|
Size: 4384
Comment:
|
← Revision 42 as of 2025-10-30 16:41:50 ⇥
Size: 8349
Comment:
|
| Deletions are marked like this. | Additions are marked like this. |
| Line 2: | Line 2: |
| ''Authors: ***'' | ''Authors: Chinmay Chinara, Samuel Medina Villalon, Takfarinas Medani, Raymundo Cassani, Anand Joshi, Christian Bénar, Richard Leahy'' |
| Line 6: | Line 6: |
| Please note that this tutorial is intended for users already familiar with Brainstorm. It does not provide detailed explanations of the software's interface or theoretical foundations. | Please note that this tutorial is intended for users already familiar with Brainstorm. It does not provide detailed explanations of the software's interface or theoretical foundations. |
| Line 8: | Line 9: |
| * Make sure you complete the [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/seeg/Introduction|CT to MRI co-registration]] and [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/seeg/SeegContactLocalization|Contact localization and labeling]] advanced tutorial before proceeding any further. | * Make sure you complete the [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/seeg/ct2mri|CT to MRI co-registration]] and [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/seeg/SeegContactLocalization|Contact localization and labeling]] advanced tutorials before proceeding any further. |
| Line 15: | Line 16: |
| '''GARDEL''' ('''G'''UI for '''A'''utomatic '''R'''egistration and '''D'''epth '''E'''ectrode '''L'''ocalization) was developed by a multidisciplinary team as part of the [[https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29605667/|EpiTools]] suite, led by Samuel Medina Villalon (Aix‑Marseille University & AP‑HM, Marseille), Rodrigo Manuel Paz (University of Buenos Aires–CONICET), Nicolas Roehri, Stanislas Lagarde, Fabrice Pizzo, Bruno Colombet, Fabrice Bartolomei, Romain Carron, and Christian Bénar, all contributing through [[https://www.inserm.fr/en/about-us/|INSERM]] and partnering institutions across France, Argentina, and Switzerland. This international group combined clinical neurophysiology and advanced imaging expertise to create GARDEL, enabling fully automatic detection and anatomical labeling of SEEG contacts thereby laying a strong foundation for streamlining SEEG analysis in research workflows. | {{attachment:gardel_logo.png||align="right",width="250px"}} |
| Line 17: | Line 18: |
| == Prerequisites == | '''GARDEL''' ('''G'''UI for '''A'''utomatic '''R'''egistration and '''D'''epth '''E'''ectrode '''L'''ocalization) was developed by a multidisciplinary team as part of the [[https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29605667/|EpiTools]] suite, led by Samuel Medina Villalon (Aix‑Marseille University & AP‑HM, Marseille), Rodrigo Manuel Paz (University of Buenos Aires–CONICET), Nicolas Roehri, Stanislas Lagarde, Fabrice Pizzo, Bruno Colombet, Fabrice Bartolomei, Romain Carron, and Christian Bénar in the [[https://ins-amu.fr/dynamap|DynaMap Team]] of the INS institute. This group combined clinical neurophysiology and advanced imaging expertise to create GARDEL, enabling fully automatic detection and anatomical labeling of SEEG contacts thereby laying a strong foundation for streamlining SEEG analysis in research workflows. == Requirements == |
| Line 19: | Line 22: |
| * Follow the tutorial [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/seeg/SeegContactLocalization|Contact localization and labeling]] to generate the isosurface from the CT * '''GARDEL''' [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/Plugins|Brainstorm plugin]] needs to be installed for doing the automatic detection of the contacts. == Import the anatomy == Link to SEEG analysis tutorial to import the MRI and CT along with generating the CAT12 surfaces. '''TODO: Add relevant screenshots<<BR>><<BR>>''''''TODO: Talk about working in the CT space (better resolution -> better automatic localization)''' == Contact localization == === Generate Isosurface === * Link to SEEG analysis tutorial to create a thresholded mesh from the CT. * Talk about why this is required for automatic detection '''TODO: Add relevant screenshots''' |
* Follow the tutorial [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/seeg/SeegContactLocalization#Generate_isosurface|Contact localization and labeling]] to generate the isosurface from the CT with a threshold of '''2400''' Hounsfield Unit. This threshold plays a key part in the automatic detection as the the better segmented the electrodes are the better is the detection. After much trial and error, 2400 threshold gave the best results. * GARDEL [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/Plugins|brainstorm plugin]] needs to be installed for doing the automatic detection of the contacts. If you are using Brainstorm from MATLAB, GARDEL requires the [[https://www.mathworks.com/products/image-processing.html|Image Processing Toolbox]]. The [[https://www.mathworks.com/products/parallel-computing.html|Parallel Computing Toolbox]] is recommended but not required. |
| Line 36: | Line 27: |
| * Choose '''MRI+CT+IsoSurf''' from the popup menu (more details about the menu can be found [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/SeizureFingerprinting#Start_implantation|here]]). This takes you to the functional tab. '''Subject01 > Implantation > SEEG/ECOG (0)''' channel gets created. All expected figures open up. Panel iEEG loads up in the panel viewer. * Click on '''Auto > GARDEL'''. Click '''Yes''' on the disclaimer that pops up. * In few minutes, you can see the electrodes being rendered live on the figures. While GARDEL is a great tool but there could be some bad detections due to factors mentioned in the disclaimer. It is always good to verify the results carefully. * If there are any bad detections, they can be post-processed using editing features available within Brainstorm. More details can be found [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/seeg/SeegContactLocalization#Edit_the_contacts_positions|here]]. |
* Choose '''MRI+CT+!IsoSurf''' from the popup menu (more details about the menu can be found [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/seeg/SeegContactLocalization#Start_implantation|here]]). While any of the options can be chosen from the menu, this gives the option to visualize and interact both in 3D and 2D. * In the iEEG panel, click on '''Electrodes > Automatic localization > GARDEL'''. Click '''Yes''' on the disclaimer that pops up.<<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:auto_gardel_menu.png||width="450"}} <<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:2_disclaimer.png||width="350"}} * In few minutes, you can see the electrodes being rendered live on the figures.<<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:1_gardel_detect.png||width="650"}} <<BR>><<BR>> <<HTML(<center><iframe width="560" height="315" src="https://www.youtube.com/embed/4rP7QXzVOdE?vq=highres" frameborder="0" allow="accelerometer; autoplay; encrypted-media; gyroscope; picture-in-picture" allowfullscreen></iframe></center>)>> |
| Line 41: | Line 31: |
| '''TODO: Show some bad detections with this tutorial data and steps how to correct them here''' '''TODO: Add relevant screenshots''' |
== Recommendations == * While GARDEL is a great tool but there could be some bad detections (that can be seen above) due to factors mentioned in the disclaimer. It is always good to verify the results carefully. * The case above is a particularly complex one and it can be seen that there are a lot of overlapping and concentrated electrodes that are mostly touching and they are difficult to separate. GARDEL does fail to detect them and would require manual correction. It can very well be achieved using the editing features available within Brainstorm (check the [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/seeg/SeegContactLocalization#Edit_the_contacts_positions|Edit the contact positions]] section). * There could be another case of bad detection where some contacts may be grouped into different electrodes even though they belong to the same one. In this case, select all the electrodes and use the ''' {{attachment:iconFusion.gif}} (Merge selected electrodes)''' button in the iEEG panel (shortcut '''Ctrl+M''') to merge them together.<<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:merge_electrodes.png||width="450"}} * A way to achieve much more accurate localization of the contacts using GARDEL is to work with the full resolution of the CT (as it is much higher than that of MRI). There are two ways by which this can be achieved: 1. One way is to follow the same steps as in [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/seeg/ct2mri|CT to MRI co-registration]], but do not reslice the CT after co-registering it to the MRI, so that the resolution of the CT is preserved. Then proceed with the same steps for SPM skull stripping, generating Isosurface and then running GARDEL on it. 1. Another way is to work in the CT space entirely. To do that, import the CT first, compute [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/ImportAnatomy#MNI_normalization|MNI normalization]] (to set the fiducials on the CT), import MRI, coregister MRI to CT, run SPM skull stripping, generating Isosurface and then running GARDEL. Natively, GARDEL actually recommends working in the CT space. Please refer to their paper (linked in Articles section below) for more details. A video showing the automatic detection of contacts in the CT space using the GARDEL's sample data as provide in their [[https://gitlab-dynamap.timone.univ-amu.fr/public_shared_tools/gardel/-/wikis/home|website]] can be seen as under.<<BR>><<BR>> <<HTML(<center><iframe width="560" height="315" src="https://www.youtube.com/embed/PHi4YgiOwDU?vq=highres" frameborder="0" allow="accelerometer; autoplay; encrypted-media; gyroscope; picture-in-picture" allowfullscreen></iframe></center>)>> |
| Line 47: | Line 41: |
| * [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/forums/t/bipolar-montage-creation-export-after-gardel/|Bipolar montage creation/export after GARDEL]] |
|
| Line 48: | Line 44: |
| * S. Medina Villalon, R. Paz, N. Toehri, S. Lagarde, F. Pizzo, B. Colombet, F. Bartolomei, R. Carron, C.-G. Bénar. [[https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneumeth.2018.03.018|EpiTools, A software suite for presurgical brain mapping in epilepsy: Intracerebral EEG]]. <<BR>> Journal of Neuroscience Methods 2018. * Chinmay Chinara, Raymundo Cassani, Takfarinas Medani, Anand A Joshi, Samuel Medina Villalon, Yash S Vakilna, Johnson P Hampson, Kenneth Taylor, Francois Tadel, Dileep Nair, Christian G Bénar, Sylvain Baillet, John C Mosher, Richard M Leahy. [[https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC12458114/|sEEG-Suite: An Interactive Pipeline for Semi-Automated Contact Localization and Anatomical Labeling with Brainstorm]]. <<BR>> bioArxiv (September 2025). |
|
| Line 49: | Line 48: |
| * [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/seeg/ct2mri|CT to MRI co-registration]] * [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/seeg/SeegContactLocalization|Contact localization and labeling]] * [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/seeg/SeizureFingerprinting|Time-Frequency Fingerprint Analysis for Epileptogenic Zone Localization]] * [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/Epileptogenicity|Epileptogenicity]] |
Automatic SEEG Contact Localization using GARDEL
Authors: Chinmay Chinara, Samuel Medina Villalon, Takfarinas Medani, Raymundo Cassani, Anand Joshi, Christian Bénar, Richard Leahy
This tutorial describes how to perform automatic SEEG contact localization in Brainstorm using GARDEL.
Please note that this tutorial is intended for users already familiar with Brainstorm. It does not provide detailed explanations of the software's interface or theoretical foundations.
For comprehensive introductory material, refer to the Brainstorm introduction tutorials.
Make sure you complete the CT to MRI co-registration and Contact localization and labeling advanced tutorials before proceeding any further.
NOT FOR CLINICAL USE:
The methods and software implementations presented in this tutorial have not been certified as medical devices. They are intended for research purposes only and should not be used for clinical decision-making.
Contents
Introduction
GARDEL (GUI for Automatic Registration and Depth Eectrode Localization) was developed by a multidisciplinary team as part of the EpiTools suite, led by Samuel Medina Villalon (Aix‑Marseille University & AP‑HM, Marseille), Rodrigo Manuel Paz (University of Buenos Aires–CONICET), Nicolas Roehri, Stanislas Lagarde, Fabrice Pizzo, Bruno Colombet, Fabrice Bartolomei, Romain Carron, and Christian Bénar in the DynaMap Team of the INS institute. This group combined clinical neurophysiology and advanced imaging expertise to create GARDEL, enabling fully automatic detection and anatomical labeling of SEEG contacts thereby laying a strong foundation for streamlining SEEG analysis in research workflows.
Requirements
Complete the CT to MRI co-registration to have the data and the required anatomy set up.
Follow the tutorial Contact localization and labeling to generate the isosurface from the CT with a threshold of 2400 Hounsfield Unit. This threshold plays a key part in the automatic detection as the the better segmented the electrodes are the better is the detection. After much trial and error, 2400 threshold gave the best results.
GARDEL brainstorm plugin needs to be installed for doing the automatic detection of the contacts. If you are using Brainstorm from MATLAB, GARDEL requires the Image Processing Toolbox. The Parallel Computing Toolbox is recommended but not required.
Automatic contact localization using GARDEL
Right click on Subject01, and choose SEEG/ECOG implantation.
Choose MRI+CT+IsoSurf from the popup menu (more details about the menu can be found here). While any of the options can be chosen from the menu, this gives the option to visualize and interact both in 3D and 2D.
In the iEEG panel, click on Electrodes > Automatic localization > GARDEL. Click Yes on the disclaimer that pops up.
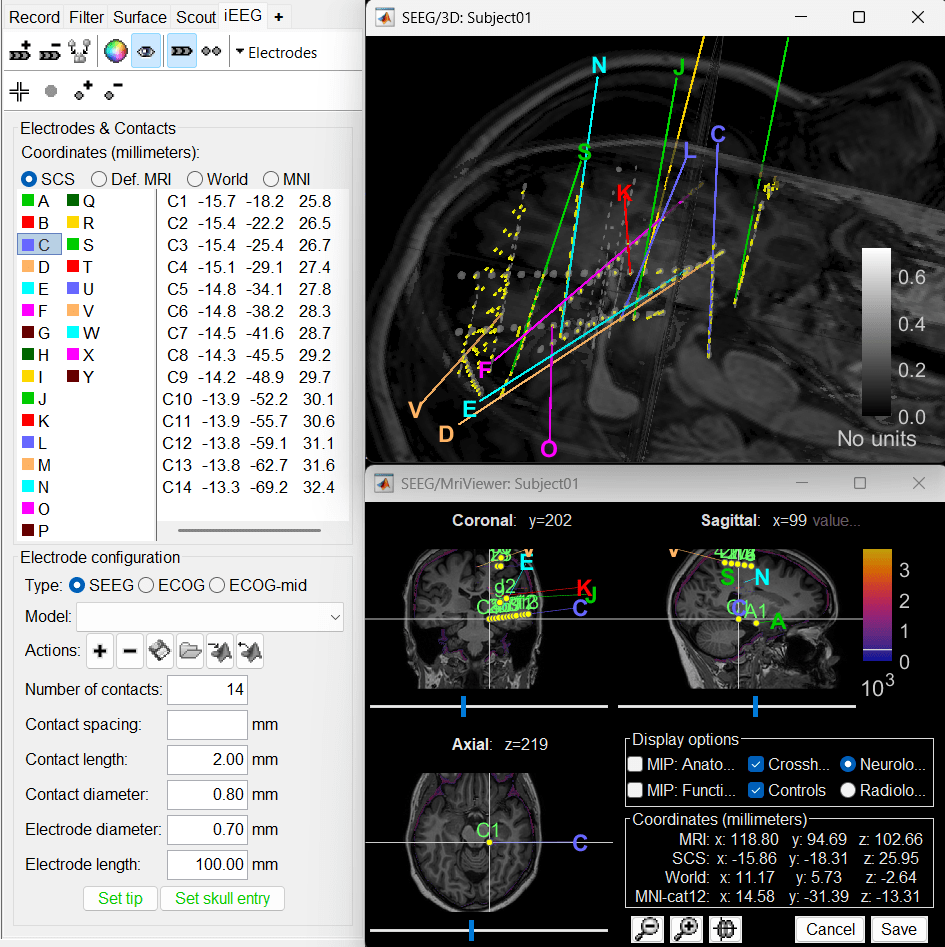
In few minutes, you can see the electrodes being rendered live on the figures.
Recommendations
- While GARDEL is a great tool but there could be some bad detections (that can be seen above) due to factors mentioned in the disclaimer. It is always good to verify the results carefully.
The case above is a particularly complex one and it can be seen that there are a lot of overlapping and concentrated electrodes that are mostly touching and they are difficult to separate. GARDEL does fail to detect them and would require manual correction. It can very well be achieved using the editing features available within Brainstorm (check the Edit the contact positions section).
There could be another case of bad detection where some contacts may be grouped into different electrodes even though they belong to the same one. In this case, select all the electrodes and use the
 (Merge selected electrodes) button in the iEEG panel (shortcut Ctrl+M) to merge them together.
(Merge selected electrodes) button in the iEEG panel (shortcut Ctrl+M) to merge them together.
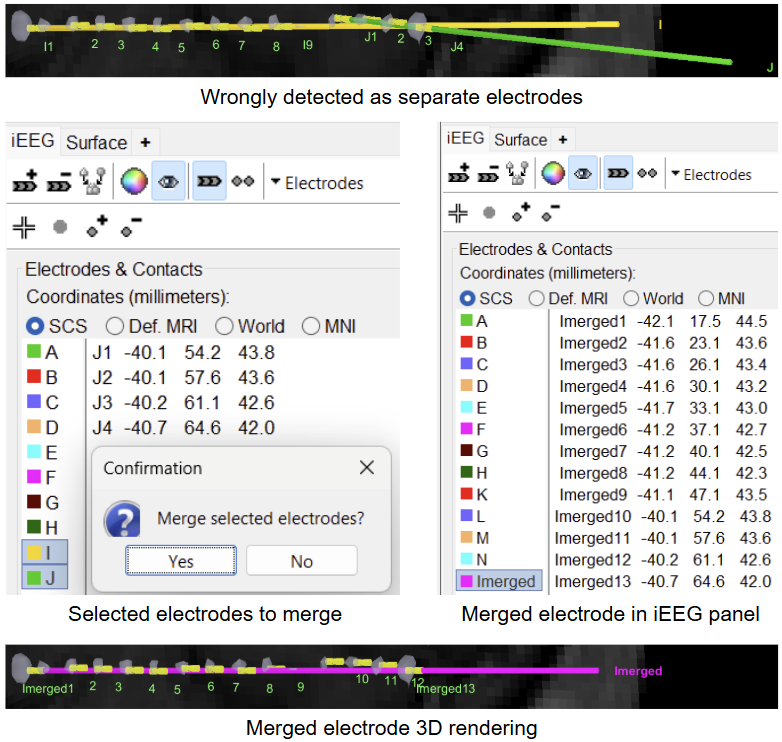
- A way to achieve much more accurate localization of the contacts using GARDEL is to work with the full resolution of the CT (as it is much higher than that of MRI). There are two ways by which this can be achieved:
One way is to follow the same steps as in CT to MRI co-registration, but do not reslice the CT after co-registering it to the MRI, so that the resolution of the CT is preserved. Then proceed with the same steps for SPM skull stripping, generating Isosurface and then running GARDEL on it.
Another way is to work in the CT space entirely. To do that, import the CT first, compute MNI normalization (to set the fiducials on the CT), import MRI, coregister MRI to CT, run SPM skull stripping, generating Isosurface and then running GARDEL. Natively, GARDEL actually recommends working in the CT space. Please refer to their paper (linked in Articles section below) for more details. A video showing the automatic detection of contacts in the CT space using the GARDEL's sample data as provide in their website can be seen as under.
Additional Documentation
Forum discussions
Articles
S. Medina Villalon, R. Paz, N. Toehri, S. Lagarde, F. Pizzo, B. Colombet, F. Bartolomei, R. Carron, C.-G. Bénar. EpiTools, A software suite for presurgical brain mapping in epilepsy: Intracerebral EEG.
Journal of Neuroscience Methods 2018.Chinmay Chinara, Raymundo Cassani, Takfarinas Medani, Anand A Joshi, Samuel Medina Villalon, Yash S Vakilna, Johnson P Hampson, Kenneth Taylor, Francois Tadel, Dileep Nair, Christian G Bénar, Sylvain Baillet, John C Mosher, Richard M Leahy. sEEG-Suite: An Interactive Pipeline for Semi-Automated Contact Localization and Anatomical Labeling with Brainstorm.
bioArxiv (September 2025).
