|
Size: 8556
Comment:
|
Size: 8542
Comment:
|
| Deletions are marked like this. | Additions are marked like this. |
| Line 2: | Line 2: |
| ''Authors: Francois Tadel, Elizabeth Bock, ''''''John C Mosher, ''Sylvain Baillet'' | ''Authors: Francois Tadel, Elizabeth Bock, John C Mosher, Sylvain Baillet'' |
| Line 19: | Line 19: |
| The time series figure is similar to the ones that were presented in the previous tutorials, with a few new elements. The navigation bar at the bottom represents the time of the entire raw file, where the events are also represented by dots. The ''''<<<'''' and ''''>>>'''' buttons are the same as the ones in the time panel, and jump to the previous/next segment in the file. Clicking on the bar or dragging the red cursor change the current time window as well. | The time series figure is similar to the ones that were presented in the previous tutorials, with a few new elements. The navigation bar at the bottom represents the time of the entire raw file, where the events are also represented by dots. The '''<<<''' and '''>>>''' buttons are the same as the ones in the time panel, and jump to the previous/next segment in the file. Clicking on the bar or dragging the red cursor change the current time window as well. |
| Line 59: | Line 59: |
Tutorial 5: Review continuous files
Authors: Francois Tadel, Elizabeth Bock, John C Mosher, Sylvain Baillet
Contents
Review the recordings
Open the file
Right-click on the data file > MEG (all) > Display time series.
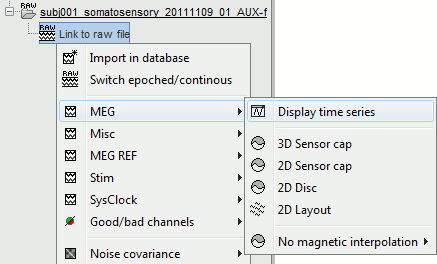
You can see new information in the tab "Record" and a figure showing the recordings.
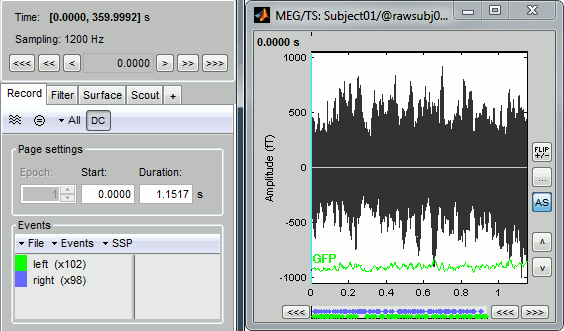
Navigate in time
As described in the basic tutorials, you can set the current time by using either the time panel (buttons and text field), or the figure (click on the white or grey areas of the figure). But you can notice that only a few seconds are visible in the figure, while the time panel (top left of the previous figure), indicates that we have 360s of recordings. Only a small block of the continuous file has been loaded in memory. This small time window can be configured with the tab Record/Page settings, with the text boxes Start and Duration.
The time series figure is similar to the ones that were presented in the previous tutorials, with a few new elements. The navigation bar at the bottom represents the time of the entire raw file, where the events are also represented by dots. The <<< and >>> buttons are the same as the ones in the time panel, and jump to the previous/next segment in the file. Clicking on the bar or dragging the red cursor change the current time window as well.
Sensor selection
Let's switch to a nicer representation of the recordings time series: click on the "Display mode" button in the toolbar of the Record tab.
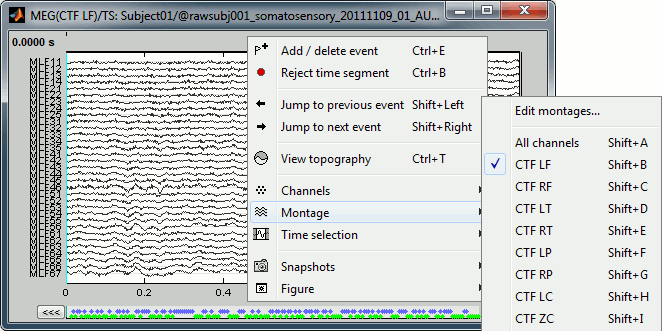
Now the traces are displayed in columns, but all the channels are displayed in the same figure, which makes it unreadable. Select a subset of channels by right-clicking on the figure > Montages, with the drop-down menu in the Record tab or with a keyboard shortcut (Shift+A, B, C...). Default groups of sensors are available for some MEG systems, but you can also create your own groups of sensors with the menu "Edit montages". The montage editor is described in the next tutorial.
Amplitude scale
In this display mode, the amplitude scale is represented on the right of the figure. You can adjust this vertical scale:
Use the buttons "^" and "v" on the right side of the figure. The shortcuts for those buttons are indicated in the tooltips (leave the mouse for a short while over a button)
Hold the Shift key and move the mouse wheel, or use the keys "+" and "-".
Use the button "..." on the right side of the figure ("Set scale manually") to set the scale to a precise level.
When scrolling in time to a different page, the amplitude scale is by default kept. You can change this behavior to re-evaluate automatically an optimal scale each time you change the current time window. This option is called "Auto-scale amplitude" and is disabled by default. To activate it: click on the "AS" button on the right of the figure, or check the menu "Display > Auto-scale amplitude" in the Record tab.
Display options
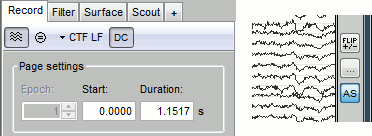
Remove DC offset: Button [DC] in the Record tab. When selected, for each channel, the average value over the entire current time window is subtracted from the channel values. This means that if you change the length of the time window, the value that is removed from each channel may change. It doesn't make much sense to disable this option for unprocessed MEG recordings.
Apply CTF compensation: Button [CTF] in the Record tab. Enable/disable the CTF noise correction based on the reference sensors, when it is not already applied in the file. In the current file, the CTF 3rd order gradient compensation is already applied, therefore this option is not available.
Flip +/-: Button in the right part of the time series figure. Exchange the direction of the Y axis, useful mostly for clinical EEG.
Set scale manually: Button [...] in the figure. Forces a defined amplitude scaling.
Auto-scale amplitude: Button [AS] in the figure. When selected, the vertical scale is adapted to the maximum value over the time window when the time window changes. When not selected: the vertical scales keeps its last value when you jump to another part of the file.
Online filter
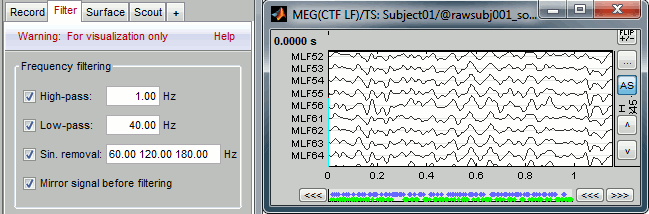
With the Filter tab, you can apply a band-pass filter to the recordings, or remove a set of specific frequencies (example: the 50Hz or 60Hz power lines contamination and their harmonics). The filters are applied only to the time window that is currently loaded; hence if the segment is too short for the required filters, the results could be inaccurate.
The option "Mirror signal before filtering" triples artificially the length of the signal with a mirror symmetry on each side, to avoid the strong edge effects that those filters can generate. Those online filters are not very accurate, they just provide a quick estimate for visualization only, the results are not saved anywhere. To filter properly the continuous files, please use the Process1 tab.
After testing the high-pass, low-pass and notch filters, uncheck them. If not you will probably forget about them, and they will stay on until you restart Brainstorm.
Shortcut summary
Keyboard shortcuts
Left / right arrows:
- No other key: Change current time, sample by sample
With Control key: Jump to previous/next time segment (same as the "<<<" and ">>>" buttons)
With Shift key: Jump to next event of the selected group
On MacOS, these shortcuts are different: please read the tooltips from the buttons ">", ">>", and ">>>" in the time panel to get the appropriate shortcuts.
Page-up / page-down:
- Same as left/right arrows, but faster (10 samples at a time)
If epochs are defined in the file: Control + page-up/page-down jumps to the next/previous epoch.
F3/Shift+F3: Jump to the next/previous epoch or page
F4/Shift+F4: Jump to the next/previous half-page
Plus / minus: Adjust the vertical scale of the time series
Control + E: Add / delete event occurrence
Control + T: Open a 2D topography window at the current time
Shift + Letter: Changes the set of electrodes currently displayed in the figure (list available by right-clicking on the figure > Display setup > ...)
Enter: Display the selected channels in a separate figure (selected channels = lines on which you clicked, that are shown in red)
Escape: Unselect all the selected channels
Delete: Mark the selected channels as bad
Mouse shortcuts
Mouse click on a channel: Select the channel
Mouse click: Change current time
Mouse click + Shift: For the selection of the current time (do not select any sensor, even when clicking on a line)
Mouse click + move: Select time range
Mouse wheel: Zoom around current time
Control + mouse wheel: Zoom vertically
Shift + mouse wheel: Adjust the vertical scale of the time series
Right-click: Display popup menu
Right-click + move: Move in a zoomed figure
Double click: Restore initial zoom settings (but do not restore the vertical scale of the time series)
