|
Size: 738
Comment:
|
Size: 1430
Comment:
|
| Deletions are marked like this. | Additions are marked like this. |
| Line 8: | Line 8: |
| == Source analysis == Let's reproduce the same observations at the source level. The concepts related with the source estimation are not discussed here; for more information, refer to the introduction tutorials #6 to #8. First, '''delete''' all the files related with the source estimation calculated in the previous tutorials, available in the ''(Common files)'' folder: the head model, the noise covariance and inverse model. We can now provide a better estimate of the noise (affects the inverse model), and we defined new SSP operators (affects the head model). |
|
| Line 11: | Line 16: |
| {{attachment:forward.gif}} | {{http://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/TutRawAvg?action=AttachFile&do=get&target=forward.gif|forward.gif|class="attachment"}} |
Tutorial 13: Head model
Authors: Francois Tadel, Elizabeth Bock, John C Mosher, Sylvain Baillet
Contents
From continuous tutorials:
Source analysis
Let's reproduce the same observations at the source level. The concepts related with the source estimation are not discussed here; for more information, refer to the introduction tutorials #6 to #8.
First, delete all the files related with the source estimation calculated in the previous tutorials, available in the (Common files) folder: the head model, the noise covariance and inverse model. We can now provide a better estimate of the noise (affects the inverse model), and we defined new SSP operators (affects the head model).
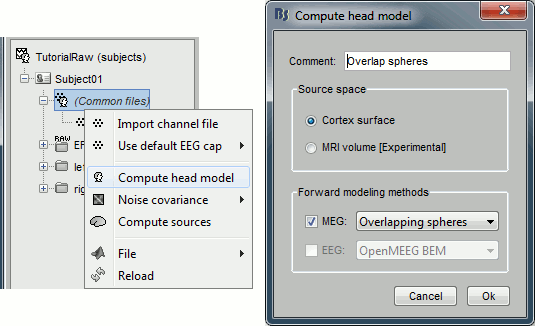
Head model
Right-click on any node that contains the channel file (including the channel file itself), and select: "Compute head model". Leave all the default options: cortex source space, and overlapping spheres. The lead field matrix is saved in file "Overlapping spheres" in (Common files).