|
Size: 3904
Comment:
|
Size: 6299
Comment:
|
| Deletions are marked like this. | Additions are marked like this. |
| Line 5: | Line 5: |
| This tutorial introduces the generalized eigenvalue de-artifacting instrument (GEDAI) algorithm which is an unsupervised EEG denoising method based on the leadfield filtering. | This tutorial introduces the generalized eigenvalue de-artifacting instrument ([[https://github.com/neurotuning/GEDAI-master|GEDAI]]) algorithm which is an unsupervised EEG denoising method based on the leadfield filtering. |
| Line 12: | Line 12: |
| {{attachment:gedai_diagram.png||width="60%"}} | {{attachment:gedai_diagram.jpg||width="80%"}} |
| Line 16: | Line 16: |
{{attachment:gedai_result.png||width="60%"}} |
{{attachment:gedai_result.jpg||width="100%"}} |
| Line 24: | Line 23: |
| {{attachment:install_plugin.png||width="60%"}} | {{attachment:gedai_install.png||width="60%"}} |
| Line 28: | Line 27: |
| {{attachment:plugin_manager.png||width="60%"}} |
|
| Line 32: | Line 29: |
| {{attachment:successfully_installed.png||width="60%"}} | {{attachment:gedai_confirm.png||width="60%"}} |
| Line 34: | Line 31: |
| By following these steps, you will successfully install the bst-neuromaps plugin. | * The README file will appear; after thoroughly reviewing it, click on the "I agree" button to confirm your acceptance of the plugin's terms and conditions. By following these steps, you will successfully install the GEDAI plugin. |
| Line 37: | Line 36: |
| '''[TODO]''' Expanding these points | |
| Line 39: | Line 37: |
| === On GEDAI provided data === * Create a new protocol * Importing data * Install GEDAI plugin * Running GEDAI process Description of the process GUI and each of their elements * Results |
Now that GEDAI has been installed as a plugin, we can use it on the example data that is provided by the GEDAI team. * Download the example file `empirical_NOISE_EOG_EMG.set` in the GEDAI repository.<<BR>> [[https://github.com/neurotuning/GEDAI-master/raw/refs/heads/main/example%20data/empirical_NOISE_EOG_EMG.set|Direct download link]]<<BR>> * Select from the menu '''File > Create new protocol''' Name the new protocol TutorialGEDAI and select the options:<<BR>> Yes, use protocol's default anatomy,<<BR>> No, use one channel file per acquisition run.<<BR>> * Switch now to the Functional data view of your database contents (<<Icon(iconStudyDBSubj.gif)>>), then right-click on the newly created TutorialGEDAI node > '''New subject > Subject01'''. Keep the default options defined for the protocol. * Right-click on Subject01 > '''Review raw file''': * Select the appropriate EEG file format: '''EEG: EEGLAB(*.set)''' * Select the data file: `empirical_NOISE_EOG_EMG.set` * A figure showing the EEG electrodes and the default anatomy is open. Close this figure, we will deal with correct electrode locations after. * A new folder '''empirical_NOISE_EOG_EMG '''is created, inside of it there is the '''Channel file''' (`EEGLAB channels (27)`), and the '''Link to raw file ''', a link to the original data file. * Add the correct locations for the EEG electrodes, right-click on the channel file > '''Add EEG positions > ICBM152 > Generic > ASA 10-20 94''' {{attachment:gedai_channel_loc.png||width="60%"}} * In the Process1 box: Drag and drop the '''Link to raw file'''. * Run process '''Artifacts > GEDAI''':<<BR>> * '''Artifact threshold type''': `auto` * '''Epoch size in wave cycles''': `12 cycles` * '''Low-cut frequency''': `05Hz` * '''Leadfield matrix''': `Freesurfer (precomputed)` * Check '''User parallel processing''' * Check '''Visualize artifacts''' * Uncheck '''Enable''' in the ENOVA bad epoch rejection section . {{attachment:gedai_process.png||width="60%"}} * Run the process * A new figure comparing the original data, i.e., EEG plus artifacts, in red, and the GEDAI-cleaned data, i.e., EEG with major artifacts removed in blue. You can explore the data in this figure to see how artifacts were handled. . {{attachment:gedai_viz.png||width="90%"}} * Besides the figure, a new folder named '''empirical_NOISE_EOG_EMG_gedai''' is created. This contains the GEDAI-cleaned data. |
Generalized Eigenvalue De-Artifacting Instrument (GEDAI)
Authors: Tomas Ros, Yingqi Huang, Takfarinas Medani, Raymundo Cassani
This tutorial introduces the generalized eigenvalue de-artifacting instrument (GEDAI) algorithm which is an unsupervised EEG denoising method based on the leadfield filtering.
Introduction
EEG signals may be considered to be a mixture of electrical activities from a brain “signal” (sub)space, and one containing different types of non-cerebral noise or “artifacts”. This mixture may be “unmixed” by linear decomposition techniques (e.g. PCA or ICA) into separate "components" with individual source locations and respective time-courses. However, although PCA and ICA leverage statistical properties within mixed data to recover underlying sources, they are "blind" source separation methods, functioning without a priori knowledge of the original signals or their mixing process. GEDAI combines theoretical knowledge of the brain’s “signal” subspace with generalized eigenvalue decomposition (GEVD) to automatically separate brain and artifact components. Here, a theoretical model of EEG generation is used as an estimate of the brain’s “noise-free” subspace. An overview of This is shown in the Panel A of the figure below.
Panels B, C and D show these steps at more detail. Panel B: each data covariance matrix (dataCOV) is decomposed into source components with GEVD. Panel C: The GEVD uses a fixed theoretical reference matrix (refCOV) across all epochs, based on the leadfield matrix of an EEG forward model. Panel D: To determine the optimal threshold separating brain and artifactual subspaces, output EEG data is evaluated using the Signal & Noise Subspace Alignment Index (SENSAI). This is done by respectively maximizing and minimizing the subspace similarities of the retained "signal" and removed "noise" with the refCOV.

Install
Being a Brainstorm plugin, GEDAI plugin can be installed, updated and removed directly from the Brainstorm GUI. For further information, see the plugins tutorial.
From the main window go to Plugins > Artifacts > gedai > Install.

A message will appear saying, "Plugin gedai is not installed on your computer. Download the latest version of GEDAI now?" click 'Yes'.
- The plugin will be downloaded and installed automatically. Once installed, you will see a confirmation message.

- The README file will appear; after thoroughly reviewing it, click on the "I agree" button to confirm your acceptance of the plugin's terms and conditions.
By following these steps, you will successfully install the GEDAI plugin.
Using GEDAI
Now that GEDAI has been installed as a plugin, we can use it on the example data that is provided by the GEDAI team.
Download the example file empirical_NOISE_EOG_EMG.set in the GEDAI repository.
Direct download link
Select from the menu File > Create new protocol Name the new protocol TutorialGEDAI and select the options:
Yes, use protocol's default anatomy,
No, use one channel file per acquisition run.
Switch now to the Functional data view of your database contents (
 ), then right-click on the newly created TutorialGEDAI node > New subject > Subject01.
), then right-click on the newly created TutorialGEDAI node > New subject > Subject01.
Keep the default options defined for the protocol.
Right-click on Subject01 > Review raw file:
Select the appropriate EEG file format: EEG: EEGLAB(*.set)
Select the data file: empirical_NOISE_EOG_EMG.set
- A figure showing the EEG electrodes and the default anatomy is open. Close this figure, we will deal with correct electrode locations after.
A new folder empirical_NOISE_EOG_EMG is created, inside of it there is the Channel file (EEGLAB channels (27)), and the Link to raw file , a link to the original data file.
Add the correct locations for the EEG electrodes, right-click on the channel file > Add EEG positions > ICBM152 > Generic > ASA 10-20 94
In the Process1 box: Drag and drop the Link to raw file.
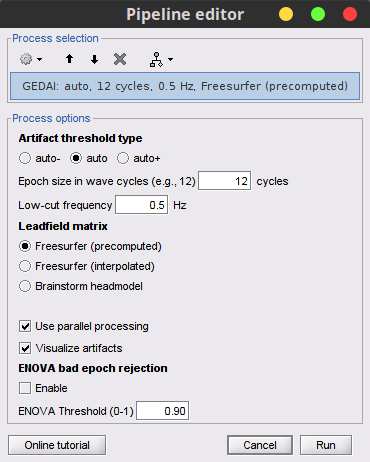
Run process Artifacts > GEDAI:
Artifact threshold type: auto
Epoch size in wave cycles: 12 cycles
Low-cut frequency: 05Hz
Leadfield matrix: Freesurfer (precomputed)
Check User parallel processing
Check Visualize artifacts
Uncheck Enable in the ENOVA bad epoch rejection section
- Run the process
- A new figure comparing the original data, i.e., EEG plus artifacts, in red, and the GEDAI-cleaned data, i.e., EEG with major artifacts removed in blue. You can explore the data in this figure to see how artifacts were handled.

Besides the figure, a new folder named empirical_NOISE_EOG_EMG_gedai is created. This contains the GEDAI-cleaned data.
On epilepsy EEG
- We can use GEDAI on the raw EEG data in the Epilepsy tutorial
Additional documentation
Related tutorials
Articles
* Ros, T., Férat, V., Huang, Y., Colangelo, C., Kia, S. M., Wolfers, T., Vulliemoz, S., & Michela, A. (2025).
Return of the GEDAI: Unsupervised EEG denoising based on leadfield filtering.
bioRxiv : The Preprint Server for Biology.


