SEEG contact localization and labeling
Authors: Chinmay Chinara, Takfarinas Medani, Raymundo Cassani, Yash Shashank Vakilna, Johnson Hampson, Anand Joshi, John Mosher, Sylvain Baillet, Richard Leahy
Brainstorm allows to creation and annotation of intracranial electrodes and contacts. Users can also then export these as a text file with all the positions that can be used in Brainstorm or any other program.
Make sure you complete the previous tutorial on CT to MRI co-registration to have the data and the required anatomy set up.
Contents
Generate isosurface
This creates a thresholded mesh from the CT by separating the contacts out from rest of the CT. This aids the user towards localization of the electrodes and its contacts more accurately.
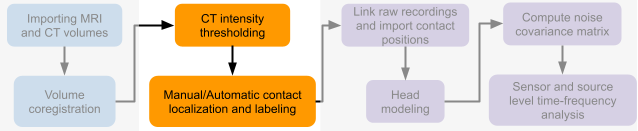
The first thing required is to define a good threshold (which we call isoValue) that will separate out the contacts from the rest of the CT. Just open the CT file (by double clicking on it), click on the MIP: Functional in the MRI Viewer, use the Data Options > Amplitude slider in the Surface tab to browse through the threshold, and once you are satisfied with getting a good separation of the contacts, hover on the slider to get the desired value and keep a note of it (to the nearest integer). In this case the value is 2276.
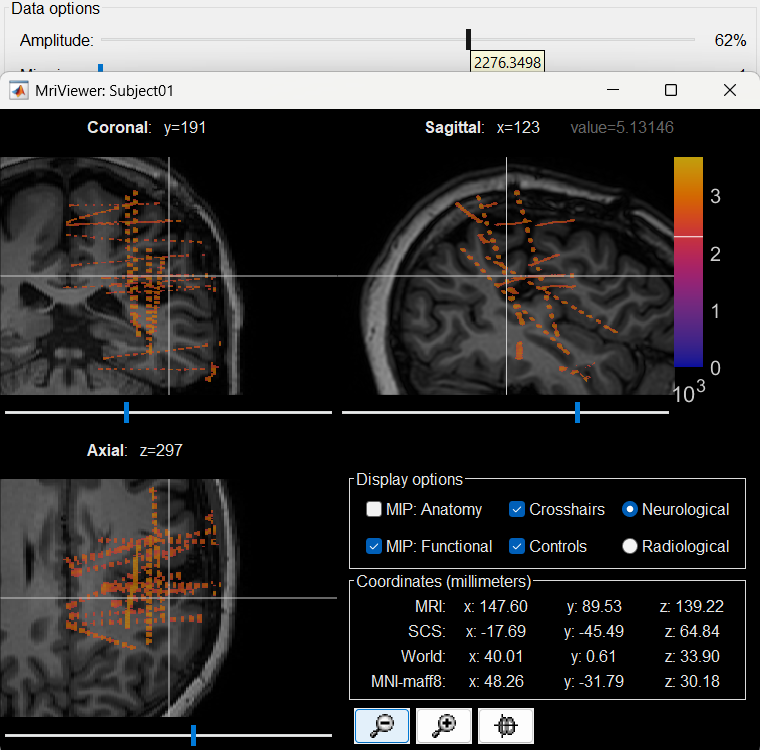
Right click on post_CT_spm_reslice_masked_spm> CT segmentation > Generate SEEG/ECoG isosurface.
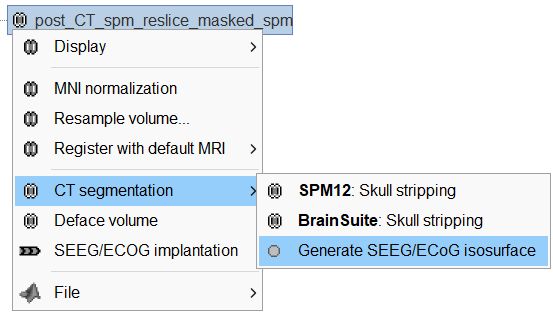
This will bring the Generate isosurface window. This window shows 4 values: the Background level, White level, Max Intensity and the suggested Set isoValue, all of them given in the Hounsfield Unit (HU) scale. The first 3 values are calculated automatically from the histogram of the CT and are displayed for reference. The editable isoValue field shows an estimated best guess based on mean of White Level and Max Intensity. Since we got a better value in step-1 above, set the value to 2276 and press OK.
An isosurface is generated showing the contact as blobs overlayed on the 3D MRI slices. The Thresh slider under Surface options can be further used to update the isosurface mesh with different isoValues. You can choose to save the last changed isoValue on closing the figure.
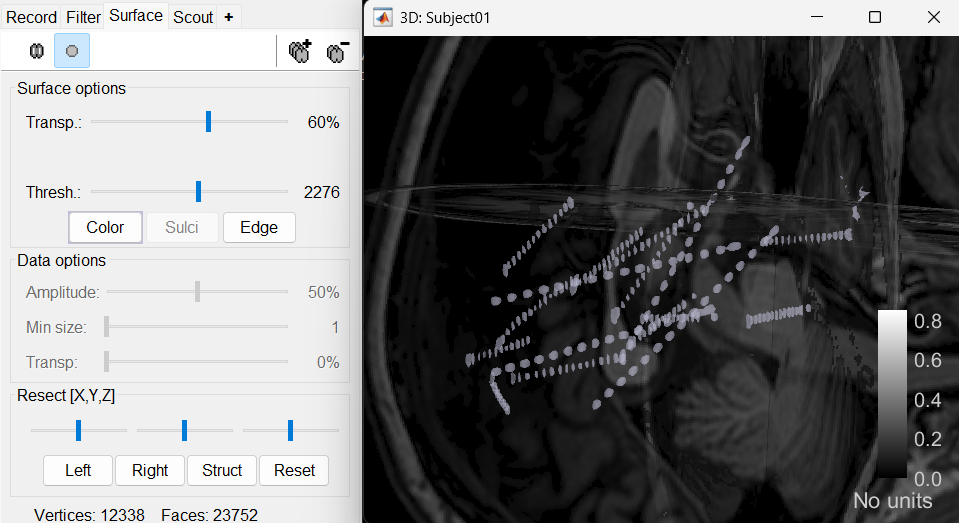
Start implantation
Right click on Subject01, and choose SEEG/ECOG implantation.
The SEEG/ECOG implantation menu pops to choose which modalities you want to use for doing your implantation with.
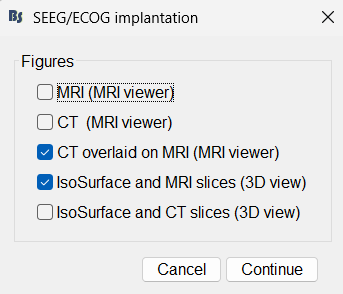
MRI (MRI viewer): MRI viewer figure with MRI volume only.
CT (MRI viewer): MRI viewer figure with CT volume only.
CT overlaid on MRI (MRI viewer): MRI viewer figure with the CT overlaid on the MRI.
IsoSurface and MRI slices (3D view): 3D figure with the IsoSurface and 3D MRI slices.
IsoSurface and CT slices (3D view): 3D figure with the IsoSurface and 3D CT slices.
Select CT overlaid on MRI (MRI viewer) and IsoSurface and MRI slices (3D view). This takes you to the functional tab. Subject01 > Implantation > SEEG/ECOG (0) channel gets created. All expected figures open up. Panel iEEG loads up in the panel viewer. Move around the 3D slices to get a clear view of the contacts so that they can be clicked on.
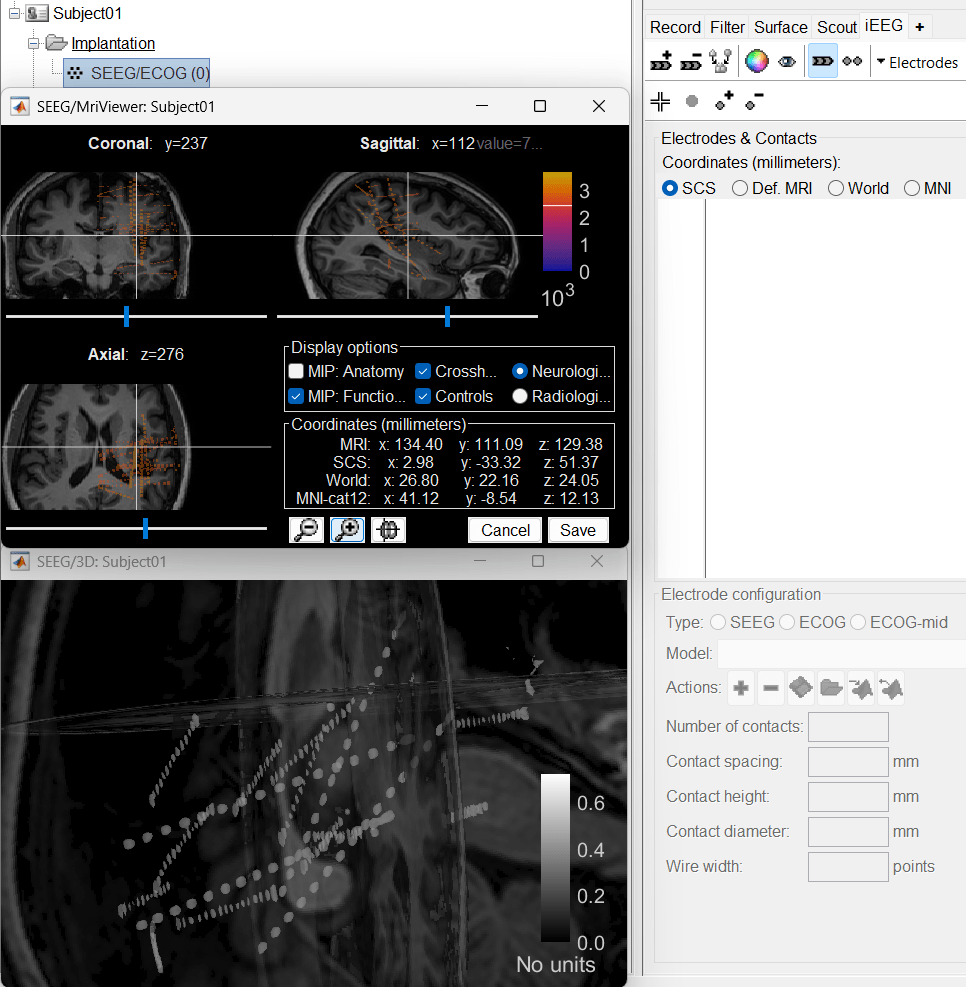
- The section below talks about the iEEG panel in details.
Panel iEEG
In this interface, "electrode" refers to entire depth electrode implanted in the head of the patient while "contact" refers to recording sites on the electrode. There are multiple contacts on an electrode, and one contact corresponds to one channel of data in the channel file and the recordings.
SEEG depth electrodes are graphical objects, they are defined independently from the SEEG contacts available in the channel file and recordings. A contact/channel is associated to a depth electrode using the Group property of the channel, accessible with a right-click on the channel file > Edit channel file.
- The contact names must start with one or more letters (the name of the electrode) followed by a number representing the index of the contact on the electrode. Contact #1 is at the tip of the electrode, and is therefore the deeper contact of the electrode. If the convention used in your recordings is different, you may have to edit the electrodes properties in order to get them displayed correctly.
- Buttons in the toolbar:
Coordinates (millimeters) radio buttons: Users can switch between the different coordinate systems (SCS, Def. MRI, World, MNI) to change the coordinate values of the contacts.
- "Def. MRI" refers to the coordinates of the subject's default MRI.
 (Add new electrode): Adds an entry for a new depth electrode. The new electrode will not be displayed until you set its properties and position. This will not add or remove SEEG contacts or channels of data.
(Add new electrode): Adds an entry for a new depth electrode. The new electrode will not be displayed until you set its properties and position. This will not add or remove SEEG contacts or channels of data.  (Remove selected electrodes): Deletes a depth electrode from the list, but does not modify the list of SEEG contacts or channels of data.
(Remove selected electrodes): Deletes a depth electrode from the list, but does not modify the list of SEEG contacts or channels of data.  (Merge selected electrodes): Join two or more selected depth electrodes from the list. This will remove the selected electrodes after creating a new merged electrode with all their contacts combined in them. This will not modify the channels of the data (Shortcut: Ctrl+M).
(Merge selected electrodes): Join two or more selected depth electrodes from the list. This will remove the selected electrodes after creating a new merged electrode with all their contacts combined in them. This will not modify the channels of the data (Shortcut: Ctrl+M).  (Set color for selected electrodes): Self explanatory.
(Set color for selected electrodes): Self explanatory.  (Show/hide selected electrodes): To hide an electrode in the 3D figures and MRI viewer, select it in the list then click on this button. Select all the electrodes with the standard shortcut Ctrl+A.
(Show/hide selected electrodes): To hide an electrode in the 3D figures and MRI viewer, select it in the list then click on this button. Select all the electrodes with the standard shortcut Ctrl+A. Display contacts as:
 (Depth electrodes) /
(Depth electrodes) /  (Spheres).
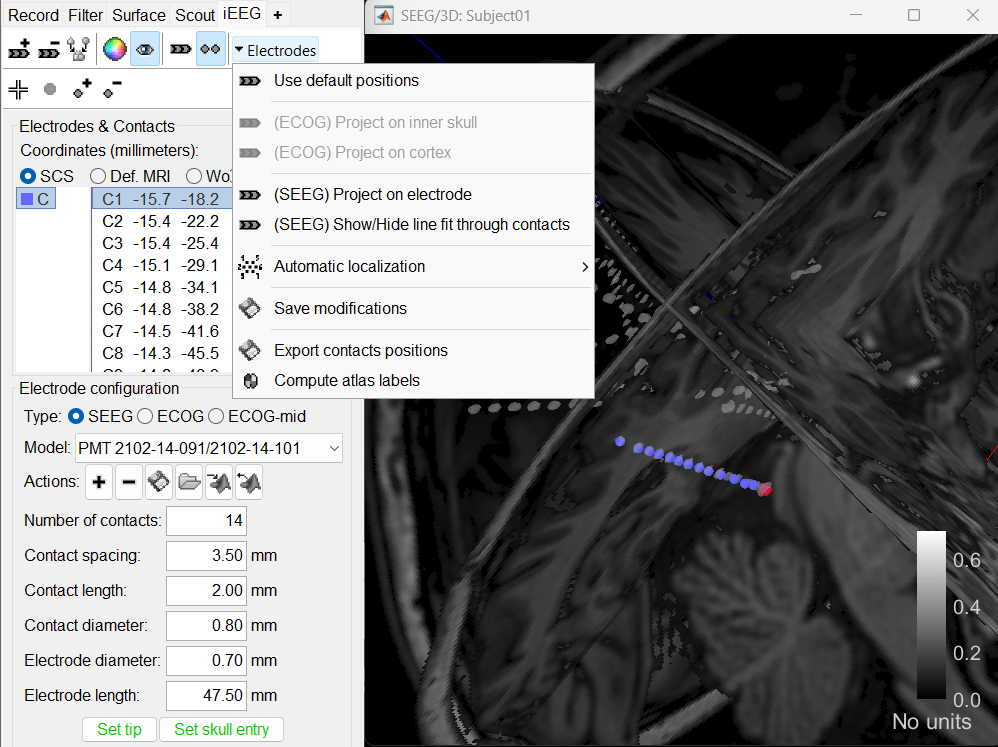
(Spheres). Electrodes > Use default positions: For each of the selected electrodes, the current positions of the SEEG contacts are discarded and replaced with the default positions of the contacts on the electrode. The properties used for setting the position of the contacts are the contact spacing, the tip of the electrode and the entry point in the skull. Contact #i is placed along the electrode at (i-1)*contact_spacing millimeters from the tip of the electrode.
Electrodes > (ECOG) Project on inner skull: This is used to project the ECOG grid to the inner skull. More details.
Electrodes > (ECOG) Project on cortex: This is used to project the ECOG grid to the cortex.
Electrodes > (SEEG) Project on electrode: For each of the selected electrodes, the contacts are projected orthogonally on the electrode. This menu can be useful for aligning contacts that were marked one by one.
Electrodes > (SEEG) Show/Hide line fit through contacts: Performs line fitting through the contacts in 3D figure.
Electrodes > Automatic localization: Different methods to perform automatic contact localization in Brainstorm.
Electrodes > Save modifications: Save the current modifications to the channel file. Otherwise, the modifications are saved only when you close the figure (dialog box "Save modifications to channel file?")
Electrodes > Export contacts positions: Save the 3D positions of the SEEG contacts in a text file, using one of the file formats supported by Brainstorm.
Electrodes > Compute atlas labels: Compute automatic anatomical labeling of contacts based on selected atlases.
 (Select surface point): Activates coordinate selection in 3D figure (Shortcut: Ctrl+P).
(Select surface point): Activates coordinate selection in 3D figure (Shortcut: Ctrl+P).  (Select surface centroid): Activates centroid selection of surface in 3D figure. This option activates for use (turns red) only when the
(Select surface centroid): Activates centroid selection of surface in 3D figure. This option activates for use (turns red) only when the  button is selected and the 3D figure has an IsoSurface present otherwise it appears grayed out (
button is selected and the 3D figure has an IsoSurface present otherwise it appears grayed out (  ). Use this to toggle between centroid (
). Use this to toggle between centroid (  ) and surface (
) and surface (  ) point selection in the IsoSurface.
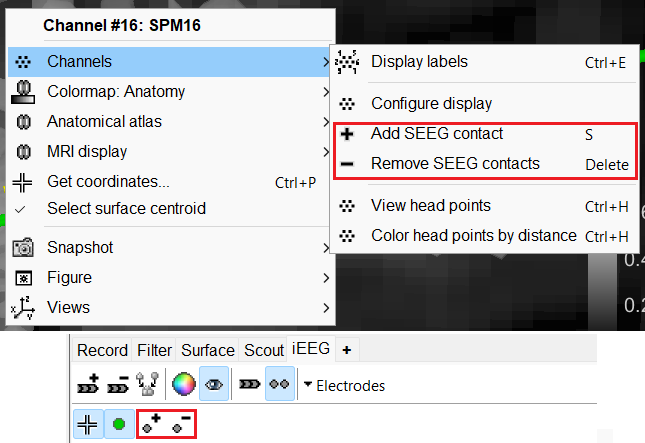
) point selection in the IsoSurface.  (Add SEEG contact): Adds a new contact to the selected SEEG electrode in the list. This will not modify the channels of the data (Shortcut: S).
(Add SEEG contact): Adds a new contact to the selected SEEG electrode in the list. This will not modify the channels of the data (Shortcut: S).  (Remove SEEG contacts): Deletes selected contacts from the list for an SEEG electrode, but does not modify the channels of the data (Shortcut: Delete).
(Remove SEEG contacts): Deletes selected contacts from the list for an SEEG electrode, but does not modify the channels of the data (Shortcut: Delete).
Electrode properties: Properties that have an impact on the position of the contacts.
- If you edit the properties, the modifications will apply to all the selected electrodes in the current channel file. Check what is selected before making changes.
Type: SEEG/ECOG
Model: List of electrode models. If you select an entry in this menu, it will copy the default properties for this model to the selected electrodes. If you are using electrodes that are not in this list, please post on the specification of your devices on the user forum and we will add them to this list.
Number of contacts: Number of recording sites on the electrode. By default, this is set for SEEG to the maximum index found in a group of contacts. Example: electrode C is associated to channels C1, C2, C3, ..., C14 > detected number of contacts is 14.
Contact spacing: Distance between the centers of two consecutive contacts in the electrode. In this example dataset, the default value corresponds to the average distance observed between pairs of adjacent contacts.
Set tip: Select one electrode in the list, then move the cursor of the MRI viewer to the tip of the selected electrode (center of the first contact), and finally click on [Set tip].
Set skull entry: Select one electrode in the list, then move the cursor of the MRI viewer to the point where the depth electrode enters the skull, and finally click on [Set skull entry]. This position does not correspond to any contact, it is used only to estimate the direction of the depth electrode.
- Display options: Properties that only affect the way the electrodes are renderer graphically.
Contact length: Defines the length of the yellow cylinder that represents the contacts along the electrode axis, or the diameter of the sphere when the electrodes are not rendered.
Contact diameter: Diameter of the yellow cylinders representing the contacts. By default, this value is slightly larger than the electrode diameter so that it is rendered correctly. If you use the same value as the electrode diameter, the contacts might not be visible.
Electrode diameter: Diameter of the cylinder representing the SEEG depth electrode.
Electrode length: Length of the cylinder representing the SEEG depth electrode.
Localization of SEEG contacts can be done manually (in the following section) or automatically (advanced section below). We recommend starting with the manual method so that you get a hang of the GUI elements and implantation techniques in Brainstorm. These will come in handy when you would need to do some post-processing after doing the automatic contact localization.
Manual contact localization
Before we start the implantation a prior knowledge of the implantation scheme is required in order to have the correct labels of the various electrodes used. One way here is to have a look at the recordings file and get a knowledge of that. Brainstorm matches the channel names to that of the recordings while importing the positions to them.
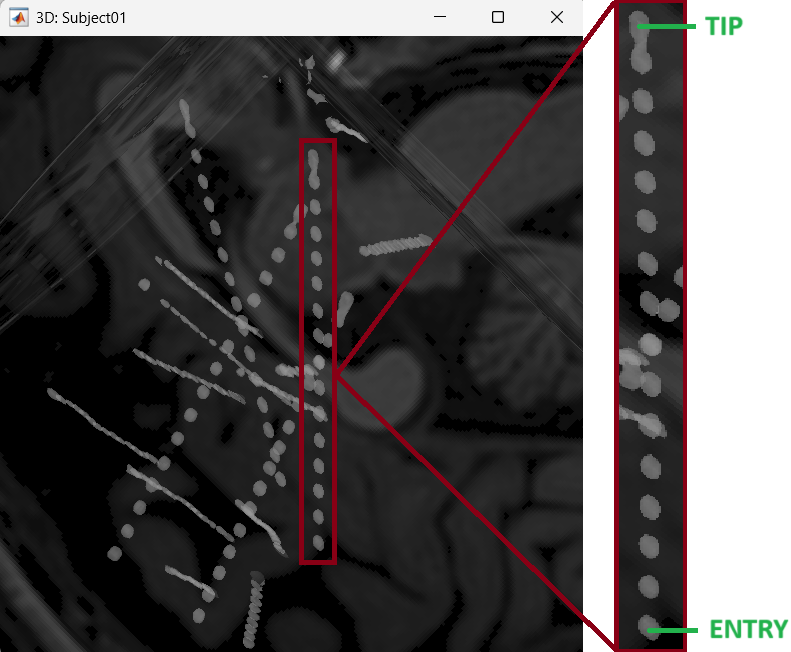
After performing steps above, we will have the Panel iEEG along with the MRI Viewer and 3D figure open. We will be working on the electrode marked below.
On Panel iEEG Click on the + (Add new electrode). This opens up the Add electrode window. For this e.g. enter POP (it is one of the electrodes in the recordings available in this tutorial data) and press OK.
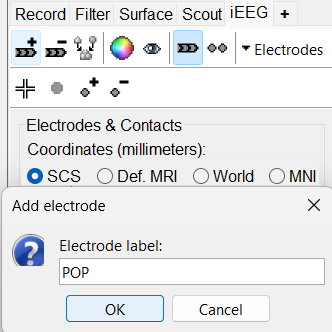
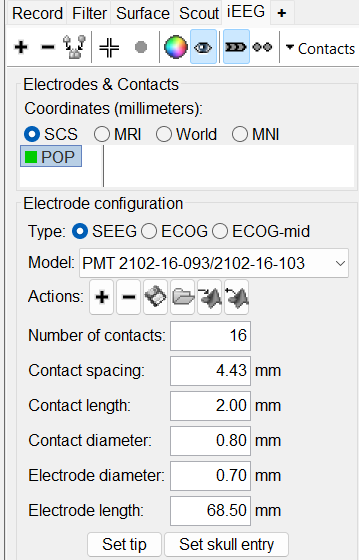
This creates an electrode POP in selected state, and at the bottom the Electrode configuration section of the panel becomes active. Select the following:
Type: SEEG
Model: Choose PMT 2102-16-093/2102-16-103 from the drop down list. This will automatically set the other parameters in the section. More details for these parameters can be found in the advanced section here.
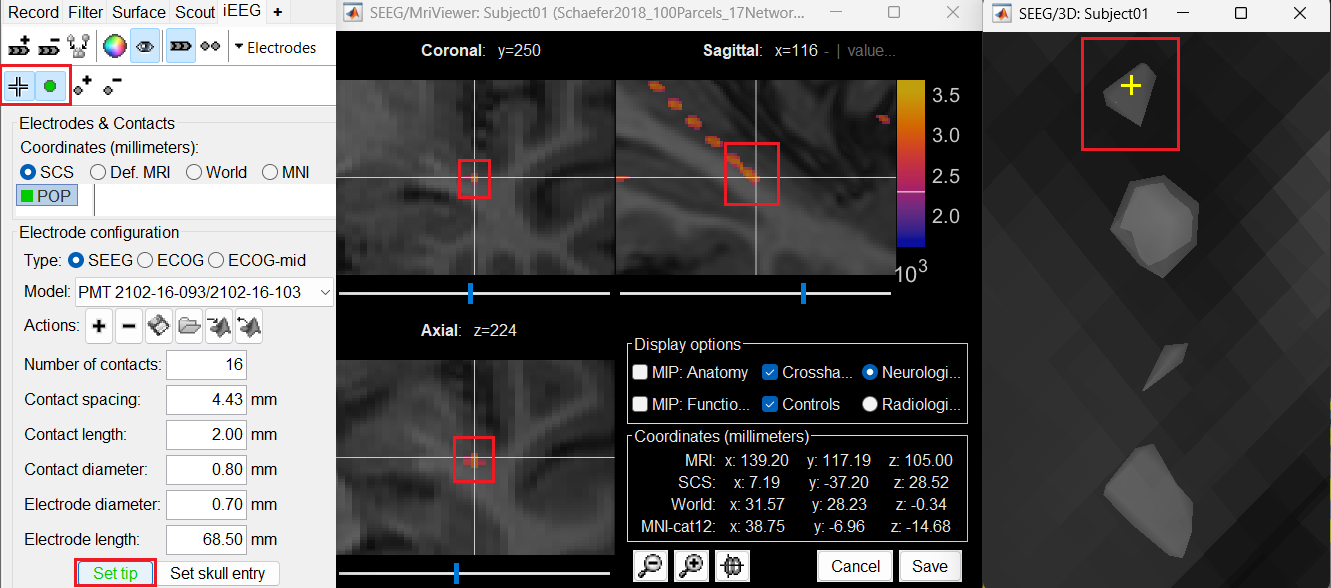
Set tip: Choose the location of the electrode's contact that is deepest in the brain. While we can use the MRI Viewer to set this location (as mentioned here), but to get a more accurate location we will leverage the 3D isosurface as described below.
As seen in the first figure in this section, the tip contact blob is not well separated form its adjacent contact. As mentioned in the Generate isosurface section, switch to Surface tab, use the Thresh slider to adjust the isovalue to approximately 3100 and a readjusted isosurface will be generated that separates out the tip area contacts.

Switch back to the iEEG tab, click the
 button (shortcut: Ctrl+P) to activate surface point selection mode.
button (shortcut: Ctrl+P) to activate surface point selection mode. Click on the
 button to activate selecting centroid of the candidate contact blob in the isosurface.
button to activate selecting centroid of the candidate contact blob in the isosurface. Choose the tip contact in the readjusted 3D isosurface and this should plot a yellow crosshair marker point on the center of the blob and also update the MRI Viewer's crosshair. At the bottom in click Set tip and the button turns green indicating that the tip has been set. This point in 3D is at the centroid of the blob which gives a more accurate location of the contact compared to the same if chosen from the MRI.
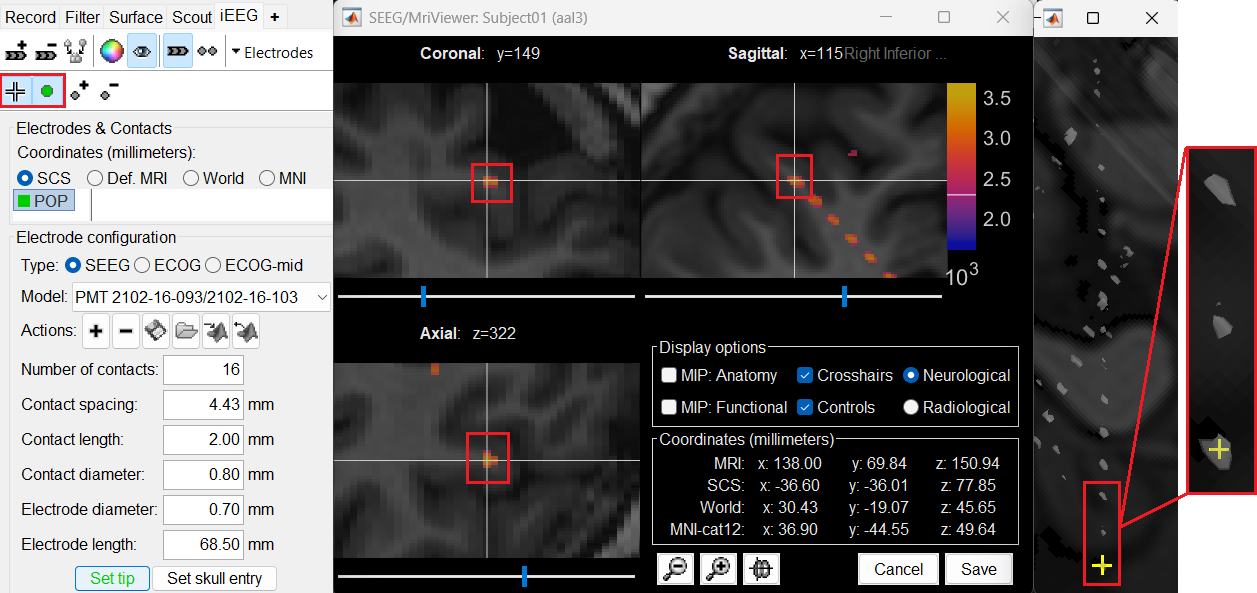
Set skull entry: Choose the point in the 3D isosurface which is going to be set as the skull entry. This point can be any of the contacts other than the tip preferably closer to the skull so that we get an orientation of the electrode.
This should plot a yellow crosshair marker point on the blob and also update the MRI Viewer's crosshair.
At the bottom of iEEG tab, click Set skull entry and the button turns green indicating that the entry point has been set. All the figures get updated with the an electrode based on the above configuration. The properties used for setting the position of the contacts are the contact spacing, the tip of the electrode and the entry point in the skull. Contact #i is placed along the electrode at (i-1)*contact_spacing millimeters from the tip of the electrode.
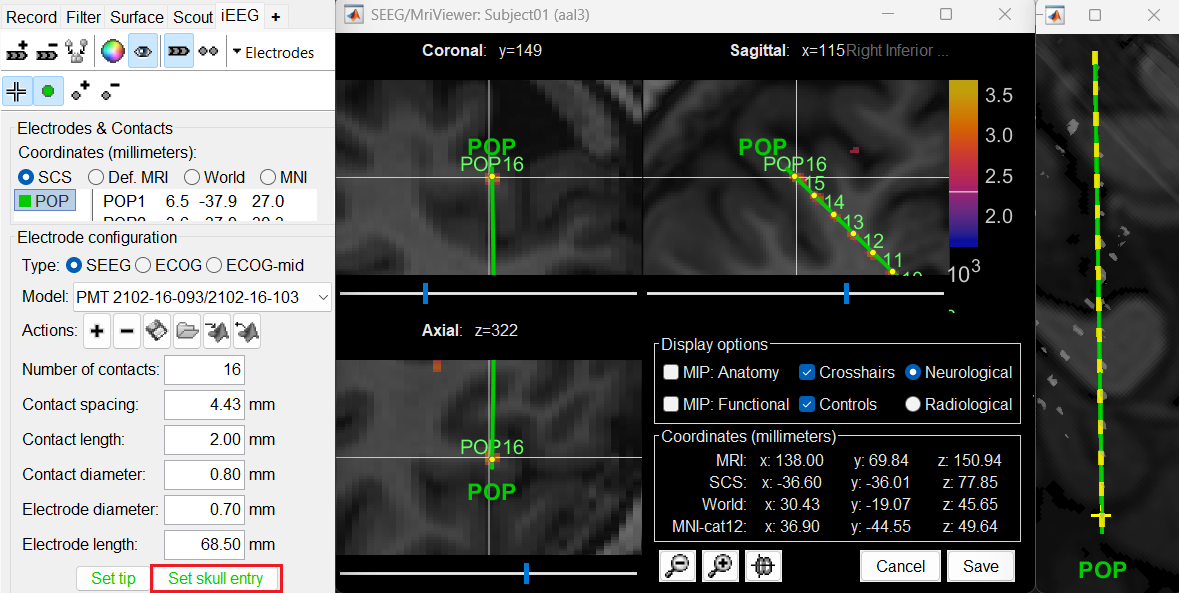
Click on Contacts > Save Modifications to update the channel information in the database.

Repeat the steps for creating implantations for all the other electrodes one by one and save the modifications. Each time you can see the channel file SEEG/ECOG being updated.
When you are done with everything, close all the figures and a prompt appears asking to save the changes. Just click Yes for everything. If all localized properly, the Implantation folder should now have channel file that defines the locations of all the 230 contacts.
To make this tutorial easier to reproduce and follow, we also distribute the positions of the contacts (that were localized using the steps above) exported as a .tsv file: tutorial_seizure_fingerprinting/recordings/Subject01_electrodes_mm.tsv. You can directly import them into the Implantation folder:
Right click on Implantation > Import channel file, choose type as EEG: BIDS electrodes.tsv, subject space mm (*.tsv), browse and select the .tsv file, click Open
Set the scaling factor as 1 (the positions in this .tsv file are in millimeters, the expected unit for this file format is also millimeters, there is no adjustment to make here)
Set the import reference MRI as post_CT_spm_reslice_masked_spm (as the implantation was done on it) and press OK.
Select Yes to replace the existing channel file and all the 230 contacts are updated in the channel. We will use this to link to the recordings in the section below.

In some cases, additional correction of the contacts may be required. To edit the individual contacts refer to the Edit the contacts positions advanced section.
Automatic contact localization
Brainstorm now supports automatically identifying the contact positions of implanted SEEG electrodes within a patient’s brain from a post implantation CT image. This method plays a critical role in both clinical and research settings, as it saves a lot of time compared to having to manually mark each and every contact. Automatic detection of contacts in Brainstorm is currently supported using the GARDEL tool. Visit the link to know more.
Automatic anatomical labeling of contacts
Brainstorm can manage anatomical atlases, both at the volume and at the surface level. You can import an MNI-based anatomical parcellation and use it to label the SEEG contacts. Refer to corresponding section in the Epileptogenicity tutorial for more details.
Edit the contacts positions
The trajectory of electrode while implantation may not always follow a straight line as there could be bending introduced when the neurosurgeon inserts the electrode. In such cases we need to move these contacts to more appropriate positions.
For this section we will consider one such electrode from our dataset above which is marked below. Switch to anatomy tab, open the isosurface file under Subject01 and using the Thresh slider in the Surface tab set the isoValue to approximately 2280.
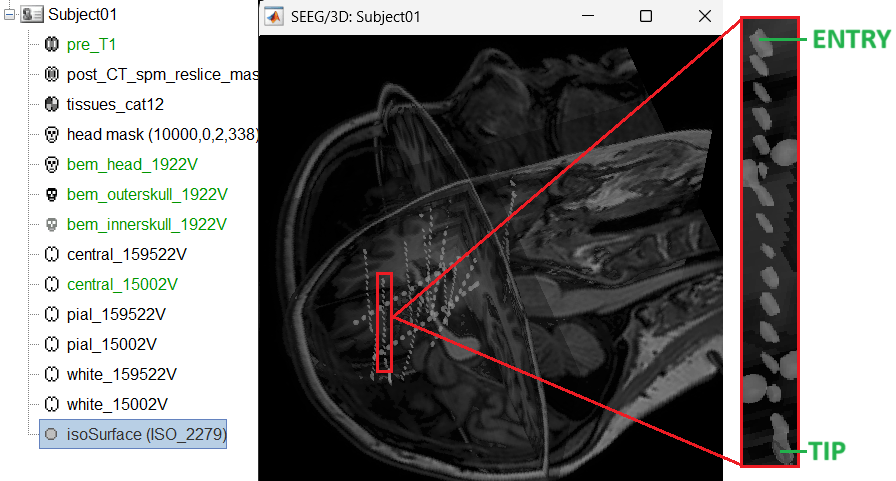
- This is a complex case where:
- The tip is not well separated from its adjacent contact.
- One of the contacts in the middle can be seen joined to another electrode's contact.
Play with the Thresh slider under Surface tab to get a good threshold that separates them out.
As per the sections Start implantation and Create electrodes and plot contacts manually above, create an SEEG electrode named SPM with model PMT 2102-16-091/2102-16-101. Switch to Surface tab first and change the isosurface threshold to approximately 2680 to get a clean tip for marking and then switch back to iEEG tab to do the implantation.
Set the isosurface threshold back to approximately 2280 for clear view of the 3D blobs. Select the 3D figure and toggle between the electrode (
 ) and sphere (
) and sphere (  ) modes to get the figures as under using buttons in iEEG panel. Keep it in the sphere mode for better visibility. The contacts definitely need to be corrected and moved to their right positions.
) modes to get the figures as under using buttons in iEEG panel. Keep it in the sphere mode for better visibility. The contacts definitely need to be corrected and moved to their right positions.
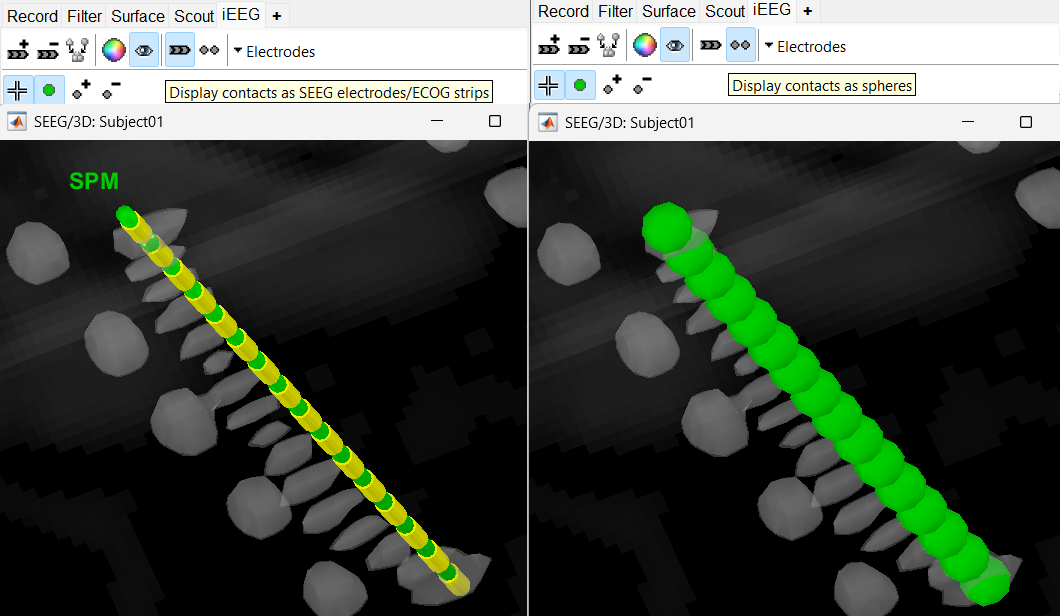
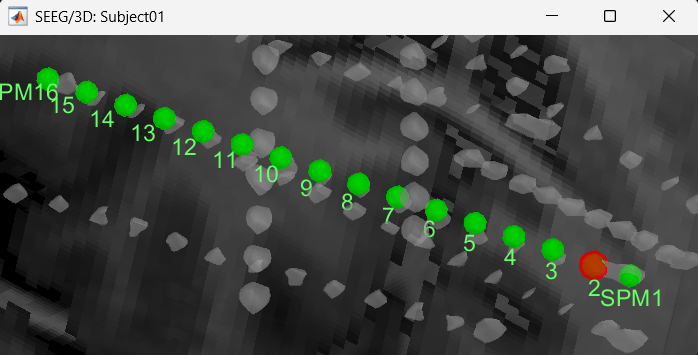
Display the contact labels in 3D figure by right clicking Channels > Display labels. It can be seen that the contacts SPM2-SPM16 are incorrect. Let us first correct contact SPM2.
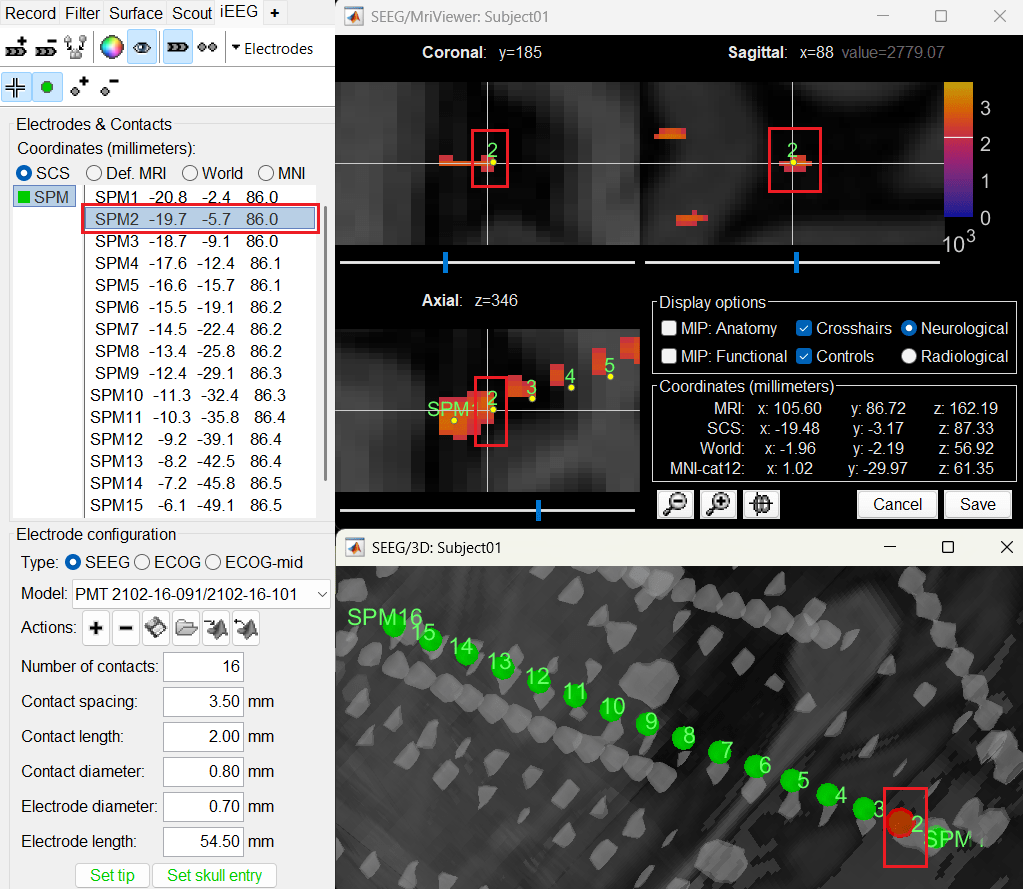
Switch to Surface tab, set the isosurface threshold back to approximately 2680 for separating out the tip and its adjacent contact blob (SPM2). Since the isosurface blobs are the correct ones, we can use them as ground truth guide to correct the contacts. Switch to iEEG tab, click the
 button (shortcut: Ctrl+P; to turn on surface point selection), click the
button (shortcut: Ctrl+P; to turn on surface point selection), click the  button (to turn on centroid selection in surface) and click the correct 3D blob. That places a yellow crosshair on the blob and updates the MRI Viewer crosshair as well.
button (to turn on centroid selection in surface) and click the correct 3D blob. That places a yellow crosshair on the blob and updates the MRI Viewer crosshair as well.
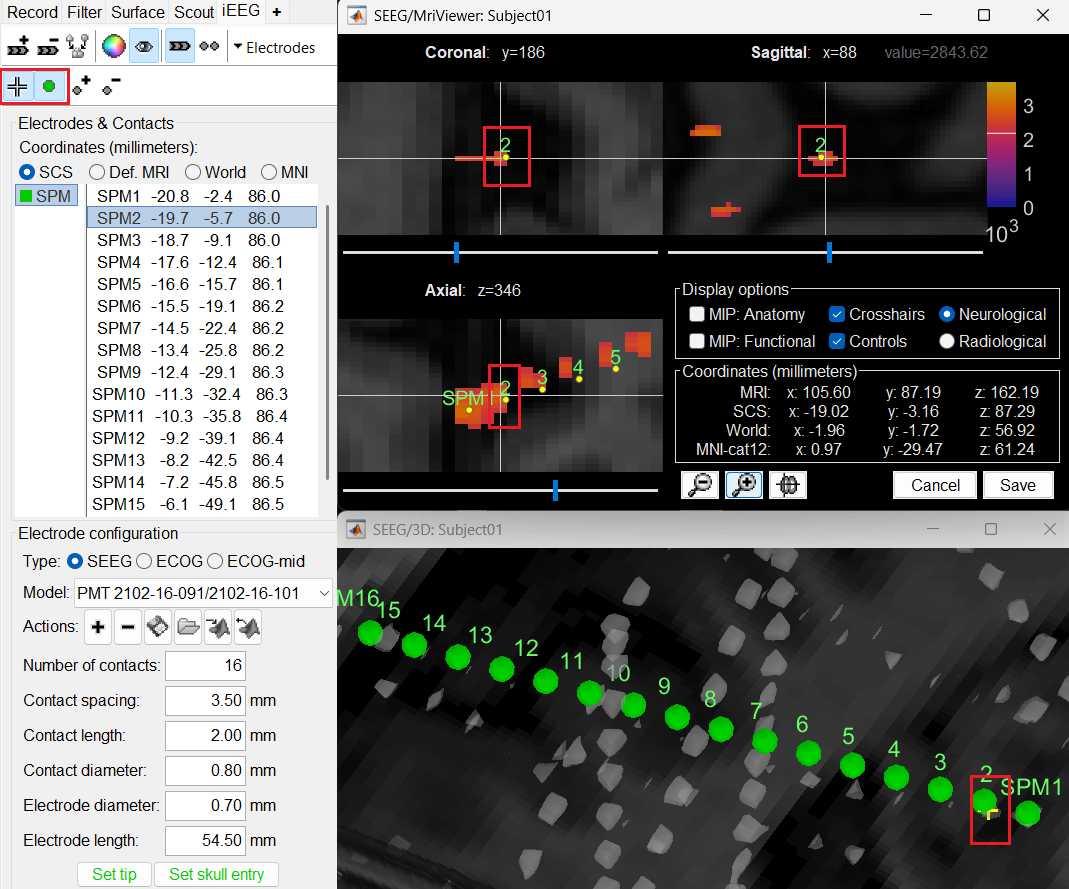
Without clicking anywhere else, move your cursor to the MRI Viewer, right click and go to Electrodes > Set electrode position (or press Ctrl+S). From the Set electrode position window choose SPM2 and press OK. This will update the position of SPM2 only in the MRI Viewer.
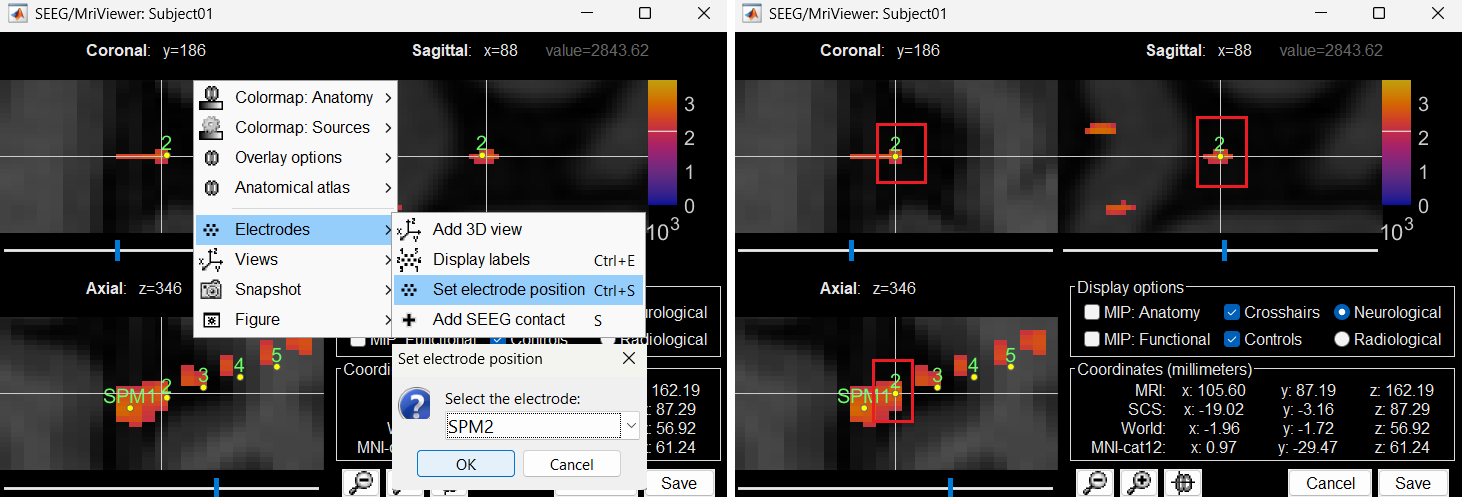
Click on Save and it closes all the windows and updates the channel file and number of channels in the database explorer.
Right click on Subject01 > SEEG/ECOG implantation. Click Continue for working on the existing implantation. Choose MRI+CT+IsoSurf to show all the figures. Switch to Surface tab, set the isosurface threshold back to approximately 2280 for clear view of the 3D blobs. Select the 3D figure and in the Panel iEEG, choose the sphere (
 ) mode for display. You will now see the updated contact in the 3D figure as well.
) mode for display. You will now see the updated contact in the 3D figure as well.
Follow the above steps to update all the remaining contacts as required. Unfortunately, Brainstorm currently does not have a way to handle curved electrodes display yet: if you move the contacts, the electrode remains represented as a straight line. This is a display issue only, which has no impact on any computation, but we hope to improve it at some point.
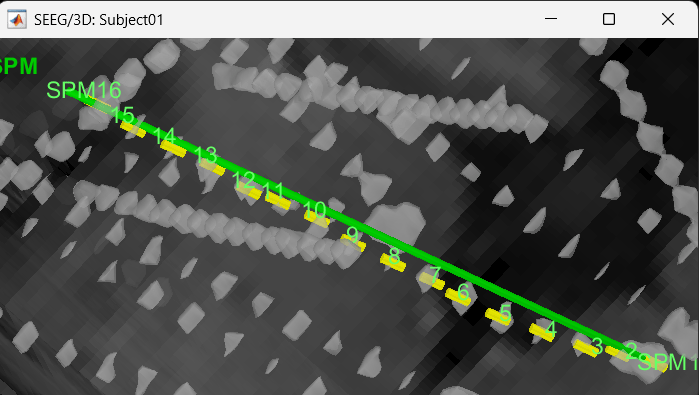
We have a functionality called line fitting that can help better view the trajectory in the 3D figure with sphere (
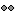 ) display mode. Choose the electrode and click Contacts > Show/Hide line fit through contacts.
) display mode. Choose the electrode and click Contacts > Show/Hide line fit through contacts.
You can also edit the position of a contact directly in the MRI Viewer by clicking on its dot in one of the slice and moving it around. To do it you need to open the MRI Viewer in edit mode by right clicking on the channel file > MRI registration > Edit ... (MRI Viewer:...). Modifications are not saved immediately to the database and can be cancelled when you close the window.
You can also use the Add contact and Remove contacts feature in Brainstorm to edit the contacts.
Add contact can be done in the following ways:
Right click SEEG channel > Display sensors (SEEG: 3D MRI Viewer) > Surface tab (add isosurface) > Select electrode in panel iEEG > Turn on Select Surface Point > Select a location on the isosurface > click
 (Add SEEG contact) in iEEG panel or press shortcut key S
(Add SEEG contact) in iEEG panel or press shortcut key S Right click SEEG channel > Display sensors (SEEG: 3D MRI Viewer) > Surface tab (add isosurface) > Select electrode in panel iEEG > Turn on Select Surface Point > Select a location on the isosurface > right click Channels > Add SEEG contact or press shortcut key S
Right click SEEG channel > Display sensors (SEEG: MRI Viewer) > Select electrode in panel iEEG > Set crosshair at a location in MRI Viewer > click
 (Add SEEG contact) in iEEG panel or press shortcut key S
(Add SEEG contact) in iEEG panel or press shortcut key S Right click SEEG channel > Display sensors (SEEG: MRI Viewer) > Select electrode in panel iEEG > Set crosshair at a location in MRI Viewer > right click Electrodes> Add SEEG contact or press shortcut key S
Remove contacts can be done in the following ways:
Select contacts in panel iEEG > press Delete or Backspace
Select contacts in panel iEEG > click
 (Remove SEEG contacts)
(Remove SEEG contacts) Select the contact in 3D figure > press Delete or Backspace
Select the contact in 3D figure > right click Channels > Remove contact
- The numbering of the contacts is automatically maintained in ascending order from tip to skull entry.
If user deletes all the contacts then then the number of contacts in this case goes down to 0 since all the contacts were deleted. It comes to a state like starting an SEEG electrode implantation from scratch but in this case the number of contacts need to be updated to the desired.
Export the contacts position
You can export the contacts created in Brainstorm as a text file to be used later in Brainstorm or in an external software.
Right click on the Implantation > SEEG/ECOG channel file, click File > Export to file, choose type as EEG: BIDS electrodes.tsv, subject space mm (*.tsv), set file name as Subject_electrodes_mm.tsv click Save, set the export reference MRI as post_CT_spm_reslice_masked_spm (as the implantation was done on it) and press OK.
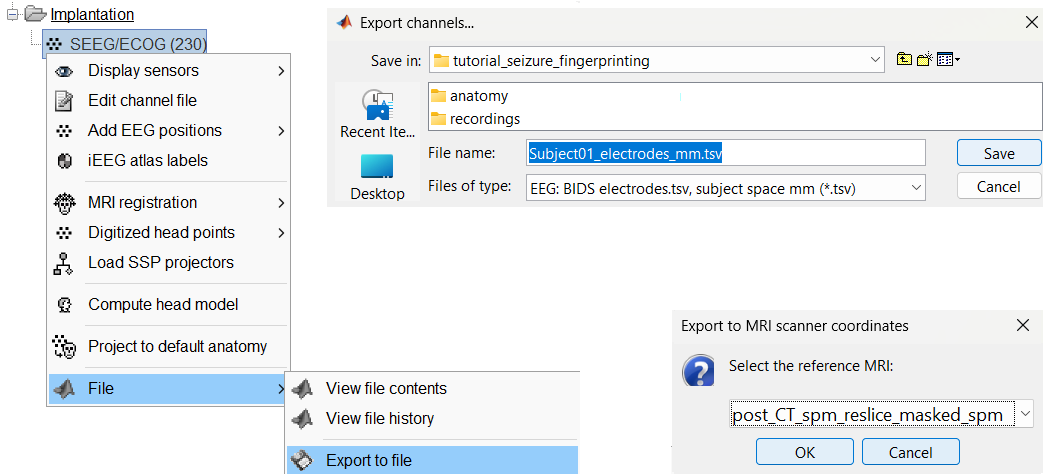
This exports the positions in the file in world coordinates.
Additional Documentation
Forum discussions
Articles
Chinmay Chinara, Raymundo Cassani, Takfarinas Medani, Anand A Joshi, Samuel Medina Villalon, Yash S Vakilna, Johnson P Hampson, Kenneth Taylor, Francois Tadel, Dileep Nair, Christian G Bénar, Sylvain Baillet, John C Mosher, Richard M Leahy. sEEG-Suite: An Interactive Pipeline for Semi-Automated Contact Localization and Anatomical Labeling with Brainstorm.
bioArxiv (September 2025).
