UNDER CONSTRUCTION
ECoG/sEEG tutorial
Authors: Francois Tadel, Marcel Heers.
This tutorial introduces some concepts that are specific to the management of ECoG/sEEG recordings in the Brainstorm environment. It is based on a clinical case from the Epilepsy Center at the University Hospital of Freiburg, Germany.
Note that the operations used here are not detailed, the goal of this tutorial is not to introduce Brainstorm to new users. For in-depth explanations of the interface and theoretical foundations, please refer to the introduction tutorials.
NOT FOR CLINICAL USE:
The performance characteristics of the methods and software implentation presented in this tutorial have not been certified as medical devices and should be used for research purposes only.
Contents
- Dataset description
- Download and installation
- Import the anatomy
- Access the recordings
- Editing the contacts positions
- Display the depth electrodes
- Display the SEEG recordings
- Review recordings
- Import epochs of interest
- Time-frequency analysis (pre-onset baseline)
- Time-frequency analysis (separate baseline)
- Video-EEG
- Importing realistic surfaces
- Volume coregistration
- On the hard drive
- Scripting
Dataset description
License
This tutorial dataset (EEG and MRI data) remains proprietary of the Epilepsy Centre, University Hospital Freiburg, Germany. Its use and transfer outside the Brainstorm tutorial, e.g. for research purposes, is prohibited without written consent from the Epilepsy Centre in Freiburg. For questions please contact A. Schulze-Bonhage, MD, PhD: andreas.schulze-bonhage@uniklinik-freiburg.de
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the patient for providing his dataset for this tutorial, the clinical team of the Epilepsy Center Freiburg for the aquisition of the dataset and Verena Schulte for her help in preparing the dataset for the tutorial.
Clinical description
The patient is a 38yr male who suffered from drug resistant focal epilepsy since his 13th year of age with two different types of focal aware seizures that rarely evolved at nighttime to bilateral tonic-clonic seizures. Seizure type I consisted of daily aware focal seizures with myoclonic or clonic jerks of the right leg that occasionally led to falls. Type II consisted of formication paraesthesias that propagated from the right calf to the hip region. It could be provoked by stress or hot weather and occurred 2-3 times a week. In the presurgical 3T epilepsy MRI no structural abnormality was detected.
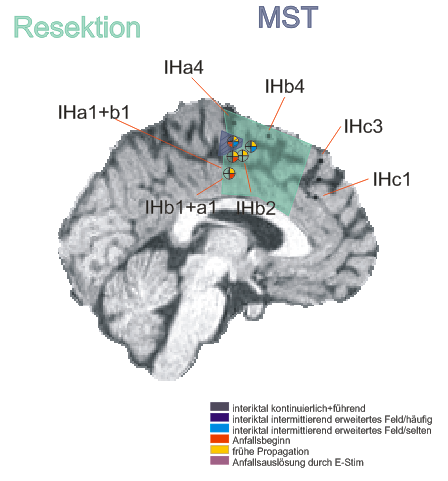
Implantation scheme
After non-invasive telemetry intracranial recordings were performed. It was decided to implant a 64 channels Ad-Tech subdural grid with 8x8 contacts (stainless steel, 10mm between centers of contacts, 2.3mm diameter exposure) over the left fronto-centro-parietal convexity covering the central region. The most inferior lateral row of contacts of the grid electrode is named A and the row of contacts next to the midline is named H. The contacts of the grid have numbers between 1-8 with the most posterior contacts of each row starting with number 1.
Additionally, 3 interhemispheric Ad-Tech strip electrodes with 4 contacts each named from posterior to anterior with IHA being the most posterior followed by IHB and IHC being the most anterior strip electrode. The numbering convention is that the deepest contact is named contact "1": and the most superficial contact of each electrode has the highest number.
In addition, 2 Ad-Tech sEEG electrodes were implanted in the right parietal lobe facing to the insula (TA & TB, distance between centers of contacts: 10mm, diameter: 0.86mm). Both sEEG electrodes have 10 electrode contacts each. The contacts are counted from anterior to posterior starting with contact number 1 at the tip of each sEEG electrode.
The figure illustrating the electrode positions was created as reported by Kovalev et al. 2005.
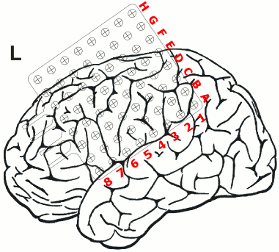
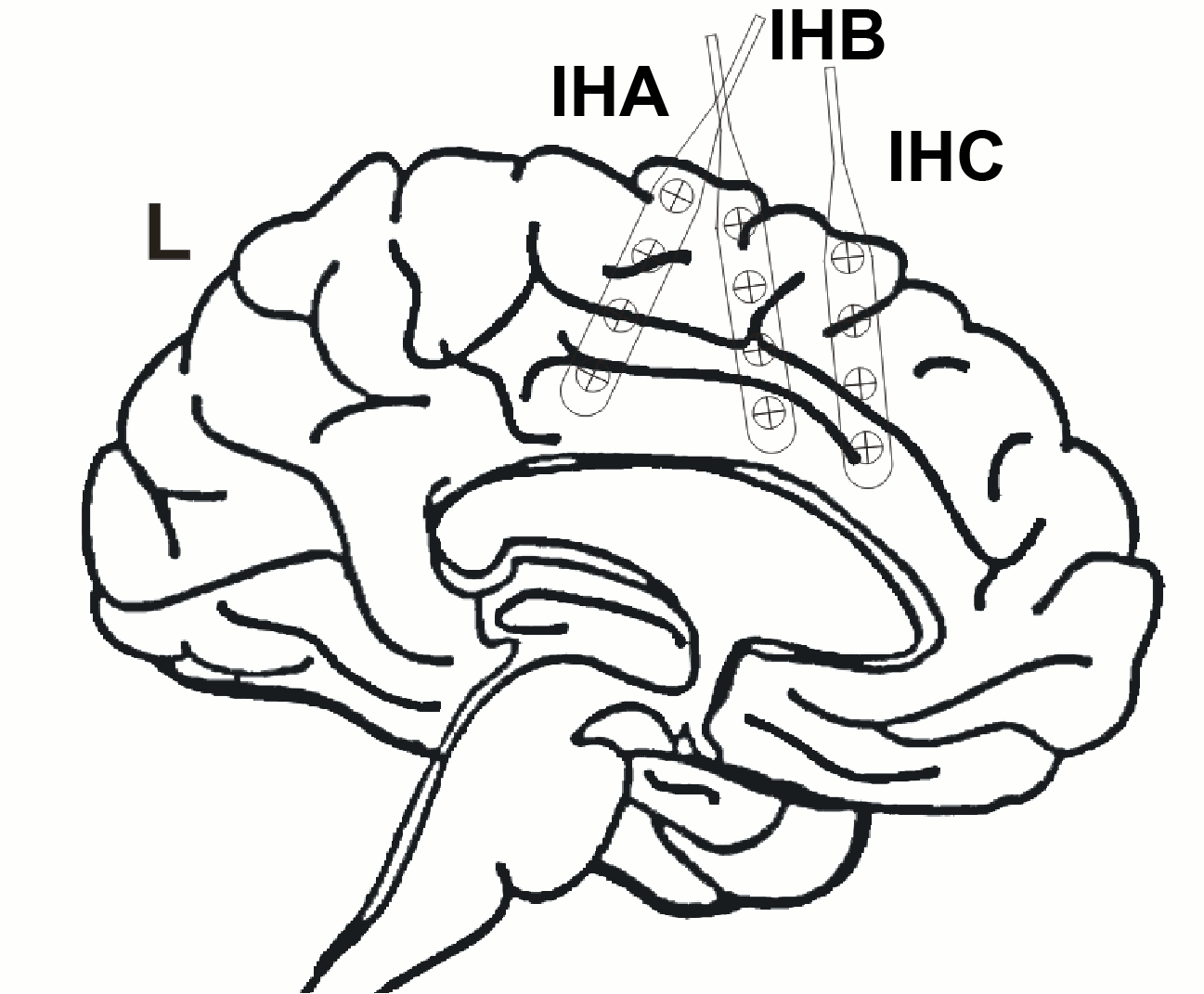
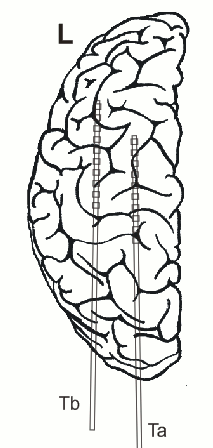
Recordings
The EEG data distributed here was recorded at 1024Hz, using a Neurofile NT digital video-EEG system with 128 channels and a 16-bit A/D converter. The signal was filtered in the recording system with a high-pass filter with a time constant of 1 second (cut-off frequency ~ 0.16Hz) and a low-pass filter with a cut-off frequency of 344 Hz.
Clinical evaluation
Interictal findings:
Repetitive sharp waves and interictal fast epileptic activity in the gamma frequency band (FEA; for advanced spectral analysis of FEA see also (Heers et al., 2018)) was almost continuously recorded in contacts G5-6 extending towards H5-6 or F5-6 and less frequently expanding to H3-4 & 7, IHA1-3, IHB1-3
Ictal findings:
- Seizure onset pattern: Repetitive gamma bursts interrupted by sharp slow waves in G5-6, H3-4 and IHA1-3
- Semiology: Myoclonic and clonic movements of the right leg intermingled with not clearly localizing habitual formication paraesthesias of the right leg
Electrical stimulation:
- Stimulation of contacts G5: habitual myoclonic seizures
- Stimulation of contact G6: habitual paraesthesias of the right leg
- Detailed function mapping was performed, which is not reported in detail here.
Resection, histopathology and postsurgical outcome:
- Resection of the posterior part of the superior frontal gyrus anterior of the precentral gyrus including the cingulate gyrus was performed. Because there was overlap between the primary motor cortex (confirmed by functional mapping) at contact H3 position H3, which was also involved in the seizure onset zone this brain area was spared and only multiple subpial transections were added here.
- Histological examination revealed focal cortical dysplasia type Ib (Palmini et al., 2004). After surgery the patient developed a severe SMA syndrome with diminished activity, problems in movement initiation and speech production from which he recovered completely after rehabilitation.
- After surgery the patient remained completely seizure free (Engel IA outcome, follow up 10 years).
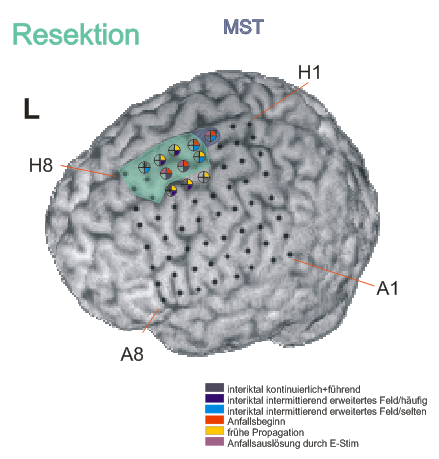
References
Heers M, Helias M, Hedrich T, Dümpelmann M, Schulze-Bonhage A, Ball T (2018): Spectral bandwidth of interictal fast epileptic activity characterizes the seizure onset zone. NeuroImage Clin 17.
Kovalev D, Spreer J, Honegger J, Zentner J, Schulze‐Bonhage A, Huppertz HJ (2005): Rapid and fully automated visualization of subdural electrodes in the presurgical evaluation of epilepsy patients. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:1078–1083.
Palmini A, Najm I, Avanzini G, Babb T, Guerrini R, Foldvary-Schaefer N, Jackson G, Luders HO, Prayson R, Spreafico R, Vinters H V (2004): Terminology and classification of the cortical dysplasias. Neurology 62:S2-8.
Files
The dataset we distribute with this tutorial follows the Brain Imaging Data Structure (BIDS) standard for neuroimaging data organization. This specification was first established for MRI and fMRI (Gorgolewski, 2016) and then refined with an extension dedicated to iEEG (Holdgraf, 2019). The files that will be imported in this tutorial are the following:
sample_ecog/
derivatives/: Everything that cannot be considered as raw data
freesurfer/sub-ecog01_ses-preimp/: Result of the FreeSurfer 7.1.1 segmentation for subject ecog01 (T1 pre-implantation)
sub-ecog01/: Raw data for subject ecog01
ses-preimp/: Imaging exams performed before the implantation of the ECoG/sEEG.
anat/sub-ecog01_ses-preimp_T1w.nii.gz: T1-weighted MRI pre-implantation
ses-postimp/: Exams performed with the sEEG/ECoG devices implanted.
anat/sub-ecog01_ses-postimp_T1w.nii.gz: T1-weighted MRI post-implantation
ieeg/..._task-seizure_run-01_ieeg.eeg: 1 hour ECoG+sEEG recordings with 3 seizures (saved using the BrainVision file format, with the header files .vhdr and .vmrk)
ieeg/..._space-IXI549Space_electrodes.tsv: Position of the contacts in MNI space (SPM12 Segment non-linear normalization)
ieeg/..._space-other_electrodes.tsv: Position of the contacts in world coordinates
All the anatomical images have been de-identified with mri_deface from FreeSurfer 6.
Download and installation
Requirements: You have already followed all the introduction tutorials and you have a working copy of Brainstorm installed on your computer.
Go to the Download page of this website, and download the file: sample_ecog.zip
- Unzip it in a folder that is not in any of the Brainstorm folders (program folder or database folder)
- Start Brainstorm (Matlab scripts or stand-alone version).
Select the menu File > Create new protocol. Name it "TutorialEcog" and select the options:
"No, use individual anatomy",
"No, use one channel file per acquisition run".
Import the anatomy
Pre-implantation MRI
Right-click on the TutorialEpimap folder > New subject > Subject01.
Keep the default options you defined for the protocol.- Switch to the "anatomy" view of the protocol.
Right-click on the subject node > Import MRI:
Set the file format: "All MRI file (subject space)"
Select the file:Do you want to apply the transformation to the MRI file? YES
The MRI viewer opens automatically. Click on "Click here to compute MNI transformation". It computes an affine transformation between the subject space and the MNI ICBM152 space, and sets default positions for all the anatomical landmarks.
![[ATTACH] [ATTACH]](/moin_static198/brainstorm1/img/attach.png)
- Click on [Save] to close the MRI viewer.
Post-implantation MRI
- The pre-implantation MRI will be used as the anatomical reference for this subject. We will now import a second scan done after the sEEG/ECoG implantation, on which we can see the recording contacts. In this dataset, the post-implantation volume is another T1 MRI scan (contacts hyposignal appear in black), but it is more commonly a CT scan (contacts hypersignal appear in white).
Right-click on the subject node > Import MRI:
Select the file:Do you want to apply the transformation to the MRI file? YES
This will reorient the MRI in Brainstorm's standard orientation, so you can see the coronal/sagittal/axial views correctly oriented.How to register the new volume? IGNORE
The two volumes have already been coregistered with SPM. See the section Volume coregistration for more details on this option.Reslice the volume? YES
This will rewrite the volume with the orientation and resolution of the pre-implantation MRI, so that the two volumes can be overlaid in the MRI viewer. You may answer no to this question when the resolution of the pre-implantation MRI is very low and/or when you want to edit the positions of the fiducials in the original post-implantation volume (CT or MRI).The MRI viewer opens automatically, showing the post-implantation volume as a colored layer on top of the previous volume. Adjust the transparency and amplitude threshold of this layer in the section "Data options" of the Surface tab, adjust its colormap with the popup menu of the figure. Use this display to validate that the coregistration of the two volume is correct, all the parts of the head must align well.
Generate default surfaces
Right-click on the pre-implantation MRI > SPM canonical surfaces.
- Leave the default option selected (20484). This represents the resolution of SPM template surface used in this process. The higher the better, but it will slow down significantly the computation of the epileptogenicity maps.
These surfaces will be used later, in the computation of the epileptogenicity maps. Read the advanced sections of this page for information on how to use realistic surfaces from BrainVISA or FreeSurfer.
![[ATTACH] [ATTACH]](/moin_static198/brainstorm1/img/attach.png)
Access the recordings
Link the recordings
- Switch to the "functional data" view (2nd button, on top of the database explorer).
Right-click on the subject folder > Review raw file:
Select the file format: "SEEG: Deltamed/Micromed/..."
Select all the SEEG recordings: tutorial_epimap/seeg/*.TRC
The new files "Link to raw file" let you access directly the contents of the original SEEG files. The menu "Review raw file" does not actually copy any data to the database. More information.
Edit the contacts positions
In order to generate epileptogenicity maps, we need accurate 3D positions for the contacts of the depth electrodes. Placing the contacts requires a good understanding of the implantation scheme reported by the neurosurgeon, and some skills in reading MRI scans. To make this tutorial easier to reproduce and follow, we distribute the positions of the contacts saved in a text file (folder /anat/implantation). For instructions to place the SEEG contacts using Brainstorm, read the advanced section Editing the contacts positions.
- The channel files "Micromed channels" contain the name of the channels, but not their positions. We need to import or edit separately the positions of the SEEG contacts.
- Click on the [+] next to the three SZ folders, select all the channel files simultaneously.
Right-click one channel file > Add EEG positions > Import from file:
Select the file format: "EEG: ASCII: Name, XYZ (*.*)"
Select the file: tutorial_epimap/anat/implantation/elec_pos_patient.txt
![[ATTACH] [ATTACH]](/moin_static198/brainstorm1/img/attach.png)
Select a scaling factor: 0.1 (keep the default selection)
The positions in this text file are in millimeters, while the expected unit for "EEG: ASCII" is the centimeter. This option means that the values will be interpreted as 0.1*cm, ie. millimeters.
![[ATTACH] [ATTACH]](/moin_static198/brainstorm1/img/attach.png)
Apply MRI transformation? YES
This will interpret the coordinates in the text file as positions in the referential defined by the voxel-to-world transformation (vox2ras) transformation available in the MRI, if applicable (in NIfTI format, this corresponds to matrices qform or sform). If you answer no here, it would load the positions as Brainstorm SCS coordinates and try to realign them based on the NAS/LPA/RPA landmarks.
![[ATTACH] [ATTACH]](/moin_static198/brainstorm1/img/attach.png)
- At the end, you get a report indicating how many channels from the SEEG recordings were attributed a new 3D position. The channels are matched by name: the position file you import must include the labels of the channels and they must be named exactly in the the same way as in your recordings.
The type of the channels for which a position was not found is set to EEG_NO_LOC, in order to ignore them when processing the SEEG data. In this example dataset, the channels that are not found are "fz" and "cz", which are indeed not SEEG contacts.
You should always validate that the type of all the channels has been detected correctly. Check also that the names are correct and using the same convention for all the contact of a given electrode. These are entered manually, and typing errors are frequent. Right-click on a channel file > Edit channel file.
![[ATTACH] [ATTACH]](/moin_static198/brainstorm1/img/attach.png)
To edit one channel, double-click on the text to modify. To edit multiple channels, select them all and right-click > Set channel group/type. The column Group corresponds to the name of the depth electrode. It is detected based on the channel type and name. If you include as SEEG a channel that detected as something else or rename a channel, you would need to manually update the channel name.
MNI coordinates: Note that you can also import 3D positions in MNI coordinates. This example dataset includes the MNI coordinates of all the contacts, they are available in the file "elec_pos_patient.txt". To import this file correctly, make sure you select a file format that explicitly mentions MNI coordinates. In this example, it would be: "EEG: ASCII: Name, XYZ_MNI (*.*)".
If you don't have the positions for the SEEG contacts, or if they don't look correctly aligned, you can directly place them in the MRI viewer. See the section Editing the contacts positions.
Editing the contacts positions
If you don't have access to the positions of the SEEG contacts in a text file, as illustrated in this tutorial, you can place the contacts in the MRI viewer.
After adding the continuous files to the database, right-click on the channel file > MRI registration > Edit (MRI Viewer: ...). Select one of the post-implantation volumes, that shows clear artifacts around the SEEG contacts.
![[ATTACH] [ATTACH]](/moin_static198/brainstorm1/img/attach.png)
- If the resolution of the pre and post volumes is similar, which is the case in this tutorial, it doesn't matter much if you place the contacts on the resliced or the original post volume. But in the case of a post-implantation CT scan, the resolution is often much higher in the CT. In this case, prefer editing the channel file on the original high-resolution CT rather than on the low-resolution resliced CT volume.
Add the missing information for the electrodes: for positioning the SEEG contacts based on the tip and orientation of the depth electrodes, we need to know the distance between two adjacent contacts on the electrode. In the iEEG tab, select an electrode and fill the field "contact spacing" if it is empty. If the value is the same for all the electrodes, select all the electrodes at once (Ctrl+A) and enter the contact spacing. In the case of these DIXI electrodes, the contact spacing is 3.5mm.
![[ATTACH] [ATTACH]](/moin_static198/brainstorm1/img/attach.png)
- Then mark all the electrodes one by one:
- In the iEEG tab, select one electrode.
- In the MRI Viewer, place the cursor at the tip of the depth electrode.
In the iEEG tab, click on button [Set tip], the button turns green.
In the MRI Viewer, place the cursor at the entrance of the electrode in the skull, or anywhere else along the depth electrode if this is more convenient. We don't use the actual position of this point, we only use it to estimate the direction of the electrode from its tip. Then click on button [Set skull entry]. The button turns green and the electrode appears in the MRI viewer.
- If there are contacts available for this electrode, this would also place them along the depth electrode. If the positions for these contacts was already defined, you should get a warning asking whether you want to update their positions.
From time to time, you can click on the menu Contacts > Save modifications in the iEEG tab. This would prevent you from losing your work if anything unexpected happens.
When you are done with marking all the electrodes, click on [Save] in the MRI viewer. You can then display the electrodes you placed in 3D (right-click on the channel file > Display sensors).
![[ATTACH] [ATTACH]](/moin_static198/brainstorm1/img/attach.png)
You can also start defining an implantation scheme without any recordings in your database. You can use this option for creating a text file with all the contacts positions, and use it in Brainstorm or any other program.
Go back to the subject anatomy, right-click on the appropriate post-implantation volume > SEEG/ECOG implantation.
![[ATTACH] [ATTACH]](/moin_static198/brainstorm1/img/attach.png)
- It creates a new folder "Implantation" in the subject, and starts editing an empty channel file. You need to create the electrodes and set their models (or all their properties) before placing them in the MRI viewer. When you place an electrode, it creates all the corresponding contacts, while in the previous case, it was only setting the position of the existing contacts.
At any moment, you can export the 3D positions of the contacts you created to a text file with the menu Contacts > Export contacts positions in the iEEG tab.
- When you are done, click on [Save] in the MRI viewer. It saves the new channel file and updates the number of channels in the database explorer.
Display the depth electrodes
3D figures
Right-click on the channel file > Display sensors > Explore all the options available.
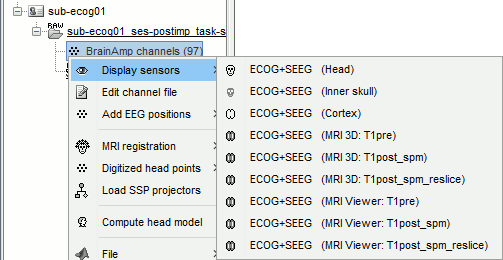
You can render the SEEG depth electrodes in 3D together with the subject anatomy: surfaces, pre- or post-implantation volumes. You can add more anatomy elements to the figure with the button "Add a surface" at the top-right of the Surface tab. For more help: Display the anatomy.
Click on a contact to select it, right-click on it to get its name:
MRI Viewer
You can also display the contacts in the MRI viewer, on top of the the pre- or post-implantation volumes. By default, the electrode is displayed in a slice if there is a SEEG contact associated to it in the slice.
To display all the electrodes, select the option "MIP: Functional". For a glass-brain view, select at the same time the option "MIP: Anatomy".
Zoom in/out with the buttons or the associated shortcuts (Ctrl+Scroll or +/-) and explore the volume with (Shift+)x/y/z. Additional display options are available in the popup menu for this figure. All the shortcuts are listed in this tutorial.
You can edit the position of a contact directly by clicking on its dot in one of the slice and moving it around. Modifications are not saved immediately and can be cancelled when you close the window. Alternatively, you can right-click on the figure > Set electrode position.
Panel iEEG
When opening SEEG/ECOG recordings, the panel iEEG is added to the Brainstorm window. You can use it to edit the display properties of the depth electrodes. In this interface, "electrode" refers to entire depth electrode implanted in the head of the patient while "contact" refers to recording sites on the electrode. There are multiple contacts on an electrode, and one contact corresponds to one channel of data in the channel file and the recordings.
![[ATTACH] [ATTACH]](/moin_static198/brainstorm1/img/attach.png)
SEEG depth electrodes are graphical objects, they are defined independently from the SEEG contacts available in the channel file and recordings. A contact/channel is associated to a depth electrode using the Group property of the channel, accessible with a right-click on the channel file > Edit channel file.
- In this example, the depth electrodes available in the panel iEEG have been detected automatically based on the names and positions of the data channels. In the convention used here, the contact names must start with one or more letters (the name of the electrode) followed by a number representing the index of the contact on the electrode. Contact #1 is at the tip of the electrode, and is therefore the deeper contact of the electrode. If the convention used in your recordings is different, you may have to edit the electrodes properties in order to get them displayed correctly.
- Buttons in the toolbar:
Add an electrode: Adds an entry for a new depth electrode. The new electrode will not be displayed until you set its properties and position. This will not add or remove SEEG contacts or channels of data.
Remove selected electrodes: Deletes a depth electrode from the list, but does not modify the list of SEEG contacts or channels of data.
Set color for selected electrodes: Self explanatory.
Show/hide selected electrodes: To hide an electrode in the 3D figures and MRI viewer, select it in the list then click on this button. Select all the electrodes with the standard shortcut Ctrl+A.
Display contacts as: Depth electrodes / Spheres.
Contacts > Set default positions: For each of the selected electrodes, the current positions of the SEEG contacts are discarded and replaced with the default positions of the contacts on the electrode. The properties used for setting the position of the contacts are the contact spacing, the tip of the electrode and the entry point in the skull. Contact #i is placed along the electrode at (i-1)*contact_spacing millimeters from the tip of the electrode.
Contacts > Project on electrode: For each of the selected electrodes, the contacts are projected orthogonally on the electrode. This menu can be useful for aligning contacts that were marked one by one.
Contacts > Save modifications: Save the current modifications to the channel file. Otherwise, the modifications are saved only when you close the figure (dialog box "Save modifications to channel file?")
Contacts > Export contacts positions: Save the 3D positions of the SEEG contacts in a text file, using one of the file formats supported by Brainstorm.
Electrode properties: Properties that have an impact on the position of the contacts.
- If you edit the properties, the modifications will apply to all the selected electrodes in the current channel file. Check what is selected before making changes.
Type: SEEG/ECOG
Model: List of electrode models. If you select an entry in this menu, it will copy the default properties for this model to the selected electrodes. If you are using electrodes that are not in this list, please post on the specification of your devices on the user forum and we will add them to this list.
Number of contacts: Number of recording sites on the electrode. By default, this is set for SEEG to the maximum index found in a group of contacts. Example: electrode s' is associated to channels s'1, s'2, s'3, s'10, s'11, s'12 => detected number of contacts is 12.
Contact spacing: Distance between the centers of two consecutive contacts in the electrode. In this example dataset, the default value corresponds to the average distance observed between pairs of adjacent contacts.
Set tip: Select one electrode in the list, then move the cursor of the MRI viewer to the tip of the selected electrode (center of the first contact), and finally click on [Set tip].
Set skull entry: Select one electrode in the list, then move the cursor of the MRI viewer to the point where the depth electrode enters the skull, and finally click on [Set skull entry]. This position does not correspond to any contact, it is used only to estimate the direction of the depth electrode. More details.
- Display options: Properties that only affect the way the electrodes are renderer graphically.
Contact length: Defines the length of the yellow cylinder that represents the contacts along the electrode axis, or the diameter of the sphere when the electrodes are not rendered.
Contact diameter: Diameter of the yellow cylinders representing the contacts. By default, this value is slightly larger than the electrode diameter so that it is rendered correctly. If you use the same value as the electrode diameter, the contacts might not be visible.
Electrode diameter: Diameter of the cylinder representing the SEEG depth electrode.
Electrode length: Length of the cylinder representing the SEEG depth electrode.
Display the SEEG recordings
SEEG time series
Right-click on any "Link to raw file" > SEEG > Display time series.
![[ATTACH] [ATTACH]](/moin_static198/brainstorm1/img/attach.png)
- For instructions on how to use this viewer, please refer to these tutorials:
- Typical display configuration includes:
Set the page duration to 20s or 30s: Record tab > Page settings.
Change the display mode to "columns": Record tab > Toolbar > First button.
Change the montage (bipolar/monopolar): Record tab > Drop-down menu.
Note all the default montages available for SEEG: you can display all the contacts at once, or each electrode individually.- Set visualization filters: Filter tab.
- Disable the automatic scaling when changing page: Button [AS] in the time series figure.
- Adjust the amplitude scale: Right-click+move up/down, or buttons [^] and [v].
Set the resolution precisely: Right-click on the figure > Figure > Set axes resolution.
With the menus "3D electrodes" you can visualize the SEEG values at the current time point. Move the time cursor and it will update the values represented on the SEEG contacts.
![[ATTACH] [ATTACH]](/moin_static198/brainstorm1/img/attach.png)
Interpolate on the anatomy
From the same SEEG display menu, you can also project the SEEG values on the MRI or the cortex. You can edit the colormap for the displayed values like any other colormap.
MRI volume: All the voxels in the neighborhood of a contact are attributed the value associated with this contact. In the figure below, both "MIP: functional" and "MIP: anatomy" options are selected (maximum intensity projection along each axis = "glass brain" view).
Cortex surface: The values of the vertices are interpolated from the nearest SEEG contacts (the magnitude decreases with the distance to the contact).
![[ATTACH] [ATTACH]](/moin_static198/brainstorm1/img/attach.png)
2D topography
Two additional popup menus allow you to display the SEEG recordings grouped by electrode, but without any 3D information: 2DLayout and 2DElectrodes.
Review recordings
Power spectrum
We recommend you always start your data analysis with a spectral evalution of the recordings, it may help you identify bad channels. This is described in tutorials Power spectrum and EEG and epilepsy.
- In Process1, select all the continuous files (SZ1, SZ2, SZ3: link to raw files or folders).
Run process Frequency > Power spectrum density (Welch): All file, Length=10s, Overlap=50%.
![[ATTACH] [ATTACH]](/moin_static198/brainstorm1/img/attach.png)
Double-click on the PSD files to display them. Some channels have noise levels that are obviously higher than the others and should therefore be considered as suspicious.
Left = SZ1 (v'1,f'1), Center = SZ2 (v'1,t'8), Right = SZ3 (o'1,t'8)
![[ATTACH] [ATTACH]](/moin_static198/brainstorm1/img/attach.png)
- If the spectrum plots are too noisy and difficult to read, you can recompute them with lower frequency resolution. Decrease the duration of the estimator window, possibly down to 1s depending on the sampling frequency. This will estimate the PSD by averaging the power of more time windows with less data bins, the result will be smoother.
Bad channels
We will now to review the recordings of the three seizures recorded for this subject: SZ1, SZ2, SZ3. All the following steps are illustrated only for SZ1 but need to be reproduced for the other files.
Double-click on SZ1/Link to raw file to open the SEEG recordings for the first seizure.
We need to mark the bad channels using a "monopolar" montage (common reference). If you are currently reviewing the recordings with a bipolar montage, switch it back to "All channels", using the menu in the toolbar of the record tab or with the popup menu of the time series figure. Otherwise, marking a signal as bad (eg. "v'2-v'1") would actually mark two channels as bad ("v'1" and "v'2"), while only one contact ("v'1") is not recording properly.
Click on the channels that you consider as bad to select them. For SZ1, select v'1 and f'1.
Press the delete key, or use the popup menu Channels > Mark selected as bad.
![[ATTACH] [ATTACH]](/moin_static198/brainstorm1/img/attach.png)
- Close the figure and repeat for the two other files.
Import epochs of interest
At this point of the analysis, we are still looking at the original files, no SEEG data was copied to the database. The montages are saved in the Brainstorm preferences, the bad channels and new events are saved in the links of the database but not reported to the original .TRC files. If you delete your protocol at this point, you would only lose the event marking and bad channel selection.
We are now going to import two segments of recordings for each seizure file: the seizure (10s before and 40s after the onset) and the baseline (all the segment selected). This will make real copies of the data in the database, so we can run additional processes on them.
Import in database
Right-click on SZ1 / Link to raw file > Import in database:
- Time window: All, the only interesting point is to have access to the Onset marker.
- Split in time blocks: Disabled
Use events: Enabled, select Onset
Epoch time: [-10000, +40000] ms (imports -10s to 40s around the event "Onset")
- Remove DC offset: Disabled
- Resample: Disabled
- At the end, you should have three new folders SZ1/SZ2/SZ3, the same name as the original .TRC files, but without the tag "raw" on top. These new folders contain copies of the SEEG recordings, if you delete these folders from the database explorer, you lose the recordings they contain.
The imported epochs are saved with a new timing: for the seizure onsets, the reference time t=0s is now the event "Onset", which has been removed from the list. You can still see the other marker Seizure, which should be slightly before 0s. For the baselines, the reference t=0 is the beginning of the segment.
![[ATTACH] [ATTACH]](/moin_static198/brainstorm1/img/attach.png)
Time-frequency analysis (pre-onset baseline)
The aim of this section is to evaluate the frequency range for the computation of the epileptogenicity maps. We need to identify which frequency band is the most representation and specific of the high-frequency activity at the beginning of the seizures.
Starting from this step, you need to have the SPM12 toolbox installed on your computer and added to your Matlab path. We need here the multitaper functions from the FieldTrip toolbox, which are also already in the SPM package.
- In Process1, select all the Onset bipolar files.
Select the process: Frequency > FieldTrip: ft_mtmconvol (Multitaper): (do not run)
Time window: [-10, 10]s
Sensor types: SEEG
Taper: hanning
Frequencies: 10:3:220
Modulation factor: 10
Time resolution: 1000ms
Measure: Magnitude
Save average: Disabled
Add the process: Standardize > Baseline normalization:
Baseline: [-10, -1]s
Method: Z-score transformation
Overwrite: Enabled
Add the process: Average > Average files:
Group files: Everything
Function: Arithmetic average
- Four new files are available in the database: one for each bipolar Onset epoch, and one average, saved in folder "Intra-subject".
Right-click on the average time-frequency map > All channels. Then you can click on a channel to open it in a separate figure. Change the colormap to "GIN" and the colormap maximum to [-0.1,+0.1]*10^2 to reproduce the figures below.
Time-frequency analysis (separate baseline)
Another approach is to normalize the time-frequency maps based on the baseline file used for the computation of the epileptogenicity maps, instead of the short baseline immediately before the seizure onset. This is a bit more complicated but produces maps that are more coherent with the epileptogenicity measures used in the next section. To increase the educational value of this section, let's manage the time differently: we'll compute the time-frequency decomposition for the entire Onset epochs (-10s,+40s) and then extract only the section we are interested in.
Start by deleting all the time-frequency files computed in the previous section: select them in the database explorer and press the Delete key, or select the subject folder in Process1 with button [Process time-freq] selected and use process File > Delete files > Delete selected files.
- In Process1, select all the bipolar files (Onset and Baseline).
Run the process: Frequency > FieldTrip: ft_mtmconvol (Multitaper):
- In Process2, select the time-frequency file for the baseline in FilesA, and for the onset in FilesB. You can either select the time-domain epochs and click on the buttons [Process time-freq], or select directly the time-frequency files generated with the previous step. Note the order in these lists matters: make sure you select the Onset and Baseline files in the exact same order.
Select the process: Standardize > Baseline normalization (do not run immediately):
Baseline: All file
Method: Z-score transformation
Add process: Average > Average files:
Group files: Everything
Function: Arithmetic average
Run the pipeline. In output, you get the three normalized time-frequency maps for the three Onset epochs, plus the average of these three files. As expected, the time definition of the average file is [-10,+40]s. In order to produce similar figures as the ones from the previous section, we will extract the same time window as before (-10s to +10s).
![[ATTACH] [ATTACH]](/moin_static198/brainstorm1/img/attach.png)
- In Process1, select the average time-frequency map.
Run process Extract > Extract time, time window = [-9.5, 9.53]s (FieldTrip's multitaper function cuts a piece of the recordings to account for possible edge effects).
Create a movie with the SEEG signals
Saving the conclusions of your visual exploration as a video file is an efficient solution for keeping track of your analyses and sharing them with your colleagues. In such a movie, it can be interesting to display simultaneously the original SEEG recordings with the epileptogenicity maps. However, if you try to open the two files, you get an error message explaining that Brainstorm cannot display two files with different time definitions at the same time.
A solution to go around this limitation is to resample the epileptogenicity results (one value every two seconds = 0.5Hz) with the same frequency as the SEEG recordings (initially 512Hz). This would multiply the size of the file containing the epileptogenicity results by 2*512, creating a file of several Gb. To avoid wasting too much disk space and risking to crash Matlab by creating gigantic variables, we can cut and downsample the SEEG recordings of interest. Let's illustrate this with the seizure SZ2.
In Process1, select the file SZ2_bipolar_2/Onset.
Select process Extract > Extract time: 0-20 s
- Run the execution. The output is a downsampled version of the first 20s after the seizure onset.
In Process2, select:
FilesA = Resampled seizure recordings SZ2_bipolar_2/Onset | time (target time definition)
FilesB = Stat results Epileptogenicity_surface/EI_SZ2_120_200_3 (file to resample)Run process Standardize > Interpolate time: You can try the interpolation methods "nearest" or "linear", depending on if you would like to see the real statistical results or smooth (but inaccurate) transitions between the steps of two seconds for which the epileptogenicity maps were computed.
- The new resampled epileptogenicity file has the same time definition as the resampled seizure SEEG recordings: the two can now be opened simultaneously.
- After creating all the files you want to display, open them simultaneously and position the various figures on your screen the way you would like them to appear in the movie. Note that the text is displayed with a fixed size, it doesn't change if you reduce the size of the figures, so if you make the figures smaller the text will be bigger relatively to the graphics, making it possibly more readable in your screen captures.
To display only a subset of channels in the figure, either use an existing predefined montage, create a montage with the Montage editor, or select the channels you want in the time series figures and use the menu "Create from selection".
Right-click on any of the figures > Snapshot > Movie (time): All figures. You can experiment the effect of the various parameters to obtain exactly the movie you want. The figure on which you right-click will show a time stamp at the bottom-left corner in the movie.
The video file generated can be viewed on any computed, added to a website or included in a slide of a presentation.
Video-EEG
Importing realistic surfaces
Instead of using the default SPM canonical surfaces, you can use realistic cortex envelopes, extracted with FreeSurfer, BrainSuite or BrainVISA. Instead of importing the anatomy as described previously (pre MRI then post MRI), follow these steps. Note that this cannot be done with the simplified interface in the Guidelines tab.
Right-click on the subject folder > Import anatomy folder:
- Select file type: "BrainVISA folder"
- Select folder: tutorial_epimap/anat/MRI/brainvisa/
- Number of vertices: 15000
When the MRI viewer shows up asking for fiducial points, click on "Click here to compute MNI transformation", then click on [Save] when the computation is done.
![[ATTACH] [ATTACH]](/moin_static198/brainstorm1/img/attach.png)
- This is the anatomy of the subject (MRI pre-implantation) processed with the Morphologist pipeline of BrainVISA 4.5. The MRI pre-implantation is now imported, but the post-implantation is still missing.
Right-click on the subject folder > Import MRI:
Import the volume exactly as previously, following these guidelines.
When importing the volumes processed with FreeSurfer, you probably need to register the volume, as FreeSurfer rewrites the volume with a different orientation. Select option [SPM] instead of [Ignore].
In the subject anatomy folder, you can decide to use the pial surface ("cortex") or the grey-white interface ("white") for the computation of the epileptogenicity maps. As these surfaces are fairly different, it may leed to very different results. A SEEG contact close to one surface can be too far from the other to be taken into account in the computation. Make this choice carefully. To change the default surface, right-click > Set as default cortex, or simply double-click on it. Just avoid selecting the high-resolution surfaces (126000 vertices) or the computation will take forever.
Then you can repeat all the steps previously presented. The results may look different depending on the surface you selected (left=cortex, right=white).
![[ATTACH] [ATTACH]](/moin_static198/brainstorm1/img/attach.png)
Volume coregistration
When importing two volumes successively in the subject anatomy, you need to coregister all the new volumes with the first volume imported, otherwise you wouldn't be able to do anything with them. The questions that are asked when importing a second volume are the following.
Transformation: This has nothing to do with the coregistration with the first volume, you also got this question when importing the first volume. If you answer "yes" for the first volume, you should probably answer "yes" here as well.
![[ATTACH] [ATTACH]](/moin_static198/brainstorm1/img/attach.png)
Registration: How to register the new volume with the previous one?
![[ATTACH] [ATTACH]](/moin_static198/brainstorm1/img/attach.png)
SPM: Uses the SPM toolbox to estimate the rigid transformation from the new volume to the reference volume (the first volume imported). It modifies the voxel=>world transformation in the second volume (vox2ras 4x4 matrix). If you skip this registration step, you can run it later by right-clicking on the second file > Register with default MRI > SPM: Register only.
MNI: Uses SPM code (embedded in Brainstorm) to estimate an affine transformation from each of the two volumes to the MNI normalized space. The transformation from the new volume to the reference is approximated with the two successive MNI transformations: (voxel_new=>MNI) => inv(voxel_ref=>MNI). This gives inaccurate results, and does not guarantee a rigid transformation (there might be slight scaling factor introduced). Do not use this option, unless you have no other option available.
Ignore: Considers that the two volumes are already coregistered. This option will keep the original voxel=>world transformations available in the .nii files, and assume they bring the two volumes in the same space.
Reslice: You have the option to rewrite the new volume so that it matches voxel by voxel the reference volume. If you know that the new file was already registered and resliced before you imported it in Brainstorm, answer NO to this question. Otherwise, this option is necessary if you are expecting to overlay the two volumes in the MRI viewer. If you do not reslice the volume, you would still be able to edit the positions of the SEEG contacts on one or the other volume, but not to superimpose them to check they were registered correctly. This is a limitation of the MRI viewer that will be improved at some point.
![[ATTACH] [ATTACH]](/moin_static198/brainstorm1/img/attach.png)
All these options are also available after importing the file. Right-click on the second file > Register with default MRI. The reslice option previously presented corresponds to the menu "Reslice / vox2ras transform". The other reslicing options offer alternatives based on the MNI coordinates or the SCS coordinates, which are most of the time a lot less accurate.
![[ATTACH] [ATTACH]](/moin_static198/brainstorm1/img/attach.png)
On the hard drive
The definition of the depth electrodes is saved in the channel file, in the field IntraElectrodes. It contains all the information that can be edited in the iEEG tab. The position of the SEEG contacts is saved in the field Channel(i).Loc, as described in the tutorial Channel file. ChannelMat.IntraElectrodes is an array of structures with the following fields.
Name: String identifying the depth electrode in the iEEG tab.
Type: String identifying the type of device, 'SEEG' or 'ECOG'.
Model: String identifying the make and model of the electrode (eg. 'DIXI D08-05AM Microdeep'). This is of known electrode models is accessible with panel_ieeg('GetElectrodeModels').
Loc: [3xN] positions with all the relevant points for the device (tip and entry for SEEG depth electrode, 4 corners for ECOG grid).
Color: [1x3] color vector.
ContactNumber: Number of SEEG/ECOG contacts on this device.
ContactSpacing: Distance between the centers of two contacts in the electrode (meters).
ContactDiameter: Diameter of the yellow cylinders representing the contacts (meters).
ContactLength: Length of the yellow cylinder representing the contacts (meters).
ElecDiameter: Diameter of the cylinder representing the SEEG depth electrode (meters).
ElecLength: Length of the cylinder representing the SEEG depth electrode (meters).
Visible: 0 or 1, indicates in the electrode should be rendered in the figures.
Scripting
The following script from the Brainstorm distribution reproduces the analysis presented in this tutorial page: brainstorm3/toolbox/script/tutorial_ecog.m