|
Size: 8746
Comment:
|
Size: 8758
Comment:
|
| Deletions are marked like this. | Additions are marked like this. |
| Line 74: | Line 74: |
| * At the end of the process, make sure that the file "cortex_15000V" is selected (downsampled pial surface, that will be used for the source estimation). If it is not, double-click on it to select it as the default cortex surface.<<BR>><<BR>> SCREEN CAPTURE | * At the end of the process, make sure that the file "cortex_15000V" is selected (downsampled pial surface, that will be used for the source estimation). If it is not, double-click on it to select it as the default cortex surface.<<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:anatomy.gif}} |
Yokogawa/KIT tutorial
Authors: Francois Tadel, Ei-ichi Okumura, Takashi Asakawa.
This tutorial introduces some concepts that are specific to the management of MEG/EEG files recorded with Yokogawa/KIT systems in the Brainstorm environment.
Contents
License
This tutorial dataset (MEG/EEG and MRI data) remains proprietary of Yokogawa Electric Corporation, Japan. Its use and transfer outside the Brainstorm tutorial, e.g. for research purposes, is prohibited without written consent from Yokogawa Electric Corporation.
Description of the experiment
This tutorial is based on a simple median nerve stimulation experiment:
- Unilateral median nerves were percutaneously stimulated using monophasic square-wave impulses with a duration of 0.3 ms at 2.8 Hz.
- The stimulus intensity was set at the motor threshold to evoke mild twitches of the thumb.
- The stimulus onsets were recorded as low-to-high TTL with a trigger channel labeled as "Trigger01".
- The total number of stimuli in the dataset was 336.
- The data was recorded with a Yokogawa 160 axial gradiometer system at Yokogawa Electric Corporation, Kanazawa, Japan.
Export recordings from Meg160
To import Yokogawa/KIT data files (.con, .raw, .ave) into Brainstorm, a data export process is required beforehand. The data export function is available in Meg160, which is data analysis software equipped in most of Yokogawa/KIT systems.
The dataset used in this tutorial has already been exported using this procedure. It is described here so that later you can export your own recordings to Brainstorm.
If your software does not support the functions used below, please contact Yokogawa via
http://www.yokogawa.com/me/index.htm
Export the digitizer file
- If a wave data file and the corresponding digitizer file are ready for use, there is no additional operation required.
- If no digitizer file is available, you need first to extract the head surface points:
In Meg160, select the menu: File > Import and Export > BESA Text Export > Surface Point File
- Check that the fiducial points are properly pointed, and then click the [OK] button
- A surface point file (.sfp) is automatically created. It includes the position data of: the fiducial points, the marker points and other points describing the head shape
Export the recordings
In Meg160, select the menu: File > Import and Export > Third-Party Export
- On some systems, this menu is name [BESA Binary Export]
- An operation panel for data export shows up
- When using digitizer data:
- Select [Digitizer]
Enter the digitizer file in the [Point Filename] box
(.txt file generally available under the corresponding "Scan" folder)Enter the label file in the [Label Filename] box
(DigitizeLabel.txt generally located in the "C:\Meg160\AppInfo" folder)
- When using surface point data instead:
- Select [Surface Point File]
- Enter the surface point file (.sfp) created previously.
- Enter an output file name in [Third-party Export Dataset]
- Click on [Create Export File]
- Use this exported file in Brainstorm
Download and installation
- Requirements: You have already followed all the introduction tutorials and you have a working copy of Brainstorm installed on your computer.
Go to the Download page of this website, and download the file: sample_yokogawa.zip
Unzip it in a folder that is not in any of the Brainstorm folders (program folder or database folder)
- Start Brainstorm (Matlab scripts or stand-alone version)
Select the menu File > Create new protocol. Name it "TutorialYokogawa" and select the options:
"No, use individual anatomy",
"No, use one channel file per condition".
Import the anatomy
Right-click on the TutorialYokogawa folder > New subject > Subject01
- Leave the default options you set for the protocol
Right-click on the subject node > Import anatomy folder:
Set the file format: "FreeSurfer folder"
Select the folder: sample_yokogawa/anatomy
- Number of vertices of the cortex surface: 15000 (default value)
- Set the 6 required fiducial points (indicated in MRI coordinates):
- NAS: x=128, y=227, z=93
- LPA: x=48, y=130, z=69
- RPA: x=214, y=130, z=76
- AC: x=128, y=148, z=116
- PC: x=128, y=123, z=117
- IH: x=128, y=131, z=176 (anywhere on the midsagittal plane)
At the end of the process, make sure that the file "cortex_15000V" is selected (downsampled pial surface, that will be used for the source estimation). If it is not, double-click on it to select it as the default cortex surface.
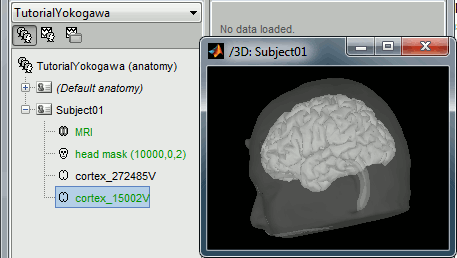
Without the individual MRI
If you do not have access to an individual MR scan of the subject (or if its quality is too low to be processed with FreeSurfer), but if you have digitized the head shape of the subject using a tracking system, you have an alternative: deform one of the Brainstorm templates (Colin27 or ICBM152) to match the shape of the subject's head.
For more information, read the following tutorial: Warping default anatomy
Access the recordings
Link the recordings
- Switch to the "functional data" view.
Right-click on the subject folder > Review raw file:
- Select the file format: "MEG/EEG : Yokogawa/KIT"
Select the file: sample_yokogawa/data/SEF_000-export.con
Answer NO when asked to refine the registration using head points. In this dataset, we only have access to the positions of the electrodes and three additional markers on the forehead. The automatic registration doesn't work well in this case, we are going to fix this registration manually.
- The new file "Link to raw file" lets you access directly the contents of the MEG/EEG recordings
- The channel file "KIT channels" in the (Common files) folder contains the name of the channels and the position of the corresponding sensors.
Refine the MRI registration
Right-click on the channel file > MRI registration > Edit... (EEG)
- The white points are the electrodes, the green points are the additional digitized head points. To display the label of the electrodes, click on the [LABEL] button in the toolbar.
- Now try to manipulate the position of the EEG+MEG sensors using rotations and translations only.
- The objective is to have all the points close to the surface and the three forehead points inside the little peaks on the surface (due to markers in the MRI).
- Click on [OK] when done.
Read the the stimulation information
Right-click on the "Link to raw file" > Trigger > Display time series
- In the Record tab, switch to a column view of the sensors (first button in the toolbar)
- You can see that all the trigger lines are flat except for "Trigger01", which contains the information of the electric stimulation. We are going to read this trigger channel and convert it to a list of events
- Drag and drop the "Link to raw file" in the Process1 box.
Run the process "Import recordings > Read from channel"
- Event channel = Trigger01
- Option selected "TTL": detect peaks of 5V/12V on an analog channel
- Do not select the option Accept zeros as trigger values
Right-click on the "Link to raw file" > Trigger > Display time series
- Check that the peaks of the triggers channel have correctly been identified
Pre-process recordings
Evaluation
Two of the typical pre-processing steps consist in getting rid of the contamination due to the power lines (50 Hz or 60Hz) and of the frequencies we are not interested in (a low-pass filter to remove the high-frequencies and a high-pass filter to remove the very slow components of the signals). Let's start with the spectral evaluation of this file.
Drag the "Link to raw file" to the Process1 box and run the process "Frequency > Power spectrum density (Welch)". Configure it as illustrated in the following figure (window length=10s, overlap=50%).
Double-click on the new PSD file to display it.
Epoching and averaging
Import recordings
Average epochs
Source analysis
Head model
Noise covariance matrix
Inverse model
Z-score normalization
Regions of interest
Scripting
Graphic edition
Generate Matlab script
Feedback
