PET processing in Brainstorm
Authors: Diellor Basha
This describes how to import and process PET volumes to perform multimodal analyses in Brainstorm...
Introduction
Positron Emission Tomography (PET) is a powerful imaging technique widely used in medical and scientific research to study metabolic and functional processes in the body. PET processing involves a series of computational and analytical steps to transform raw data into meaningful visualizations and quantitative insights. These steps ensure accurate reconstruction, correction, and analysis of PET scans, enabling researchers and clinicians to draw precise conclusions.
This page provides an overview of the essential methods, tools, and considerations involved in PET processing, aiming to support both newcomers and experienced users in achieving optimal results. Whether you're exploring biological pathways, assessing disease progression, or validating experimental findings, understanding the fundamentals of PET processing is key to leveraging the full potential of this versatile imaging modality.
The Brainstorm extension for PET supports importing, processing, registering, visualizing, and analyzing PET data within Brainstorm. PET functionality and workflow are designed to facilitate the analysis of multimodal neuroimaging data by allowing the user to co-analyze MEG, PET and MRI-derived data.
Method Overview
Import the anatomy
- Start Brainstorm
Select the menu File > Create new protocol. Name it "XXXXXX" and select the options:
"No, use individual anatomy",
"No, use one channel file per acquisition run".
Reference MRI
Go to the Anatomy view
Right-click on the XXXXXX top node > New subject > Subject01.
Keep the default options you defined for the protocol.Switch to the Anatomy view of the protocol.
Right-click on the subject node > Import MRI.
Set the file format: MRI: NIfTI-1 (*.nii;*.nii.gz)???.
Select: ???????.niiThe MRI viewer opens automatically. Click on "Click here to compute MNI normalization", option "maff8".
Click on Save to close the MRI viewer. New node named preMRI is created.
PET volume
The MRI volume above will be used as the anatomical reference for this subject. We will now import a PET scan done on the same subject. In this dataset, PET scan corresponds to XXXX.
Right-click on the subject node > Import PET.
Select: ????.niiChoose Yes for the transformation for MRI orientation.
- Choose the import options for PET
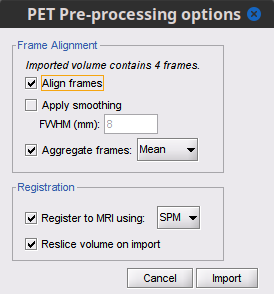
Align frames: Description on what happens, method, etc
Check this optionApply smoothing: Description
Check this option, and set FWHM to XX mmAggregate frames: Description
Select meanRegister to MRI using:: Description
Check this option, and set method to SPMReslice volume:: Description
Check this option
You can also decide to not perform any of these actions, and perform them once the PET volume is imported. IMAGE OF CONTEXT MENUS, for frame alignment and co-registration
Additional documentation
Related tutorials
Articles
Nolte G, Bai O, Wheaton L, Mari Z, Vorbach S, Hallett M.
Identifying true brain interaction from EEG data using the imaginary part of coherency.
Clinical Neurophysiology. 2004 Oct;115(10):2292–307.
Forum discussions
Overlaying PET on cortex: https://neuroimage.usc.edu/forums/t/30241
