|
Size: 104
Comment:
|
Size: 12699
Comment:
|
| Deletions are marked like this. | Additions are marked like this. |
| Line 1: | Line 1: |
| = Tutorials: First steps = <<TableOfContents(2)>> |
= Tutorial 2: First steps = Objectives: Create a protocol with one subject, that uses the default anatomy Colin27. |
| Line 4: | Line 4: |
| == Running Brainstorm for the first time == 1. |
<<TableOfContents(2,2)>> == Starting Brainstorm for the first time == 1. Start Matlab, go to brainstorm3 directory, and type "brainstorm" in Matlab command window.<<BR>> {{{ BST> Starting Brainstorm: BST> ================================= BST> Version: 3.1.130731 (31-Jul-2013) BST> Checking internet connectivity... ok BST> Compiling main interface files... BST> Emptying temporary directory... BST> Deleting old process reports... BST> Loading configuration file... BST> Loading default channel selections... BST> Initializing user interface... BST> Starting OpenGL engine... BST> Reading plugins folder... BST> ================================= }}} 1. Read and accept the licence file. 1. Specify Brainstorm database directory. Read carefully what is written in the [[Tutorials/BstFolders|previous chapter]]. Safe choices are for example: * '''Windows''': My documents\brainstorm_db * '''Linux''': /home/username/brainstorm_db * '''MacOS''': Documents/brainstorm_db == Main interface window == {{attachment:main_window.gif}} == Create first protocol == 1. Click on the File menu, and select, and select ''New protocol''.<<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:menuFile.gif}} 1. Edit the protocol name and enter: "!TutorialFirstSteps". It will automatically update the paths (''Anatomy path'' and ''Datasets path''). 1. ''Default properties for the subjects'': * These are the default settings that are used when creating new subjects. It is then possible to override those settings for each subject individually. * Our objective is to create one subject that uses the default anatomy Colin27, so select the option "''Yes, use protocol's default anatomy''". * The option selected for ''Default channel file'' is not important because we are not going to import recordings (and channel files, ie. files that describe each sensor: position, orientation, name...). This point will be described in another tutorial. 1. Once you get something like the following figure, click on ''Create''.<<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:createNewProtocol.gif}} == Protocol exploration == The protocol is created and you can now see it in the database explorer. It is represented by the top-most node in the tree. * You can switch between anatomy and functional data with the first three buttons in the toolbar. There are no subjects in the database yet, so the ''Functional data'' views are empty. However, in the ''Anatomy ''view, there is a ''(Default anatomy)'' node; it contains the MRI and the surfaces that can be used by default for the subjects without individual anatomy. * The default anatomy used in Brainstorm is based on the ''Colin27 ''MRI volume provided by the Montreal Neurological Institute (MNI): an average of 27 T1-weighted scans of Colin Holmes brain ([[http://www.bic.mni.mcgill.ca/~louis/stx_history.html|more info]]). The surfaces here were extracted from this average MRI with !FreeSurfer. * Display the ''Anatomy ''view, and click on the small "+" to expand the contents of the ''(Default anatomy)'' node. There is one MRI and several surfaces, identified by different icons. * Everything you can do with a node (anatomy files, subjects, protocol) is accessible by right-clicking on it. Take a few minutes to explore all the popup menus by yourself. Don't be afraid of clicking everywhere, at this point you cannot damage anything. . {{attachment:treeNewProtocol.gif}} == Fiducials selection (MRI Viewer) == A few more details about the MRI and the fiducials: Right-click on the MRI file > Edit MRI... . {{attachment:mriViewer.gif}} * You can navigate in the volume by clicking anywhere in the slices, or by using the sliders below each image. * Once you have clicked on any orientation, you can use the '''mouse wheel''' to move to the next/previous slice in the same orientation. * '''Zoom '''in and out with the magnifying glass buttons at the bottom of the figure * There are three small buttons above each image. They may be useful when you import your own MR volumes, if they are not oriented in the way Brainstorm wants them (e.g. you see the ''Sagittal ''title on top of the coronal view; or the small white "''P''", which is supposed to indicate the posterior part of the head, points the nose). Leave your mouse a few seconds over any button to read its description tooltip. Click on them and try to understand what they are doing. * Image contrast can be changed with the mouse: click and hold the right button on one image, and move your mouse up and down (this operation will be later referred as ''right-click+move''). * Right-clicking in any view shows a popup menu that will be described in the following tutorials. * You can define six points on the MRI: * Three to define the Subject Coordinate System (SCS):<<BR>>Nasion (NAS), Left pre-auricular point (LPA), Right pre-auricular point (RPA) * Three to define the Normalized coordinate system (NCS):<<BR>>Anterior commissure (AC), Posterior commissure (PC), and any Interhemispheric point (IH) * More information about how to define the fiducial points on the CoordinateSystems page. * To define a point, position the three views at the point your want to define (pointed by the 3 crosses), and click on the ''Set ''button. Later you can click on ''View ''to move the views to this point again. * You can see that all the points are already defined on this MRI, but you should always check their positions. For many reasons, each research group has a different way to define those points. So you may not position the ears or the nasion exactly the same way as we do. Do not hesitate to move the fiducials to better fit your needings. * The ''Display options'' panel allows to hide some of the components. If the ''MIP/Anatomy ''checkbox is selected, the Maximum Intensity Power is displayed instead of the regular slices: At each point, the value displayed is the maximum value across all the slices. * The ''Coordinates ''panel shows the (x,y,z) coordinates in the coordinate systems managed by Brainstorm: MRI and SCS. * Once you're done, click on ''Cancel ''(unless you really want to save all your experimentations). == MRI visualization == There are many different ways to display the MR volumes. Right click on the ''T1-MRI'' in ''Default anatomy'', menu ''Display''. <<BR>>Just click everywhere and try all the options by yourself, it is the best way to learn.<<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:popupMri.gif}} ==== MRI Viewer ==== Already introduced in this tutorial. Note: it is the default visualization mode; when you double-click on the T1-MRI file, it brings up the MRI Viewer. ==== Axial / coronal / sagittal slices ==== {{attachment:mriSlicesContact.gif||height="231",width="210"}} * '''Zoom''': mouse wheel (or two finger-move on a !MacBook pad) * '''Move '''in zoomed image: click + move * '''Adjust contrast''': right click + move up/down * Colormap selection in menu * Save as image in menu ==== 3D orthogonal slices ==== ||<tablewidth="200px"> {{attachment:mriSlices3d.gif||height="229",width="292"}} || {{attachment:menuShortcut.gif}} || * Simple mouse operations * '''Rotate''': click + move * '''Zoom''': mouse wheel (two finger-move on a !MacBook pad) * '''Move object''': left+right click + move * '''Move MRI slices''': right click + move along direction of the slice (or ''Resect ''panel in ''Surfaces ''tab) * '''Colormap contrast/brightness''': click on the colorbar, and move up/down (brightness) or left/right (contrast) * '''Reset view''': double click * '''Reset colormap''': double-click on the colorbar * Popup operations (right-click on the figure) * '''Colormap''': Full ''Anatomy ''colormap edition (detailed in next tutorial) * '''MRI Display''': For now, contains only the MIP option (Maximum Intensity Power). If checked, for each orientation: displays the maximum along all the slices instead of the proper slice. * '''Get coordinates''': Pick a point in any 3D view and get its coordinates * '''Snapshots''': save images or movies from this figure * '''Figure''': change background color, display axes and menus for an advanced figure editing and management using Matlab tools. * '''Views''': configure camera position with pre-defined settings. * Keyboard shortcuts: * Notice the indications in the right part of the popup menu (''CTRL+A'' in front of ''Figures>Axes'', ''"1"'' in front of ''Views>Left''), they represent the keyboard shortcut for each menu. * Views shortcuts (0,1,2...9 and "="): Remember them, they will be very useful when exploring the cortical sources. It is much faster to press a key to switch from left to right hemisphere, than having to rotate the brain with the mouse. * Surfaces tab (in the Brainstorm main window): * This panel is dedicated to the surfaces display, but some controls can also be useful for 3D MRI view. * ''Transparency ''slider * ''Smooth ''slider: it changes the threshold applied to the MRI slices. If you set it zero, you will see the full slices, as extracted from the volume. * ''Resect ''panel: you can change the position of the slices with the three sliders. == Surfaces visualization == There is only one way to display the surfaces: in 3D figures. To display a surface you can either double-click on it or right-click > Display. * It is the same type of figure than previously (3D), thus all the mouse and keyboard operations are the same. * If you display two surfaces from the same anatomy directory, they will be displayed on the same figure. * Surfaces tab: more options are available<<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:panelSurfaces.gif}} * Open the ''Cortex ''surface and try all the buttons and sliders. Then do the same with the ''Scalp ''surface (''Head''). All the controls should have some effect on the display, except the sliders in the "''Data options''" panel. They are useful only when some additional data is mapped on the surfaces. * Multiple surfaces: If you have more than one surface in a figure, you need to select the surface you want to edit before changing its properties. The list of the available surfaces is displayed on top of the ''Surfaces ''tab. * You can also quickly add or remove surfaces in any 3D figure with the top-right buttons of the ''Surfaces ''tab. == Coordinates tab == * Close all the figures. Open the cortex surface again. * Right-click on the 3D figure, select "Get coordinates". A new window appears. * Click anywhere on the cortex surface: a big yellow cross appears, and the coordinates of the point are displayed in all the available coordinates systems (see page: CoordinateSystems) * MRI: MR volume, in milimeters (multiplied with the Voxsize field in the MRI file). * SCS: Subject Coordinates System, in milimeters * MNI: Montreal Neurological Institute standard coordinates * You can click on "View / MRI" to see where this point is located in the MRI, using the MRI Viewer. <<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:panelCoord.gif}} {{attachment:panelCoordPt.gif}} == Create a subject == If you explored well, you should have found the "''New subject''" menu in the protocol's popup menu. Click on it. ||<tablewidth="200px"#ffffff style="vertical-align:top; "> {{attachment:menuNewSubject.gif}} || {{attachment:createNewSubject.gif}} || * Usually, the only thing you need to do here is to edit the name of the subject. * But you can also override here the protocol's defaults regarding the sharing of anatomy and channel file between subjects and conditions. For the example, leave selected the "''Yes, use default anatomy''" option. Then click on ''Save''. * You should see a the new subject in both ''Anatomy ''and ''Functional data'' views. * In the Anatomy view, the subject node only contains a link called (Default anatomy). It is here just to remind that the subject is using the default ''MNI Colin27'' anatomy.<<BR>> {{attachment:subjectDefaultAnat.gif}} == Change the default anatomy == {{attachment:changeDefault1.gif}} {{attachment:changeDefault2.gif}} {{attachment:changeDefault3.gif}} == Feedback == <<EmbedContent(http://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm3_register/get_feedback.php?Tutorials/TutFirstSteps)>> == Next == Now you know how to create a protocol with a default anatomy, and visualize MR volumes and surfaces. Next step: how to [[Tutorials/TutImportAnatomy|import an individual anatomy]] for a subject. |
Tutorial 2: First steps
Objectives: Create a protocol with one subject, that uses the default anatomy Colin27.
Contents
Starting Brainstorm for the first time
Start Matlab, go to brainstorm3 directory, and type "brainstorm" in Matlab command window.
BST> Starting Brainstorm: BST> ================================= BST> Version: 3.1.130731 (31-Jul-2013) BST> Checking internet connectivity... ok BST> Compiling main interface files... BST> Emptying temporary directory... BST> Deleting old process reports... BST> Loading configuration file... BST> Loading default channel selections... BST> Initializing user interface... BST> Starting OpenGL engine... BST> Reading plugins folder... BST> =================================
- Read and accept the licence file.
Specify Brainstorm database directory. Read carefully what is written in the ?previous chapter. Safe choices are for example:
Windows: My documents\brainstorm_db
Linux: /home/username/brainstorm_db
MacOS: Documents/brainstorm_db
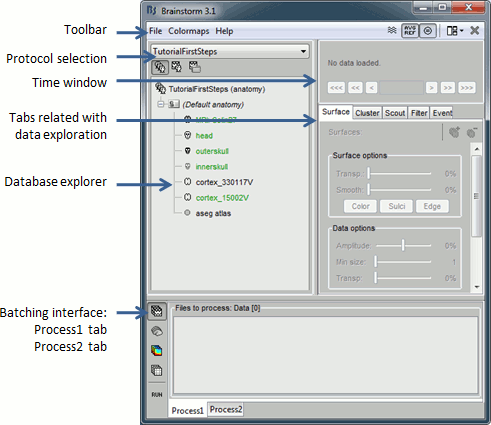
Main interface window
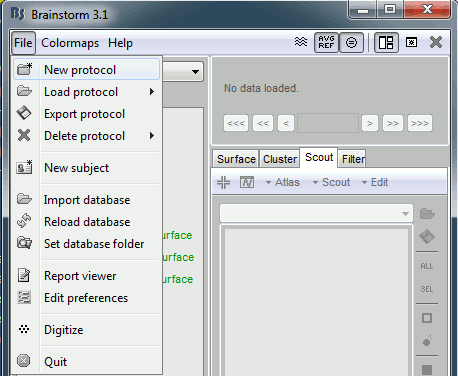
Create first protocol
Click on the File menu, and select, and select New protocol.
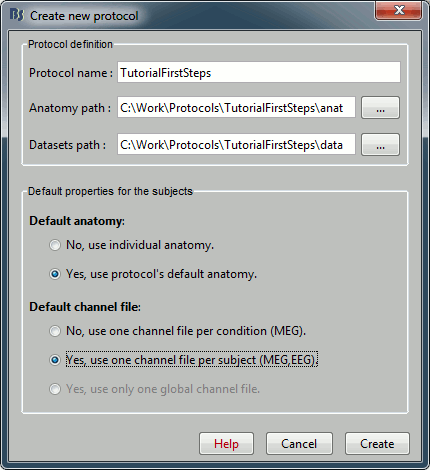
Edit the protocol name and enter: "TutorialFirstSteps". It will automatically update the paths (Anatomy path and Datasets path).
Default properties for the subjects:
- These are the default settings that are used when creating new subjects. It is then possible to override those settings for each subject individually.
Our objective is to create one subject that uses the default anatomy Colin27, so select the option "Yes, use protocol's default anatomy".
The option selected for Default channel file is not important because we are not going to import recordings (and channel files, ie. files that describe each sensor: position, orientation, name...). This point will be described in another tutorial.
Once you get something like the following figure, click on Create.
Protocol exploration
The protocol is created and you can now see it in the database explorer. It is represented by the top-most node in the tree.
You can switch between anatomy and functional data with the first three buttons in the toolbar. There are no subjects in the database yet, so the Functional data views are empty. However, in the Anatomy view, there is a (Default anatomy) node; it contains the MRI and the surfaces that can be used by default for the subjects without individual anatomy.
The default anatomy used in Brainstorm is based on the Colin27 MRI volume provided by the Montreal Neurological Institute (MNI): an average of 27 T1-weighted scans of Colin Holmes brain (more info). The surfaces here were extracted from this average MRI with FreeSurfer.
Display the Anatomy view, and click on the small "+" to expand the contents of the (Default anatomy) node. There is one MRI and several surfaces, identified by different icons.
- Everything you can do with a node (anatomy files, subjects, protocol) is accessible by right-clicking on it. Take a few minutes to explore all the popup menus by yourself. Don't be afraid of clicking everywhere, at this point you cannot damage anything.
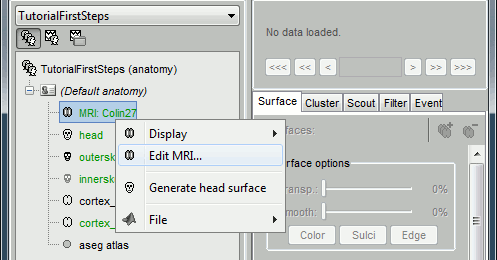
Fiducials selection (MRI Viewer)
A few more details about the MRI and the fiducials: Right-click on the MRI file > Edit MRI...
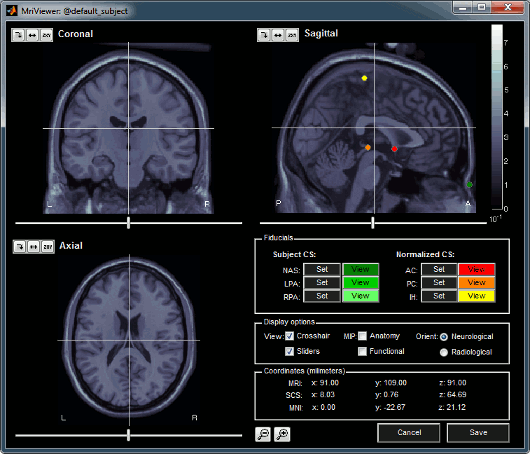
- You can navigate in the volume by clicking anywhere in the slices, or by using the sliders below each image.
Once you have clicked on any orientation, you can use the mouse wheel to move to the next/previous slice in the same orientation.
Zoom in and out with the magnifying glass buttons at the bottom of the figure
There are three small buttons above each image. They may be useful when you import your own MR volumes, if they are not oriented in the way Brainstorm wants them (e.g. you see the Sagittal title on top of the coronal view; or the small white "P", which is supposed to indicate the posterior part of the head, points the nose). Leave your mouse a few seconds over any button to read its description tooltip. Click on them and try to understand what they are doing.
Image contrast can be changed with the mouse: click and hold the right button on one image, and move your mouse up and down (this operation will be later referred as right-click+move).
- Right-clicking in any view shows a popup menu that will be described in the following tutorials.
- You can define six points on the MRI:
Three to define the Subject Coordinate System (SCS):
Nasion (NAS), Left pre-auricular point (LPA), Right pre-auricular point (RPA)Three to define the Normalized coordinate system (NCS):
Anterior commissure (AC), Posterior commissure (PC), and any Interhemispheric point (IH)More information about how to define the fiducial points on the CoordinateSystems page.
To define a point, position the three views at the point your want to define (pointed by the 3 crosses), and click on the Set button. Later you can click on View to move the views to this point again.
- You can see that all the points are already defined on this MRI, but you should always check their positions. For many reasons, each research group has a different way to define those points. So you may not position the ears or the nasion exactly the same way as we do. Do not hesitate to move the fiducials to better fit your needings.
The Display options panel allows to hide some of the components. If the MIP/Anatomy checkbox is selected, the Maximum Intensity Power is displayed instead of the regular slices: At each point, the value displayed is the maximum value across all the slices.
The Coordinates panel shows the (x,y,z) coordinates in the coordinate systems managed by Brainstorm: MRI and SCS.
Once you're done, click on Cancel (unless you really want to save all your experimentations).
MRI visualization
There are many different ways to display the MR volumes. Right click on the T1-MRI in Default anatomy, menu Display.
Just click everywhere and try all the options by yourself, it is the best way to learn.
MRI Viewer
Already introduced in this tutorial.
Note: it is the default visualization mode; when you double-click on the T1-MRI file, it brings up the MRI Viewer.
Axial / coronal / sagittal slices
Zoom: mouse wheel (or two finger-move on a MacBook pad)
Move in zoomed image: click + move
Adjust contrast: right click + move up/down
- Colormap selection in menu
- Save as image in menu
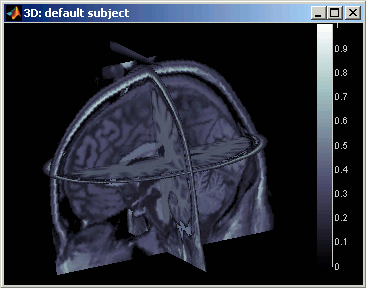
3D orthogonal slices
|
|
- Simple mouse operations
Rotate: click + move
Zoom: mouse wheel (two finger-move on a MacBook pad)
Move object: left+right click + move
Move MRI slices: right click + move along direction of the slice (or Resect panel in Surfaces tab)
Colormap contrast/brightness: click on the colorbar, and move up/down (brightness) or left/right (contrast)
Reset view: double click
Reset colormap: double-click on the colorbar
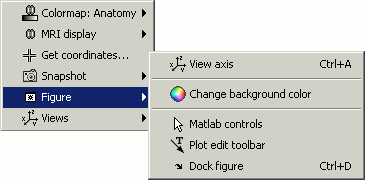
- Popup operations (right-click on the figure)
Colormap: Full Anatomy colormap edition (detailed in next tutorial)
MRI Display: For now, contains only the MIP option (Maximum Intensity Power). If checked, for each orientation: displays the maximum along all the slices instead of the proper slice.
Get coordinates: Pick a point in any 3D view and get its coordinates
Snapshots: save images or movies from this figure
Figure: change background color, display axes and menus for an advanced figure editing and management using Matlab tools.
Views: configure camera position with pre-defined settings.
- Keyboard shortcuts:
Notice the indications in the right part of the popup menu (CTRL+A in front of Figures>Axes, "1" in front of Views>Left), they represent the keyboard shortcut for each menu.
- Views shortcuts (0,1,2...9 and "="): Remember them, they will be very useful when exploring the cortical sources. It is much faster to press a key to switch from left to right hemisphere, than having to rotate the brain with the mouse.
- Surfaces tab (in the Brainstorm main window):
- This panel is dedicated to the surfaces display, but some controls can also be useful for 3D MRI view.
Transparency slider
Smooth slider: it changes the threshold applied to the MRI slices. If you set it zero, you will see the full slices, as extracted from the volume.
Resect panel: you can change the position of the slices with the three sliders.
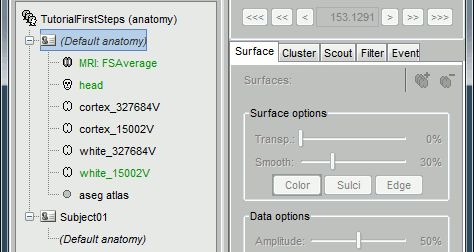
Surfaces visualization
There is only one way to display the surfaces: in 3D figures. To display a surface you can either double-click on it or right-click > Display.
- It is the same type of figure than previously (3D), thus all the mouse and keyboard operations are the same.
- If you display two surfaces from the same anatomy directory, they will be displayed on the same figure.
Surfaces tab: more options are available
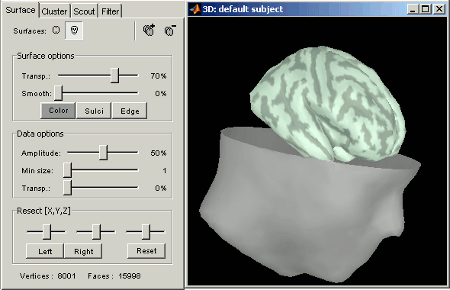
Open the Cortex surface and try all the buttons and sliders. Then do the same with the Scalp surface (Head). All the controls should have some effect on the display, except the sliders in the "Data options" panel. They are useful only when some additional data is mapped on the surfaces.
Multiple surfaces: If you have more than one surface in a figure, you need to select the surface you want to edit before changing its properties. The list of the available surfaces is displayed on top of the Surfaces tab.
You can also quickly add or remove surfaces in any 3D figure with the top-right buttons of the Surfaces tab.
Coordinates tab
- Close all the figures. Open the cortex surface again.
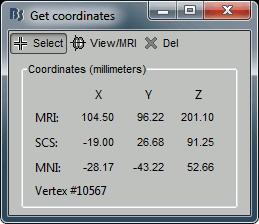
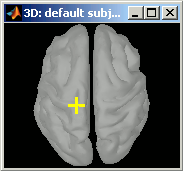
- Right-click on the 3D figure, select "Get coordinates". A new window appears.
Click anywhere on the cortex surface: a big yellow cross appears, and the coordinates of the point are displayed in all the available coordinates systems (see page: CoordinateSystems)
- MRI: MR volume, in milimeters (multiplied with the Voxsize field in the MRI file).
- SCS: Subject Coordinates System, in milimeters
- MNI: Montreal Neurological Institute standard coordinates
You can click on "View / MRI" to see where this point is located in the MRI, using the MRI Viewer.
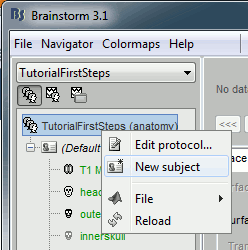
Create a subject
If you explored well, you should have found the "New subject" menu in the protocol's popup menu. Click on it.
|
|
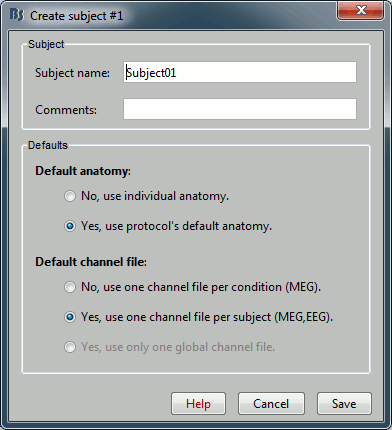
- Usually, the only thing you need to do here is to edit the name of the subject.
But you can also override here the protocol's defaults regarding the sharing of anatomy and channel file between subjects and conditions. For the example, leave selected the "Yes, use default anatomy" option. Then click on Save.
You should see a the new subject in both Anatomy and Functional data views.
In the Anatomy view, the subject node only contains a link called (Default anatomy). It is here just to remind that the subject is using the default MNI Colin27 anatomy.
Change the default anatomy
Feedback
Next
Now you know how to create a protocol with a default anatomy, and visualize MR volumes and surfaces.
Next step: how to ?import an individual anatomy for a subject.