|
Size: 74
Comment:
|
Size: 2205
Comment:
|
| Deletions are marked like this. | Additions are marked like this. |
| Line 1: | Line 1: |
| ## page was renamed from TutImportAnatomy | |
| Line 3: | Line 2: |
| Objectives: Import anatomy for CTF MEG tutorial. <<TableOfContents>> == Create protocol == 1. Download '''bst_tutorial_somatotopy_ctf.zip''' file ([[http://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm3_register/download.php|Download]] section), and unzip it somewhere. Data description in the next tutorial. * Warning: Do '''NOT '''unzip it in the Brainstorm '''database or program directories'''. This package contains files in original file formats, and need to be imported through the interface to be processed with Brainstorm. 1. Create a new protocol called ''TutorialCTF ''with the following options: * "No, use individual anatomy", because the individual subject anatomy is available * "No, use one channel file per condition (MEG)", because we are going to process regular MEG data in the next tutorial 1. Create a new subject (let's keep the default name: ''Subject01'') == Import MRI == 1. Go to the ''Anatomy ''view of the protocol files (very first button in Brainstorm window toolbar). 1. Right click on subject node, and select menu "''Import MRI...''"<<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:menuImportMri.gif}} 1. Select file "TutorialCtf/Anatomy/01.mri". 1. If you didn't modified any Brainstorm option yet, you should get an error message, saying "Unrecognized format, try switching byte order". This is because not all the computers process the binary data the same way. To learn more about endianness, you can consult [[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Endianness|this Wikipedia page]]. Depending on the type of computer which wrote the binary files, you may need to read them as ''little-endian'' or ''big-endian''. To change this setting, go to the ''Options > Byte order'' menu in main window. You may need to modify this setting again to import other files.<<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:menuByteOrder.gif}} 1. Try to import the MRI again. It should be working now. The MRI viewer is displayed, together with a message box that tells you what to do. Follow the instructions. The MRI is already well oriented so you can directly process with the fiducials selection. If you are not sure how to do this, consult this page: CoordinateSystems. |
Import individual anatomy
Objectives: Import anatomy for CTF MEG tutorial.
Create protocol
Download bst_tutorial_somatotopy_ctf.zip file (Download section), and unzip it somewhere. Data description in the next tutorial.
Warning: Do NOT unzip it in the Brainstorm database or program directories. This package contains files in original file formats, and need to be imported through the interface to be processed with Brainstorm.
Create a new protocol called TutorialCTF with the following options:
- "No, use individual anatomy", because the individual subject anatomy is available
- "No, use one channel file per condition (MEG)", because we are going to process regular MEG data in the next tutorial
Create a new subject (let's keep the default name: Subject01)
Import MRI
Go to the Anatomy view of the protocol files (very first button in Brainstorm window toolbar).
Right click on subject node, and select menu "Import MRI..."
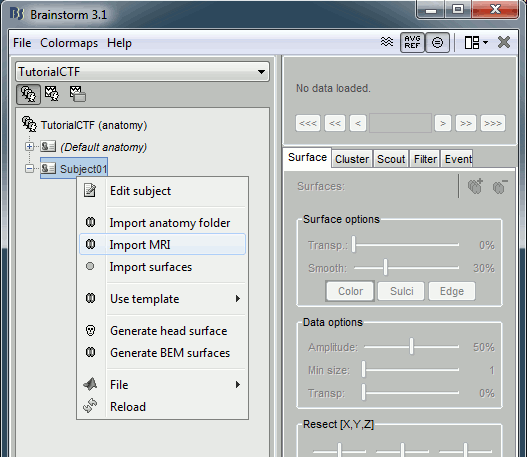
- Select file "TutorialCtf/Anatomy/01.mri".
If you didn't modified any Brainstorm option yet, you should get an error message, saying "Unrecognized format, try switching byte order". This is because not all the computers process the binary data the same way. To learn more about endianness, you can consult this Wikipedia page. Depending on the type of computer which wrote the binary files, you may need to read them as little-endian or big-endian. To change this setting, go to the Options > Byte order menu in main window. You may need to modify this setting again to import other files.
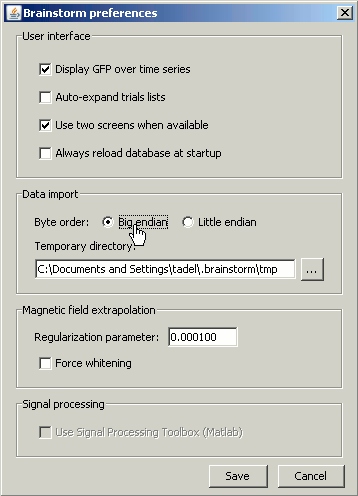
Try to import the MRI again. It should be working now. The MRI viewer is displayed, together with a message box that tells you what to do. Follow the instructions. The MRI is already well oriented so you can directly process with the fiducials selection. If you are not sure how to do this, consult this page: CoordinateSystems.
