|
Size: 1499
Comment:
|
Size: 16101
Comment:
|
| Deletions are marked like this. | Additions are marked like this. |
| Line 1: | Line 1: |
| = Tutorial: Scouts = This tutorial is based on Sabine Meunier's somatotopy experiment, called ''TutorialCTF ''in your Brainstorm database. |
= Tutorial 8: Scouts = In Brainstorm jargon, a ''scout '' is a region of interest defined on the cortical surface: a subset of vertices of this surface. This document explains how to create one or several scouts, use them to retrieve the activity in specific brain regions, and compare between conditions. |
| Line 4: | Line 4: |
| A ''scout ''in Brainstorm designates a region of interest on the cortical surface. It is defined by a subset of the vertices of this surface.This document will explain how to create one or several scouts, use them to retrieve the activity of specific parts of the brain, and compare between conditions. <<TableOfContents(2)>> |
<<TableOfContents(2,2)>> |
| Line 9: | Line 7: |
| Almost all the features related to the scouts manipulation are accessible in the Scouts tab in main Brainstorm window. We are going to use this panel to create a scout that includes the cortical area that we observed in the previous tutorial: the one that responds to the stimulation of the right thumb. | Almost all the features related to the scouts manipulation are accessible in the ''Scout'' tab in the main Brainstorm window. We are going to use this panel to create a scout that includes the cortical area that we observed in the previous tutorial: the one that responds to the stimulation of the right thumb. |
| Line 11: | Line 9: |
| 1. Select the protocol ''TutorialCTF'', and display the times series for ''Subject01 / !StimRightThumb / ERP'' (double-click). | === First vertex (seed) === 1. Select the protocol ''TutorialCTF'', and display the times series for ''Subject01 / Right / ERF'' (double-click). |
| Line 14: | Line 13: |
| 1. Switch to the ''Scouts'' tab, click on the first button (a big cross), and then click in the middle of the red stain in left hemisphere in the 3D figure (rotate and zoom before if necessary). A small dot with the labe "1" appears where you clicked. Your first scout is created, and contains only one vertex for the moment.<<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:panelScouts.gif}} - {{attachment:scouts1.gif}} 1. |
1. Switch to the ''Scout'' tab, click on the first button in the toolbar (the big cross), and then click in the middle of the red stain in left hemisphere in the 3D figure (rotate and zoom before if necessary). A small dot with the label "1" appears where you clicked. Your first scout is created, and contains only one vertex for the moment. It is now referenced in ''Available scouts'' list.<<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:firstScout.gif}} 1. Rename the scout into "'''LeftSS'''", for left somatosensory cortex: double-click on it in the ''Available scouts'' list, or scouts menu ''Edit > Rename''. 1. Click on the second button in the ''Scouts ''panel toolbar, tooltip: ''Display scouts time series''. And you will get the time course of this particular source for the whole time window (-50ms to 250ms).<<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:scoutsTS1.gif}} === Growing a scout === In this case, the source is so focal that we could even use only the first vertex we selected to represent this area. But most of the time, the aim of a scout is to get the average activity of a larger region; so for the example, let's grow this scout. The buttons in in the ''Scout size'' panel offer basic operations to define scout extension. * ''''>'''': Add the closest vertex (respect to the seed) to the current scout. * ''''<'''': Remove the furthest vertex (respect to the seed) from the current scout. * ''''>>'''': Grow scout in all directions * ''''<<'''': Shrink scout in all directions * ''''Constrained'''': If this button is pressed, only the vertices that have a sources value above the threshold will be added to the scout (its growth will be limited to the red patch on the surface). * Last method to add points to a scout: select the ''Select point'' button (big cross in the toolbar), and then '''select again''' the "LeftSS" scout. All the points you would click on the cortex would be added to the selected scout. Now: add about 20 vertices with button '>>', '''not '''in ''Constrained ''mode, and display the scout values again. You can notice that the overall shape is the same as the scout with only one vertex, but the amplitudes are much lower. This is because the time series of all the sources in this scout have been averaged. And as we averaged the maximum values with lower values, the result is lower. {{attachment:scoutGrow.gif}} == Scout function == How are the scouts time series calculated? For the scout LeftSS we have 20 signals, coming from 20 different dipoles with different orientations, that are combined into one unique signal. In the list of available scouts, you can see the indication "[mean]" next to the name of the scout. It represents the name of the function that is used for combined all the time series into one. This function can be changed individually for each scout, with the menu ''Edit > Set scout function'' in the Scout tab. ==== List of the functions ==== Here is a description of the different options. The effect of the function depends if you are processing sources with constrained (1 signal per vertex) or unconstrained (3 signals per vertex) orientations. For more details, see the code of bst_scout_value.m. * '''Mean''': * Constrained: Average all the signals * Unconstrained: Average the signals for each orientation separately, then combine the three orientations by taking the first mode of the PCA decomposition. * '''PCA''': * Constrained: Take the first mode of the PCA decomposition of all the signals. * Unconstrained: Take the first mode of the PCA decomposition of the signals orientation by orientation, then combine the three orientations by taking the first mode of the PCA decomposition again. * '''Fast PCA''': Same as ''PCA'' function, but computes the first PCA decomposition based only on a subset of the most powerful signals. It gives very similar results, but its computation is much faster for scouts that group a large number of dipoles (>50). * '''Mean(norm)''': * Constrained: Average the absolute values of all the signals * Unconstrained: Compute the norm of the three orientations (sqrt(signals_x^2 + signals_y^2 + signals_z^2))), and then average those norms across all the vertices. * '''Max''': * Constrained: For each time point, get the maximum across all the vertices [signed maximum in amplitude value: m = max(abs(signal)), scout = sign(signal(m)) * m] * Unconstrained: For each time point, 1) get the vertex that has the maximum norm across all the orientations, 2) we take the values for three orientation at this vertex and 3) combine the three orientations by taking the first mode of the PCA decomposition. * '''Power''': * Constrained: Average the power of all the signals (signal^2) * Unconstrained: 1) For each vertex, sum the power of the three orientation and 2) average those powers across all the vertices => mean(signals_x^2 + signals_y^2 + signals_z^2) * '''All''': Do not apply any operation on the scouts signals, and display the time series of all the sources at the same time. ==== "Absolute" display option ==== As said in the previous tutorial, the minimum norm current amplitudes can positive or negative. Which means that the values of the scouts, depending on the function that is used, may be positive or negative too. Most of the time we are interested in visualizing the absolute values of the scouts time series, to compare the activation level in different conditions or subjects. For this purpose, on top of the selection of the scout function, you can choose to display the absolute values of the scouts instead of their real values by selecting the "Abs" button in the toolbar. Uncheck this option, and display again the activation of scout LeftSS for condition Right. {{attachment:absButton.gif}} Note that it is a display option, it is not saved in the scouts themselves. It is used ONLY when displaying the scouts time series with the "Display" button of the Scout tab. In all other cases, like the extraction of the scouts values from a script, this "Abs" option is going to be ignored. ==== Testing the functions ==== Now, leave this "Abs" option unselected for testing all the scouts functions one by one. {{attachment:compFunc.gif}} Select again the "Abs" display again, for the rest of the tutorial. == Multiple scouts == We are going to create an other scout for the other condition: the stimulation of the left thumb. 1. Close all figures (toolbar button). 1. Display the times series for ''Subject01 / Left / ERF'' (double-click). 1. Display the associated sources (Ctrl+S). 1. Go to the main response peak (46 ms). 1. Adjust the threshold value to get only a very focal point (about 85%). 1. Create a new scout at this point. Name it ''RightSS'', for Right Somato-Sensory cortex. 1. Grow it to the same number of vertices as the ''LeftSS ''scout (about 15 vertices). 1. Select both scouts (Ctrl+click) and click on ''Display scouts time series'' button (second button in toolbar).<<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:scouts2.gif}} <<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:scoutsTS_LR.gif}} 1. You can also display the values of the two scouts on the same graph. Just check the ''Overlay > Scouts'' checkbox in the Scout tab.<<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:scoutsTS_LR_overlay.gif}} 1. You can observe something that we expected: the activity in the '''right somatosensory cortex''' is much higher than in the left somatosensory cortex for a stimulation of the '''left thumb'''. == Load/save scouts == In case you close the Brainstorm window, delete or unload your scouts (and this will happen in the next few minutes), save the scouts before going further. * Select both scouts at the same time (Ctrl+click), and click the ''Save scouts'' button.<<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:saveScouts.gif}} * All the scouts will be saved in the same .mat file, in the subject's anatomy folder (same directory as the MRI and surfaces). * To load them later, just click the ''Load scouts'' button, and select the file. == Display scouts time series from the database tree == You have to display the sources on the cortex to create the scouts. But once they are created, you can directly display the scouts time series from the tree. It means that you can quickly compare the values for a scout between many different conditions without having to open them all. 1. Close all the figures (button in toolbar). 1. Select the first scout (LeftSS) 1. Right-click on Right / ERF / MN > Cortical activations > Scouts time series.<<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:treeRight.gif}} - 1. You can also display many sources files at the same time. Select at the same time the sources files from condition Left and Right > right-click > Cortical activations > Scouts time series<<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:treeLR_TS.gif||height="169px",width="354px"}} 1. You can superimpose the two traces by selecting the ''Overlay > Conditions'' checkbox in ''Scout ''panel. We see now the activation of the LeftSS scout for the stimulation of both thumbs.<<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:panelOverlayCond.gif}} 1. This menu "Scouts time series" is present at all the levels in the tree. Try right-clicking on Subject01 > Scouts time series. 1. If you select a node in the database tree and click on the ''Display scouts time series'' button in the ''Scout ''tab, it would have exactly the same effect. <<BR>>Try selecting '''both scouts''' in the list, select '''Subject01 '''in the tree, overlay / conditions, and then click on this button. You will seethe reponse for each scout in both conditions.<<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:scoutsOverlayBoth.gif||height="219px",width="505px"}} == Scout toolbar and menus == Let's spend a few minutes to explore all the menus in the ''Scout ''tab. Please click on all of them, it's the best way to remember. If you delete or alter the scouts LeftSS and RightSS: just reload them from the file you've just created. === Menu: New === . {{attachment:menuNew.gif}} * '''Define in 3D view''': Same as clicking on the first button of the toolbar (Select point = big cross). * '''Define in MRI slices''': Open an interface to draw a 3D ROI, slice by slice. * Define the 3D mask using the different drawing tools. * Adjust the MRI contrast with right-click+move on the MRI image. * Move through the slices with the mouse wheel, the small image on the left, or the slider. * Once you are done, click on ''Ok''. A new scout is created, including all the vertices that are located inside the 3D mask. * __Warning__: Only the vertices contained in the 3D mask are kept, all the volume information is lost. It means that the mask you intedend to draw might be really different from what you get as a scout at the end...<<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:menuEditMriMask.gif}} * '''Find maximal value''': Find the vertex with the maximal intensity at the current time, and create a scout centered on it. * '''Surface clustering''': Create a parcellation of the cortex surface in scouts of equivalent size. Can be useful for studying the connectivity between different regions of the brain. Experimental feature. * '''Correlation with sensor''': Create a new scout with all the sources that are strongly correlated with a given sensor. Experimental feature. * Now delete all the scouts you have created by selecting them and pressing the ''Delete ''key. The keyboard shortcut Ctrl+A selects all the elements in the list. * Load again your intial LeftSS and RightSS scouts from the file (as described in the "Load/save scouts" section) === Menu: Edit === . {{attachment:menuEdit.gif}} * '''Set scout function''': Set the scout function for the selected scouts. * '''Rename''': Rename the selected scout. <<BR>>Shortcut: double-click. * '''Set color''': Change the display color of scout patch in 3D figures. * '''Remove''': Delete selected scouts. Shortcut: ''Delete'' key * '''Merge''': Join two or more selected scouts. * '''Deselect all''': Deselect all the scouts in the list. Shortcut: ''Escape ''key. * '''Add vertices''': The user can select some points on the cortex surface and add them to the scout.<<BR>>Equivalent: Click on ''Select point'' (first toolbar button), then select the scout in list, and select 3d points. * '''Edit in MRI''': Open the same interface as menu New > Define in MRI slices, in order to edit the scout. * '''Expand (correlation)''': Computes the correlation between the values for the scout's seed (first point) and all the other sources. The sources that have correlation coefficient superior to a given threshold are added to the scout. Correlation is computed with the Matlab ''corrcoef ''function. * '''Find maximal value''': Move the scout's seed to the source that has the maximum amplitude '''in the scout''', at current time. * '''Remove vertices''': Remove the scout's vertices permanently from the cortex surface. <<BR>>__Warning__: This is a menu that can be used only when defining the subject's anatomy. Never do that if you already have headmodels or sources based on this surface... * '''Simulation''': Forward model of selected scouts. Simulate the scalp data that would be recorded if only the selected cortex region was activated; all the other sources are set to zero. Create a new data file in the database.<<BR>>If no scout selected: simulate recordings produced by the activity of the entire cortex. === Menu: View === . {{attachment:menuView.gif}} * '''View time series''': Same as the ''View time series'' button in the toolbar. * '''View on cortex''': Open a 3D figure with the cortex and the selected scout (if such a figure does not exist yet). * '''View in MRI Viewer''': Display the scout as a 3D mask in the MRI Viewer (anatomy only, no functional information)<<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:scoutInMriViewer.gif}} * '''Center MRI on scout''': When a MRI figure (3D or MRI Viewer) is opened: center view on the scout's seed. === Menu: View > 3D display options === * '''Show selected scouts''': If selected, only the scouts that are selected are displayed in the figures. Useful when you have many scouts defined, or if you want to produce MRI images with just one colored area. * '''Show all scouts''': If selected, all the scouts are displayed in all the figures, whether they are selected or not. Default. * '''Show scout patch''': Display full scout patch in MRI/3D figures. If not selected: display only the seed of the scout. * '''Limit MRI sources to scouts''': In all MRI views: display only sources values for the visible scouts. If not selected, display the sources for all the cortical surface.<<BR>>To test this menu: open first a view of the sources in the MRI Viewer. Right-click on sources file > Cortical activations > Display on MRI (MRI Viewer), and go to intersting time point (around 45ms), and slices (around somato-sensory cortex).Set the data threshold to 0 (Surface tab).<<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:mriSelScout.gif}} ON<<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:mriAll.gif}} OFF == Next == Next step, the [[Tutorials/TutProcesses|Processes tab]]. |
Tutorial 8: Scouts
In Brainstorm jargon, a scout is a region of interest defined on the cortical surface: a subset of vertices of this surface. This document explains how to create one or several scouts, use them to retrieve the activity in specific brain regions, and compare between conditions.
Contents
Creating a scout
Almost all the features related to the scouts manipulation are accessible in the Scout tab in the main Brainstorm window. We are going to use this panel to create a scout that includes the cortical area that we observed in the previous tutorial: the one that responds to the stimulation of the right thumb.
First vertex (seed)
Select the protocol TutorialCTF, and display the times series for Subject01 / Right / ERF (double-click).
- Display the associated sources (try it from the time series figure: Ctrl+S, or figure popup menu)
- Go to 46ms, and set the data threshold around 80%.
Switch to the Scout tab, click on the first button in the toolbar (the big cross), and then click in the middle of the red stain in left hemisphere in the 3D figure (rotate and zoom before if necessary). A small dot with the label "1" appears where you clicked. Your first scout is created, and contains only one vertex for the moment. It is now referenced in Available scouts list.
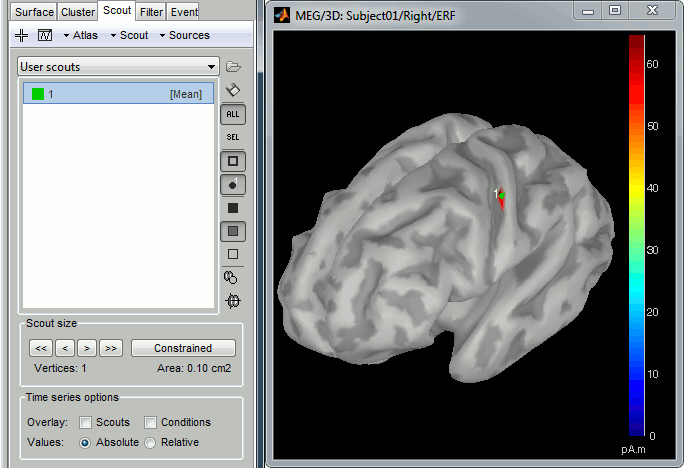
Rename the scout into "LeftSS", for left somatosensory cortex: double-click on it in the Available scouts list, or scouts menu Edit > Rename.
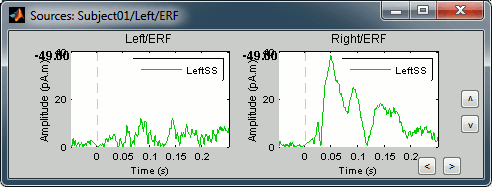
Click on the second button in the Scouts panel toolbar, tooltip: Display scouts time series. And you will get the time course of this particular source for the whole time window (-50ms to 250ms).
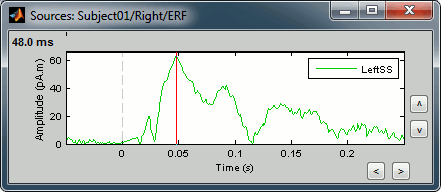
Growing a scout
In this case, the source is so focal that we could even use only the first vertex we selected to represent this area. But most of the time, the aim of a scout is to get the average activity of a larger region; so for the example, let's grow this scout. The buttons in in the Scout size panel offer basic operations to define scout extension.
'>': Add the closest vertex (respect to the seed) to the current scout.
'<': Remove the furthest vertex (respect to the seed) from the current scout.
'>>': Grow scout in all directions
'<<': Shrink scout in all directions
'Constrained': If this button is pressed, only the vertices that have a sources value above the threshold will be added to the scout (its growth will be limited to the red patch on the surface).
Last method to add points to a scout: select the Select point button (big cross in the toolbar), and then select again the "LeftSS" scout. All the points you would click on the cortex would be added to the selected scout.
Now: add about 20 vertices with button '>>', not in Constrained mode, and display the scout values again. You can notice that the overall shape is the same as the scout with only one vertex, but the amplitudes are much lower. This is because the time series of all the sources in this scout have been averaged. And as we averaged the maximum values with lower values, the result is lower.
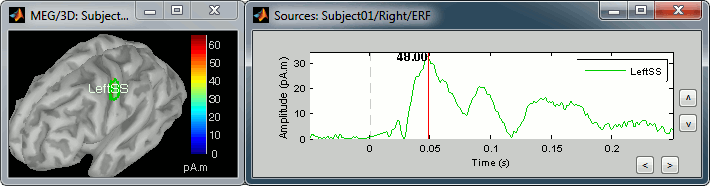
Scout function
How are the scouts time series calculated? For the scout LeftSS we have 20 signals, coming from 20 different dipoles with different orientations, that are combined into one unique signal. In the list of available scouts, you can see the indication "[mean]" next to the name of the scout. It represents the name of the function that is used for combined all the time series into one. This function can be changed individually for each scout, with the menu Edit > Set scout function in the Scout tab.
List of the functions
Here is a description of the different options. The effect of the function depends if you are processing sources with constrained (1 signal per vertex) or unconstrained (3 signals per vertex) orientations. For more details, see the code of bst_scout_value.m.
Mean:
- Constrained: Average all the signals
- Unconstrained: Average the signals for each orientation separately, then combine the three orientations by taking the first mode of the PCA decomposition.
PCA:
- Constrained: Take the first mode of the PCA decomposition of all the signals.
- Unconstrained: Take the first mode of the PCA decomposition of the signals orientation by orientation, then combine the three orientations by taking the first mode of the PCA decomposition again.
Fast PCA: Same as PCA function, but computes the first PCA decomposition based only on a subset of the most powerful signals. It gives very similar results, but its computation is much faster for scouts that group a large number of dipoles (>50).
Mean(norm):
- Constrained: Average the absolute values of all the signals
Unconstrained: Compute the norm of the three orientations (sqrt(signals_x2 + signals_y2 + signals_z^2))), and then average those norms across all the vertices.
Max:
- Constrained: For each time point, get the maximum across all the vertices [signed maximum in amplitude value: m = max(abs(signal)), scout = sign(signal(m)) * m]
- Unconstrained: For each time point, 1) get the vertex that has the maximum norm across all the orientations, 2) we take the values for three orientation at this vertex and 3) combine the three orientations by taking the first mode of the PCA decomposition.
Power:
- Constrained: Average the power of all the signals (signal^2)
Unconstrained: 1) For each vertex, sum the power of the three orientation and 2) average those powers across all the vertices => mean(signals_x2 + signals_y2 + signals_z^2)
All: Do not apply any operation on the scouts signals, and display the time series of all the sources at the same time.
"Absolute" display option
As said in the previous tutorial, the minimum norm current amplitudes can positive or negative. Which means that the values of the scouts, depending on the function that is used, may be positive or negative too. Most of the time we are interested in visualizing the absolute values of the scouts time series, to compare the activation level in different conditions or subjects.
For this purpose, on top of the selection of the scout function, you can choose to display the absolute values of the scouts instead of their real values by selecting the "Abs" button in the toolbar. Uncheck this option, and display again the activation of scout LeftSS for condition Right.
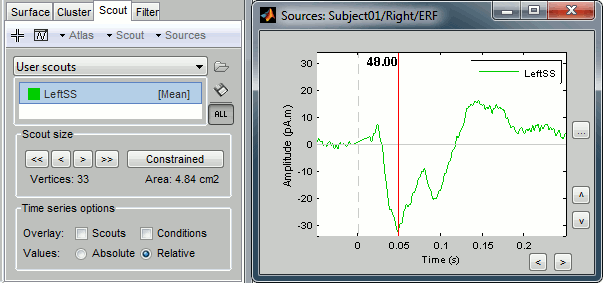
Note that it is a display option, it is not saved in the scouts themselves. It is used ONLY when displaying the scouts time series with the "Display" button of the Scout tab. In all other cases, like the extraction of the scouts values from a script, this "Abs" option is going to be ignored.
Testing the functions
Now, leave this "Abs" option unselected for testing all the scouts functions one by one.
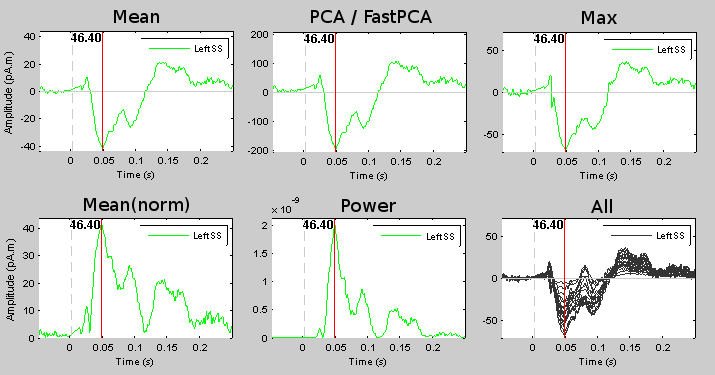
Select again the "Abs" display again, for the rest of the tutorial.
Multiple scouts
We are going to create an other scout for the other condition: the stimulation of the left thumb.
- Close all figures (toolbar button).
Display the times series for Subject01 / Left / ERF (double-click).
- Display the associated sources (Ctrl+S).
- Go to the main response peak (46 ms).
- Adjust the threshold value to get only a very focal point (about 85%).
Create a new scout at this point. Name it RightSS, for Right Somato-Sensory cortex.
Grow it to the same number of vertices as the LeftSS scout (about 15 vertices).
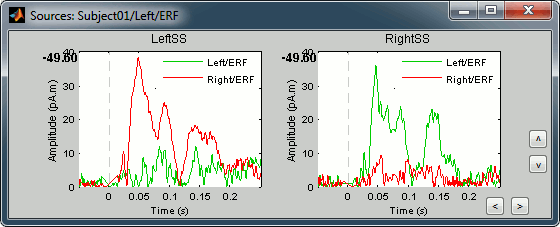
Select both scouts (Ctrl+click) and click on Display scouts time series button (second button in toolbar).
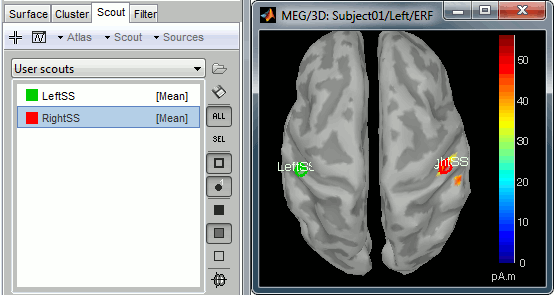
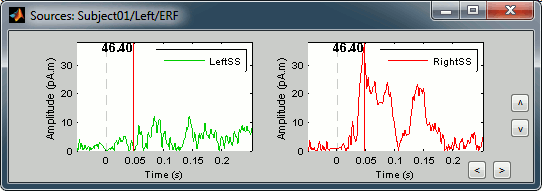
You can also display the values of the two scouts on the same graph. Just check the Overlay > Scouts checkbox in the Scout tab.
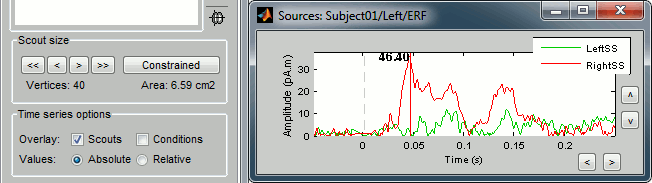
You can observe something that we expected: the activity in the right somatosensory cortex is much higher than in the left somatosensory cortex for a stimulation of the left thumb.
Load/save scouts
In case you close the Brainstorm window, delete or unload your scouts (and this will happen in the next few minutes), save the scouts before going further.
Select both scouts at the same time (Ctrl+click), and click the Save scouts button.
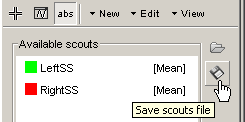
- All the scouts will be saved in the same .mat file, in the subject's anatomy folder (same directory as the MRI and surfaces).
To load them later, just click the Load scouts button, and select the file.
Display scouts time series from the database tree
You have to display the sources on the cortex to create the scouts. But once they are created, you can directly display the scouts time series from the tree. It means that you can quickly compare the values for a scout between many different conditions without having to open them all.
- Close all the figures (button in toolbar).
- Select the first scout (LeftSS)
Right-click on Right / ERF / MN > Cortical activations > Scouts time series.
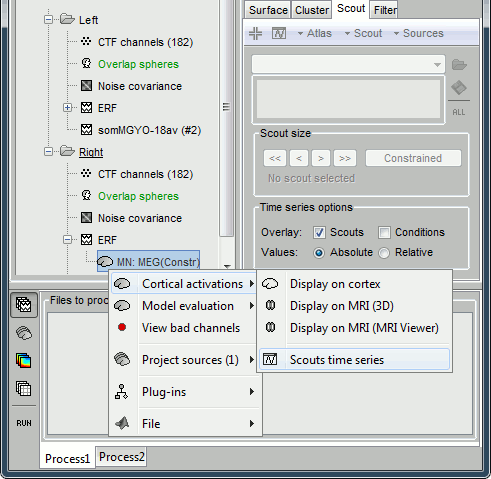 -
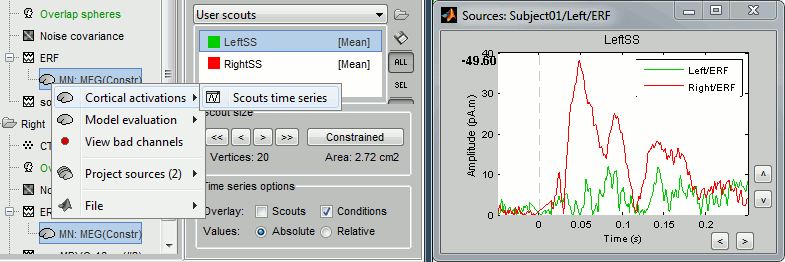
- You can also display many sources files at the same time. Select at the same time the sources files from condition Left and Right > right-click > Cortical activations > Scouts time series
You can superimpose the two traces by selecting the Overlay > Conditions checkbox in Scout panel. We see now the activation of the LeftSS scout for the stimulation of both thumbs.
This menu "Scouts time series" is present at all the levels in the tree. Try right-clicking on Subject01 > Scouts time series.
If you select a node in the database tree and click on the Display scouts time series button in the Scout tab, it would have exactly the same effect.
Try selecting both scouts in the list, select Subject01 in the tree, overlay / conditions, and then click on this button. You will seethe reponse for each scout in both conditions.
Scout toolbar and menus
Let's spend a few minutes to explore all the menus in the Scout tab. Please click on all of them, it's the best way to remember. If you delete or alter the scouts LeftSS and RightSS: just reload them from the file you've just created.
Menu: New
Define in 3D view: Same as clicking on the first button of the toolbar (Select point = big cross).
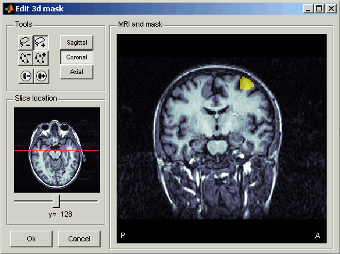
Define in MRI slices: Open an interface to draw a 3D ROI, slice by slice.
- Define the 3D mask using the different drawing tools.
- Adjust the MRI contrast with right-click+move on the MRI image.
- Move through the slices with the mouse wheel, the small image on the left, or the slider.
Once you are done, click on Ok. A new scout is created, including all the vertices that are located inside the 3D mask.
Warning: Only the vertices contained in the 3D mask are kept, all the volume information is lost. It means that the mask you intedend to draw might be really different from what you get as a scout at the end...
Find maximal value: Find the vertex with the maximal intensity at the current time, and create a scout centered on it.
Surface clustering: Create a parcellation of the cortex surface in scouts of equivalent size. Can be useful for studying the connectivity between different regions of the brain. Experimental feature.
Correlation with sensor: Create a new scout with all the sources that are strongly correlated with a given sensor. Experimental feature.
Now delete all the scouts you have created by selecting them and pressing the Delete key. The keyboard shortcut Ctrl+A selects all the elements in the list.
- Load again your intial LeftSS and RightSS scouts from the file (as described in the "Load/save scouts" section)
Menu: Edit
Set scout function: Set the scout function for the selected scouts.
Rename: Rename the selected scout.
Shortcut: double-click.Set color: Change the display color of scout patch in 3D figures.
Remove: Delete selected scouts. Shortcut: Delete key
Merge: Join two or more selected scouts.
Deselect all: Deselect all the scouts in the list. Shortcut: Escape key.
Add vertices: The user can select some points on the cortex surface and add them to the scout.
Equivalent: Click on Select point (first toolbar button), then select the scout in list, and select 3d points.Edit in MRI: Open the same interface as menu New > Define in MRI slices, in order to edit the scout.
Expand (correlation): Computes the correlation between the values for the scout's seed (first point) and all the other sources. The sources that have correlation coefficient superior to a given threshold are added to the scout. Correlation is computed with the Matlab corrcoef function.
Find maximal value: Move the scout's seed to the source that has the maximum amplitude in the scout, at current time.
Remove vertices: Remove the scout's vertices permanently from the cortex surface.
Warning: This is a menu that can be used only when defining the subject's anatomy. Never do that if you already have headmodels or sources based on this surface...Simulation: Forward model of selected scouts. Simulate the scalp data that would be recorded if only the selected cortex region was activated; all the other sources are set to zero. Create a new data file in the database.
If no scout selected: simulate recordings produced by the activity of the entire cortex.
Menu: View
View time series: Same as the View time series button in the toolbar.
View on cortex: Open a 3D figure with the cortex and the selected scout (if such a figure does not exist yet).
View in MRI Viewer: Display the scout as a 3D mask in the MRI Viewer (anatomy only, no functional information)
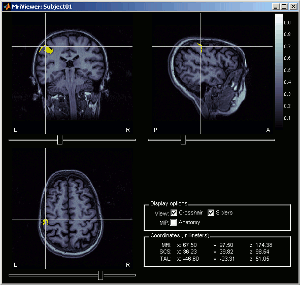
Center MRI on scout: When a MRI figure (3D or MRI Viewer) is opened: center view on the scout's seed.
Menu: View > 3D display options
Show selected scouts: If selected, only the scouts that are selected are displayed in the figures. Useful when you have many scouts defined, or if you want to produce MRI images with just one colored area.
Show all scouts: If selected, all the scouts are displayed in all the figures, whether they are selected or not. Default.
Show scout patch: Display full scout patch in MRI/3D figures. If not selected: display only the seed of the scout.
Limit MRI sources to scouts: In all MRI views: display only sources values for the visible scouts. If not selected, display the sources for all the cortical surface.
To test this menu: open first a view of the sources in the MRI Viewer. Right-click on sources file > Cortical activations > Display on MRI (MRI Viewer), and go to intersting time point (around 45ms), and slices (around somato-sensory cortex).Set the data threshold to 0 (Surface tab).
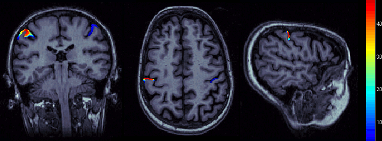 ON
ON
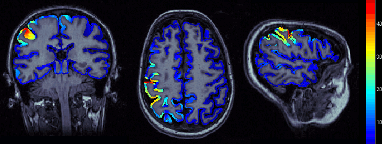 OFF
OFF
Next
Next step, the ?Processes tab.
