|
Size: 12852
Comment:
|
Size: 12928
Comment:
|
| Deletions are marked like this. | Additions are marked like this. |
| Line 62: | Line 62: |
| [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/reviewMEEGForward?highlight=(duneuro)|From our experience]], a value of 0,1 for the tetrahedral volume achieves similar results as the OpenMeeg computed from the same surfaces. We have also noticed that the result with v = 0,001 is almost similar to v = 0,01. Increasing the mesh resolution needs more time to generate the mesh, more time to perform the FEM computation and of course more memory to store the mesh in the disc. | [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/reviewMEEGForward?highlight=(duneuro)|From our tests]], a FEM head model with a value of 0,1 for the tetrahedral volume achieves similar results as the OpenMeeg head model computed from the same surfaces. We have also noticed that the result with v = 0,001 is almost similar to v = 0,01. Increasing the mesh resolution needs more time to generate the mesh, more time to perform the FEM computation and of course more memory to store the mesh in the database. |
| Line 71: | Line 73: |
| Here are some examples using only 2 tissues. This option could be useful for investigation of tissue influence on the EEG/MEG on the forward solution or on the source localization, or analyzing only SEEG within brain volume ... | Here are some examples using only 2 tissues. This option could be useful for investigation of tissues influence on the EEG/MEG on the forward solution or on the source localization, furthermore, this option could be used for analyzing only SEEG within brain volume. |
| Line 113: | Line 115: |
| The "Shift node" option will perform the adaptative mesh generation, that move the node on the interface either inward or outward, in order to fit the geometry as explained [[http://www.fieldtriptoolbox.org/tutorial/headmodel_eeg_fem/|here]], and shown in this figure (from Fieldtrip webpage). {{attachment:nodeShiftFigure.JPG||height="240",width="500"}} |
The "Shift node" option calls the adaptative mesh generation. The process moves the nodes located on the interface either inward or outward in order to fit the geometry as explained [[http://www.fieldtriptoolbox.org/tutorial/headmodel_eeg_fem/|here]]. This figure shows an example (from Fieldtrip webpage), left the unshifted and on the right the shifted. |
| Line 116: | Line 117: |
| {{attachment:nodeShiftFigure.JPG||height="200",width="500"}} | |
| Line 117: | Line 119: |
| The following figure an example of the mesh obtained with field trip option. | This method is fast compare to the previous options, the following figures show examples of the mesh obtained with fieldtrip option from the ICBM model. |
| Line 119: | Line 121: |
| {{attachment:fieldTripMeshICBM.JPG||height="350",width="700"}} If you have the MRI of the subject and Adaptative hexahedral mesh {{attachment:ernieFieldtrip.JPG||height="450",width="350"}} |
{{attachment:fieldTripMeshICBM.JPG||height="300",width="700"}} |
Realistic head model: FEM mesh generation
[TUTORIAL UNDER DEVELOPMENT: NOT READY FOR PUBLIC USE]
Authors: Takfarinas Medani
Introduction
This tutorial presents the methods integrated to brainstorm used to generate the FEM mesh.
The FEM mesh is required for the finite element method computation. The FEM computation could be used for most of the known modalities: EEG/MEG forward problem, TMS or TDSC stimulation and for intracranial modalities like sEEG and ECOG.
In this tutorial, we present the different methods available with brainstorm to generate the FEM mesh and how to use them from the brainstorm GUI.
Mesh tools
Brainstorm integrates a list of open-source tools. These tools are commonly used by the FEM community to generate either tetrahedral or hexahedra mesh.
Here is the list of the available methods in brainstorm:
- iso2mesh: this option merges the brainstorm surfaces available on the subject and then generate the tetrahedral mesh.
- Brain2mesh: this option uses the MRI available on the subject, then it calls SPMsegmentation of the volume into 5 tissues (white, gray, SCF, skull and skin). After that, it calls iso2mesh (internally) to generate the tetrahedral mesh.
- SimNibs : this option, recommended for a realistic model, calls the headrecoprocess, it uses the MRIs of the subject, and then calls SPM and CAT for the segmentation. Then the mesh generation is performed internally by integrated tools (netgen, gmesh and meshfixe).
- Fieldtrip : this option call the Fieldtrip pipeline, based on the segmentation of the MRI then the hexahedral mesh generation.
You can display the full list and a short description by right click on the MRI of the subject and then click the item "Generate FEM Mesh"
iso2mesh
iso2mesh is a Matlab /octave-based mesh generation and processing toolbox. It can create 3D tetrahedral finite element (FE) mesh from surfaces, 3D binary and gray-scale volumetric images such as segmented MRI/CT scans.
Requirement
it If iso2mesh is not installed in your computer, Brainstrom will download the last release from this webpage and install it when it is needed. However, you can also download the iso2mesh from the github and add it to your Matlab path.
When and how to use it
iso2mesh is used as the basic option by brainstorm to generate FEM mesh from surfaces mesh.
Assuming the situation where you have surfaces mesh of your subject available and you have already computed the OpenMeegforward problem. If you want to use the duneuro FEM to compute the forward model, you need to generate the FEM mesh from a similar surface used by OpenMeeg Here is the way to do it :
- Richt-click on the subject: In this way, brainstorm will load the inner, outer and the head from the subject data. if any of these surfaces is missing, an error will be displayed.
- Select the 'Generate FEM mesh' item,
- Select the iso2mesh option,
- Set the iso2mesh parameters,
- These options are used by the surf2mesh function.
Select either MergeMesh or MergeSurf.
Max tetrahedral volum : is the maximum volume of the tetrahedral element in the mesh. Pourcentage of the element to keep: parameter between 0-100%, it used to keep or not the original input surface nodes.
Also, a full example is explained in this page.
Here is a view of mesh obtained with different values of the Max volume = [10, 1, 0.1, 0.01] with a keep ratio = 100%.
From our tests, a FEM head model with a value of 0,1 for the tetrahedral volume achieves similar results as the OpenMeeg head model computed from the same surfaces. We have also noticed that the result with v = 0,001 is almost similar to v = 0,01.
Increasing the mesh resolution needs more time to generate the mesh, more time to perform the FEM computation and of course more memory to store the mesh in the database.
If intersections are present on the surfaces mesh, the iso2mesh FEM mesh generation fails (tetgen) and an error will be displayed on the screen. If you face this problem, you need to check the surfaces and/or regenerate new surfaces from the MRI.
other application
You can also select any surface mesh, or multiple surfaces (with Shift key), on the brainstorm anatomy windows and then generate tetrahedral mesh by following the same steps explained above.
Here are some examples using only 2 tissues. This option could be useful for investigation of tissues influence on the EEG/MEG on the forward solution or on the source localization, furthermore, this option could be used for analyzing only SEEG within brain volume.
brain2mesh
Brain2Mesh is a MATLAB/Octave based 3D mesh generation toolbox dedicated to the creation of high-quality multi-layered brain mesh models.
Requirement
Brain2Mesh is developed by the same team that developed the iso2mesh toolbox. Therefore iso2mesh is required. So if these toolboxes are not available on your computer, Brainstorm will download the last release and install it when it's needed.
You may also need the SPM12 toolbox. Brain2mesh is used only to generate tetrahedral mesh from the segmentation output. Therefore a segmentation of the MRI will be performed by SPM when this option is called.
More parameters will be added in the next version. If you are using this method you can request our support to help you or to add these parameters asap.
When and how to use it
This option is used when you have the individual MRI of the subject either T1 or T1 and T2. As said before, the SPM toolbox is required. The time required for this option is around 1 hour. here is the view of the obtained mesh from a T1 MRI
This option is based on the brain2mesh toolbox, we keep the default options. We will add more flexibility to control these options in the next future. However, if you want to use this option and you need support, we can help... just post your question on the forum or email us.
Fieldtrip
This option call ?the process of fieldtrip MRI segmentation (function ft_volumesegment) and hexahedral mesh generation (ft_meshprepare) develloped by the SimBio team.
Requirement
To use this option, the Fieldtrip and SPM toolbox should be in your matlab.
When and how to use it
This option can be called by two processes, either from the MRI or from any segmented tissue available on the brainstorm database.
The mesh generation with the method is faster. It converts all the voxels to hexahedral mesh.
Only the hexahedral mesh is available for this method. You can either call this option from the MRI data or from any segmentation data available on the subject. If you call it from the MRI, a segmentation is processed first, then the mesh. If you call from the tissues, only the mesh process will be performed.
Right-click on the MRI (or the tissues), then "Generate FEM Mesh" then select Fieldtrip option. There are two parameters that the user needs to set, the downsampling of the volume and the node shift ratio.
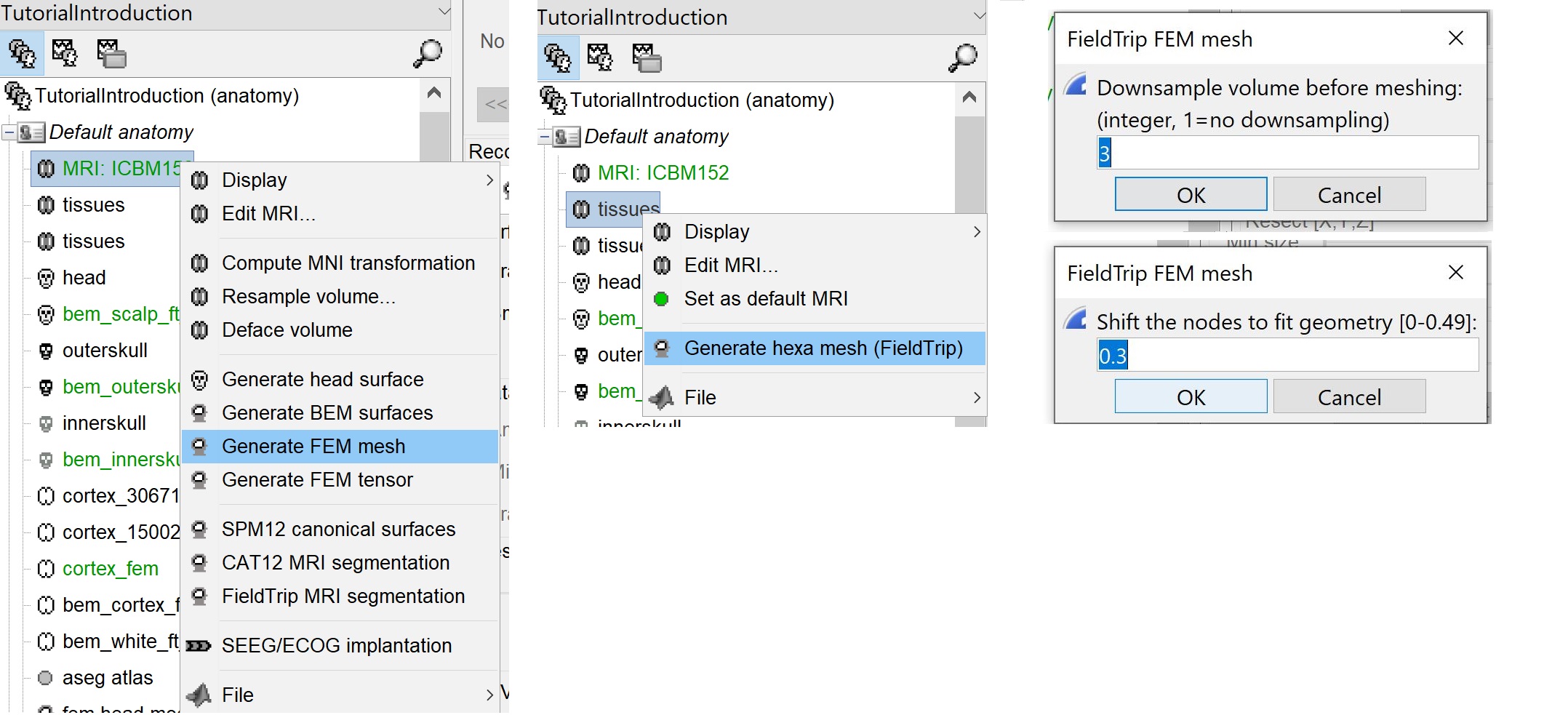
The option "Downsamp volume before meshing" will reduce the number of voxel by this factor.
The "Shift node" option calls the adaptative mesh generation. The process moves the nodes located on the interface either inward or outward in order to fit the geometry as explained here. This figure shows an example (from Fieldtrip webpage), left the unshifted and on the right the shifted.
This method is fast compare to the previous options, the following figures show examples of the mesh obtained with fieldtrip option from the ICBM model.
SimNIBS
Installation
Please follow the instructions on this webapge (new brainstorm page that explains how to generate the head model is under development)
in order to do the SimNibs software should be installed on your computer.
FEM Head model generation with SimNibs
This method used the SimNibs software. So to call this process, you need to download and install the SimNibs software, the process of the installation is explained in the SimNibs webpage : https://simnibs.github.io/simnibs/build/html/installation/simnibs_installer.html.
When you have installed SimNibs, Brainstorm can call the main function used for the mesh generation frm the main graphical interface. Depemding on your computer performances, this process will take between 2 to 5 hours. We highly recommend to close all other running process and application on our computer in order to speed this process.
1- Create new subject within the current protocole
2- Load the T1 of the subject to the brainstorm database.
3- Associate a T2 mri to the subject if it's available (this is better for csf/skull/scalp segmentation)
4- Right-click on the subject, select the "Generate FEM mesh"
- Select "SIMNIBS", and choose the "Tetrahedral element" and keep the other options to the default value.
The headreco function is fully integrated to brainstorm. With this option, brainstorm can reconstruct a tetrahedral head mesh from T1- and T2-weighted structural MR images. It runs also with only a T1w image, but it will achieve more reliable skull segmentations when a T2w image is supplied.
https://www.fil.ion.ucl.ac.uk/spm/software/spm12/
Tissue anisotropy estimation
Brainsuite Installation [TODO]
Volume generation from surface files
Volume generation from T1/T2 MRI data
You can also generate your own FEM head model and then load it to brainstorm. However the automatic head model generation from from imaging techniques are not accurate and most of the time visual checking are needed and manual correction are required.
==> this depends lagely on the quality of the T1/T2 MRI image(https://simnibs.github.io/simnibs/build/html/tutorial/head_meshing.html).
This step is based on the "roast" toolbox (link to roast : https://github.com/andypotatohy/roast
) that we adapted for the MEEG forward computation. If you want to generate your own FEM head model from an MRI, you will need to download these file (link), then run the bst process as explained here.
- If there is a MRI file with the string "T2" in the subject anatomy folder, it will use it
- Otherwise, if you select explicitly two MRI files with CTRL+Click, it will use the first one as the T1 and the second one as the T2 (this needs to be documented in the tutorial)
FEM Head model template
- Load the FEM volumic mesh (template created from ICBM T1 MRI using SimNibs)
- Load the surface mesh (template created also from ICBM using ICBM ) and then generates the volume mesh (either tetra or hexa) by calling the tetgen process cia iso2mesh toolbox (if hexa are desired, the tetra mesh will be converted to hexa ... )
https://github.com/brainstorm-tools/brainstorm3/issues/185#issuecomment-576749612
Head model based on the level set approach
TODO and Validate
