|
Size: 14483
Comment:
|
← Revision 77 as of 2024-07-22 20:17:48 ⇥
Size: 16261
Comment:
|
| Deletions are marked like this. | Additions are marked like this. |
| Line 1: | Line 1: |
| = Tutorial 11: Artifact detection = ''Authors: Francois Tadel, Elizabeth Bock, John C Mosher, Sylvain Baillet'' |
= Tutorial 12: Artifact detection = ''Authors: Francois Tadel, Elizabeth Bock, Sylvain Baillet'' |
| Line 4: | Line 4: |
| The previous tutorial illustrated how to remove noise patterns occurring continuously and at specific frequencies. However, most of the events that contaminate the MEG/EEG recordings are not permanent, span over a large frequency range or overlap with the frequencies of the brain signals of interest. Frequency filters are not appropriate to correct for eye movements, breathing movements, heartbeats or other muscle activity. | The previous tutorials illustrated how to remove noise patterns occurring continuously and at specific frequencies. However, most of the events that contaminate the MEG/EEG recordings are not persistent, span over a large frequency range or overlap with the frequencies of the brain signals of interest. Frequency filters are not appropriate to correct for eye movements, breathing movements, heartbeats or other muscle activity. |
| Line 6: | Line 6: |
| Other approaches exist to correct for those artifacts, based on the spatial signature of the artifacts. If an event is very reproducible and occurs always at the same position (eg. eye blinks and heartbeats), the sensors will always record the same values when it occurs. We can identify the topographies corresponding to this artifact (ie spatial distributions of values at one time point) and remove them from the recordings. This spatial decomposition is the basic idea behind two widely used approaches: the '''SSP '''(Signal-Space Projection) and '''ICA '''(Independent Component Analysis) methods. We will describe those approaches in the next tutorial. The SSP method is based on the spatial decomposition of the MEG/EEG recordings for a selection of time samples during which the artifact is present. Therefore we need to identify when each type of artifact is occurring in the recordings. This tutorial shows how to detect automatically some well defined artifacts: the blinks and the heartbeats. |
For getting rid of reproducible artifacts, one popular approach is the Signal-Space Projection (SSP). This method is based on the spatial decomposition of the MEG/EEG recordings for a selection of time samples during which the artifact is present. Therefore we need to identify when each type of artifacts occurs in the recordings. This tutorial shows how to automatically detect some well defined artifacts: the blinks and the heartbeats. |
| Line 16: | Line 14: |
| * Configuration: Page of '''3 seconds''', view in columns, selection of the "'''CTF LT'''" sensors (the left-temporal sensors will be a good example to show at the same time the two types of artifacts). * Add the '''EOG''': Right-click on the link > EOG > Display time series<<BR>>Two channels are classified as EOG: a vertical electrooculogram (VEOG) recorded with a bipolar montage of electrodes placed below and above one eye, and an horizontal electrooculogram (HEOG) recorded with two electrodes placed on the temples of the subject. * Add the '''ECG''': Right-click on the link > ECG > Display time series<<BR>>This electrocardiogram was recorded with a bipolar montage of electrodes across the chest. * Scroll through the recordings using the '''F3''' shortcut until you find a large blink. |
* '''Configuration''': Page of '''3 seconds''', view in columns, selection of the "'''CTF LT'''" sensors (the left-temporal sensors will be a good example to show at the same time the two types of artifacts). * '''EOG''': Right-click on the link > EOG > Display time series. Two channels are classified as EOG: * '''VEOG''': Vertical electrooculogram (two electrodes placed below and above one eye) * '''HEOG''': Horizontal electrooculogram (two electrodes placed on the temples of the subject) * On these traces, there is not much happening for most of the recordings except for a few bumps. This subject is sitting very still and not blinking much. We can expect MEG recordings of a very good quality. * '''ECG''': Right-click on the link > ECG > Display time series.<<BR>>The electrocardiogram was recorded with a bipolar montage of electrodes across the chest. You can recognize the typical shape of the electric activity of the heart (P, QRS and T waves). * '''Find a blink''': Scroll through the recordings using the '''F3''' shortcut until you see a large blink. |
| Line 21: | Line 22: |
| * To keep the scale fixed between to pages: Uncheck the button [AS] in the figure (auto-scale) * You should observe a nice blink at 20.8s. <<BR>>On the same page, you should be able to observe a few heartbeats (19.8s, 20.6s, 21.3s). * The additional data channels (ECG and EOG) contain precious information that we will use for the automatic detection of the blinks and heartbeats. We strongly recommend that you always record these signals in your own experiments, it helps a lot with the data analysis. <<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:observe.gif||height="271",width="662"}} |
* To keep the scale fixed between two pages: Uncheck the button '''[AS]''' (auto-scale). * For instance, you can observe a nice blink at 20.8s (red cursor in the screen capture below). * On the same page, you should be able to observe the contamination due to a few heartbeats, corresponding to the peaks of the ECG signal (eg. 19.8s, shown as a blue selection below). * The additional data channels (ECG and EOG) contain precious information that we can use for the automatic detection of the blinks and heartbeats. We strongly recommend that you always record these signals during your own experiments, it helps a lot with the data pre-processing. <<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:observe.gif||height="289",width="685"}} |
| Line 25: | Line 27: |
| == Detection (GUI) == You could scroll the |
== Detection: Heartbeats == In the Record tab, select the menu: '''"Artifacts > Detect heartbeats"'''. |
| Line 28: | Line 30: |
| == Detection (Script) == Let's perform the same detection operations on '''Run #02''': |
* It automatically opens the pipeline editor, with the process "Detect heartbeats" selected. * '''Channel name''': Name of the channel that is used to perform the detection. Select or type "'''ECG'''". * '''Time window''': Time range that the algorithm should scan for amplitude peaks. Leave the default values to process the entire file, or check the option '''[All file]'''. * '''Event name''': Name of the event group created for saving the detected events. Enter "'''cardiac'''".<<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:detect_ecg.gif||height="254",width="549"}} * Click on Run. After the process stops, you can see a new event category "'''cardiac'''". The 464 (aprox.) heartbeats for 360s of recordings indicate an average heart rate of 77bpm, everything looks normal. * You can check a few of them, to make sure the "cardiac" markers really indicate the ECG peaks. Not all peaks need to be detected, but you should have a minimum of 10-20 events marked for removing the artifacts using SSP, described in the following tutorials.<<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:detect_ecg_done.gif||height="127",width="517"}} |
| Line 31: | Line 37: |
| == Detection: Blinks == Now do the same thing for the blinks: Menu "'''Artifacts > Detect eye blinks'''". |
|
| Line 32: | Line 40: |
| * Channel name: '''VEOG''' * Time window: '''All file''' * Event name: '''Blink''' <<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:detect_eog.gif||height="257",width="550"}} * Run, then look quickly at the 15 detected blinks (shortcut: Shift+Right arrow). <<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:detect_eog_done.gif||height="130",width="535"}} |
|
| Line 33: | Line 45: |
| = From Walkthrough = . |
== Remove simultaneous blinks/heartbeats == We will use these event markers as the input to our SSP cleaning method. This technique works well if each artifact is defined precisely and as independently as possible from the other artifacts. This means that we should try to avoid having two different artifacts marked at the same time. |
| Line 36: | Line 48: |
| . o SSP > Detect heartbeats > ECG | Because the heart beats every second or so, there is a high chance that when the subject blinks there is a heartbeat not too far away in the recordings. We cannot remove all the blinks that are contaminated with a heartbeat because we would have no data left. But we have a lot of heartbeats, so we can do the contrary: remove the markers "cardiac" that are occurring during a blink. |
| Line 38: | Line 50: |
| . o SSP > Detect eye blinks > VEOG | In the Record tab, select the menu "'''Artifacts > Remove ''''''simultaneous'''". Set the options: |
| Line 40: | Line 52: |
| . o SSP > Remove simultaneous > cardiac / blink / 250ms | * Remove events named: "'''cardiac'''" * When too close to events: "'''blink'''" * Minimum delay between events: '''250ms''' <<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:detect_simult.gif||height="257",width="550"}} |
| Line 42: | Line 56: |
| . o SSP > Compute SSP: Heartbeats ('''Do __not__ use existing SSP''') | After executing this process, the number of "cardiac" events goes from '''465''' to '''456'''. The deleted heartbeats were all less than 250ms away from a blink. |
| Line 44: | Line 58: |
| . § Display 2D topography for the first spatial component (clearly a heartbeat) | == Run #02: Running from a script == Let's perform the same detection operations on '''Run #02''', using this time the '''Process1''' box. |
| Line 46: | Line 61: |
| . § Select component #1: It is clearly a cardiac component | * Close everything with the '''[X]''' button at the top-right corner of the Brainstorm window. * Select the run '''AEF #02''' in the Process1 box, then select the following processes: * '''Events > Detect heartbeats:''' Select channel '''ECG''', check "All file", event name "cardiac". * '''Events > Detect eye blinks:''' Select channel '''VEOG''', check "All file", event name "blink". * '''Events > Remove simultaneous''': Remove "'''cardiac'''", too close to "'''blink'''", delay '''250ms'''.<<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:detect_script.gif||height="286",width="506"}} * Open the Run#02 recordings (MEG+EOG+ECG) and verify that the detection worked as expected. You should get '''472 cardiac''' events and '''19 blink''' events. |
| Line 48: | Line 68: |
| . § Show the influence of the projector on the sensors LT | <<TAG(Advanced)>> |
| Line 50: | Line 70: |
| . o SSP > Compute SSP: Eye blinks ('''Do __not__ use existing SSP''') | == Artifacts classification == If the EOG signals are not as clean as here, the detection processes may create more than one category, for instance: '''blink''', '''blink2''', '''blink3'''. The algorithm not only detects specific events in a signal, it also classifies them by shape. For two detected events, the signals around the event marker have to be sufficiently correlated (> 0.8) to be classified in the same category. At the end of the process, all the categories that contain less than 5 events are deleted. |
| Line 52: | Line 73: |
| . § Display the 2D topography for the first spatial component (clearly a blink) | In the good cases, this can provide an automatic classification of different types of artifacts, for instance: blinks, saccades and other eye movements. The tutorial [[Tutorials/MedianNerveCtf|MEG median nerve (CTF)]] is a good illustration of appropriate classification: '''blink''' groups the real blinks, and '''blink2''' contains mostly saccades. |
| Line 54: | Line 75: |
| . § Show the influence of the projector on the sensors LT | . {{attachment:detect_classification.gif||height="148",width="653"}} |
| Line 56: | Line 77: |
| . o Load additional bad segments: File > Add events from file > '''events_bad_01.mat<<BR>> '''> File format: Brainstorm (events*.mat) | In the bad cases, the signal is too noisy and the classfication fails. It leads to either many different categories, or none if all the categories have less than 5 events. If you don't get good results with the process "Detect eye blinks", you can try to run a '''custom detection''' with the classification disabled. |
| Line 58: | Line 79: |
| . o Close all, save modifications | At the contrary, if you obtain one category that mixes multiple types of artifacts and would like to automatically separate them in different sub-groups, you can try the process "'''Events > Classify by shape'''". It is more powerful than the automatic classification from the event detection process because it can run on multiple signals at the same type: first it reduces the number of dimensions with a PCA decomposition, then runs a similar classification procedure. |
| Line 60: | Line 81: |
| = From Auditory = == Heartbeats and eye blinks == * Select the two AEF runs in the Process1 box. * Select successively the following processes, then click on [Run]: * '''Events > Detect heartbeats:''' Select channel '''ECG''', check "All file", event name "cardiac". * '''Events > Detect eye blinks:''' Select channel '''VEOG''', check "All file", event name "blink". * '''Events > Remove simultaneous''': Remove "'''cardiac'''", too close to "'''blink'''", delay '''250ms'''. |
<<TAG(Advanced)>> |
| Line 68: | Line 83: |
| = From continuous = == Identify the artifacts == The first step is to identify several repetitions of the artifact (the vectors '''b'''<<HTML(<sub>)>>''1''<<HTML(</sub>)>>...'''b'''<<HTML(<sub>)>>''m''<<HTML(</sub>)>>). We need to set markers in the recordings that indicate when the events that we want to correct for occur. To help with this task, it is recommended to always record with bipolar electrodes the activity of the eyes (electro-oculogram or EOG, vertical and horizontal), the heart (electro-cardiogram or ECG), and possibly other sources of muscular contaminations (electromyogram or EMG). In this example, we are going to use the ECG and vertical EOG traces to mark the cardiac activity and the eye blinks. Two methods can be used, manual or automatic. |
== Detection: Custom events == These two processes "Detect heartbeats" and "Detect eye blinks" are in reality shortcuts for a generic process "'''Detect custom events'''". This process can be used for detecting any kind of event based on the signal power in a specific frequency band. We are not going to use it here, but you may have to use it if the standard parameters do not work well, or for detecting other types of events. |
| Line 72: | Line 86: |
| === EOG/ECG channels === * Select the protocol '''TutorialRaw''' created in the previous tutorial, and select the "Functional data" view (second button in the toolbar on top of the database explorer). * Double-click on the '''clean''' continuous recordings ("'''Raw | notch(60Hz 120Hz 180Hz)'''") to open the MEG recordings. * Set the length of the reviewed time window to '''3 seconds''' (in the Record tab, text box "Duration") * Right-click on the continuous recordings again > '''Misc > Display time series'''. . {{http://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/TutRawSsp?action=AttachFile&do=get&target=tsMisc.gif|tsMisc.gif|height="148",width="577",class="attachment"}} * In this file the channel type "'''Misc'''" groups the two channels '''EEG057 '''('''ECG''', in green) and '''EEG058 '''('''vertical EOG''', in red). This configuration depends on the acquisition setup, and can be redefined afterwards in Brainstorm (right-click on the channel file > Edit channel file, and then change manually the string in the column Type for any channel). * Use the shortcuts introduced in the previous tutorial to adjust the vertical scale of this display: Shift+mouse wheel, +/- keys, or the buttons on the right side of the figure. * Then go further in time to see what is happening on those channels over the time: use the "'''>>>'''" buttons, or the associated shortcuts (read the tooltips of the button) * '''ECG''': On the green trace, you can recognize the very typical shape of the electric activity of the heart (P, QRS and T waves). This is a very good example, the signal is not always that clean. * '''EOG''': On the red trace, there is not much happening for most of the recordings except for a few bumps, typical of eye blinks, eg. at 33.590s. This subject is sitting very still and not blinking much. We can expect MEG recordings of a very good quality. * You can observe the contamination from a blink on the left-frontal sensors: move to '''33.590s''' (you can use the text boxes in the time panel, the Record tab, or the scrollbar in the figure), and select a subset of sensors (Shift+B, or right-click on the figure > Display setup > CTF LF) . {{http://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/TutRawSsp?action=AttachFile&do=get&target=megEog.gif|megEog.gif|height="265",width="475",class="attachment"}} |
* The signal to analyze is read from the continuous file (options "Channel name" and "Time window"). * '''Frequency band''': The signal is filtered in a frequency band where the artifact is easy to detect. For EOG: 1.5-15Hz ; for ECG: 10-40Hz. * '''Threshold''': An event of interest is detected if the absolute value of the filtered signal value goes over a given number of times the standard deviation. For EOG: 2xStd, for ECG: 4xStd * '''Minimum duration between two events''': If the filtered signal crosses the threshold several times in relation with the same artifact (eg. muscle activity in an EMG channel), we don't want to trigger several events but just one at the beginning of the activity. This parameter would indicate the algorithm to take only the maximum value over the given time window; it also prevents from detecting other events immediately after a successful detection. For the ECG, this value is set to 500ms, because it is very unlikely that the heart rate of the subject goes over 120 beats per minute. * '''Ignore the noisy segments''': If this option is selected, the detection is not performed on the segments that are much noisier than the rest of the recordings. * '''Enable classification''': If this option is selected, the events are classified by shape in different categories, based on correlation measure. In the end, only the categories that have more than 5 occurrences are kept, all the other successful detections are ignored. <<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:detect_custom.gif||height="435",width="313"}} |
| Line 86: | Line 93: |
| === Manual marking === Create a new category of markers "'''blink_manual'''", using the menu Events > Add group. Select this new group. Review the file, and mark the peaks you observe on the vertical EOG trace, using the '''Ctrl+E''' keyboard shortcut. Do that for a few eye blinks. |
<<TAG(Advanced)>> |
| Line 89: | Line 95: |
| {{http://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/TutRawSsp?action=AttachFile&do=get&target=markEog.gif|markEog.gif|height="174",width="496",class="attachment"}} | == In case of failure == If the signals are not as clean as in this sample dataset, the automatic detection of the heartbeats and blinks may fail with the standard parameters. You may have to use the process "Detect custom events" and adjust some parameters. For instance: |
| Line 91: | Line 98: |
| You could repeat the same operation for all the blinks, then for all the ECG peaks and jump to the next chapter of the tutorial and compute the SSP. It would be uselessly time consuming, as there is a process that does it for you automatically. However, it is good to remember how to do it manually because you may face some cases where you don't have clean ECG/EOG, or if you want to correct for another type of artifact. | * If nothing is detected: decrease the amplitude threshold, or try to adjust the frequency band. * If too many events are detected: increase the amplitude threshold or the minimum duration between two events. * If too many categories of events are generated, and you have a very little number of events in the end: disable the classification. * To find the optimal frequency band for an artifact, you can open the recordings and play with the online band-pass filters in the Filter tab. Keep the band that shows the highest amplitude peaks. |
| Line 93: | Line 103: |
| === Automatic detection: EOG === In the Record tab, select the menu: '''SSP > Detect eye blinks'''. It opens automatically the pipeline editor, with the process "Detect eye blinks" selected: |
If you cannot get your artifacts to be detected automatically, you can browse through the recordings and mark all the artifacts manually, as explained in the tutorial [[Tutorials/EventMarkers|Event markers]].. |
| Line 96: | Line 105: |
| * '''Channel name''': Name of the channel that is used to perform the detection. Select or type "'''EEG058'''" as it is the name of the EOG channel * '''Time window''': Time range that the algorithm should scan for the selected artifact. Leave the default values to process the entire file. * '''Event name''': Name of the event group that is created for saving all the detected events. Leave the default "blink". |
<<TAG(Advanced)>> |
| Line 100: | Line 107: |
| {{http://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/TutRawSsp?action=AttachFile&do=get&target=sspMenu.gif|sspMenu.gif|class="attachment"}} {{http://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/TutRawSsp?action=AttachFile&do=get&target=detectEog.gif|detectEog.gif|height="232",width="334",class="attachment"}} | == Other detection processes == '''Events > Detect analog trigger''' |
| Line 102: | Line 110: |
| Click on Run. After the process stops, you can see two new event categories "'''blink'''" and "'''blink2'''" in the Record tab. You can review a few of them, to make sure that they really indicate the EOG events. In the Record tab, click on the "blink" event category, then on a time occurrence to jump to it in the MEG and Misc time series figures. | * See tutorial [[http://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/StimDelays#Detection_of_the_analog_triggers|Stimulation delays]]. * This is used to detect events on any channel (MEG, EEG, STIM, Analog, etc), where the baseline is relatively stable and the events will predictably cross a threshold. This is useful when you want to detect a single time point ('''simple event''') at the '''start''' of an event, as in these examples: <<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:analog_detection_audio.png||height="127",width="250"}} {{attachment:analog_detection_pd.png||height="127",width="250"}} {{attachment:analog_detect_saccade.png||height="127",width="250"}} |
| Line 104: | Line 113: |
| Two types of events are created because this algorithm not only detects specific events in a signal, it also classifies them by shape. If you go through all the events that were detected in the two categories, you would see that the "blink" are all round bumps, typical of the '''eye blinks'''. In the category "blink2", the morphologies don't look as uniform; it mixes small blinks, and ramps or step functions followed by sharp drops that could indicate '''eye saccades'''. The saccades can be observed on the vertical EOG, but if you want a better characterization of them you should also record the horizontal EOG. The detection of the saccades should be performed with a different set of parameters, using the process "Detect custom events", introduced later in this chapter. | '''Events > Detect custom events''' |
| Line 106: | Line 115: |
| {{http://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/TutRawSsp?action=AttachFile&do=get&target=detectEogDone.gif|detectEogDone.gif|class="attachment"}} | * See tutorial [[http://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/ArtifactsDetect#Detection:_Custom_events|Artifact detection]]. * This is used to detect events on any channel (MEG, EEG, STIM, Analog, etc) where the baseline is relatively stable and the events will predictably cross a threshold. This is useful when you want to detect a '''simple event''' at the '''peak''' of an event, as in these examples:<<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:custom_detect_jump.png||height="127",width="250"}} {{attachment:custom_detect_muscle.png||height="127",width="250"}} |
| Line 108: | Line 118: |
| === Automatic detection: ECG === Now do the same thing for the heartbeats. In the Record tab, select the menu "'''SSP > Detect heartbeats'''". Configure the process to use the channel '''EEG057''' (name of the ECG channel), and leave the other options to the default values. |
'''Events > Detect events above threshold''' |
| Line 111: | Line 120: |
| {{http://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/TutRawSsp?action=AttachFile&do=get&target=sspMenu1.gif|sspMenu1.gif|class="attachment"}} {{http://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/TutRawSsp?action=AttachFile&do=get&target=detectEcg.gif|detectEcg.gif|height="228",width="330",class="attachment"}} | * See tutorial [[http://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/VisualSingle#Eye_blinks:_Detection|MEG visual: single subject]]. * This is used to detect signal on any channel (MEG, EEG, STIM, Analog, etc) that is above a defined threshold value. This is useful when you want to detect all time points when the signal is above the threshold ('''extended events'''), as in these examples: <<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:threshold_detect_blink.png||height="127",width="250"}} {{attachment:threshold_detect_event.png||height="127",width="250"}} * The extended event can be converted to a single event (when the rising or falling edge is desired). in the Record tab, select the event to convert, then in the menu '''Events > Convert to simple event > select Start, Middle, or End''' to indicate where the marker should be placed. |
| Line 113: | Line 124: |
| Click on Run. After the process stops, you can see a new event category "'''cardiac'''" in the Record tab, with 346 occurrences. You can check a few of them, to make sure that the "cardiac" markers really indicate the ECG peaks, and that there are not too many peaks that are skipped. | '''Events > Detect other artifacts''' |
| Line 115: | Line 126: |
| {{http://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/TutRawSsp?action=AttachFile&do=get&target=detectEcgDone.gif|detectEcgDone.gif|class="attachment"}} | * See tutorial [[http://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/BadSegments|Additional bad segments]] |
| Line 117: | Line 128: |
| === Automatic detection: Custom === Those two previous processes are shortcuts for a generic process "'''Detect custom events'''". We are not going to use it here, but it is interesting to introduce it to understand how the blinks and heartbeats detection work. The logic is the following: |
'''Events > Detect movement''' |
| Line 120: | Line 130: |
| * The channel to analyze is read from the continuous file, for a given time window. * '''Frequency band''': The signal is filtered in a frequency band where the artifact is easy to detect. For EOG: 1.5-15Hz ; for ECG: 10-40Hz. * '''Threshold''': An event of interest is detected if the absolute value of the filtered signal value goes over a given number of times the standard deviation. For EOG: 2xStd, for ECG: 4xStd * '''Minimum duration between two events''': If the filtered signal crosses the threshold several times in relation with the same artifact (like it would be the case for muscular activity recordings on an EMG channel), we don't want to trigger several events but just one at the beginning of the activity. This parameter would indicate the algorithm to take only the maximum value over the given time window; it also prevents from detecting other events immediately after a successful detection. For the ECG, this value is set to 500ms, because it is very unlikely that the heart rate of the subject goes over 120 beats per minute. * '''Ignore the noisy segments''': If this option is selected, the detection is not performed on the segments that are much noisier than the rest of the recordings. * '''Enable classification''': If this option is selected, the events are classified by shape, based on correlation measure. In the end, only the categories that have more than 5 occurrences are kept, all the other successful detections are ignored. |
* See tutorial [[Tutorials/MovementDetect|Detect subject movements]] |
| Line 127: | Line 132: |
| {{http://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/TutRawSsp?action=AttachFile&do=get&target=detectCustom.gif|detectCustom.gif|height="459",width="329",class="attachment"}} | '''Synchronize > Transfer events''' |
| Line 129: | Line 134: |
| == Additional information == * Elekta: jumps in the sensors * McGill guidelines * SSP cookbook |
* See tutorial [[Tutorials/EyetrackSynchro|Synchronization with eye tracker]] |
| Line 134: | Line 136: |
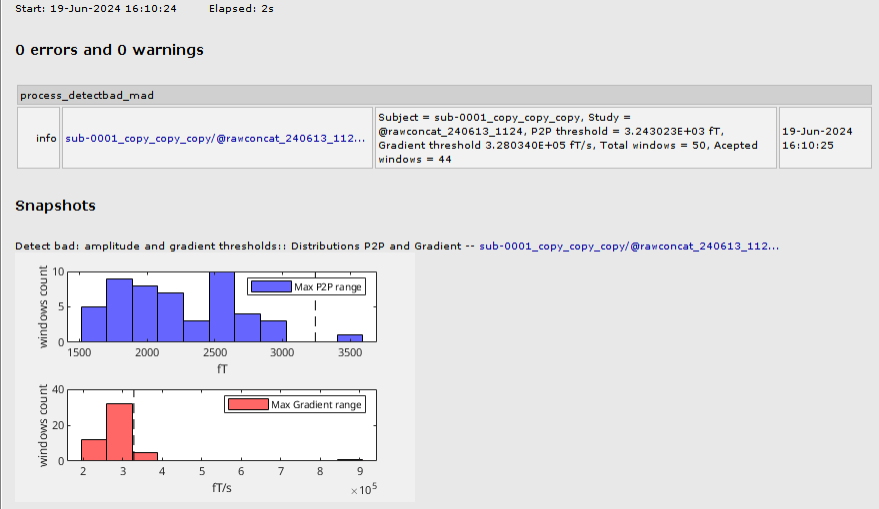
| <<EmbedContent("http://neuroimage.usc.edu/bst/get_prevnext.php?prev=Tutorials/ArtifactsFilter&next=Tutorials/ArtifactsSsp")>> | '''Artifacts > Detect bad channels: Peak-to-peak''' * '''With imported data''': Reject channels and trials from imported data. * '''With raw data''': Create bad events (specific channel or all channels) on the raw data. . This process is usually not recommended, as the amplitude of the signal is not always a good marker of the quality of the channel. '''Artifacts > Detect bad: amplitude and gradient thresholds''' * '''With imported data''': Reject trials from imported data. * '''With raw data''': Create bad events (all channels) on the raw data. Data is analyzed in windows which length is defined by the user. * This process detects artifactual segments for MEG recordings based on the distribution of the signal '''peak-to-peak amplitude''' and the signal '''numerical gradient'''. This process is based on the '''AUTO''' option of the MEG trial rejection method available in [[https://github.com/nichrishayes/ArtifactScanTool|ArtifactScanTool]]. * Segments are identified as artifactual if they surpass the specified thresholds. These thresholds can be set in two ways: '''auto''', thresholds are defined as '''n''' times the '''median absolute deviations''' (MAD) of each signal characteristic; '''manual''': user provides the thresholds. Once the process is executed, the report shows the distribution and thresholds for the two signal characteristics. <<BR>> {{attachment:mad_detect_report.png||width="450"}} <<TAG(Advanced)>> == Additional documentation == * Tutorial: [[Tutorials/MovementDetect|Detect subject movements]] * Tutorial: [[Tutorials/EyetrackSynchro|Synchronization with eye tracker]] <<HTML(<!-- END-PAGE -->)>> <<EmbedContent("http://neuroimage.usc.edu/bst/get_prevnext.php?prev=Tutorials/BadChannels&next=Tutorials/ArtifactsSsp")>> |
Tutorial 12: Artifact detection
Authors: Francois Tadel, Elizabeth Bock, Sylvain Baillet
The previous tutorials illustrated how to remove noise patterns occurring continuously and at specific frequencies. However, most of the events that contaminate the MEG/EEG recordings are not persistent, span over a large frequency range or overlap with the frequencies of the brain signals of interest. Frequency filters are not appropriate to correct for eye movements, breathing movements, heartbeats or other muscle activity.
For getting rid of reproducible artifacts, one popular approach is the Signal-Space Projection (SSP). This method is based on the spatial decomposition of the MEG/EEG recordings for a selection of time samples during which the artifact is present. Therefore we need to identify when each type of artifacts occurs in the recordings. This tutorial shows how to automatically detect some well defined artifacts: the blinks and the heartbeats.
Contents
Observation
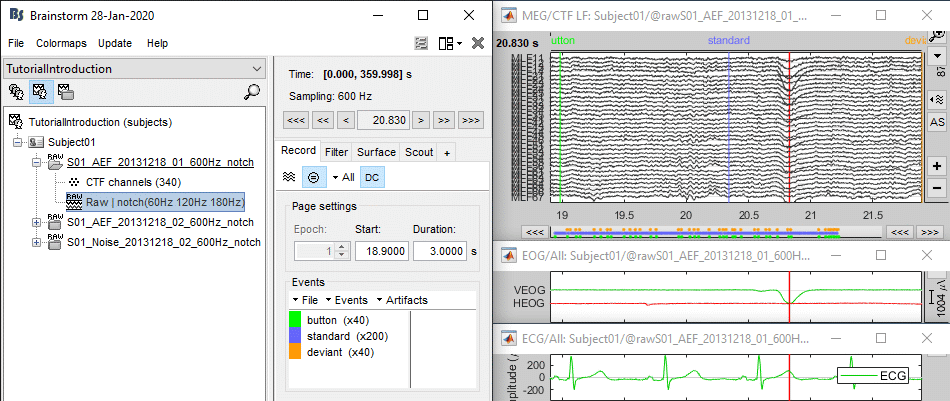
Let's start by observing the type of contamination the blinks and heartbeats cause to the MEG recordings.
Run #01: Double-click on the link to show the MEG sensors.
Configuration: Page of 3 seconds, view in columns, selection of the "CTF LT" sensors (the left-temporal sensors will be a good example to show at the same time the two types of artifacts).
EOG: Right-click on the link > EOG > Display time series. Two channels are classified as EOG:
VEOG: Vertical electrooculogram (two electrodes placed below and above one eye)
HEOG: Horizontal electrooculogram (two electrodes placed on the temples of the subject)
- On these traces, there is not much happening for most of the recordings except for a few bumps. This subject is sitting very still and not blinking much. We can expect MEG recordings of a very good quality.
ECG: Right-click on the link > ECG > Display time series.
The electrocardiogram was recorded with a bipolar montage of electrodes across the chest. You can recognize the typical shape of the electric activity of the heart (P, QRS and T waves).Find a blink: Scroll through the recordings using the F3 shortcut until you see a large blink.
- Remember you can change the amplitude scale with many shortcuts (eg. right-click + move).
To keep the scale fixed between two pages: Uncheck the button [AS] (auto-scale).
- For instance, you can observe a nice blink at 20.8s (red cursor in the screen capture below).
- On the same page, you should be able to observe the contamination due to a few heartbeats, corresponding to the peaks of the ECG signal (eg. 19.8s, shown as a blue selection below).
The additional data channels (ECG and EOG) contain precious information that we can use for the automatic detection of the blinks and heartbeats. We strongly recommend that you always record these signals during your own experiments, it helps a lot with the data pre-processing.
Detection: Heartbeats
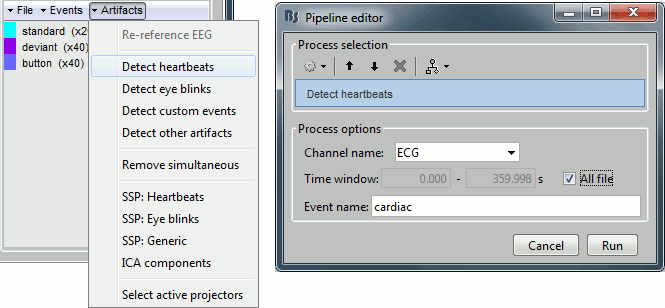
In the Record tab, select the menu: "Artifacts > Detect heartbeats".
- It automatically opens the pipeline editor, with the process "Detect heartbeats" selected.
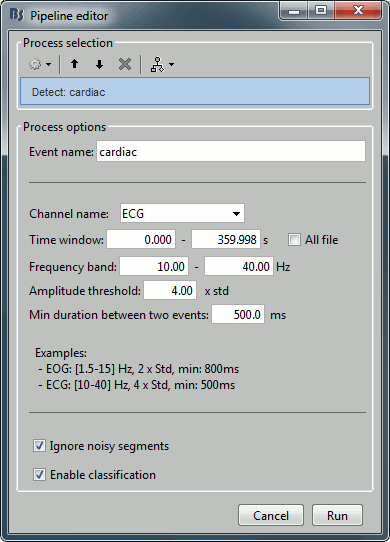
Channel name: Name of the channel that is used to perform the detection. Select or type "ECG".
Time window: Time range that the algorithm should scan for amplitude peaks. Leave the default values to process the entire file, or check the option [All file].
Event name: Name of the event group created for saving the detected events. Enter "cardiac".
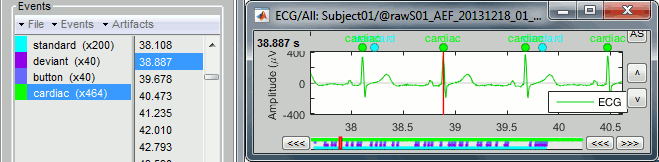
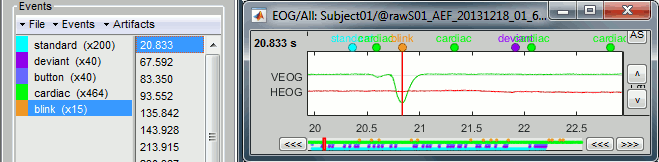
Click on Run. After the process stops, you can see a new event category "cardiac". The 464 (aprox.) heartbeats for 360s of recordings indicate an average heart rate of 77bpm, everything looks normal.
You can check a few of them, to make sure the "cardiac" markers really indicate the ECG peaks. Not all peaks need to be detected, but you should have a minimum of 10-20 events marked for removing the artifacts using SSP, described in the following tutorials.
Detection: Blinks
Now do the same thing for the blinks: Menu "Artifacts > Detect eye blinks".
Channel name: VEOG
Time window: All file
Event name: Blink
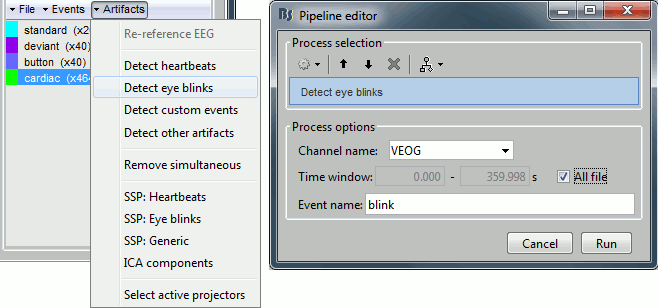
Run, then look quickly at the 15 detected blinks (shortcut: Shift+Right arrow).
Remove simultaneous blinks/heartbeats
We will use these event markers as the input to our SSP cleaning method. This technique works well if each artifact is defined precisely and as independently as possible from the other artifacts. This means that we should try to avoid having two different artifacts marked at the same time.
Because the heart beats every second or so, there is a high chance that when the subject blinks there is a heartbeat not too far away in the recordings. We cannot remove all the blinks that are contaminated with a heartbeat because we would have no data left. But we have a lot of heartbeats, so we can do the contrary: remove the markers "cardiac" that are occurring during a blink.
In the Record tab, select the menu "Artifacts > Remove simultaneous". Set the options:
Remove events named: "cardiac"
When too close to events: "blink"
Minimum delay between events: 250ms
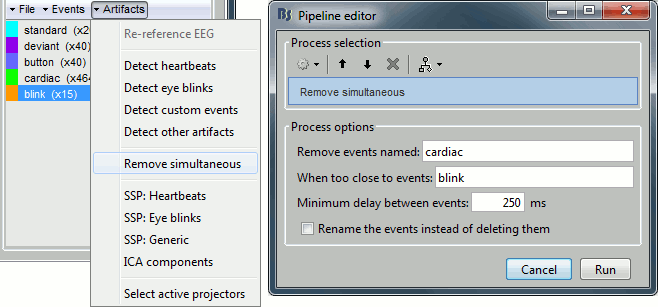
After executing this process, the number of "cardiac" events goes from 465 to 456. The deleted heartbeats were all less than 250ms away from a blink.
Run #02: Running from a script
Let's perform the same detection operations on Run #02, using this time the Process1 box.
Close everything with the [X] button at the top-right corner of the Brainstorm window.
Select the run AEF #02 in the Process1 box, then select the following processes:
Events > Detect heartbeats: Select channel ECG, check "All file", event name "cardiac".
Events > Detect eye blinks: Select channel VEOG, check "All file", event name "blink".
Events > Remove simultaneous: Remove "cardiac", too close to "blink", delay 250ms.
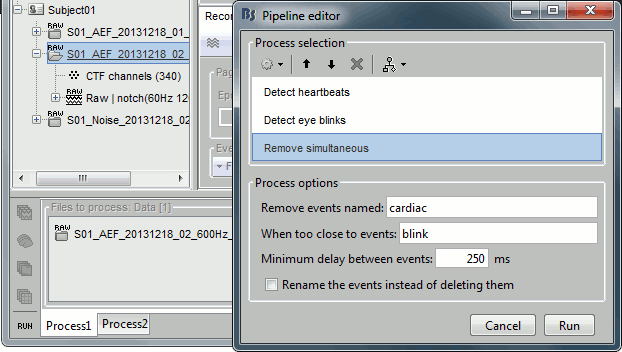
Open the Run#02 recordings (MEG+EOG+ECG) and verify that the detection worked as expected. You should get 472 cardiac events and 19 blink events.
Artifacts classification
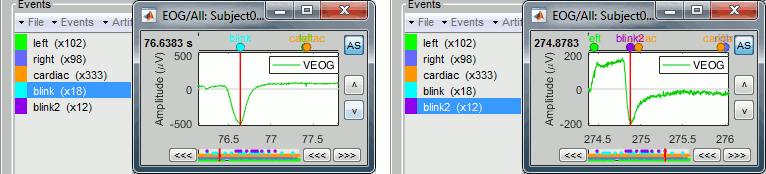
If the EOG signals are not as clean as here, the detection processes may create more than one category, for instance: blink, blink2, blink3. The algorithm not only detects specific events in a signal, it also classifies them by shape. For two detected events, the signals around the event marker have to be sufficiently correlated (> 0.8) to be classified in the same category. At the end of the process, all the categories that contain less than 5 events are deleted.
In the good cases, this can provide an automatic classification of different types of artifacts, for instance: blinks, saccades and other eye movements. The tutorial MEG median nerve (CTF) is a good illustration of appropriate classification: blink groups the real blinks, and blink2 contains mostly saccades.
In the bad cases, the signal is too noisy and the classfication fails. It leads to either many different categories, or none if all the categories have less than 5 events. If you don't get good results with the process "Detect eye blinks", you can try to run a custom detection with the classification disabled.
At the contrary, if you obtain one category that mixes multiple types of artifacts and would like to automatically separate them in different sub-groups, you can try the process "Events > Classify by shape". It is more powerful than the automatic classification from the event detection process because it can run on multiple signals at the same type: first it reduces the number of dimensions with a PCA decomposition, then runs a similar classification procedure.
Detection: Custom events
These two processes "Detect heartbeats" and "Detect eye blinks" are in reality shortcuts for a generic process "Detect custom events". This process can be used for detecting any kind of event based on the signal power in a specific frequency band. We are not going to use it here, but you may have to use it if the standard parameters do not work well, or for detecting other types of events.
- The signal to analyze is read from the continuous file (options "Channel name" and "Time window").
Frequency band: The signal is filtered in a frequency band where the artifact is easy to detect. For EOG: 1.5-15Hz ; for ECG: 10-40Hz.
Threshold: An event of interest is detected if the absolute value of the filtered signal value goes over a given number of times the standard deviation. For EOG: 2xStd, for ECG: 4xStd
Minimum duration between two events: If the filtered signal crosses the threshold several times in relation with the same artifact (eg. muscle activity in an EMG channel), we don't want to trigger several events but just one at the beginning of the activity. This parameter would indicate the algorithm to take only the maximum value over the given time window; it also prevents from detecting other events immediately after a successful detection. For the ECG, this value is set to 500ms, because it is very unlikely that the heart rate of the subject goes over 120 beats per minute.
Ignore the noisy segments: If this option is selected, the detection is not performed on the segments that are much noisier than the rest of the recordings.
Enable classification: If this option is selected, the events are classified by shape in different categories, based on correlation measure. In the end, only the categories that have more than 5 occurrences are kept, all the other successful detections are ignored.
In case of failure
If the signals are not as clean as in this sample dataset, the automatic detection of the heartbeats and blinks may fail with the standard parameters. You may have to use the process "Detect custom events" and adjust some parameters. For instance:
- If nothing is detected: decrease the amplitude threshold, or try to adjust the frequency band.
- If too many events are detected: increase the amplitude threshold or the minimum duration between two events.
- If too many categories of events are generated, and you have a very little number of events in the end: disable the classification.
- To find the optimal frequency band for an artifact, you can open the recordings and play with the online band-pass filters in the Filter tab. Keep the band that shows the highest amplitude peaks.
If you cannot get your artifacts to be detected automatically, you can browse through the recordings and mark all the artifacts manually, as explained in the tutorial Event markers..
Other detection processes
Events > Detect analog trigger
See tutorial Stimulation delays.
This is used to detect events on any channel (MEG, EEG, STIM, Analog, etc), where the baseline is relatively stable and the events will predictably cross a threshold. This is useful when you want to detect a single time point (simple event) at the start of an event, as in these examples:
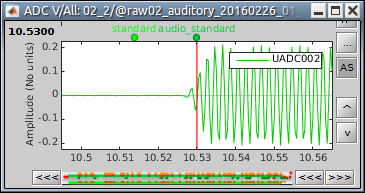
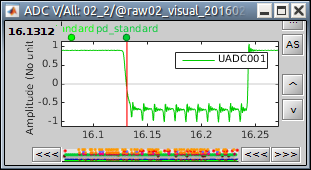
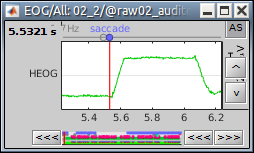
Events > Detect custom events
See tutorial Artifact detection.
This is used to detect events on any channel (MEG, EEG, STIM, Analog, etc) where the baseline is relatively stable and the events will predictably cross a threshold. This is useful when you want to detect a simple event at the peak of an event, as in these examples:
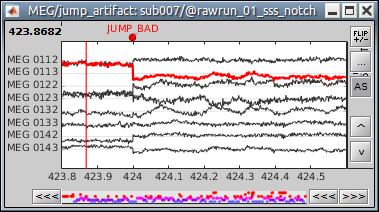
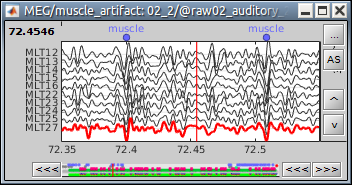
Events > Detect events above threshold
See tutorial MEG visual: single subject.
This is used to detect signal on any channel (MEG, EEG, STIM, Analog, etc) that is above a defined threshold value. This is useful when you want to detect all time points when the signal is above the threshold (extended events), as in these examples:
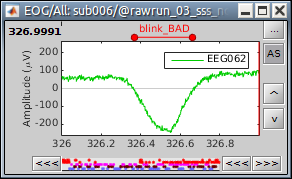
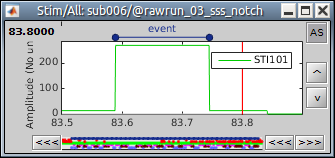
The extended event can be converted to a single event (when the rising or falling edge is desired). in the Record tab, select the event to convert, then in the menu Events > Convert to simple event > select Start, Middle, or End to indicate where the marker should be placed.
Events > Detect other artifacts
See tutorial Additional bad segments
Events > Detect movement
See tutorial Detect subject movements
Synchronize > Transfer events
See tutorial Synchronization with eye tracker
Artifacts > Detect bad channels: Peak-to-peak
With imported data: Reject channels and trials from imported data.
With raw data: Create bad events (specific channel or all channels) on the raw data.
- This process is usually not recommended, as the amplitude of the signal is not always a good marker of the quality of the channel.
Artifacts > Detect bad: amplitude and gradient thresholds
With imported data: Reject trials from imported data.
With raw data: Create bad events (all channels) on the raw data. Data is analyzed in windows which length is defined by the user.
This process detects artifactual segments for MEG recordings based on the distribution of the signal peak-to-peak amplitude and the signal numerical gradient. This process is based on the AUTO option of the MEG trial rejection method available in ArtifactScanTool.
Segments are identified as artifactual if they surpass the specified thresholds. These thresholds can be set in two ways: auto, thresholds are defined as n times the median absolute deviations (MAD) of each signal characteristic; manual: user provides the thresholds. Once the process is executed, the report shows the distribution and thresholds for the two signal characteristics.
Additional documentation
Tutorial: Detect subject movements
Tutorial: Synchronization with eye tracker