Tutorial 19: Clusters of sensors
Authors: Francois Tadel, Elizabeth Bock, Sylvain Baillet
In EEG, most of the analysis can be done directly on the electrode values. This tutorial explains how to group sensors in a cluster and overlay channels from different conditions in the same graph.
In MEG, we tend to avoid working at the sensor level because the signals are ambiguous, we work mostly in the source space, which is the topic of the next tutorials. If you are planning to work only with MEG recordings, you may skip this tutorial.
Contents
Cluster tab
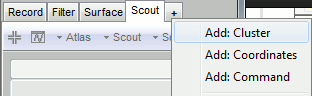
The Cluster tab is not shown by default in the Brainstorm interface.
Click on the [+] button next to the Scout tab > Add: Cluster.
If the list of tabs is too busy, you can close some of them in the same way.
The Cluster tab is similar to the Scout tab, but much simpler. It contains a toolbar to create and edit clusters, a list of existing clusters and a few display options at the bottom.
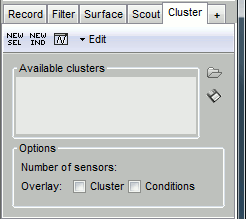
[NEW SEL]: Create a cluster containing the channels that are currently selected in the interface.
[NEW IND]: Create a cluster with channels selected by index, name or type.
[Display clusters time series]: Shows the time series of the selected clusters for all the files that are currently open in the interface.
Edit: Menus to modify the selected clusters.
Creating clusters
A cluster is a group of one or multiple channels. There are two ways for creating a new one.
Display the MEG recordings for the standard average of Run#01 (double-click on the file).
Add a 2D topography (Ctrl+T), display the sensors and select a group of them (right-click+move).
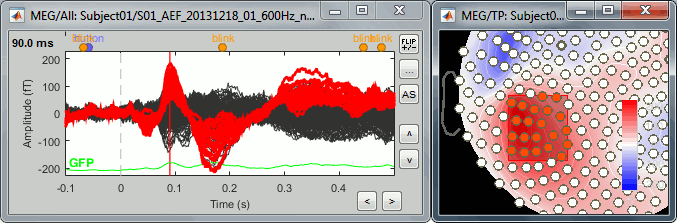
In the Cluster tab, click on [NEW SEL]. It creates a new cluster "c1".
Double-click on it to rename it to "cmax" (or menu Edit > Rename).In the Cluster tab, click on [NEW IND]. Enter the name of the sensor "MLT12". Rename it to "cmin".
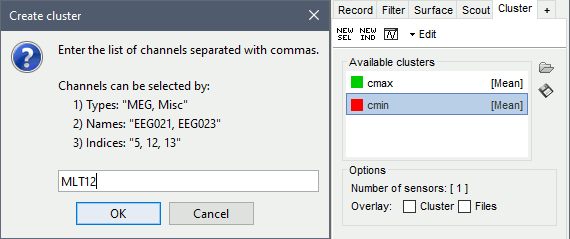
Selection: When you change the selected cluster in the list, it selects the corresponding sensors in all the figures. The number of channels involved in the selection is displayed at the bottom of the tab. You can select multiple clusters at once, holding the Ctrl/Shift/Command button while clicking.
Saving: The clusters are saved in the channel file. When you close all the figures relative to a dataset, it prompts for saving the modifications in the channel file. When opening again the dataset, the Cluster tab will open automatically to show the saved clusters.
Displaying clusters
We now have two clusters available in the list. The second one contains only one channel, displaying it corresponds to displaying the channel time series. The first one contains multiple channels, we need to apply a function to group them into one signal only.
The cluster function used to group multiple signals into one is shown on the right of the cluster list. By default it uses a simple average ("Mean"). You can edit this cluster function with the menu Edit > Set cluster function.
Select one cluster and click on the [Display cluster] button (third from the left in the toolbar).
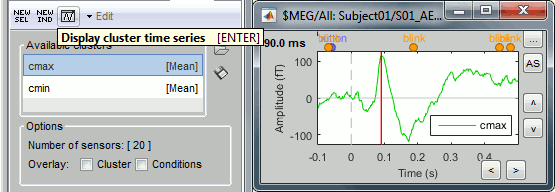
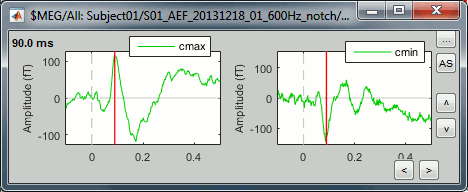
Select the two clusters at once and click on [Display cluster] again.
To have the two signals in the same graph, select the option "Overlay: Cluster". Click on [Display].
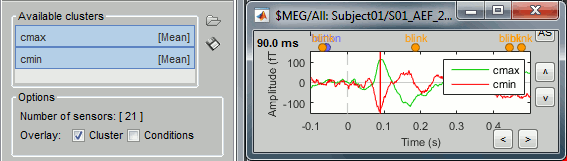
In the database explorer: Double-click on the deviant average of the same run.
Click on [Display cluster] again, now it displays the clusters values for both conditions.
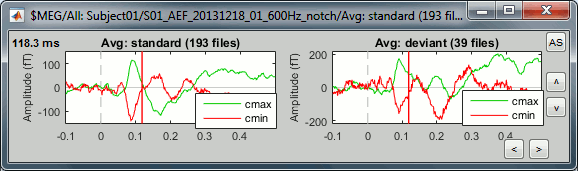
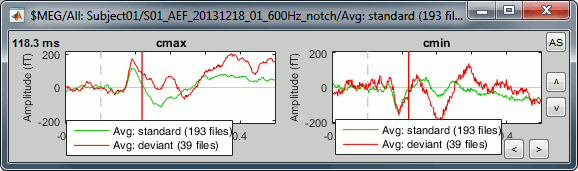
Unselect "Overlay: Cluster" and select "Overlay: Files". If both conditions are selected in the database explorer and both clusters are selected in the Cluster tab, it will group the signals in a different way: one graph per cluster, each one showing the two condition averages.
From the database explorer
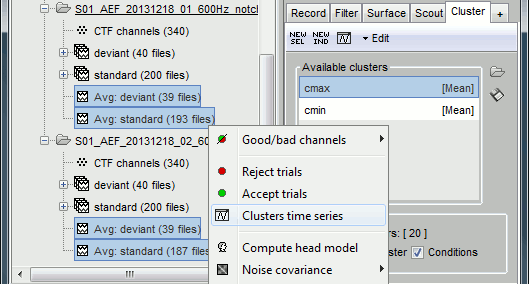
Once the clusters are defined, you can apply them to any number of files in the database in one click.
- Close all the figures with the [X] button in the top-right corner of the Brainstorm figure.
In the Cluster tab, select only one of the two clusters, select Overlay: Files.
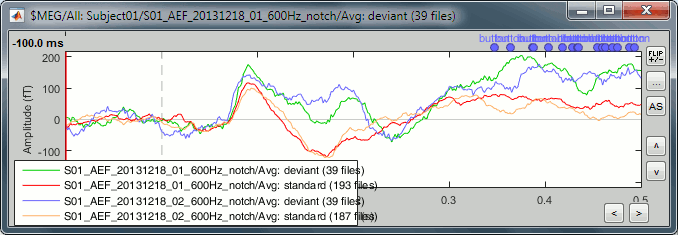
In the database explorer, select all the averages for both runs. Right-click on one of the selected files > Clusters time series. On this graph, you can verify that the selected cluster behaves in the same way in the two acquisition runs.
Processes
Extract > Clusters time series: The process computes the clusters signals and save them in a new file in the database. Select the files of interest in Process1, and select the option "Concatenate" if you want the cluster signals from all the input files to be saved in the matrix file. If the option is not selected, the process creates one new matrix file for each input file.
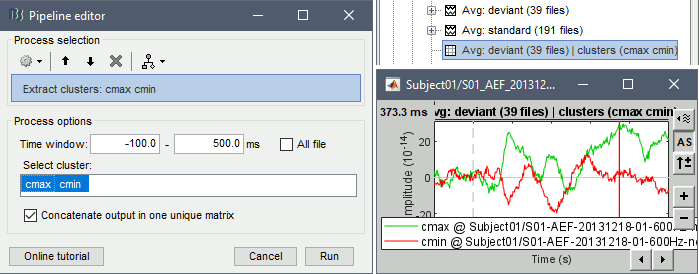
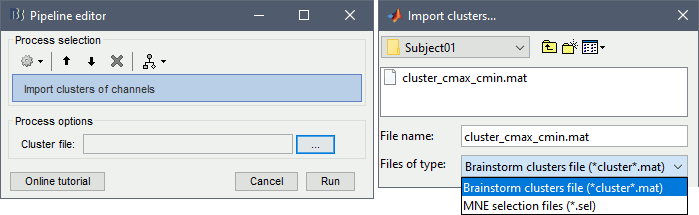
Import > Channel file > Import clusters of channels: The process allows to automate the loading of the same clusters for multiple datasets. In Process1, select at least one data file in each folder in which you want to import the clusters (it will only add it once per channel file, even if you have many data files from the same folder in input), then select the cluster file to import. This cluster file can be generated from the Cluster tab: select one or more clusters and click on the [Save] button.
Scripting
The function db_set_clusters.m allows adding clusters to multiple channels programmatically. Read the header of the function for help with the parameters. Here are some examples:
Add the clusters defined in array of structures 'sClusters' to the channel file of folder pointed by iStudy:
db_set_clusters([], iStudy, sClusters);
Copy all the clusters from a channel file to all the other channel files in the same subject:
db_set_clusters(ChannelFile, 'AllConditions');
Remove all the clusters from all the channel files in the database.
db_set_clusters([], 'AllSubjects', []);
Get a structure template for sCluster:
sCluster = db_template('cluster');Copy the clusters selected in the Clusters tab of the Brainstorm figure to specific studies:
panel_cluster('CopyClusters', iStudies);
