|
Size: 7783
Comment:
|
Size: 11236
Comment:
|
| Deletions are marked like this. | Additions are marked like this. |
| Line 2: | Line 2: |
| a log of additions, improvements and fixes to Brainstorm's distribution. == November 2011 == === Brainstorm now features tools for artifact detection and correction === * Specific channels can be scanned for automatic detection of ocular and cardiac artifacts from continuous recordings; this feature works best with dedicated control channels (i.e. ECG and EOG), * artifact modeling and attenuation using a signal space projection (SSP) approach. === Stand-alone distribution for Linux and MacOSX === We introduced a new packaging logic for the distribution of Brainstorm executable (i.e., which does require the user to run a Matlab license). The entire set of application files (Matlab scripts and compiled executable) are now integrated in the same unique archive. The executable is now platform (OS) independent as it has been reduced to a single .jar file created with Matlab's JavaBuilder, that runs on any platform supporting Matlab. To run the stand-alone version of Brainstorm, you just need to install the free, Matlab Compiler Runtime (version 7.16) foryour operating system. Read more on the [[Installation]] page. === Brainstorm course in Montreal === Part of the Brainstorm development team has moved to the[[http://www.bic.mni.mcgill.ca/ResearchLabsNeuroSPEED/HomePage|McConnell Brain Imaging Centre]] at McGill University's Montreal Neurological Institute, in Montreal, Canada. At this occasion, a full-day training session with 70 participants from across Canada has been organized for new users, back-to-back with the first MEG training workshop of the [[http://www.canada-meg-consortium.org/|Canada MEG Consortium]] ([[http://www.canada-meg-consortium.org/EN/WorkshopPictures|see pictures here]]). For more training opportunities, visit our [[http://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Training|Training]] pages. |
|
| Line 3: | Line 22: |
| === Brainstorm reference paper === Publication of a special issue of the journal Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience: [[http://www.hindawi.com/journals/cin/2011/si.ebm/|"Academic Software Applications for Electromagnetic Brain Mapping Using MEG and EEG"]]. The article describing Brainstorm will now be used as the its reference paper, please cite it in your publications (see [[CiteBrainstorm|How to cite Brainstorm]]). |
=== Brainstorm reference article === Publication of a special issue of the journal'' '''''Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience''':[[http://www.hindawi.com/journals/cin/2011/si.ebm/|Academic Software Applications for Electromagnetic Brain Mapping Using MEG and EEG]], co-edited by[[http://www.bic.mni.mcgill.ca/PeopleFaculty/BailletSylvain|Sylvain Baillet]], Karl Friston & Robert Oostenveld. We encourage Brainstorm users to cite this reference in their publications featuring analyses performed using Brainstorm (see How to cite Brainstorm). |
| Line 6: | Line 25: |
| Tadel F, Baillet S, Mosher JC, Pantazis D, Leahy RM, “Brainstorm: A User-Friendly Application for MEG/EEG Analysis,” Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience, vol. 2011, Article ID 879716, 13 pages, 2011. doi:10.1155/2011/879716 [ [[http://www.hindawi.com/journals/cin/2011/879716/|html]], [[http://downloads.hindawi.com/journals/cin/2011/879716.pdf|pdf]] ] | Tadel F, Baillet S, Mosher JC, Pantazis D, Leahy RM (2011) ''Brainstorm: A User-Friendly Application for MEG/EEG Analysis'', '''Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience''', vol. 2011, Article ID 879716, 13 pages, 2011. doi:10.1155/2011/879716 [[[http://www.hindawi.com/journals/cin/2011/879716/|html]],[[http://downloads.hindawi.com/journals/cin/2011/879716.pdf|pdf]]] |
| Line 8: | Line 27: |
| === Database explorer === The file manager has been extended to support drag'n'drop and copy-paste operations. You can now move or copy easily the files from a condition or subject to another with the mouse, or using the keyboard shortcuts CTRL+C (copy), CTRL+X (cut) and CTRL+V (paste), or the File section in the popup menu.See tutorial: [[Tutorials/TutFirstSteps|First steps]]. |
=== Great improvements in navigating the database === The file manager has been extended to support drag-and-drop and copy-paste operations. Users can now move or copy easily files from a condition or subject entry to another using the mouse, keyboard shortcuts [CTRL+C (copy), CTRL+X (cut) and CTRL+V (paste)], or the File section from the contextual menus from the GUI. |
| Line 11: | Line 30: |
| === Warping default anatomy === It is now possible to create pseudo-individual anatomies for the subjects for which you do not have any anatomical MRI. This operation is possible only if you have acquired some head points using a tracking system (eg. Polhemus Isotrak). The default anatomy (MNI/Colin27) is transformed to match those match those head points. See tutorial: [[Tutorials/TutWarping|Warping default anatomy]]. |
=== No MRI for your participants? No worries: Brainstorm can adjust a template anatomy to individual scalp points (MEG) / electrode locations (EEG) === It is now possible to generate pseudo-individual anatomies from a template, for participants for whom the anatomical MRI volume is not available. This operation is possible if digitized head (scalp) points were acquired using a tracking system (e.g., Polhemus Isotrak), which is commonplace in most MEG labs. The default anatomy (volume and surface envelopes) distributed with Brainstorm (MNI/Colin27) can be transformed (warped) to match the subject's scalp points. This is a great cost-saving alternative when individual anatomy is not accessible to investigators (not recommended for accurate, local mapping of the loci of activity though). |
| Line 14: | Line 33: |
| === Refine registration using head points === When importing MEG recordings, the registration between the sensors and the anatomy was based until now only on three points (nasion, left ear, right ear). This registration can be very imprecise in some cases. If you have digitized many head points with a tracking system before the recordings acquisition, the registration can be refined by trying to minimize the distance between the scalp surface and those digitized head points. This operation will be performed automatically for new datasets, but can also be called manually: right-click on channel file > MRI registration > Refine registration using head points. See tutorial: [[Tutorials/TutRefineReg|Refine registration using head points]]. |
See tutorial: [[Tutorials/TutWarping|Warping default anatomy]]. {{attachment:warp.jpg||height="128px",width="377px"}} === Refine MRI/MEG registration autoamtically using digitized scalp points === When importing MEG recordings, the registration between the MRI volume and the MEG was formerly based only on three fiducial points only (nasion, left ear, right ear). This approach is known be potentially of poor accuracy. If multiple (>60, typically) scalp points were digitized, the transformation between the MEG's and the MRI's referential can be refined by minimizing the average distance between the scalp surface obtained from MRI and the actual digitized head points. This operation is performed automatically in Brainstorm. See tutorial: [[http://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/TutRawViewer#Access_to_the_raw_file|Review raw recordings]]. |
| Line 18: | Line 43: |
| === BEM head model for EEG users === Great news for the EEG users, a new option is available for the computation of the head model: OpenMEEG BEM. This forward model uses a symmetric boundary element method and was developed by the French public research institute INRIA ([[http://www-sop.inria.fr/athena/software/OpenMEEG/|website]]). It uses three realistic layers (scalp, inner skull, outer skull) that can be generated in Brainstorm. It provides for EEG a much better forward solution than the previous "3-shell sphere" model. EEG users should try to switch to this method quickly. It is not necessary for MEG users, as the "overlapping spheres" method gives very similar results but much faster. See tutorial: [[Tutorials/TutBem|BEM head model]]. |
=== Improved, realistic boundary-element-modeling (BEM) head models for EEG === A new feature has been made available for a more accurate computation of EEG forward models with realistic geometry (strongly recommended). OpenMEEG generates forward models using a symmetric boundary element method that was developed by the INRIA team [[http://www-sop.inria.fr/athena/software/OpenMEEG/|ATENA]]. It considers three realistic layers (scalp, inner skull, outer skull), which can all be generated from the MRI volume using Brainstorm. |
| Line 21: | Line 46: |
| === Source estimation for the full brain volume === The head models computed with Brainstorm were until now limited to the cortex surface. This choice was following the assumption that most of the magnetic and electric activity that we record outside of the head comes from the cortex. It was a serious limitiation for users who wanted to study some deeper regions and use their own source spaces. To extend the range of analysis possible with Brainstorm, we have added the possibility to construct dipole grids that sample the full brain volume, and the appropriate visualization tools. See tutorial: [[Tutorials/TutVolSource|Volume source estimation]]. |
See tutorial: [[Tutorials/TutBem|BEM head model]]. {{attachment:openmeeg.gif||height="67px",width="248px"}} === Source estimation in full brain volume === Source models computed in Brainstorm were until now restricted to the cortical surface. To extend the range of analyses made possible with Brainstorm, and to compare Brainstorm's source estimates with those obtained using other software, source models based on dipole grids sampling the entire brain volume can be obtained and reviewed, using the same efficient tools featured in Brainstorm. See tutorial: [[Tutorials/TutVolSource|Volume source estimation]]. {{attachment:grid.jpg||height="163px",width="191px"}} {{attachment:sourcevol.jpg||height="162px",width="178px"}} {{attachment:mriviewer_vol.jpg||height="162px",width="157px"}} |
| Line 26: | Line 59: |
| The way the contributions of MEG and EEG information are balanced in the combined source estimation has been largely improved. However, we still consider this feature as very experimental and recommend the average user to reconstruct the sources for EEG and MEG separately. | The approach to combine concurrent MEG and EEG recordings to obtain a joint source model has been substantially improved. |
| Line 28: | Line 61: |
| === MRI displays: Contact sheets and smoothing === Many new tools for the visualization of sources on MRI slices. First, the sources values are smoothed in space after being re-interpolated in the MRI, which gives nicer and more readable images. The size of the smoothing kernel can be configured: right-click on the figure > MRI display. Then, those images can be used to create contact sheets along all the directions, either in time or in volume. See tutorial: [[Tutorials/TutSourceEstimation|Source estimation]]. |
=== Display of source maps in MRI volume === Added multiple options to review and visualize source maps using contact sheets and volume smoothing of activity maps. 1) source maps are spatially smoothed after interpolation in the MRI voxels. The size of the smoothing kernel can be configured: right-click on the figure > MRI display; 2) the resulting volumescan be used to create contact sheets along all viewing directions, either in time or across the volume. See tutorial: [[Tutorials/TutSourceEstimation|Source estimation]]. |
| Line 32: | Line 67: |
| === Statistical tests: correction for multiple comparisons === When displaying the results of a t-test, there is now a new tab "stat" that is shown in the main window, that allows to changed dynamically the type of correction for multiple comparisons and the threshold. |
=== Statistical inference: correction for multiple comparisons === When displaying the outcome of a t-test, there is now a new tab "stat" that is shown in the main window, which allows to adjust dynamically the type of correction applied to multiple comparisons and the p-value of the test. |
| Line 35: | Line 70: |
| === Graphical batching interface === A completely new version of the "Process" tab is available. It allows the creation of a full processing pipeline in a few clicks, that can be saved or exported as a Matlab script. The processes that are available in the interface are now written in a plug-in way, to make it much easier the future development of new processes. See tutorial: [[Tutorials/TutProcesses|Processes]]. |
=== Unique feature: Graphical batching interface === A brand new version of the "Process" tab is available. Processing pipelines can now be elaborated in a convivial way, in just a few clicks! You can also save and export your pipeline as Matlab scripts. The processes available are now written as plug-ins: you can contribute your own process and it will list automatically to your menu of available tasks that can be performed on data. See tutorial: [[Tutorials/TutProcesses|Processes]]. |
| Line 41: | Line 78: |
{{attachment:raw.jpg}} |
|
| Line 53: | Line 92: |
| Computation and visualization of time-frequency decompositions of MEG/EEG and source signals using Morlet wavelets.See tutorial: [[Tutorials/TutTimefreq|Time-frequency]]. | Computation and visualization of time-frequency decompositions of MEG/EEG and source signals using Morlet wavelets. See tutorial: [[Tutorials/TutTimefreq|Time-frequency]]. |
| Line 65: | Line 104: |
| Dipoles localizations from the Neuromag Xfit software can be imported in Brainstorm database and displayed on the same figures as Brainstorm cortical maps. See tutorial: [[Tutorials/TutXfit|Import and visualize dipoles from Neuromag Xfit]]. |
|
| Line 66: | Line 107: |
| Now using a more stable minimum norm solution. | Integration of a new minimum norm solution, with more and better tuned parameters. This algorithm is now similar to the one implemented in [[http://www.nmr.mgh.harvard.edu/martinos/userInfo/data/sofMNE.php|MNE software]]. |
| Line 70: | Line 111: |
| Any source file estimated for a given surface can be re-projected on another surface. This allows to project sources of individual subjects on the default anatomy to compare subjects. See tutorial: [[http://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/TutSourceEstimation#Project_sources_on_default_anatomy|Project sources on default anatomy]]. |
|
| Line 71: | Line 114: |
| & sensor selection | The time series can be displayed in columns. The displayed sensors can be edited with an interface similar to the selection editor in MNE software. |
| Line 73: | Line 116: |
| === Support for native 4D/BTi file format === | |
| Line 76: | Line 118: |
| Brainstorm is now self-updating. It tests at each startup if your version is older than a month; if so, it downloads a new version. The software can also be updated manually very easily (menu Help > Update Brainstorm). |
What's new
a log of additions, improvements and fixes to Brainstorm's distribution.
November 2011
Brainstorm now features tools for artifact detection and correction
- Specific channels can be scanned for automatic detection of ocular and cardiac artifacts from continuous recordings; this feature works best with dedicated control channels (i.e. ECG and EOG),
- artifact modeling and attenuation using a signal space projection (SSP) approach.
Stand-alone distribution for Linux and MacOSX
We introduced a new packaging logic for the distribution of Brainstorm executable (i.e., which does require the user to run a Matlab license). The entire set of application files (Matlab scripts and compiled executable) are now integrated in the same unique archive.
The executable is now platform (OS) independent as it has been reduced to a single .jar file created with Matlab's JavaBuilder, that runs on any platform supporting Matlab. To run the stand-alone version of Brainstorm, you just need to install the free, Matlab Compiler Runtime (version 7.16) foryour operating system.
Read more on the Installation page.
Brainstorm course in Montreal
Part of the Brainstorm development team has moved to theMcConnell Brain Imaging Centre at McGill University's Montreal Neurological Institute, in Montreal, Canada. At this occasion, a full-day training session with 70 participants from across Canada has been organized for new users, back-to-back with the first MEG training workshop of the Canada MEG Consortium (see pictures here).
For more training opportunities, visit our Training pages.
May 2011
Brainstorm reference article
Publication of a special issue of the journal Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience:Academic Software Applications for Electromagnetic Brain Mapping Using MEG and EEG, co-edited bySylvain Baillet, Karl Friston & Robert Oostenveld. We encourage Brainstorm users to cite this reference in their publications featuring analyses performed using Brainstorm (see How to cite Brainstorm).
Tadel F, Baillet S, Mosher JC, Pantazis D, Leahy RM (2011) Brainstorm: A User-Friendly Application for MEG/EEG Analysis, Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience, vol. 2011, Article ID 879716, 13 pages, 2011. doi:10.1155/2011/879716 ?html,pdf]
Great improvements in navigating the database
The file manager has been extended to support drag-and-drop and copy-paste operations. Users can now move or copy easily files from a condition or subject entry to another using the mouse, keyboard shortcuts [CTRL+C (copy), CTRL+X (cut) and CTRL+V (paste)], or the File section from the contextual menus from the GUI.
No MRI for your participants? No worries: Brainstorm can adjust a template anatomy to individual scalp points (MEG) / electrode locations (EEG)
It is now possible to generate pseudo-individual anatomies from a template, for participants for whom the anatomical MRI volume is not available. This operation is possible if digitized head (scalp) points were acquired using a tracking system (e.g., Polhemus Isotrak), which is commonplace in most MEG labs. The default anatomy (volume and surface envelopes) distributed with Brainstorm (MNI/Colin27) can be transformed (warped) to match the subject's scalp points. This is a great cost-saving alternative when individual anatomy is not accessible to investigators (not recommended for accurate, local mapping of the loci of activity though).
See tutorial: Warping default anatomy.
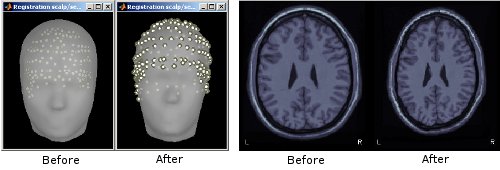
Refine MRI/MEG registration autoamtically using digitized scalp points
When importing MEG recordings, the registration between the MRI volume and the MEG was formerly based only on three fiducial points only (nasion, left ear, right ear). This approach is known be potentially of poor accuracy. If multiple (>60, typically) scalp points were digitized, the transformation between the MEG's and the MRI's referential can be refined by minimizing the average distance between the scalp surface obtained from MRI and the actual digitized head points. This operation is performed automatically in Brainstorm.
See tutorial: Review raw recordings.
April 2011
Improved, realistic boundary-element-modeling (BEM) head models for EEG
A new feature has been made available for a more accurate computation of EEG forward models with realistic geometry (strongly recommended). OpenMEEG generates forward models using a symmetric boundary element method that was developed by the INRIA team ATENA. It considers three realistic layers (scalp, inner skull, outer skull), which can all be generated from the MRI volume using Brainstorm.
See tutorial: BEM head model.

Source estimation in full brain volume
- Source models computed in Brainstorm were until now restricted to the cortical surface. To extend the range of analyses made possible with Brainstorm, and to compare Brainstorm's source estimates with those obtained using other software, source models based on dipole grids sampling the entire brain volume can be obtained and reviewed, using the same efficient tools featured in Brainstorm.
See tutorial: Volume source estimation.
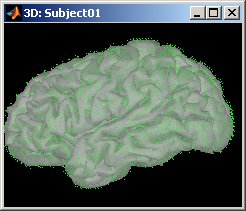
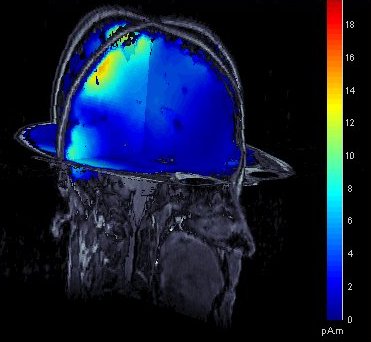
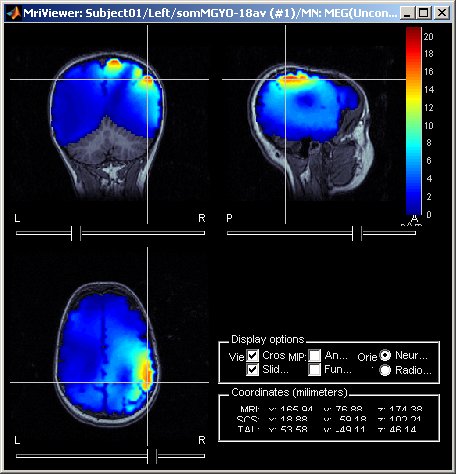
March 2011
Combined MEG/EEG source reconstruction
The approach to combine concurrent MEG and EEG recordings to obtain a joint source model has been substantially improved.
Display of source maps in MRI volume
Added multiple options to review and visualize source maps using contact sheets and volume smoothing of activity maps. 1) source maps are spatially smoothed after interpolation in the MRI voxels. The size of the smoothing kernel can be configured: right-click on the figure > MRI display; 2) the resulting volumescan be used to create contact sheets along all viewing directions, either in time or across the volume.
See tutorial: ?Source estimation.
December 2010
Statistical inference: correction for multiple comparisons
When displaying the outcome of a t-test, there is now a new tab "stat" that is shown in the main window, which allows to adjust dynamically the type of correction applied to multiple comparisons and the p-value of the test.
Unique feature: Graphical batching interface
A brand new version of the "Process" tab is available. Processing pipelines can now be elaborated in a convivial way, in just a few clicks! You can also save and export your pipeline as Matlab scripts. The processes available are now written as plug-ins: you can contribute your own process and it will list automatically to your menu of available tasks that can be performed on data.
See tutorial: ?Processes.
September 2010
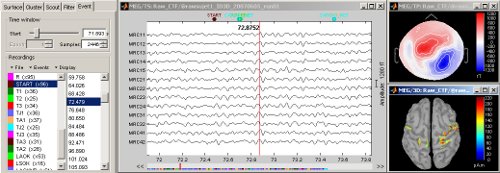
Continuous/RAW file viewer and event editor
Brainstorm can now be used to visualize and process full length continous/raw files in native format. See tutorial: ?Review raw recordings and edit markers.
Detection of bad trials / bad channels
New process available to detect bad trials or bad trials based on peak-to-peak values. The peak-to-peak threshold can be set by channel type.
Estimation of the noise covariance from continuous files
The interface that computes the noise covariance matrix can be called on continuous recordings. Right-click on link to raw file > Noise covariance.
Import/export protocols and subjects
New menus to help users exchange data easily. A full protocol can be exported as a single zip file (menu File > Export protocol), and then imported in another database (menu File > Load protocol > Load from .zip file). Same thing for a single subject: right-click on the subject > File > Export subject. The subject .zip file is actually a full protocol zip file with only the exported subject, hence it should be loaded as a protocol.
June 2010
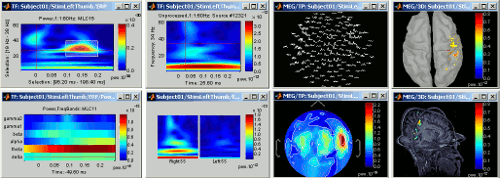
Time-frequency
Computation and visualization of time-frequency decompositions of MEG/EEG and source signals using Morlet wavelets. See tutorial: ?Time-frequency.
Brodman and Tzourio-Mazoyer atlases
Two lists of scouts have been created for the default anatomy (MNI/Colin27), inspired from the atlases of Tzourio-Mazoyer and Brodman. To access those files: display the cortex surface of the default anatomy, then in the "Scout" tab click on the "Load scouts" button, on the right of the scouts list.
Recordings visualization: 2D Layout
The 2D Layout display for recordings has been re-writen to include many tools: sensors selection, interactive gain change, zoom in time and space... See tutorial: ?Exploring the recordings.
March 2010
Support for Xfit dipoles files
Dipoles localizations from the Neuromag Xfit software can be imported in Brainstorm database and displayed on the same figures as Brainstorm cortical maps. See tutorial: ?Import and visualize dipoles from Neuromag Xfit.
Minimum norm solution
Integration of a new minimum norm solution, with more and better tuned parameters. This algorithm is now similar to the one implemented in MNE software.
Januray 2010
Project sources on default anatomy
Any source file estimated for a given surface can be re-projected on another surface. This allows to project sources of individual subjects on the default anatomy to compare subjects. See tutorial: Project sources on default anatomy.
Display channels in columns
The time series can be displayed in columns. The displayed sensors can be edited with an interface similar to the selection editor in MNE software.
December 2009
Automatic updates
Brainstorm is now self-updating. It tests at each startup if your version is older than a month; if so, it downloads a new version. The software can also be updated manually very easily (menu Help > Update Brainstorm).
