Corticomuscular coherence (CTF MEG)
[TUTORIAL UNDER DEVELOPMENT: NOT READY FOR PUBLIC USE]
Authors: Raymundo Cassani, Francois Tadel & Sylvain Baillet.
Corticomuscular coherence measures the degree of similarity between electrophysiological signals (MEG, EEG, ECoG sensor traces or source time series, especially over the contralateral motor cortex) and the EMG signals recorded from muscle activity during voluntary movements. Cortical-muscular signals similarities are conceived as due mainly to the descending communication along corticospinal pathways between primary motor cortex (M1) and the muscles attached to the moving limb(s). For consistency purposes, the present tutorial replicates, with Brainstorm tools, the processing pipeline "Analysis of corticomuscular coherence" of the FieldTrip toolbox.
Contents
Dataset description
The dataset is identical to that of the FieldTrip tutorial: Analysis of corticomuscular coherence:
- One participant,
- MEG recordings: 151-channel CTF MEG system,
- Bipolar EMG recordings: from left and right extensor carpi radialis longus muscles,
- EOG recordings: used for detection and attenuation of ocular artifacts,
- MRI: 1.5T Siemens system,
- Task: The participant lifted their hand and exerted a constant force against a lever for about 10 seconds. The force was monitored by strain gauges on the lever. The participant performed two blocks of 25 trials using either their left or right hand.
- Here we describe relevant Brainstorm tools via the analysis of the left-wrist trials. We encourage the reader to practice further by replicating the same pipeline using right-wrist trials!
Corticomuscular coherence:
Coherence measures the linear relationship between two signals in the frequency domain.
Previous studies (Conway et al., 1995, Kilner et al., 2000) have reported corticomuscular coherence effects in the 15–30 Hz range during maintained voluntary contractions.
- TODO: IMAGE OF EXPERIMENT, SIGNALS and COHERENCE
Download and installation
Pre-requisites
Please make sure you have completed the get-started tutorials, prior to going through the present tutorial.
- Have a working copy of Brainstorm installed on your computer.
Install the CAT12 Brainstorm plugin, to perform MRI segmentation from the Brainstorm dashboard.
Download the dataset
Download SubjectCMC.zip from the FieldTrip FTP server:
ftp://ftp.fieldtriptoolbox.org/pub/fieldtrip/tutorial/SubjectCMC.zip- Unzip the downloaded archive file in a folder outside the Brainstorm database or app folders (for instance, directly on your desktop).
Brainstorm
- Launch Brainstorm (via the Matlab command line or the Matlab-free stand-alone version of Brainstorm).
Select from the menu File > Create new protocol. Name the new protocol TutorialCMC and select the options:
No, use individual anatomy,
No, use one channel file per acquisition run.
Importing anatomy
Right-click on the newly created TutorialCMC node > New subject > Subject01.
Keep the default options defined for the study (aka "protocol" in Brainstorm's vernacular).Switch to the Anatomy view of the protocol (
 ).
). Right-click on the Subject01 > Import MRI:
Select the file format: All MRI files (subject space)
Select the file: SubjectCMC/SubjectCMC.mri
This step will launch Brainstorm's MRI viewer, where coronal, sagittal and axial cross-sections of the MRI volume are displayed. note that three anatomical fiducials (left and right pre-auricular points (LPA and RPA), and nasion (NAS)) are automatically identified. These fiducials are located near the left/right ears and just above the nose, respectively. Click on Save.
In all typical Brainstorm workflows from this tutorial handbook, we recommend processing the MRI volume at this stage, before importing the functional (MEG/EEG) data. However, we will proceed differently, for consistency with the original FieldTrip pipeline, and readily obtain sensor-level coherence results. We will proceed with MRI segmentation below, before performing source-level analyses.
- We still need to verify the proper geometric registration (alignment) of MRI with MEG. We will therefore now extract the scalp surface from the MRI volume.
Right-click on the MRI (
 ) > MRI segmentation > Generate head surface.
) > MRI segmentation > Generate head surface.
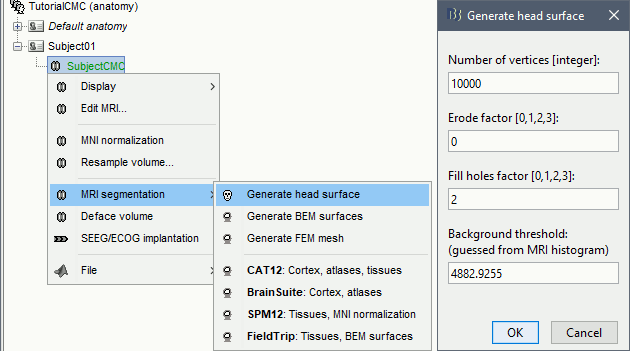
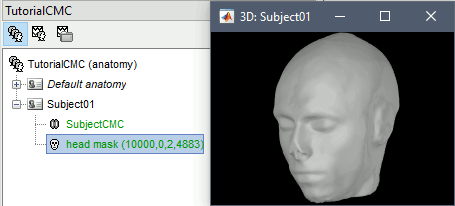
Double-click on the newly created surface to display the scalp in 3-D.
MEG and EMG recordings
Link the recordings
Switch now to the Functional data view of your database contents (
 ).
). Right-click on Subject01 > Review raw file:
Select the appropriate MEG file format: MEG/EEG: CTF(*.ds; *.meg4; *.res4)
Select the data file: SubjectCMC.ds
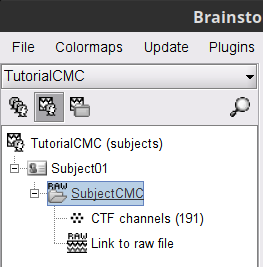
A new folder SubjectCMC is created in the Brainstorm database explorer. Note the "RAW" tag over the icon of the folder (
 ), indicating that the MEG files contain unprocessed, continuous data. This folder includes:
), indicating that the MEG files contain unprocessed, continuous data. This folder includes: CTF channels (191) is a file with all channel information, including channel types (MEG, EMG, etc.), names, 3-D locations, etc. The total number of channels available (MEG, EMG, EOG etc.) is indicated between parentheses.
Link to raw file is a link to the original data file. Brainstorm reads all the relevant metadata from the original dataset and saves them into this symbolic node of the data tree (e.g., sampling rate, number of time samples, event markers). As seen elsewhere in the tutorial handbook, Brainstorm does not create copies by default of (potentially large) unprocessed data files (more information).
MEG-MRI coregistration
This step, sometimes simply named registration, refers to the alignment of the sensors on the anatomy of the subject (more info). For this tutorial, data registration is carried out using only three anatomical landmarks present in the MRI and MEG data. According to the description of the data in the FieldTrip tutorial:
"To measure the head position with respect to the sensors, three coils were placed at anatomical landmarks of the head (nasion, left and right ear canal). [...] During the MRI scan, ear molds containing small containers filled with vitamin E marked the same landmarks. This allows us, together with the anatomical landmarks, to align source estimates of the MEG with the MRI."To verify the registration, right-click on the CTF channels node > MRI registration > Check. This opens a 3D figure showing the inner surface of the MEG helmet, the head surface, and the fiducials and axes that comprise the subject coordinate system (SCS).
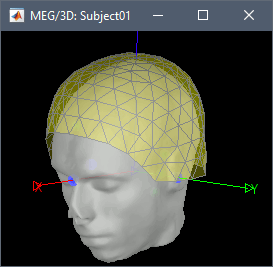
Reviewing
Right-click on Link to raw file > Switch epoched/continuous to convert the file to continuous, a technical detail proper to CTF file formatting.
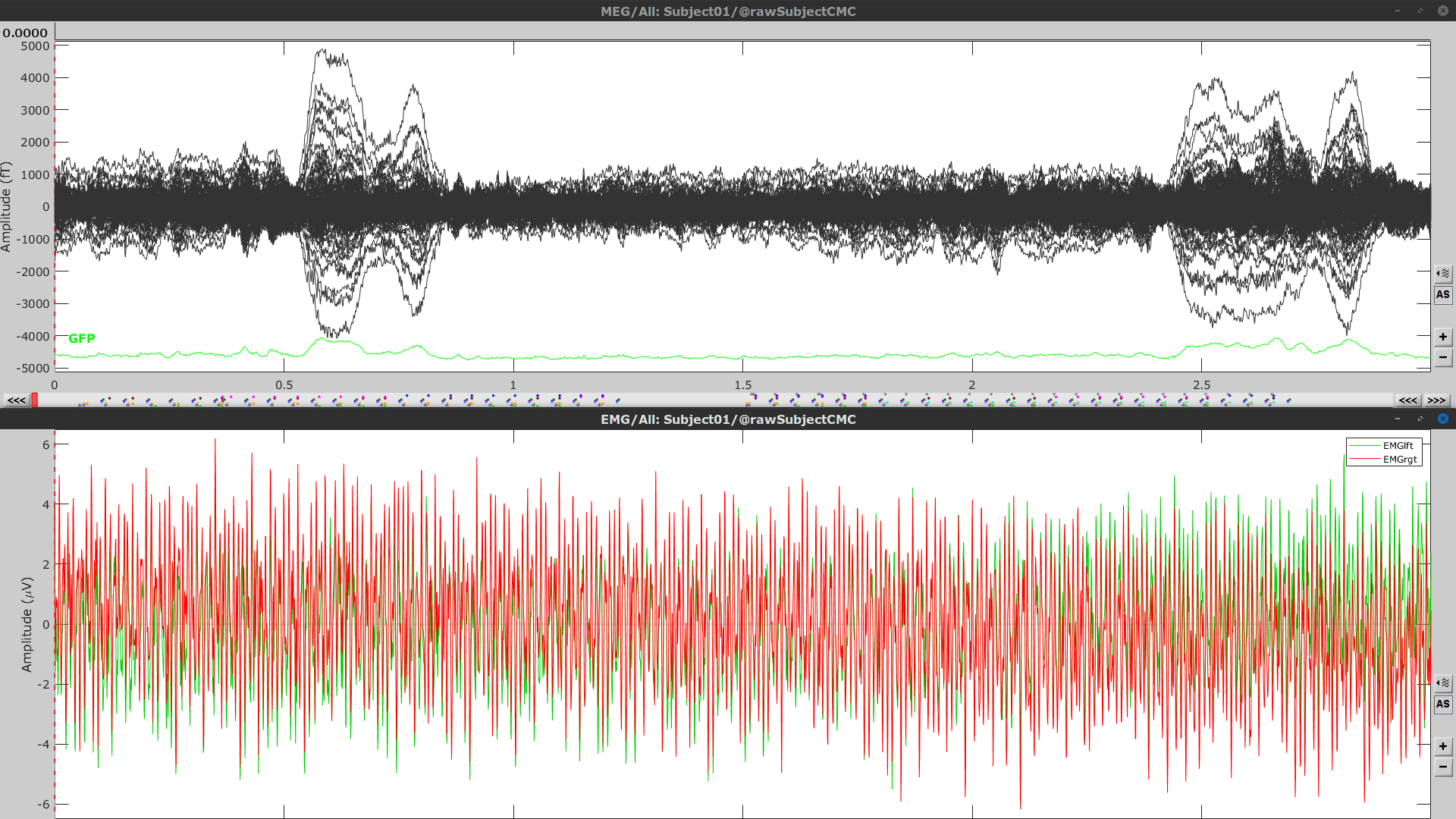
Right-click on Link to raw file > MEG > Display time series (or double-click). This will open a new visualization window to explore data time series, also enabling the Time panel and the Record tab in the main Brainstorm window (see how to best use all controls in this panel and tab to explore data time series).
Right-click on Link to raw file > EMG > Display time series.
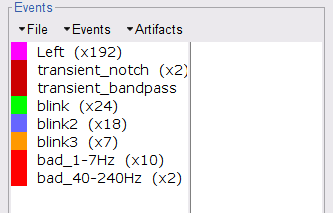
Event markers
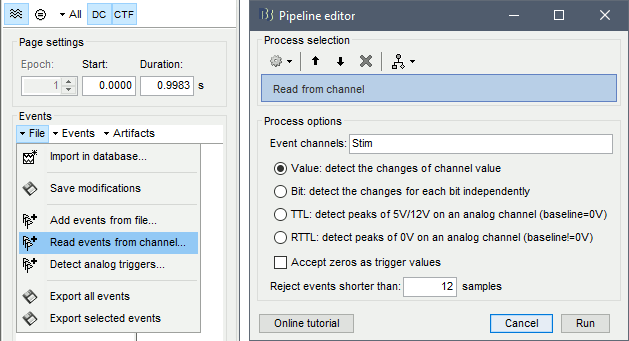
The colored dots above the data time series indicate event markers (or triggers) saved with this dataset. The trial onset information of the left-wrist and right-wrist trials is saved in an auxiliary channel of the raw data named Stim. To add these markers, these events need to be decoded as follows:
While the time series figure is open, go to the Record tab and File > Read events from channel. Event channels = Stim, select Value, Reject events shorter than 12 samples. Click Run.
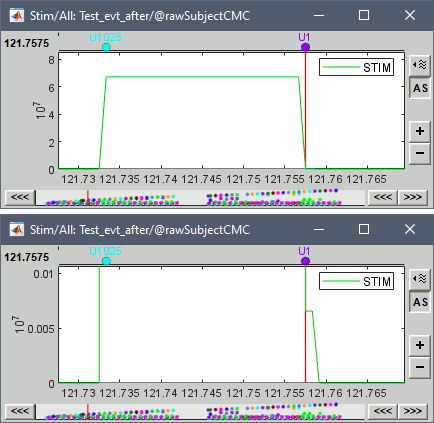
The rejection of short events is nececessary in this dataset, because in the STIM channel the transitions between values span sometimes over multiple samples. As an example, if we were not rejecting short events, an event U1 would be created at 121.76s because the transition from the event U1025 back to zero has two unwanted values at the end of the event. The rejection criteria is set to 12 samples (= 10ms at 1200Hz), because the duration of all the triggers we are interested in is longer than 15ms. This value has to be adjusted carefully for each acquisition setup.
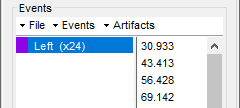
This creates new event markers now shown in the Events section of the tab, along with previous event categories. In this tutorial, we will only use events U1 through U25, which correspond to the beginning of each of the 25 trials of 10 seconds with left-wrist movements. To make sure we reproduce FieldTrip tutorial, we need to reject trial #7, event U7.
Delete unused events: Select all the events except U1-U6 and U8-25 (Ctrl+click / Shift+click), then menu Events > Delete group (or press the Delete key).
Merge events: Select all the event groups, then menu Events > Merge group > "Left". This new event category references 24 trials of the left-wrist condition, i.e. 10-second blocks of left-wrist movements.
Pre-processing
In this tutorial, we will analyze only the Left trials (left-wrist extensions). In the following sections, we will process only the first 330 s of the recordings, where the left-wrist trials were performed.
Power line artifacts
In the Process1 box: Drag and drop the Link to raw file.
Run process Frequency > Power spectrum density (Welch):
Time window: 0-330 s
Window length: 10 s
Overlap: 50%
Sensor types: MEG, EMG
Double-click on the new PSD file to visualize the power spectrum density of the data.
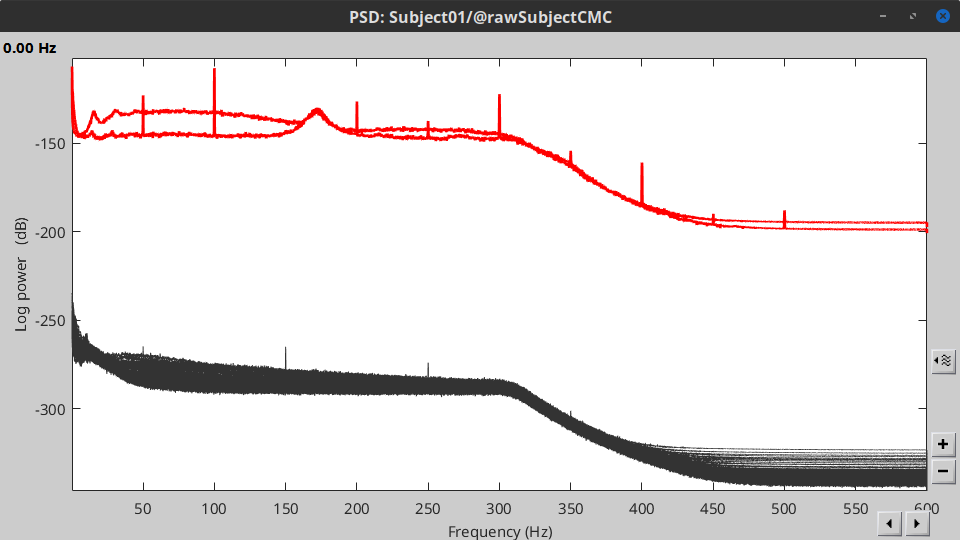
- The PSD plot shows two groups of sensors: EMG (highlighted in red above) and the MEG spectra below. Peaks at 50Hz and its harmonics (100, 150, 200Hz and above) correspond to the European power line and are clearly visible. We will use notch filters to attenuate power line contaminants at 50, 100 and 150 Hz.
In the Process1 box: Drag and drop the Raw | clean node.
Run the process Pre-processing > Notch filter with:
Check Process the entire file at once
Sensor types: MEG, EMG
Frequencies to remove (Hz): 50, 100, 150
Troubleshooting in case of memory error:
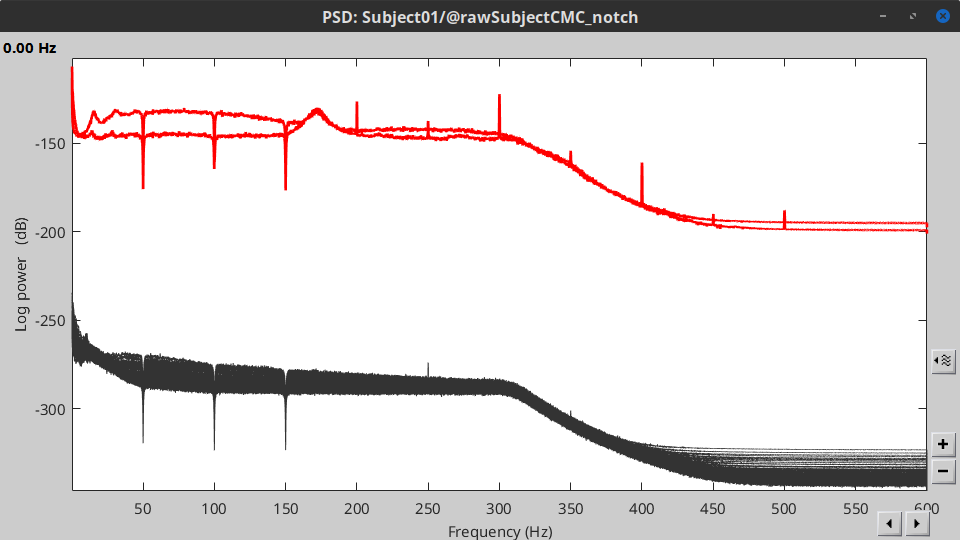
These MEG recordings have been saved before applying the CTF 3rd-order gradient compensation. The compensation weights are applied on the fly when Brainstorm reads data from the file, however this requires reading all the channels at once. By default, the frequency filter are optimized to process the channels sequentially, which is incompatible with applying the CTF compensation on the fly. This setting can be overridden with the option Process the entire file at once, but this solution has the effect of loading the entire file in memory at once, which can crash on computers with limited memory (RAM < 8Gb). If this happens to you: run the process Artifacts > Apply SSP & CTF compensation on the file first, then the notch filter without the option "Process the entire file at once" (more information).A new folder named SubjectCMC_clean_notch is created. Estimate the PSD of these signals to appreciate the effect of the notch filters applied. As above, please remember to indicate a Time window restricted from 0 to 330 s in the options of the PSD process.
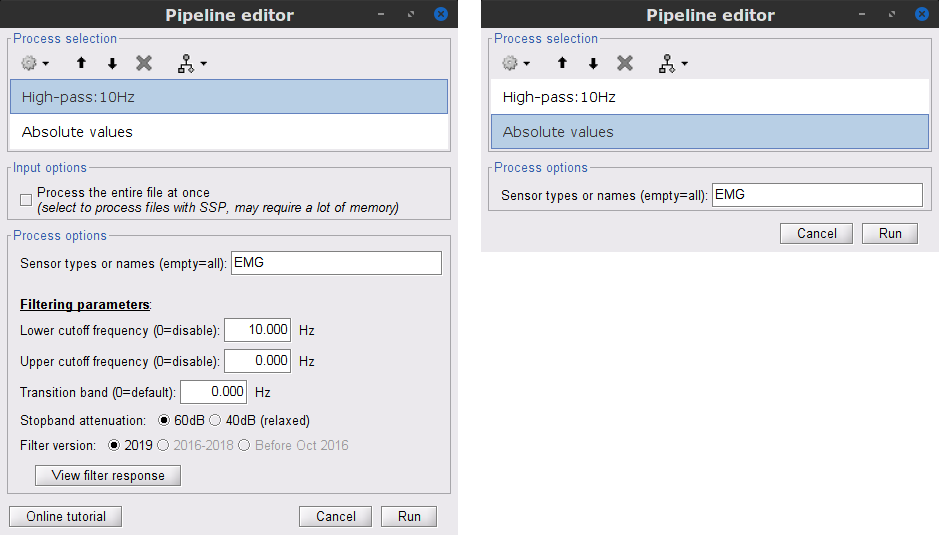
EMG: Filter and rectify
Two typical pre-processing steps for EMG consist in high-pass filtering and rectifying.
In the Process1 box: drag and drop the Raw | notch(50Hz 100Hz 150Hz) node.
Add the process Pre-process > Band-pass filter
Sensor types = EMG
Lower cutoff frequency = 10 Hz
Upper cutoff frequency = 0 Hz
Add the process Pre-process > Absolute values
Sensor types = EMG
- Run the pipeline
Delete intermediate files that won't be needed anymore: Select folders SubjectCMC_notch and SubjectCMC_notch_high, then press the Delete key (or right-click > File > Delete).

MEG: Blink SSP and bad segments
Stereotypical artifacts such eye blinks and heartbeats can be identified from their respective characteristic spatial distributions. Their contamination of MEG signals can then be attenuated specifically using Signal-Space Projections (SSPs). For more details, consult the dedicated tutorials about the detection and removal of artifacts with SSP. The present tutorial dataset features an EOG channel but no ECG. We will perform only the removal of eye blinks.
Blink correction with SSP
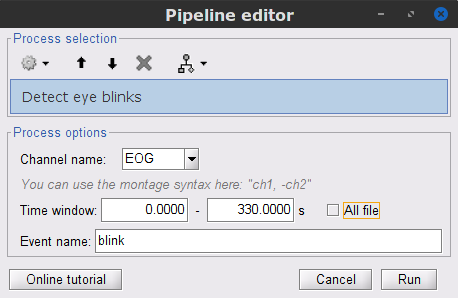
Right-click on the pre-processed file > MEG > Display time series and EOG > Display time series.
In the Record tab: Artifacts > Detect eye blinks, and use the parameters:
Channel name= EOG
Time window = 0 - 330 s
Event name = blink
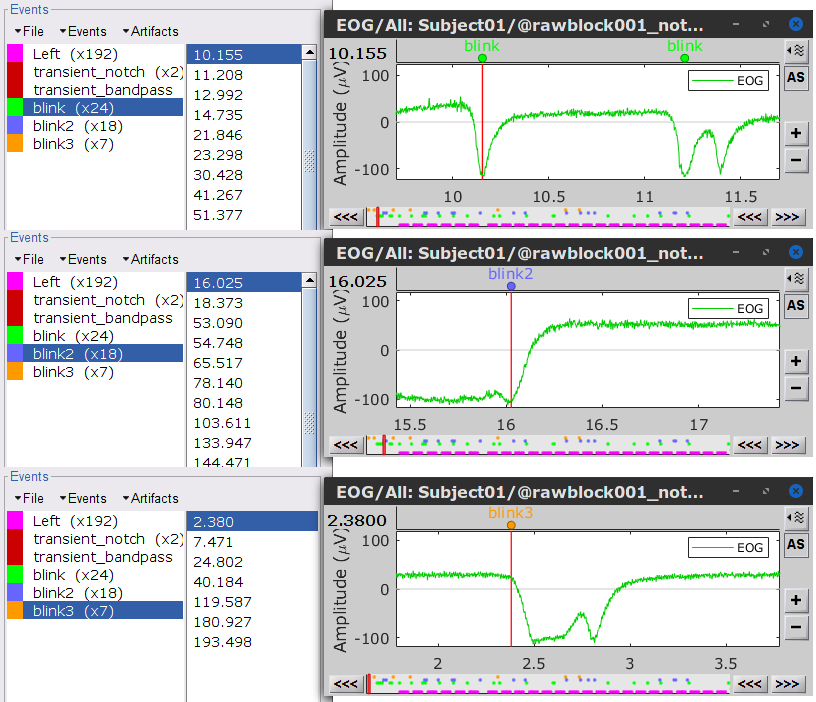
Three categories of blink events are created. Review the traces of EOG channels around a few of these events to ascertain they are related to eye blinks. In the present case, we note that the blink group contains genuine eye blinks, and that groups blink2 and blink3 capture saccade events.
To remove blink artifacts with SSP, go to Artifacts > SSP: Eye blinks:
Event name=blink
Sensors=MEG
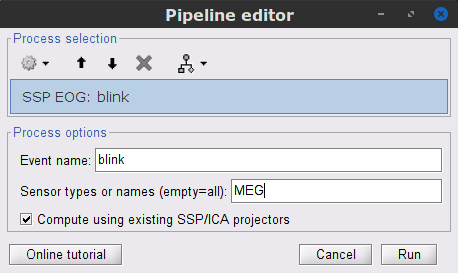
Display the time series and topographies of the first two SSP components identified. In the present case, only the first SSP component can be clearly related to blinks: percentage between brackets much higher than the others, typical spatial topography, time series highly correlated with the EOG signal. Select only component #1 for removal.
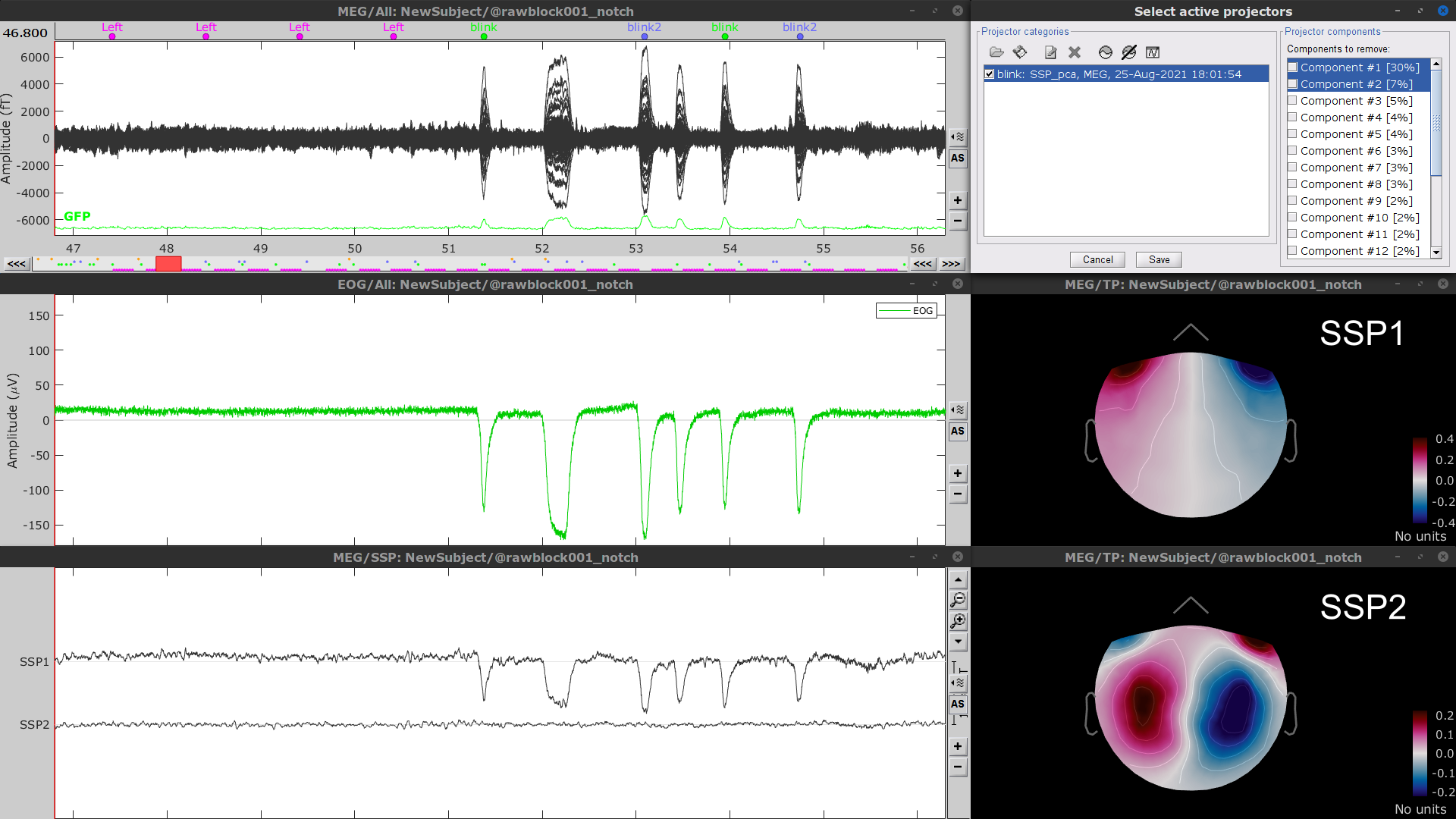
- The second SSP component could be related with other ocular artifacts. For a more precise characterization of this artifact, it could be better indicated to use the other events detected on the EOG (blink2 and blink3). We will not do this here because advanced SSP cleaning is not the main topic of this tutorial.
Close all figures: Click on the large × at the top-right of the main Brainstorm window.
Detection of "bad" data segments
Here we will use the automatic detection of artifacts to identify data segments contaminated by e.g., large eye and head movements and muscle contractions.
Display the MEG and EOG time series. In the Record tab, select Artifacts > Detect other artifacts and enter the following parameters:
Time window = 0 - 330 s
Sensor types=MEG
Sensitivity=3
Check both frequency bands 1-7 Hz and 40-240 Hz
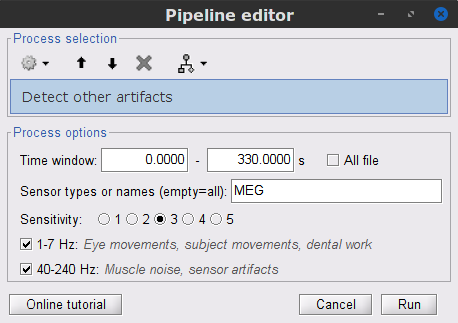
- We encourage users to review all the segments marked using this procedure. In the present case, all the segments detected clearly point at artifacts.
Select the 1-7Hz and 40-240Hz event groups and select Events > Mark group as bad. Alternatively, you can add the prefix bad_ to the event names. Brainstorm will automatically discard these data segments from further processing.
- Close all visualization windows and reply "Yes" to the save the modifications query.
Epoching
We are finished with the pre-processing of the EMG and MEG recordings. We will now extract and import specific data segments of interest into the Brainstorm database for further derivations. As mentioned previously, we will focus on the Left category of events (left wrist movements). To follow the same pipeline as the FieldTrip tutorial: we will consider 8 seconds of recordings after each trigger (out of the 10s of each trial), and split them in epochs of 1 second. In addition DC offset is removed, only for MEG signals.
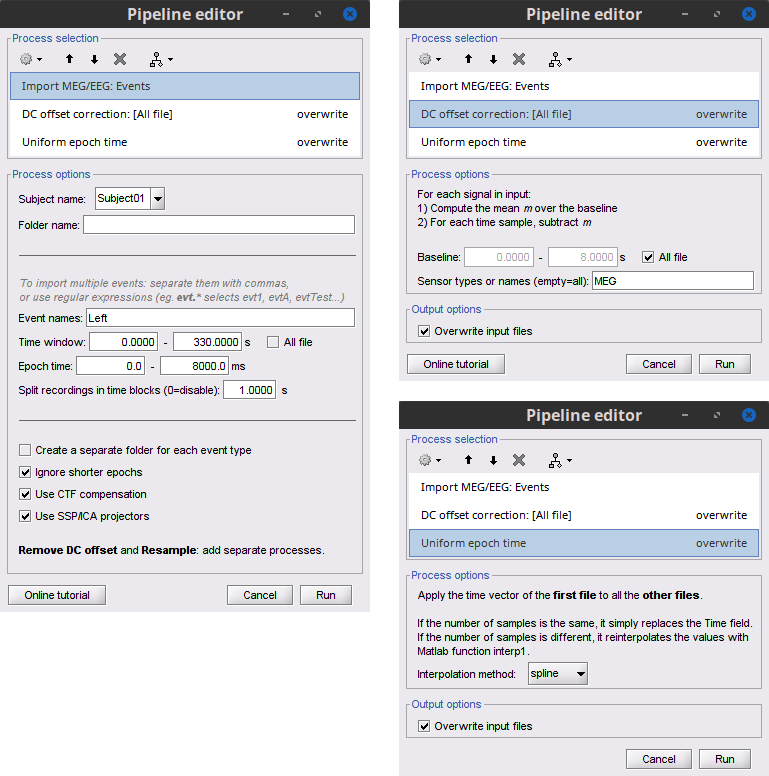
- In the Process1 box: Drag-and-drop the pre-processed file.
Select the process Import > Import recordings > Import MEG/EEG: Events:
Subject name = Subject01
Folder name = empty
Event names = Left
Time window = 0 - 330 s
Epoch time = 0 - 8000 ms
Split recordings in time blocks = 1 s
Uncheck Create a separate folder for each event type
Check Ignore shorter epochs
Check Use CTF compensation
Check Use SSP/ICA projectors
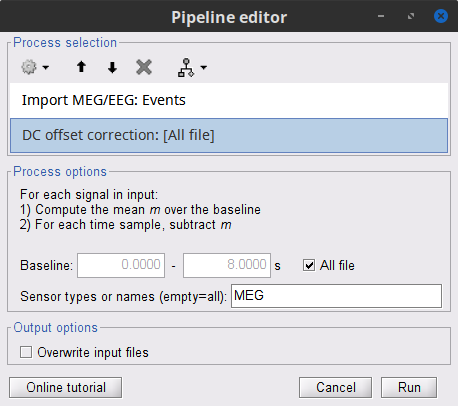
Add the process Pre-process > Remove DC offset:
Baseline = All file
Sensor types = MEG
- Run the pipeline
|
|
|
A new folder SubjectCMC_notch_high_abs without the 'raw' indication is created, including 192 epochs (24 trials x 8 epochs each). The epochs overlapping with a "bad" event are marked as bad and identified with an exclamation mark in a red circle (
 ). The bad epochs will be automatically ignored by the Process1 and Process2 tabs, and therefore excluded from further processing.
). The bad epochs will be automatically ignored by the Process1 and Process2 tabs, and therefore excluded from further processing. 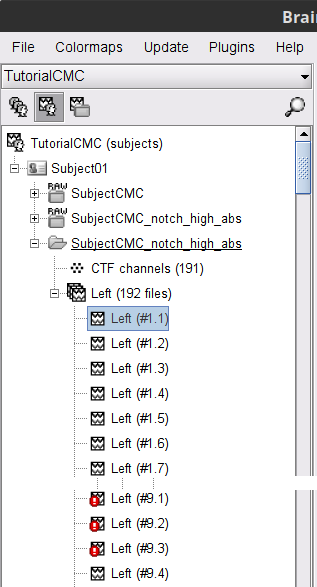
Comparison with FieldTrip
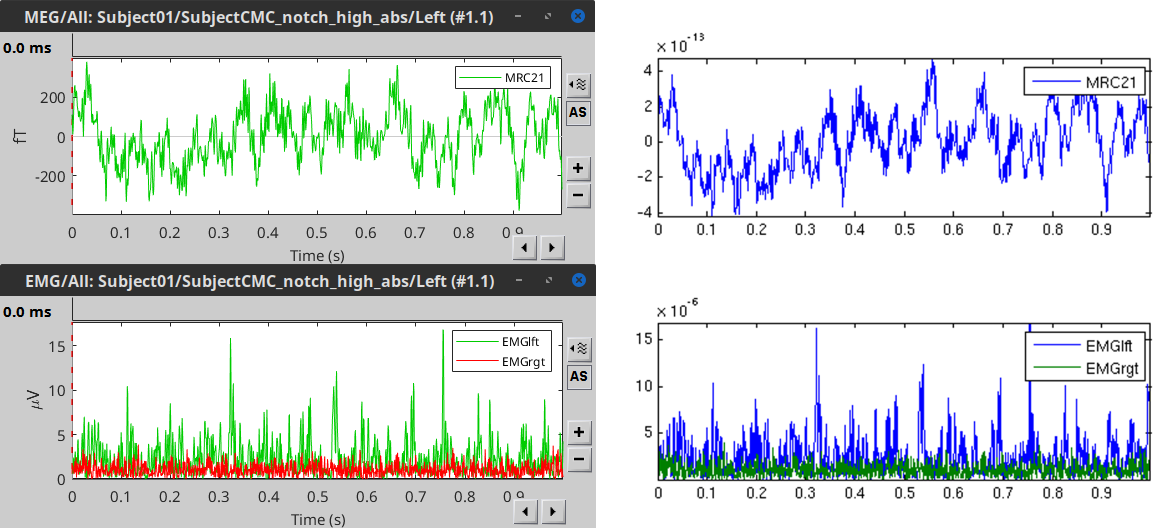
The figures below represent the EMG and MRC21 channels (sensor over the left motor-cortex) from the epoch #1.1, in Brainstorm (left) and in the FieldTrip tutorial (right).
Coherence: EMG x MEG
Let's compute the magnitude square coherence (MSC) between the left EMG and the MEG channels.
In the Process1 box, drag and drop the Left (192 files) trial group.
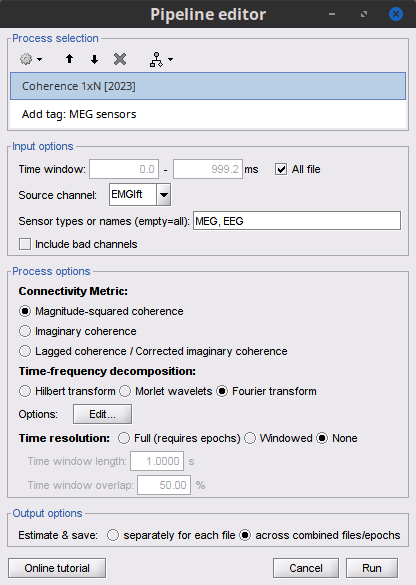
Select the process Connectivity > Coherence 1xN [2021]:
Time window = All file
The imported epochs have different times (e.g. Left#1.1: 0-1s, Left#1.2: 1-2s, Left#1.8: 7-8s), but the process offers by default only the time window of the first file, which would fail reading the next files will fail. Selecting "All file" ensures that the entire time window is read for each epoch.Source channel = EMGlft
Do not check Include bad channels nor Remove evoke response
Magnitude squared coherence
Window length for PSD estimation = 0.5 s
Overlap for PSD estimation = 50%
Highest frequency of interest = 80 Hz
Average cross-spectra of input files (one output file)
More details on the Coherence process can be found in the connectivity tutorial.
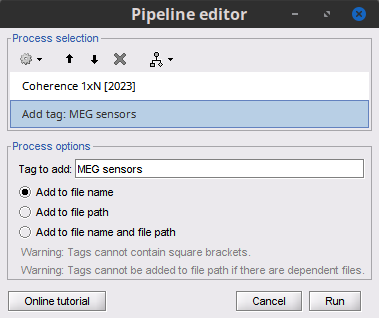
Add the process File > Add tag with the following parameters:
Tag to add = MEG sensors
Select Add to file name
- Run the pipeline
|
|
|
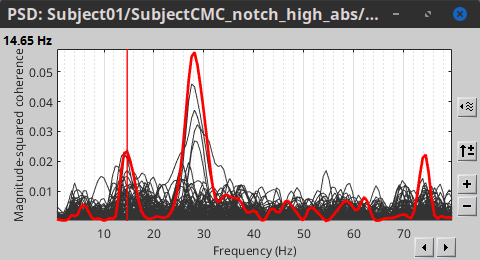
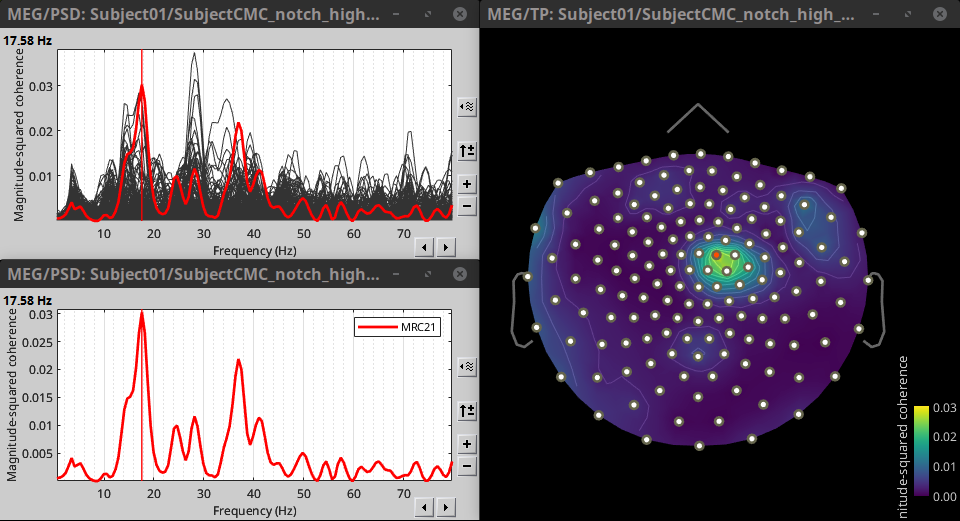
Double-click on the resulting node mscohere(0.6Hz,555win): EMGlft | MEG sensors to display the MSC spectra. Click on the maximum peak in the 15 to 20 Hz range, and press Enter to plot the selected sensor in a new figure. This spectrum corresponds to channel MRC21, and shows a large peak at 17.58 Hz. You can also use the frequency slider (under the Time panel) to explore the MSC output more precisely across frequencies.
Right-click on the spectrum and select 2D Sensor cap for a topographical representation of the magnitude of the coherence results across the sensor array. You may also use the shortcut Ctrl-T. The sensor locations can be displayed with a right-click and by selecting Channels > Display sensors from the contextual menu (shortcut Ctrl-E).
We can now average magnitude of the MSC over the beta band (15-20 Hz).
In the Process1 box, select the new mscohere file.Run process Frequency > Group in time or frequency bands:
Select Group by frequency bands
Type cmc_band / 15, 20 / mean in the text box.
The resulting file mscohere...|tfbands has only one MSC value for each sensor (the MSC average in the 15-20 Hz band). Right-click on the file to display a 2D or 3D topography.
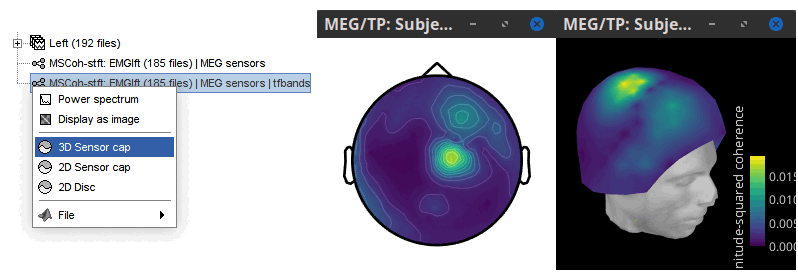
We can observe higher MSC values between the EMG signal and MEG sensor signals over the contralateral set of central sensors in the beta band. Unfortunately, sensor-level connectivity is difficult to interpret. In the rest of this tutorial, we will compute coherence at the source level.
Source estimation
MRI segmentation
In order to estimate the brain sources for these MEG recordings, we first need to reconstruct the cortex surface from the T1 MRI imported at the beginning of this tutorial. For this puropose, we decided to use CAT12 because it is fast (30-60min) and fully integrated with Brainstorm as a plugin.
Switch back to the Anatomy view of the protocol (
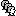 ).
). Right-click on the MRI (
 ) > MRI segmentation > CAT12:
) > MRI segmentation > CAT12: Number of vertices: 15000
Anatomical parcellations: Yes
Cortical maps: No
Keep the low-resolution central surface selected as the default cortex (central_15002V). This surface is the primary output of CAT12, and is located half-way between the pial envelope and the grey-white interface (more information). The head surface was recomputed during the process, you now have two identical head surfaces: you can either delete one or simply ignore this detail.
For quality control, double-click on the head and central_15002V surfaces to display them.

Head models
We will perform source modeling using a distributed model approach for two different source spaces: the cortex surface and the entire MRI volume. The forward model, labelled head model in Brainstorm, accounts for how neural electrical currents produce magnetic fields captured by sensors outside the head, considering head tissues electromagnetic properties and geometry, independently of actual empirical measurements (more information). As the head model depends on the source space, a distinct head model is required for the surface and volume source spaces: we will compute them both now.
Surface
Go back to the Functional data view of the database.
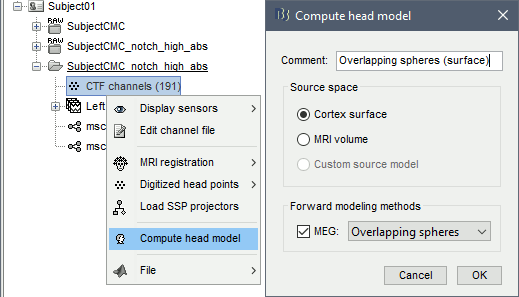
Right-click on the channel file of the imported epochs folder > Compute head model.
Comment = Overlapping spheres (surface)
Source space = Cortex surface
Forward model = MEG Overlapping spheres.
Volume
Right-click on the channel file again > Compute head model.
Comment = Overlapping spheres (volume)
Source space = MRI volume
Forward model = Overlapping spheres.
Select Regular grid and Brain
Grid resolution = 5 mm
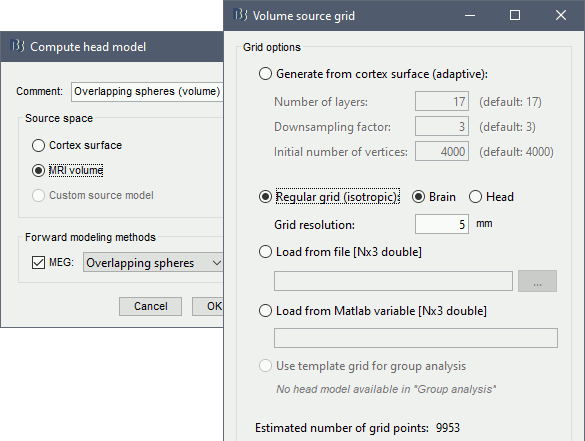
The Overlapping spheres (volume) head model is now added to the database explorer. The green color indicates this is the default head model for the current folder: this can be changed by double clicking on a different head model.
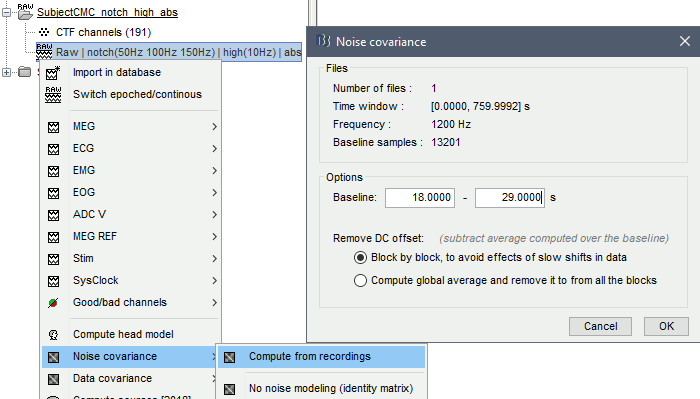
Noise covariance
The recommendation for MEG is to extract basic noise statistics from empty-room recordings. When not available, resting-state data can be used as proxies for MEG noise covariance. We will use a segment of the MEG recordings, away from the task or major artifacts: 18s-29s.
Right-click on the clean continuous file > Noise covariance > Compute from recordings.
Right-click on the Noise covariance (
 ) > Copy to other folders.
) > Copy to other folders.
Inverse models
We will now compute three inverse models, with different source spaces: cortex surface with constrained (normal to the cortex) dipole orientations, cortex surface with unconstrained orientation, and MRI volume (more information).
Surface
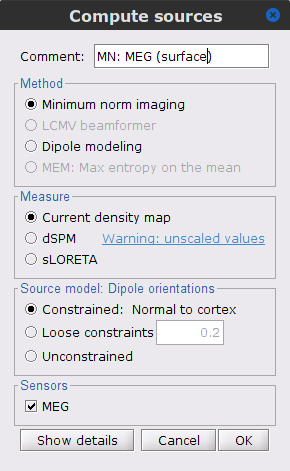
Right-click on Overlapping spheres (surface) > Compute sources:
Minimum norm imaging
Current density map
Constrained: Normal to the cortex
Comment = MN: MEG (surface)
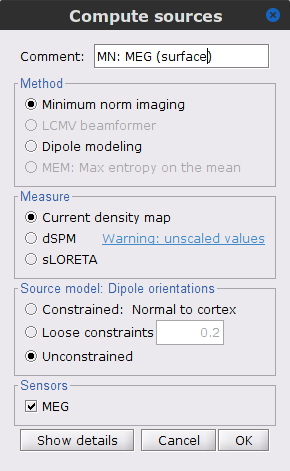
Repeat the previous step, but this time select Unconstrained in the Dipole orientations field.
|
|
|
Volume
Right-click on the Overlapping spheres (volume) > Compute sources:
Current density map
Unconstrained
Comment = MN: MEG (volume)
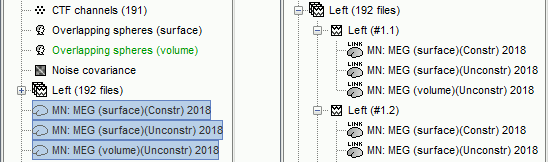
Three imaging kernels (
 ) are now available in the database explorer. Note that each trial is associated with three source links (
) are now available in the database explorer. Note that each trial is associated with three source links (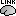 ).
). 
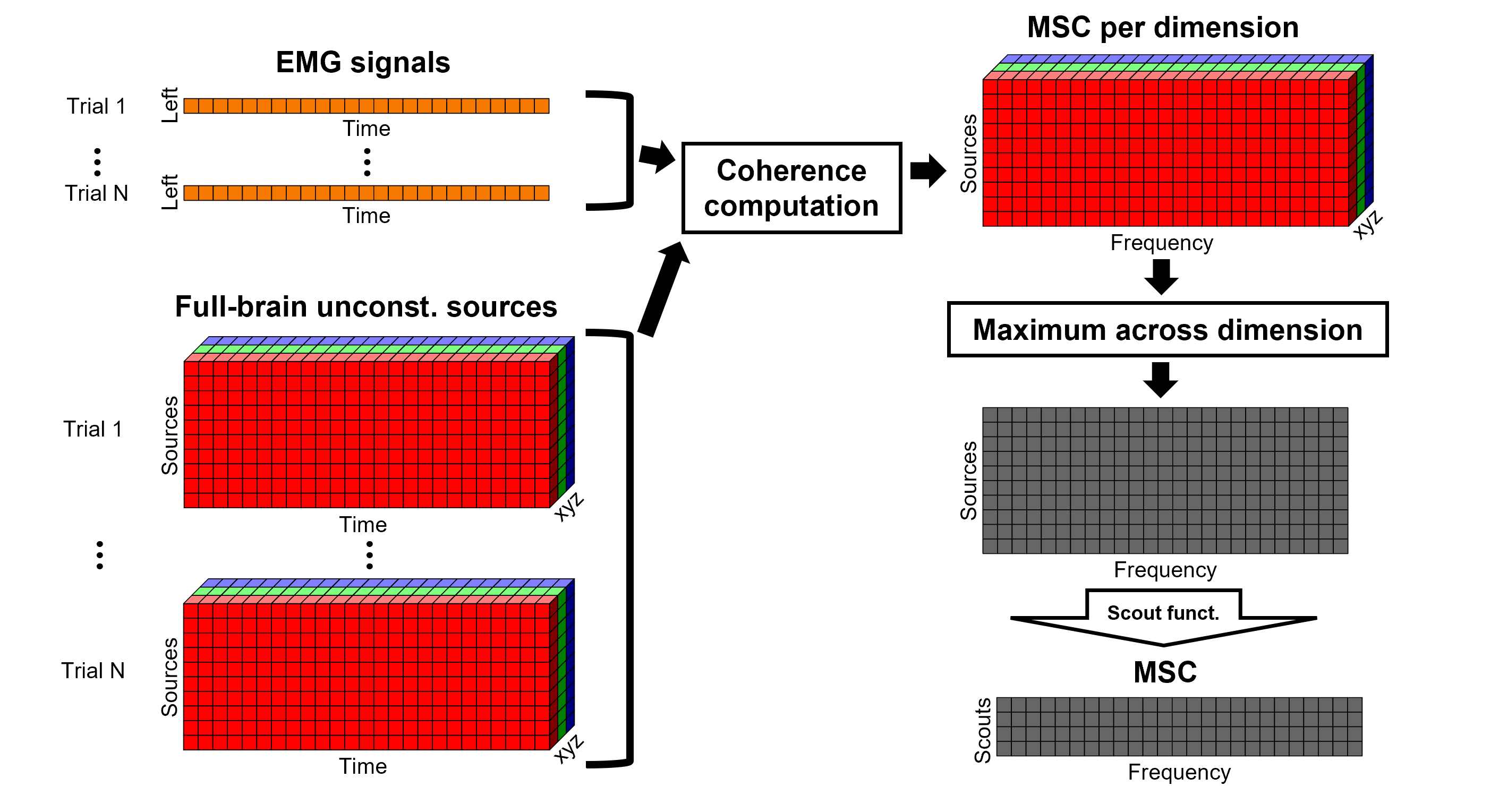
Coherence: EMG x Sources
We can now compute the coherence between the EMG signal and the brain source time series, for each of the source models. Let's start with the surface/constrained model.
To select the source maps we want to include in the coherence estimation, click on the Search Database button (
 ), and select New search. Set the parameters as shown below, and click on Search.
), and select New search. Set the parameters as shown below, and click on Search. 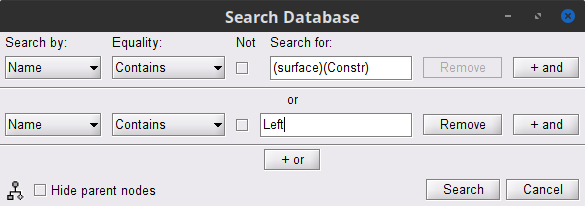
- It creates a new tab in the database explorer, showing only the files that match the criteria.
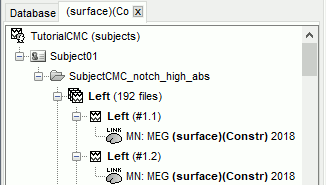
Click the Process2 tab at the bottom of the main Brainstorm window.
Files A: Drag-and-drop the Left (192 files) group, select Process recordings (
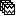 ).
). Files B: Drag-and-drop the Left (192 files) group, select Process sources (
 ).
). - Objective: Extract from the same files the EMG recordings (Files A) and the sources time series (Files B), then compute coherence between these two sets. Note that the blue labels over the file lists indicate that there are 185 "good" files (7 bad epochs).
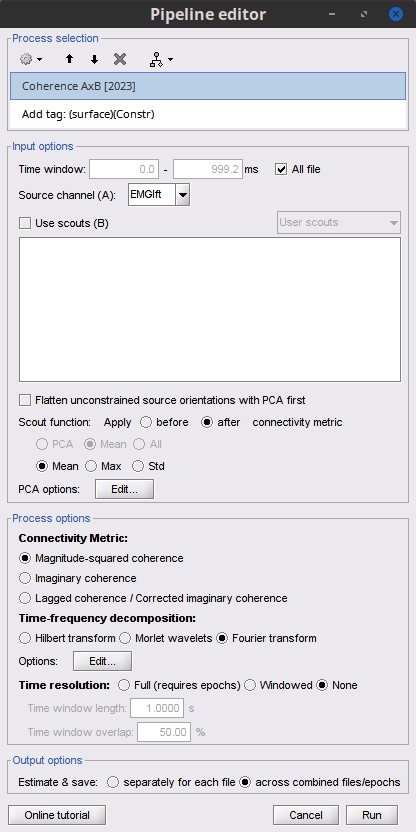
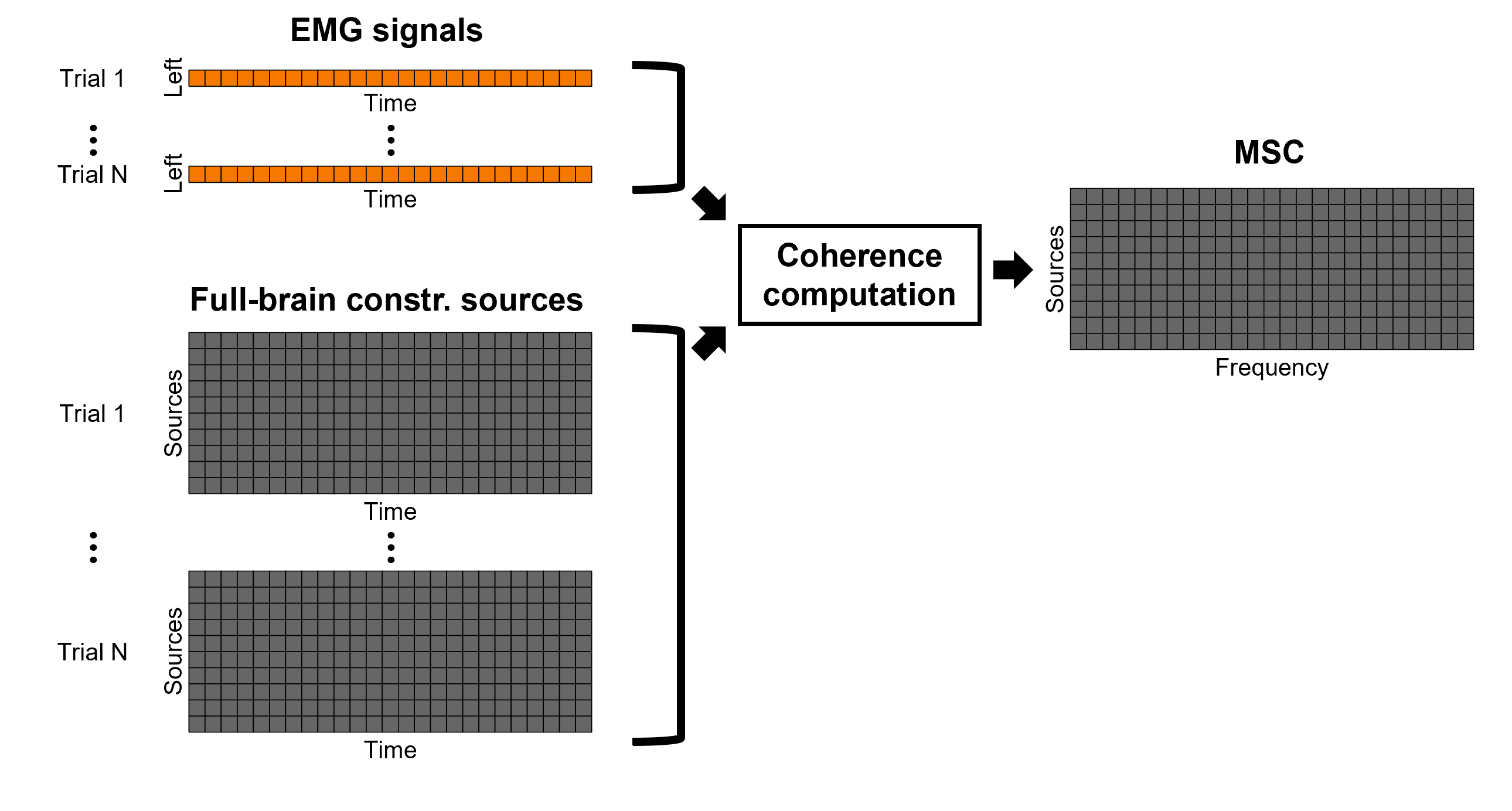
Select the process Connectivity > Coherence AxB [2021]:
Time window = All file
Source channel (A) = EMGlft
Uncheck Use scouts (B)
Do not Remove evoked responses from each trial
Magnitude squared coherence
Window length = 0.5 s, Overlap = 50%
Highest frequency = 80 Hz
Average cross-spectra.
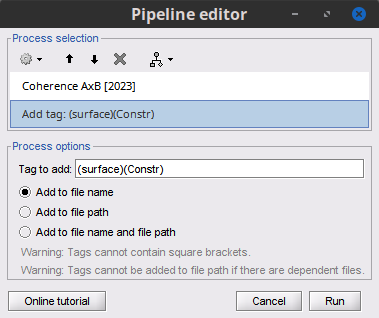
Add the process File > Add tag:
Tag to add = (surface)(Constr)
Select Add to file name
- Run the pipeline
|
|
|
Repeat the steps above to compute the EMG-sources coherence for the other source models: surface/unconstrained and volume:
Edit the search criteria: Right-click on the search tab > Edit search.
- It updates automatically the file selection in the Process2 tab.
Select the processes: Do not forget to select again All file and update the file tag.
Close the search tab. If you don't see the 3 new connectivity files
 ) in the database explorer: refresh it, by pressing [F5] or clicking again on the selected button "Functional data".
) in the database explorer: refresh it, by pressing [F5] or clicking again on the selected button "Functional data".
Surface
Double-click the 1xN connectivity files for the two (surface) source space to show the results on the cortex. If you are not familiar with the options in the cortex figures, check Display: Cortex surface. Find the location and frequency with the highest coherence value.
In the Surface tab: Smooth=30%, Amplitude=0%.
To compare visually different cortex maps, set manually the colormap range (e.g.[0 - 0.07])
Explore with coherence spectra with the frequency slider
The highest coherence value is located at 14.65 Hz, in the right primary motor cortex (precentral gyrus). To observe the coherence spectrum at a given location: right-click on the cortex > Source: Power spectrum.
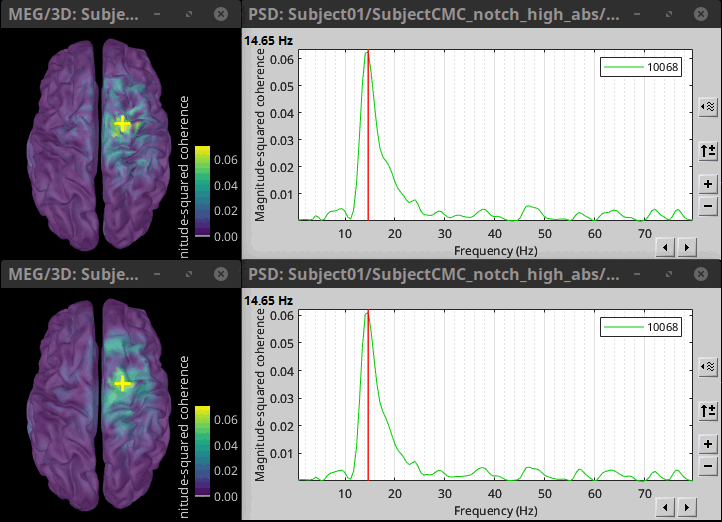
The analysis using constrained (top) and unconstrained (bottom) orientations agree in the location and frequency of the peak coherence. The main difference between these results is that unconstrained sources appear smoother, due to maximum aggregation performed across directions, explained later. These results agree with our hypothesis, previous results in the literature, and the results presented in the FieldTrip tutorial.
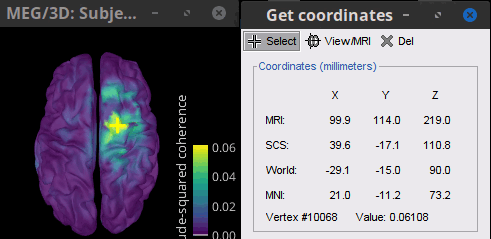
To get the 3D coordinates of the peak: right-click on the figure > Get coordinates. Then click on the right motor cortex with the crosshair cursor that appears. These coordinates can be useful to compare with the volume results.
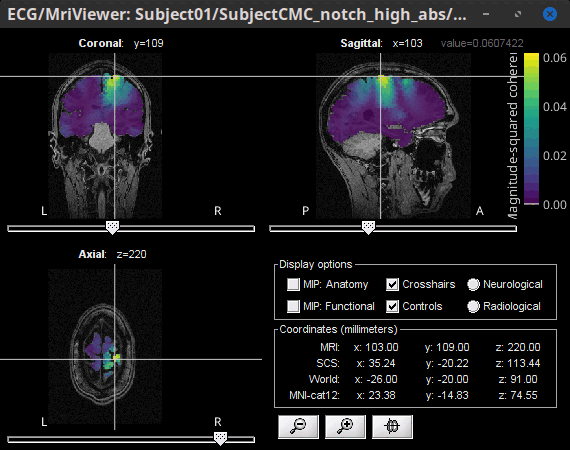
Volume
Double-click the 1xN connectivity file for the (volume) source space.
- Go to 14.65 Hz, set the data transparency to 20% (Surface tab).
- Find the peak by navigating in the volume, or using the coordinates from the surface results.
Right-click on the figure > Anatomical atlas > None. This will show the coherence value under the cursor at the top-right corner, instead of an anatomical label.
Method
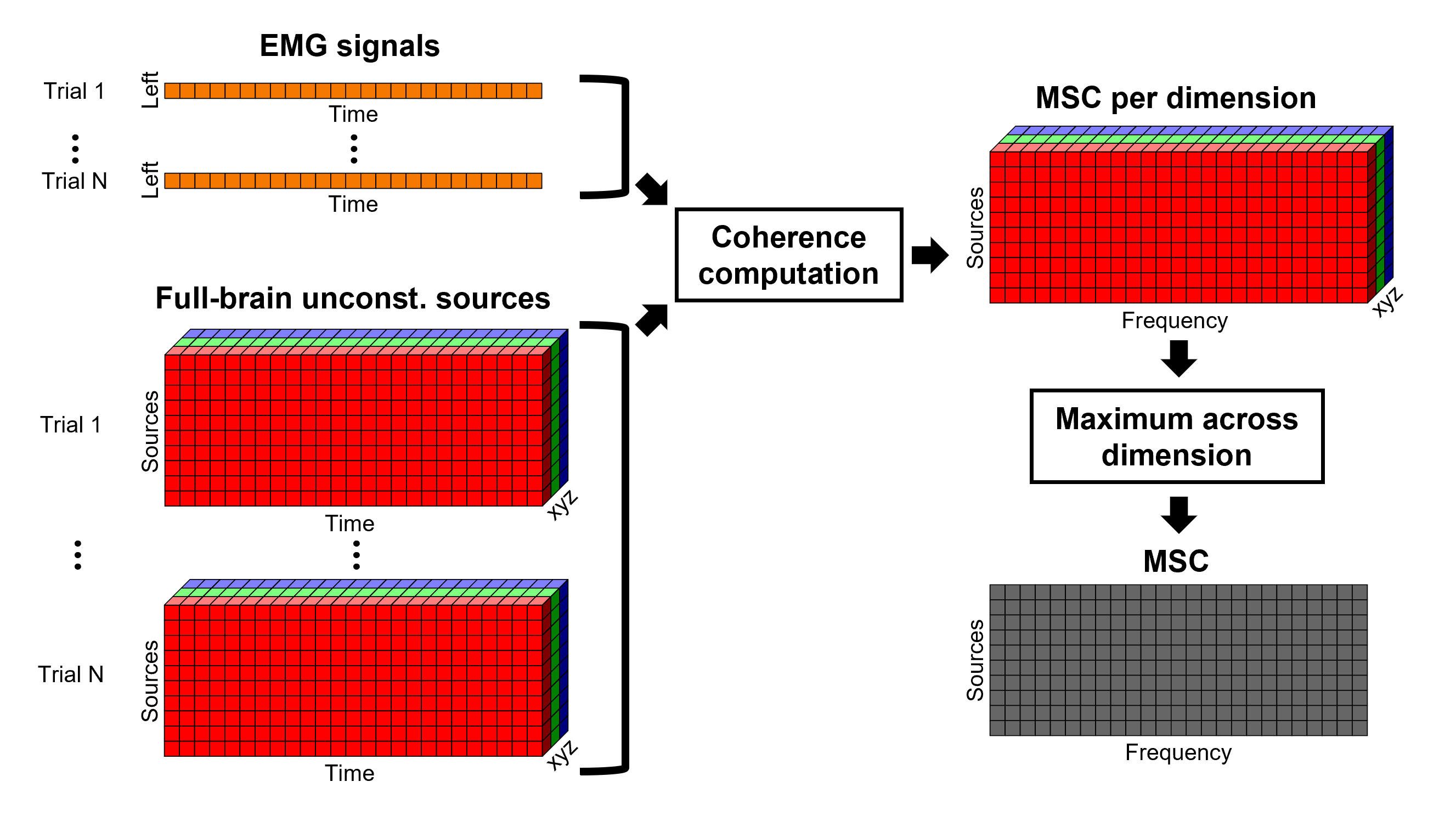
For constrained sources, each vertex in the source grid is associated with ONE time series, as such, when coherence is computed with the EMG signal (also one time series), the result is ONE coherence spectrum per vertex. In other words, for each frequency bin, there is a coherence brain map.
In the case of unconstrained or volume sources, each vertex in the grid is associated with THREE time series, each one corresponding to the X, Y and Z directions. Thus, when coherence is computed with the EMG signal (one time series), there are THREE coherence spectra. To be represented on the cortex, these three values need to be flattened into one, resulting in one coherence spectrum per vertex. For performing this dimension reduction, we decided to take the maximum across three directions, for each frequency bin for each vertex.
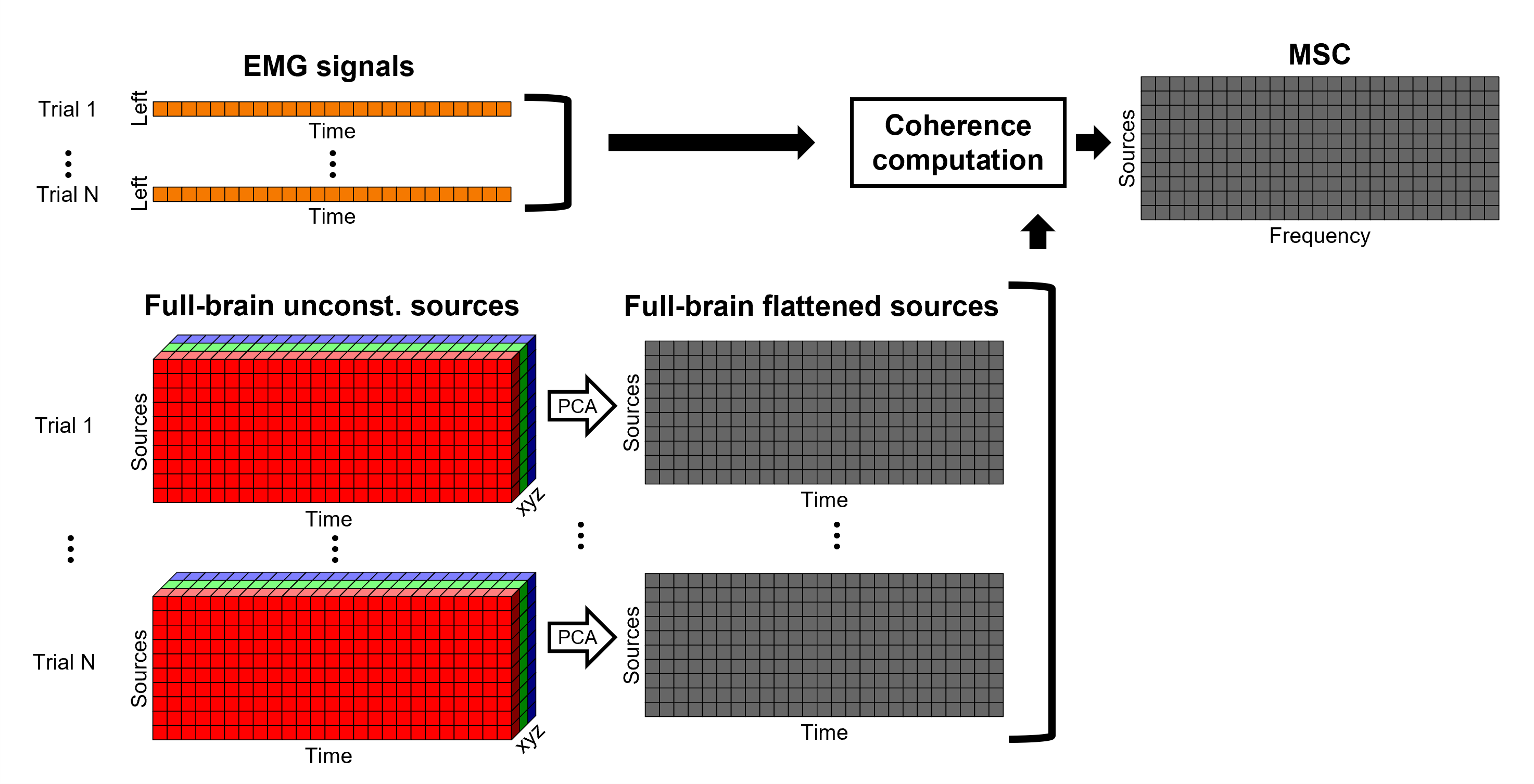
An alternative approach in the literature, to address the 3-dimensional nature of the unconstrained sources, consists in flattening the vertex X, Y and Z time series before the coherence computation; resulting in a similar case as the constrained sources. Common methods for this flattening include: PCA (only first component is kept), and (Euclidean) norm. This flattening of the time series can be performed in Brainstorm with the process: Sources > Unconstrained to flat map.
- Flattened sources are saved as full rather than recordings+kernel.
- We have tested this flattening approach with simulations and found detrimental effects on the expected results.
Coherence: EMG x Scouts
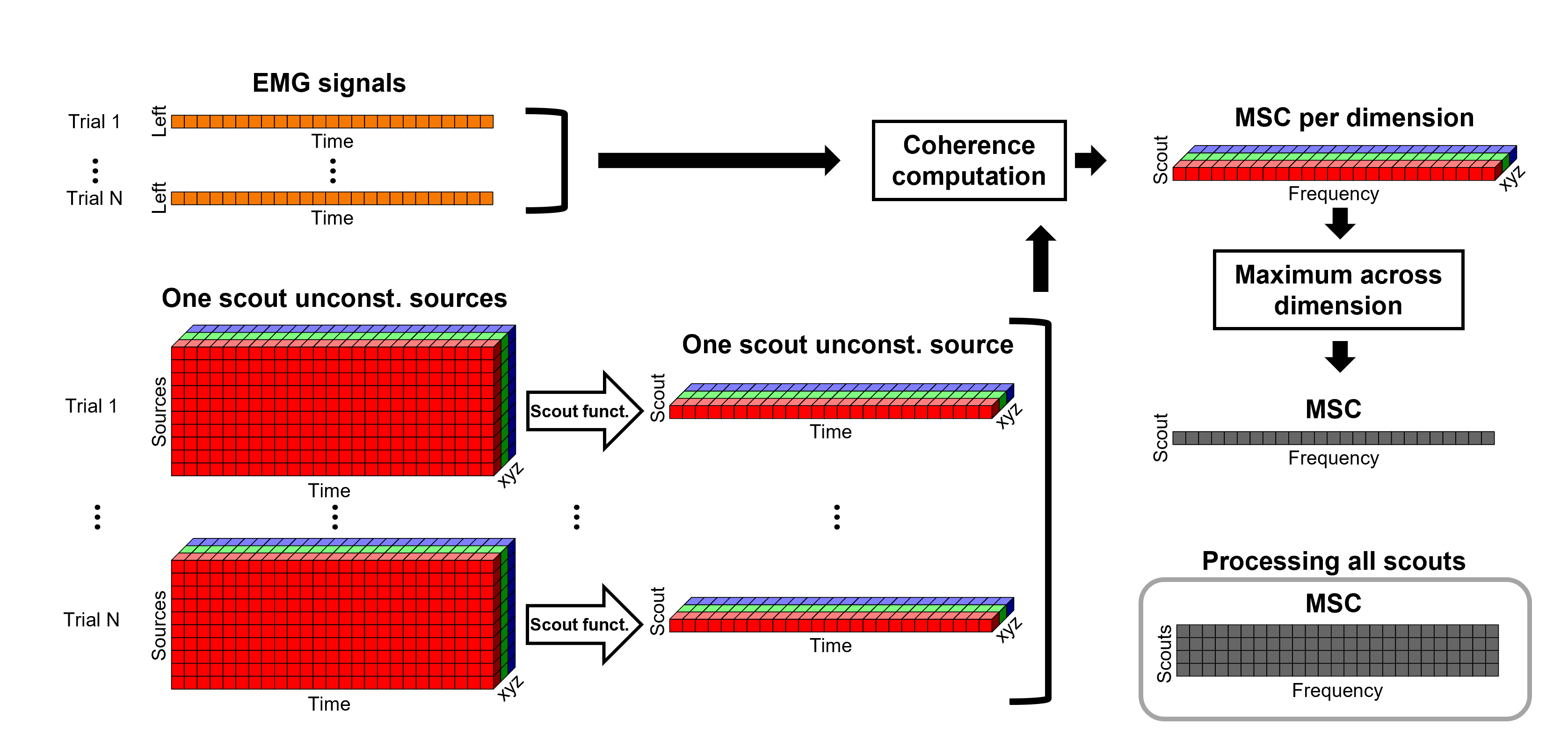
So far, we have computed coherence at the source level, thus, a coherence spectrum is computed for each of the 15002 source points. This large dimension hinders later analysis of the results. Therefore, the strategy is to reduce the dimensionality of the source space by using a surface- or volume-parcellation scheme, in Brainstorm jargon this is an atlas that is made of scouts. See the scout tutorial for detail information on atlases and scouts in Brainstorm.
Under this approach, instead of providing one result (coherence spectrum) per source vertex, one result is computed for each scout. When computing coherence (or other connectivity metrics) at the scout level, it is necessary to provide two parameters that define how the data is aggregated per scout: The scout function (mean is often used), and when the within-scout aggregation takes place (before or after the coherence computation).
Before: The scout function is applied for each direction on the vertices' source time series that make up a scout; resulting in one time series per direction per scout. Then, the scout time series are used to compute coherence with the reference signal (EMG in this tutorial), and the coherence spectra for each scout are aggregated across dimensions, as shown previously, to obtain one coherence spectrum per scout.
After: Coherence is computed between the reference signal and each direction of the vertices' source time series, as in the previous section. Then, the scout function is applied on the coherence spectra for each direction of the vertices within a scout, finally these spectra are aggregated across dimensions to obtain a coherence spectrum per scout. This option computes the coherence between the EMG and 45000 source signals, instead of a handful of times with the "before" option. The computation is therefore much longer and demanding in terms of RAM memory.
Let's here compute the coherence using scouts, using mean as scout function alongside with the Before option. We will use the Schaefer 100 parcellation atlas on the results from constrained sources.
Use Search Database (
 ) to select the Left trials with their respective (surface)(Constr) source maps, as shown in the previous section.
) to select the Left trials with their respective (surface)(Constr) source maps, as shown in the previous section. In the Process2: Left trial group into both the Files A and Files B boxes. Select Process recordings (
 ) for Files A, and Process sources (
) for Files A, and Process sources ( ) for Files B.
) for Files B. 
Open the Pipeline editor:
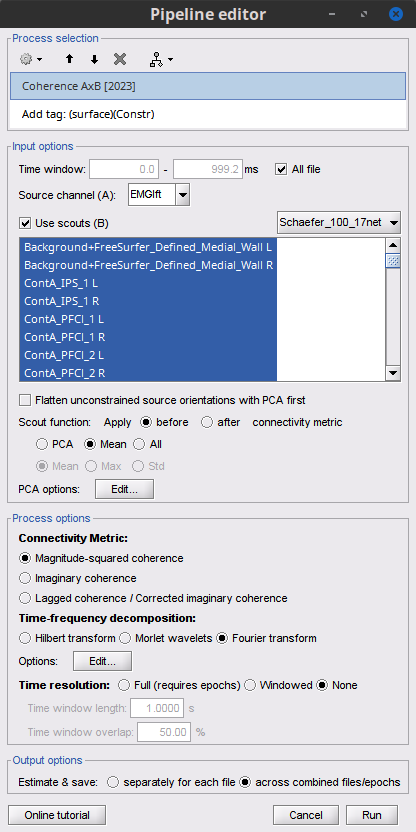
Add the process Connectivity > Coherence AxB [2021] with the following parameters:
Time window = 0 - 1000 ms or check All file
Source channel (A) = EMGlft
Check Use scouts (B)
From the menu at the right, select Schaefer_100_17net
- Select all the scouts
Scout function: Mean
When to apply the scout function: Before
Do not Remove evoked responses from each trial
Magnitude squared coherence, Window length = 0.5 s
Overlap = 50%
Highest frequency = 80 Hz
Average cross-spectra.
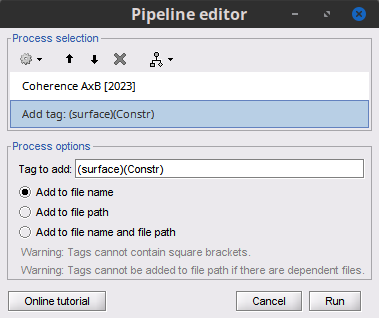
Add the process File > Add tag with the following parameters:
Tag to add = (surface)(Constr)
Select Add to file name
- Run the pipeline
|
|
|
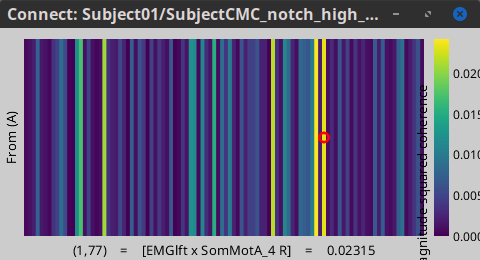
Open the output file by double-clicking on it. This time the coherence spectra are not displayed on the cortex, but they are plotted for each scout. Moreover, 1xN connectivity file can be shown as image.
|
|
|
Note that for 14.65 Hz, the highest two peaks correspond to the SomMotA_4 R and SomMotA_2 R scouts, both located over the right primary motor cortex.
The choice of the optimal parcellation scheme for the source space is not easy, this is still an active field of research. The only recommendation we can give at the moment is to use regions of interest that are small and homogenous in size.
Additional documentation
Articles
Conway BA, Halliday DM, Farmer SF, Shahani U, Maas P, Weir AI, et al.
Synchronization between motor cortex and spinal motoneuronal pool during the performance of a maintained motor task in man.
The Journal of Physiology. 1995 Dec 15;489(3):917–24.Kilner JM, Baker SN, Salenius S, Hari R, Lemon RN.
Human Cortical Muscle Coherence Is Directly Related to Specific Motor Parameters.
J Neurosci. 2000 Dec 1;20(23):8838–45.Liu J, Sheng Y, Liu H.
Corticomuscular Coherence and Its Applications: A Review.
Front Hum Neurosci. 2019 Mar 20;13:100.Sadaghiani S, Brookes MJ, Baillet S.
Connectomics of human electrophysiology.
NeuroImage. 2022 Feb;247:118788.
Tutorials
Tutorial: Functional connectivity
Tutorial: Source estimation
Tutorial: Volume source estimation
Tutorial: Scouts
Tutorial: Connectivity graphs
Scripting
The following script from the Brainstorm distribution reproduces the analysis presented in this tutorial page: brainstorm3/toolbox/script/tutorial_coherence.m