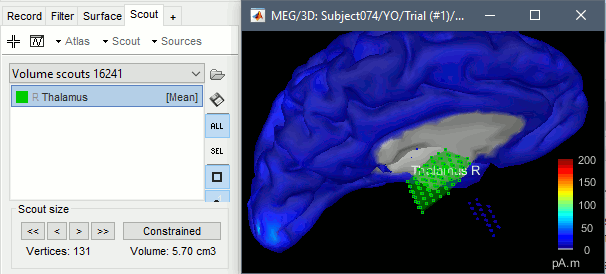
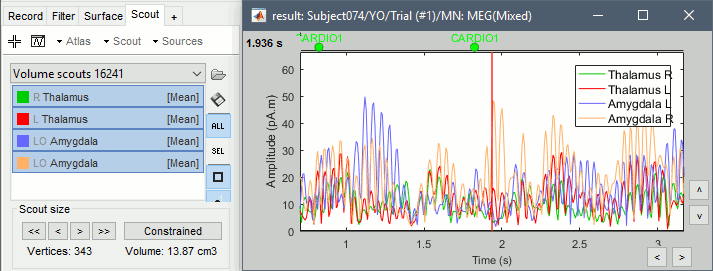
Repeat these steps for all the regions you are interested in and display the scouts time series.
References
Attal Y, Bhattacharjee M, Yelnik J, Cottereau B, Lefèvre J, Okada Y, Bardinet E, Chupin M, Baillet S (2009)
Modelling and detecting deep brain activity with MEG and EEG
IRBM, 30(3):133-138
Attal Y, Schwartz D (2013)
Assessment of Subcortical Source Localization Using Deep Brain Activity Imaging Model with Minimum Norm Operators: A MEG Study
PLOS ONE, 8(3):e59856
Dumas T, Dubal S, Attal Y, Chupin M, Jouvent R (2013)
MEG Evidence for Dynamic Amygdala Modulations by Gaze and Facial Emotions
PLOS ONE, 8(9): e74145
Additional documentation
Scripting
The following script from the Brainstorm distribution reproduces the analysis presented in this tutorial page: brainstorm3/toolbox/script/tutorial_dba.m
1 function tutorial_dba(zip_file, reports_dir)
2 % TUTORIAL_DBA: script that runs the Brainstorm deep brain activity (DBA) tutorial.
3 % https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/DeepAtlas
4 %
5 % INPUTS:
6 % - zip_file : Full path to the TutorialDba.zip file
7 % - reports_dir : Directory where to save the execution report (instead of displaying it)
8 %
9 % @=============================================================================
10 % This function is part of the Brainstorm software:
11 % https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm
12 %
13 % Copyright (c) University of Southern California & McGill University
14 % This software is distributed under the terms of the GNU General Public License
15 % as published by the Free Software Foundation. Further details on the GPLv3
16 % license can be found at http://www.gnu.org/copyleft/gpl.html.
17 %
18 % FOR RESEARCH PURPOSES ONLY. THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS," AND THE
19 % UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA AND ITS COLLABORATORS DO NOT MAKE ANY
20 % WARRANTY, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO WARRANTIES OF
21 % MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE, NOR DO THEY ASSUME ANY
22 % LIABILITY OR RESPONSIBILITY FOR THE USE OF THIS SOFTWARE.
23 %
24 % For more information type "brainstorm license" at command prompt.
25 % =============================================================================@
26 %
27 % Author: Raymundo Cassani, 2024
28
29 % Output folder for reports
30 if (nargin < 2) || isempty(reports_dir) || ~exist(reports_dir, 'dir')
31 reports_dir = [];
32 end
33 % You have to specify the folder in which the tutorial dataset is unzipped
34 if (nargin == 0) || isempty(zip_file) || ~file_exist(zip_file)
35 error('The first argument must be the full path to the dataset zip file.');
36 end
37
38 %% ===== MIXED MODEL PARAMETERS =====
39 % Cortex name
40 cortexComment = 'cortex_15002V';
41 % Surface with subcortical segmentation (ASEG)
42 subCortexComment = 'aseg atlas';
43 % Subcortical structures to keep from ASEG
44 subCortexKeep = {'Amygdala L', 'Amygdala R', 'Hippocampus L', 'Hippocampus R', 'Thalamus L', 'Thalamus R'};
45 % Mixed cortex name
46 mixedComment = 'cortex_mixed' ;
47
48 % Mixed model structures: Cortex + Subcortical structures
49 % Table with structures, and their locations and orientations constraints
50 % Location constraint : 'Surface', 'Volume', 'Deep brain'*, 'Exclude'
51 % Orientation constraint: 'Constrained', 'Unconstrained', 'Loose'
52 % * If 'Deep brain' is used as location constraint the location and orientation constraints
53 % will be set automatically according to the scout name.
54 %
55 % 'ScoutName' , 'Location' , 'Orientation'
56 mixedStructs = {'Amygdala L' , 'Deep brain', ''; ... % Deep brain --> Volume , Unconstrained
57 'Amygdala R' , 'Deep brain', ''; ... % Deep brain --> Volume , Unconstrained
58 'Hippocampus L', 'Deep brain', ''; ... % Deep brain --> Surface, Constrained
59 'Hippocampus R', 'Deep brain', ''; ... % Deep brain --> Surface, Constrained
60 'Thalamus L' , 'Deep brain', ''; ... % Deep brain --> Volume, Unconstrained
61 'Thalamus R' , 'Deep brain', ''; ... % Deep brain --> Volume, Unconstrained
62 'Cortex L' , 'Deep brain', ''; ... % Deep brain --> Surface, Constrained
63 'Cortex R' , 'Deep brain', ''}; % Deep brain --> Surface, Constrained
64
65
66 %% ===== LOAD PROTOCOL =====
67 % Start brainstorm without the GUI
68 if ~brainstorm('status')
69 brainstorm nogui
70 end
71 % Check Brainstorm mode
72 if bst_get('GuiLevel') < 0
73 error('For the moment the tutorial "tutorial_dba" is not supported on Brainstorm server mode.');
74 end
75 ProtocolName = 'TutorialDba';
76 [~, fBase] = bst_fileparts(zip_file);
77 if ~strcmpi(fBase, ProtocolName)
78 error('Incorrect .zip file.');
79 end
80 % Delete existing protocol
81 gui_brainstorm('DeleteProtocol', ProtocolName);
82 % Import protocol from zip file
83 import_protocol(zip_file);
84 % Start a new report
85 bst_report('Start');
86
87
88 %% ===== SELECT DEEP STRUCTURES =====
89 % Get Subject for Default Anatomy
90 sSubject = bst_get('Subject', bst_get('DirDefaultSubject'));
91 % Find subcortical atlas, and downsize it
92 iAseg = find(strcmpi(subCortexComment, {sSubject.Surface.Comment}));
93 newAsegFile = tess_downsize(sSubject.Surface(iAseg).FileName, 15000, 'reducepatch');
94 % Create atlas with only selected structures
95 panel_scout('SetCurrentSurface', newAsegFile);
96 sScouts = panel_scout('GetScouts');
97 [~, iScouts] = ismember(subCortexKeep, {sScouts.Label});
98 panel_scout('SetSelectedScouts', iScouts);
99 newAsegFile = panel_scout('NewSurface', 1);
100 % Find cortex
101 sSubject = bst_get('Subject', bst_get('DirDefaultSubject'));
102 iCortex = find(strcmpi(cortexComment, {sSubject.Surface.Comment}));
103 % Merge cortex with selected DBA structures
104 mixedFile = tess_concatenate({sSubject.Surface(iCortex).FileName, newAsegFile}, mixedComment, 'Cortex');
105 % Atlas with structures
106 atlasName = 'Structures';
107 % Display mixed cortex
108 hFigMix = view_surface(mixedFile);
109 [~, sSurf] = panel_scout('GetScouts');
110 iAtlas = find(strcmpi(atlasName, {sSurf.Atlas.Name}));
111 panel_scout('SetCurrentAtlas', iAtlas, 1);
112 panel_surface('SelectHemispheres', 'struct');
113 bst_report('Snapshot', hFigMix, mixedFile, 'Mix cortex: Cortex + Subcortical structures');
114 pause(1);
115 % Unload everything
116 bst_memory('UnloadAll', 'Forced');
117
118
119 %% ===== LOCATIONS AND ORIENTATIONS CONSTRAINTS =====
120 % Select atlas with structures
121 panel_scout('SetCurrentSurface', mixedFile);
122 [~, sSurf] = panel_scout('GetScouts');
123 iAtlas = find(strcmpi(atlasName, {sSurf.Atlas.Name}));
124 panel_scout('SetCurrentAtlas', iAtlas, 1);
125 % Create source model atlas
126 panel_scout('CreateAtlasInverse');
127 % Set modeling options
128 sScouts = panel_scout('GetScouts');
129 % Set location and orientation constraints
130 for iScout = 1 : length(sScouts)
131 % Select this scout
132 iRow = find(ismember(sScouts(iScout).Label, mixedStructs(:,1)));
133 % Set location constraint
134 panel_scout('SetLocationConstraint', iScout, mixedStructs{iRow,2});
135 % Set orientation constraint
136 panel_scout('SetOrientationConstraint', iScout, mixedStructs{iRow,3});
137 end
138 % Unload everything
139 bst_memory('UnloadAll', 'Forced');
140
141
142 %% ===== SOURCE ESTIMATION =====
143 % Find all recordings files for all Subjects, except 'Empty_Subject'
144 % Process: Select data files in: */*/Trial (#1)
145 sRecFiles = bst_process('CallProcess', 'process_select_files_data', [], [], ...
146 'subjectname', 'All', ...
147 'condition', '', ...
148 'tag', '', ...
149 'includebad', 0, ...
150 'includeintra', 0, ...
151 'includecommon', 0);
152 iDelete = strcmpi('Empty_Subject', {sRecFiles.SubjectName});
153 sRecFiles(iDelete) = [];
154
155 % Process: Compute head model
156 bst_process('CallProcess', 'process_headmodel', sRecFiles, [], ...
157 'comment', '', ...
158 'sourcespace', 3, ...
159 'meg', 3); % Overlapping spheres
160
161 % Display surface and volume grids
162 sStudy = bst_get('AnyFile', sRecFiles(1).FileName);
163 headmodelFile = sStudy.HeadModel.FileName;
164 hFigSrfGrid = view_gridloc(file_fullpath(headmodelFile), 'S');
165 hFigVolGrid = view_gridloc(file_fullpath(headmodelFile), 'V');
166 figure_3d('SetStandardView', hFigSrfGrid, 'top');
167 figure_3d('SetStandardView', hFigVolGrid, 'top');
168 bst_report('Snapshot', hFigSrfGrid, headmodelFile, 'Mix head model, surface grid');
169 bst_report('Snapshot', hFigVolGrid, headmodelFile, 'Mix head model, volume grid');
170 pause(1);
171 close([hFigSrfGrid, hFigVolGrid]);
172
173 % Minimum norm options
174 InverseOptions = struct(...
175 'Comment', 'MN: MEG', ...
176 'InverseMethod', 'minnorm', ...
177 'InverseMeasure', 'amplitude', ...
178 'SourceOrient', [], ...
179 'Loose', 0.2, ...
180 'UseDepth', 1, ...
181 'WeightExp', 0.5, ...
182 'WeightLimit', 10, ...
183 'NoiseMethod', 'reg', ...
184 'NoiseReg', 0.1, ...
185 'SnrMethod', 'fixed', ...
186 'SnrRms', 1e-6, ...
187 'SnrFixed', 3, ...
188 'ComputeKernel', 1, ...
189 'DataTypes', {{'MEG'}});
190
191 % Process: Compute sources [2018]
192 sSrcFiles = bst_process('CallProcess', 'process_inverse_2018', sRecFiles, [], ...
193 'output', 1, ... % Kernel only: one per file
194 'inverse', InverseOptions);
195
196 % Display sources
197 hSrcFig = view_surface_data([], sSrcFiles(1).FileName);
198 panel_time('SetCurrentTime', 4.897);
199 bst_report('Snapshot', hSrcFig, sSrcFiles(1).FileName);
200 panel_surface('SelectHemispheres', 'struct');
201 bst_report('Snapshot', hSrcFig, sSrcFiles(1).FileName);
202 pause(1);
203
204 % Unload everything
205 bst_memory('UnloadAll', 'Forced');
206
207
208 %% ===== COMPUTE STATISTICS =====
209 % Process: MEAN: [all], abs
210 sSrcAvgFiles = bst_process('CallProcess', 'process_average_time', sSrcFiles, [], ...
211 'timewindow', [], ...
212 'avg_func', 'mean', ... % Arithmetic average: mean(x)
213 'overwrite', 0, ...
214 'source_abs', 1);
215 % Split average source files by condition
216 % YF = 'Eyes closed'
217 iYF = strcmpi('YF', {sSrcAvgFiles.Condition});
218 sYfSrcAvgFiles = sSrcAvgFiles(iYF);
219 iYO = strcmpi('YO', {sSrcAvgFiles.Condition});
220 sYoSrcAvgFiles = sSrcAvgFiles(iYO);
221 % Process: Perm t-test equal [all] H0:(A=B), H1:(A<>B)
222 sTestFile = bst_process('CallProcess', 'process_test_permutation2', sYfSrcAvgFiles, sYoSrcAvgFiles, ...
223 'timewindow', [], ...
224 'scoutsel', {}, ...
225 'scoutfunc', 1, ... % Mean
226 'isnorm', 0, ...
227 'avgtime', 0, ...
228 'iszerobad', 0, ...
229 'Comment', '', ...
230 'test_type', 'ttest_equal', ... % Student's t-test (equal variance) t = (mean(A)-mean(B)) / (Sx * sqrt(1/nA + 1/nB))Sx = sqrt(((nA-1)*var(A) + (nB-1)*var(B)) / (nA+nB-2))
231 'randomizations', 1000, ...
232 'tail', 'two'); % Two-tailed
233
234 % Set display properties
235 StatThreshOptions = bst_get('StatThreshOptions');
236 StatThreshOptions.pThreshold = 0.01;
237 StatThreshOptions.Correction = 'fdr';
238 StatThreshOptions.Control = [1 2 3];
239 bst_set('StatThreshOptions', StatThreshOptions);
240 % Display test result
241 hSrcFig = view_surface_data([], sTestFile.FileName);
242 panel_surface('SelectHemispheres', 'left');
243 panel_stat('UpdatePanel');
244 bst_report('Snapshot', hSrcFig, sTestFile.FileName);
245 pause(1);
246 % Unload everything
247 bst_memory('UnloadAll', 'Forced');
248
249
250 %% ===== VOLUME SCOUTS =====
251 volumeScouts = {'Amygdala L', 'Amygdala R', 'Thalamus L', 'Thalamus R'};
252 % Load one source file
253 resultsMat = in_bst_results(sSrcFiles(1).FileName);
254 % Get headmodel, needed to retrieve information about the source grid
255 headmodelMat = in_bst_headmodel(resultsMat.HeadModelFile);
256 % Create volume atlas
257 sAtlas = db_template('atlas');
258 sAtlas.Name = sprintf('Volume %d', size(headmodelMat.GridLoc, 1));
259 panel_scout('SetCurrentSurface', headmodelMat.SurfaceFile);
260 panel_scout('SetAtlas', [], 'Add', sAtlas);
261 % Create a volume scout for each volume structure
262 iNewScouts = zeros(1,length(volumeScouts));
263 for ix = 1 : length(volumeScouts)
264 % Index of the structure in the Grid Atlas (in headmodel data)
265 iGridScout = find(strcmpi(volumeScouts{ix}, {headmodelMat.GridAtlas.Scouts.Label}));
266 % New scout
267 sNewScout = db_template('Scout');
268 sNewScout.Label = headmodelMat.GridAtlas.Scouts(iGridScout).Label;
269 sNewScout.Vertices = headmodelMat.GridAtlas.Scouts(iGridScout).GridRows;
270 sNewScout.Region = headmodelMat.GridAtlas.Scouts(iGridScout).Region(1);
271 sNewScout = panel_scout('SetScoutsSeed', sNewScout, headmodelMat.GridLoc);
272 % Register new scout
273 iNewScout = panel_scout('SetScouts', [], 'Add', sNewScout);
274 iNewScouts(ix) = iNewScout;
275 end
276 % Configure scouts display
277 panel_scout('SetScoutsOptions', 1, 1, 1, 'all', 0.7, 1, 1, 0);
278 hFigScouts = view_scouts({sSrcFiles(1).FileName}, iNewScouts);
279 bst_report('Snapshot', hFigScouts, sSrcFiles(1).FileName, 'Volume scouts');
280 pause(1);
281 % Unload everything
282 bst_memory('UnloadAll', 'Forced');
283
284
285 %% ===== SAVE REPORT =====
286 % Save and display report
287 ReportFile = bst_report('Save', []);
288 if ~isempty(reports_dir) && ~isempty(ReportFile)
289 bst_report('Export', ReportFile, reports_dir);
290 else
291 bst_report('Open', ReportFile);
292 end
293
294


















