|
Size: 12827
Comment:
|
Size: 13138
Comment:
|
| Deletions are marked like this. | Additions are marked like this. |
| Line 1: | Line 1: |
| = Tutorial 27: Advanced scripting = | = Tutorial 28: Advanced scripting = |
| Line 11: | Line 11: |
== Script generation == == Script edition == - Add loops, load files, ... == File manipulation == * Modify a structure manually: Export to Matlab/Import from Matlab * File manipulation: file_short, file_fullpath, in_bst_*... * Documentation of all file structures: point at the appropriate tutorials |
|
| Line 292: | Line 301: |
| <<EmbedContent("http://neuroimage.usc.edu/bst/get_prevnext.php?prev=Tutorials/Connectivity")>> | <<EmbedContent("http://neuroimage.usc.edu/bst/get_prevnext.php?prev=Tutorials/Workflows")>> |
Tutorial 28: Advanced scripting
[TUTORIAL UNDER DEVELOPMENT: NOT READY FOR PUBLIC USE]
Authors: Francois Tadel, Elizabeth Bock, Sylvain Baillet
This tutorial explains how to use the Brainstorm scripting interface to run a full analysis, from the raw recordings to the source reconstruction. It is based on a median nerve stimulation experiment recorded at the Montreal Neurological Institute in 2011 with a CTF MEG 275 system. The sample dataset contains 6 minutes of recordings at 1200Hz for one subject and includes 100 stimulations of each arm.
The tutorial follows the analysis steps detailed in the three advanced tutorials in the category Processing continuous recordings. You should read them before reading this tutorial, to have the explanations that go with the analysis steps.
Contents
Script generation
Script edition
- Add loops, load files, ...
File manipulation
- Modify a structure manually: Export to Matlab/Import from Matlab
- File manipulation: file_short, file_fullpath, in_bst_*...
- Documentation of all file structures: point at the appropriate tutorials
Creating the analysis pipeline
Select the menu File > Create new protocol. Name it "TutorialScript" and select the options:
"No, use individual anatomy",
"Yes, use one channel file per subject".
To start building your analysis pipeline, just click on the "Run" button in the Process1 tab. We don't need any file in input, as we are going to select the files to import in the script itself. Then add all the processes listed below. The output of each process is the input of the following one, this is why the order of the processes is important.
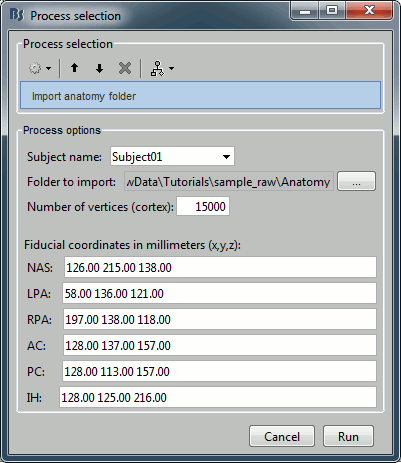
Import anatomy > Import anatomy folder
- Folder to import: sample_raw/Anatomy
File format: "FreeSurfer folder"
- Fiducials: Copy what is indicated below. This is a reason it is usually easier to do this step in interactive mode, and then run only the script starting from the next step.
- Input: None; Output: None
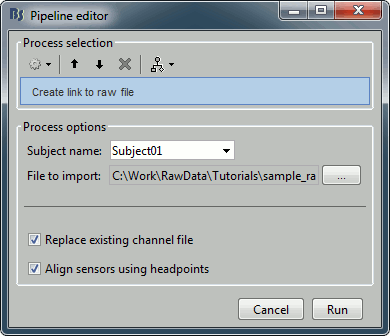
Import recordings > Create link to raw file
- File to import: Select the folder sample_raw/Data/subj001_somatosensory_20111109_01_AUX-f.ds
- Input: None; Output: Raw file
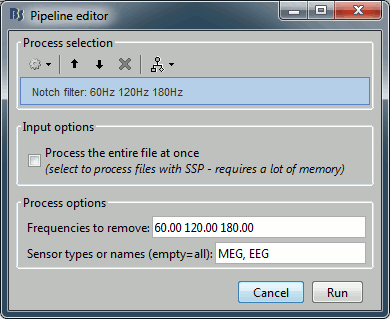
Pre-process > Notch filter
Input: Raw file ; Output: Raw file (new)
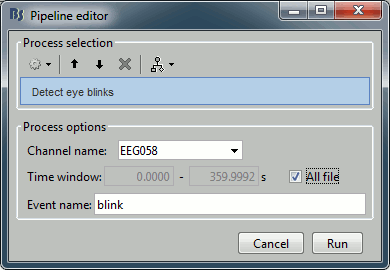
Events > Detect eye blinks
Input: Raw file ; Output: Raw file
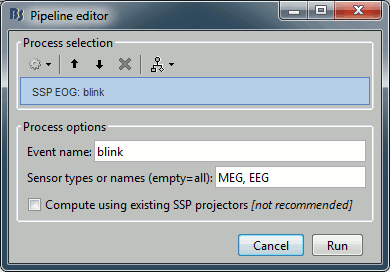
Events > Compute SSP: eye blinks
Input: Raw file ; Output: Raw file
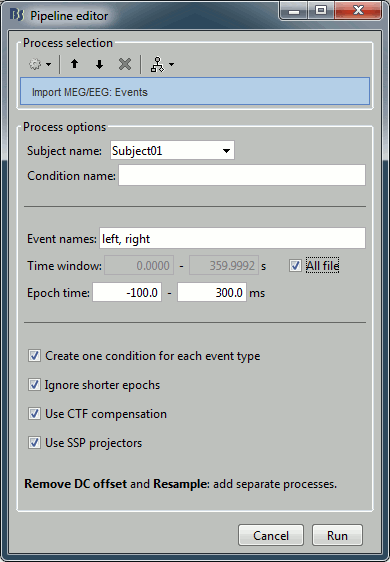
Import recordings > Import MEG/EEG : Events
Input: Raw file ; Output: 199 epochs in 2 conditions
Pre-process > Remove DC offset
Input: 199 epochs ; Output: 199 epochs
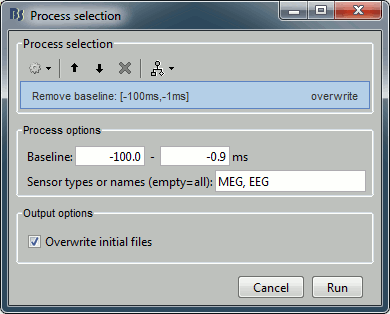
Pre-process > Add time offset
Input: 199 epochs ; Output: 199 epochs
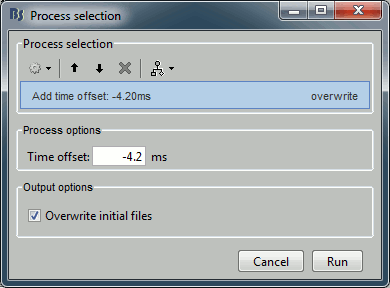
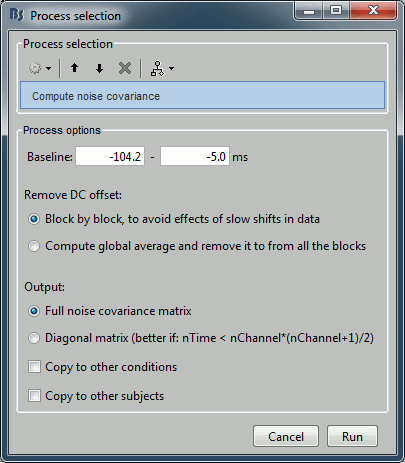
Sources > Compute noise covariance
Since the epochs are currently selected and pre-processed: we can use them to estimate the noise covariance matrix before we move on with the calculation of the average.
Input: 199 epochs ; Output: 199 epochs
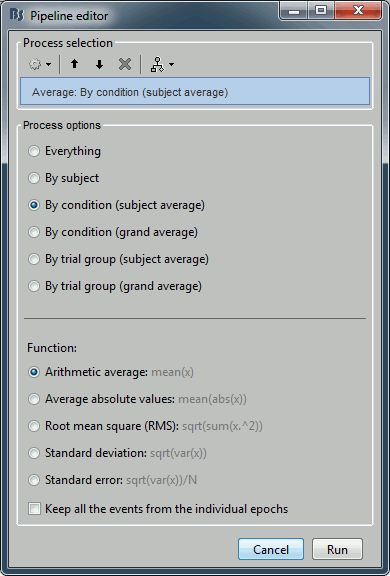
Average > Average files
Input: 199 epochs ; Output: 2 averages
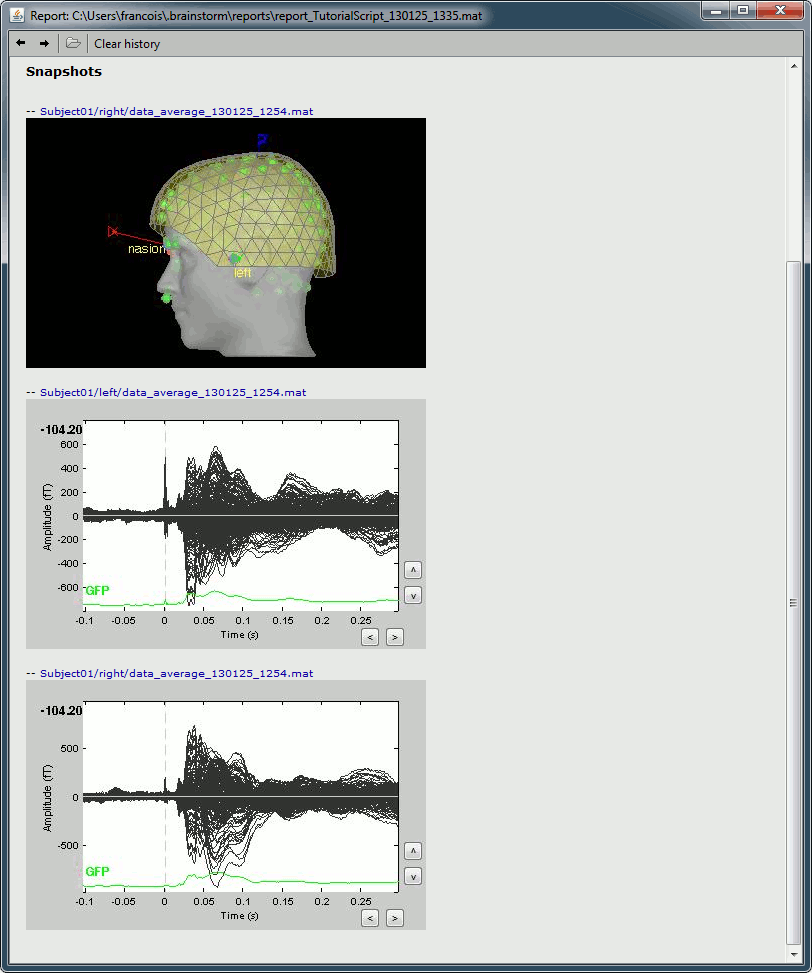
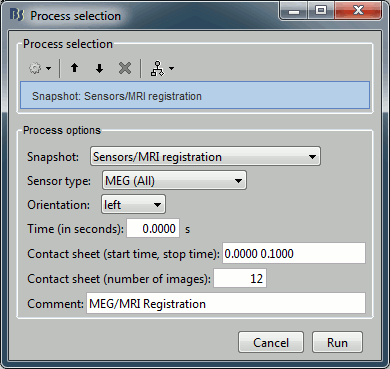
File > Save snapshot: Sensors/MRI registration
Input: 2 averages ; Output: 2 averages
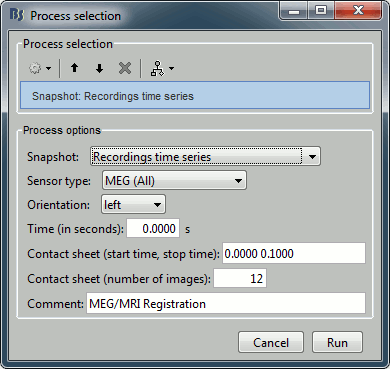
File > Save snapshot: Recordings time series
Input: 2 averages ; Output: 2 averages
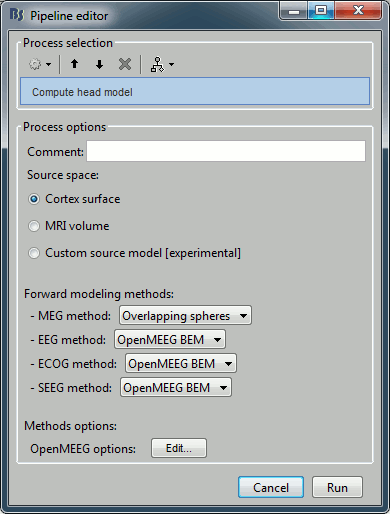
Sources > Compute head model
Input: 2 averages ; Output: 2 averages
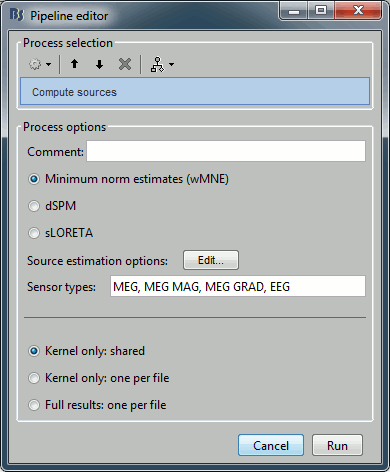
Sources > Compute sources
Input: 2 averages ; Output: all the source files (1 raw + 2 average + 199 epochs = 202 files)
Save the pipeline
Save in current workspace
Use the menus on top of the pipeline editor to save this list of processes on your computer. The menu "Save > New..." will create an entry readily available in your Brainstorm installation in the Load section of the same menu.
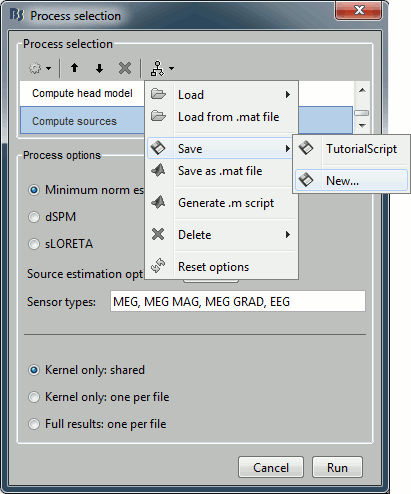
Export as script
Use the menu "Generate .m script" to create a Matlab script that would have the exact same result as running this analysis pipeline from the Brainstorm interface.
This script is also available in the Brainstorm distribution: brainstorm3/toolbox/script/tutorial_raw.m
% Script generated by Brainstorm v3.2 (22-Jul-2014)
% Input files
sFiles = [];
SubjectNames = {...
'Subject01'};
RawFiles = {...
'C:\Work\RawData\Tutorials\sample_raw\Anatomy', ...
'C:\Work\RawData\Tutorials\sample_raw\Data\subj001_somatosensory_20111109_01_AUX-f.ds'};
% Start a new report
bst_report('Start', sFiles);
% Process: Import anatomy folder
sFiles = bst_process('CallProcess', 'process_import_anatomy', ...
sFiles, [], ...
'subjectname', SubjectNames{1}, ...
'mrifile', {RawFiles{1}, 'FreeSurfer'}, ...
'nvertices', 15000, ...
'nas', [127, 212, 123], ...
'lpa', [55, 124, 119], ...
'rpa', [200, 129, 114], ...
'ac', [129, 137, 157], ...
'pc', [129, 113, 157], ...
'ih', [129, 118, 209]);
% Process: Create link to raw file
sFiles = bst_process('CallProcess', 'process_import_data_raw', ...
sFiles, [], ...
'subjectname', SubjectNames{1}, ...
'datafile', {RawFiles{2}, 'CTF'}, ...
'channelreplace', 1, ...
'channelalign', 1);
% Process: Notch filter: 60Hz 120Hz 180Hz
sFiles = bst_process('CallProcess', 'process_notch', ...
sFiles, [], ...
'freqlist', [60, 120, 180], ...
'sensortypes', 'MEG, EEG', ...
'read_all', 0);
% Process: Detect eye blinks
sFiles = bst_process('CallProcess', 'process_evt_detect_eog', ...
sFiles, [], ...
'channelname', 'EEG058', ...
'timewindow', [], ...
'eventname', 'blink');
% Process: Detect heartbeats
sFiles = bst_process('CallProcess', 'process_evt_detect_ecg', ...
sFiles, [], ...
'channelname', 'EEG057', ...
'timewindow', [], ...
'eventname', 'cardiac');
% Process: SSP EOG: blink
sFiles = bst_process('CallProcess', 'process_ssp_eog', ...
sFiles, [], ...
'eventname', 'blink', ...
'sensortypes', 'MEG, EEG', ...
'usessp', 0);
% Process: Import MEG/EEG: Events
sFiles = bst_process('CallProcess', 'process_import_data_event', ...
sFiles, [], ...
'subjectname', SubjectNames{1}, ...
'condition', '', ...
'eventname', 'left, right', ...
'timewindow', [], ...
'epochtime', [-0.1, 0.3], ...
'createcond', 1, ...
'ignoreshort', 1, ...
'usectfcomp', 1, ...
'usessp', 1, ...
'freq', [], ...
'baseline', [-0.1, -0.0008333333333]);
% Process: Add time offset: -4.20ms
sFiles = bst_process('CallProcess', 'process_timeoffset', ...
sFiles, [], ...
'offset', -0.0042, ...
'overwrite', 1);
% Process: Compute noise covariance
sFiles = bst_process('CallProcess', 'process_noisecov', ...
sFiles, [], ...
'baseline', [-0.1042, 0], ...
'dcoffset', 1, ...
'method', 1, ... % Full noise covariance matrix
'copycond', 0, ...
'copysubj', 0);
% Process: Average: By condition (subject average)
sFiles = bst_process('CallProcess', 'process_average', ...
sFiles, [], ...
'avgtype', 3, ...
'avg_func', 1, ... % Arithmetic average: mean(x)
'keepevents', 0);
% Process: Snapshot: Sensors/MRI registration
sFiles = bst_process('CallProcess', 'process_snapshot', ...
sFiles, [], ...
'target', 1, ... % Sensors/MRI registration
'modality', 1, ... % MEG (All)
'orient', 1, ... % left
'time', 0, ...
'contact_time', [0, 0.1], ...
'contact_nimage', 12, ...
'comment', 'MEG/MRI Registration');
% Process: Snapshot: Recordings time series
sFiles = bst_process('CallProcess', 'process_snapshot', ...
sFiles, [], ...
'target', 5, ... % Recordings time series
'modality', 1, ... % MEG (All)
'orient', 1, ... % left
'time', 0, ...
'contact_time', [0, 0.1], ...
'contact_nimage', 12, ...
'comment', 'Evoked response');
% Process: Compute head model
sFiles = bst_process('CallProcess', 'process_headmodel', ...
sFiles, [], ...
'comment', '', ...
'sourcespace', 1, ...
'meg', 3, ... % Overlapping spheres
'eeg', 3, ... % OpenMEEG BEM
'ecog', 2, ... % OpenMEEG BEM
'seeg', 2, ...
'openmeeg', struct(...
'BemFiles', {{}}, ...
'BemNames', {{'Scalp', 'Skull', 'Brain'}}, ...
'BemCond', [1, 0.0125, 1], ...
'BemSelect', [1, 1, 1], ...
'isAdjoint', 0, ...
'isAdaptative', 1, ...
'isSplit', 0, ...
'SplitLength', 4000));
% Process: Compute sources
sFiles = bst_process('CallProcess', 'process_inverse', ...
sFiles, [], ...
'comment', '', ...
'method', 1, ... % Minimum norm estimates (wMNE)
'wmne', struct(...
'NoiseCov', [], ...
'InverseMethod', 'wmne', ...
'ChannelTypes', {{}}, ...
'SNR', 3, ...
'diagnoise', 0, ...
'SourceOrient', {{'fixed'}}, ...
'loose', 0.2, ...
'depth', 1, ...
'weightexp', 0.5, ...
'weightlimit', 10, ...
'regnoise', 1, ...
'magreg', 0.1, ...
'gradreg', 0.1, ...
'eegreg', 0.1, ...
'ecogreg', 0.1, ...
'seegreg', 0.1, ...
'fMRI', [], ...
'fMRIthresh', [], ...
'fMRIoff', 0.1, ...
'pca', 1), ...
'sensortypes', 'MEG, MEG MAG, MEG GRAD, EEG', ...
'output', 1); % Kernel only: shared
% Save and display report
ReportFile = bst_report('Save', sFiles);
bst_report('Open', ReportFile);
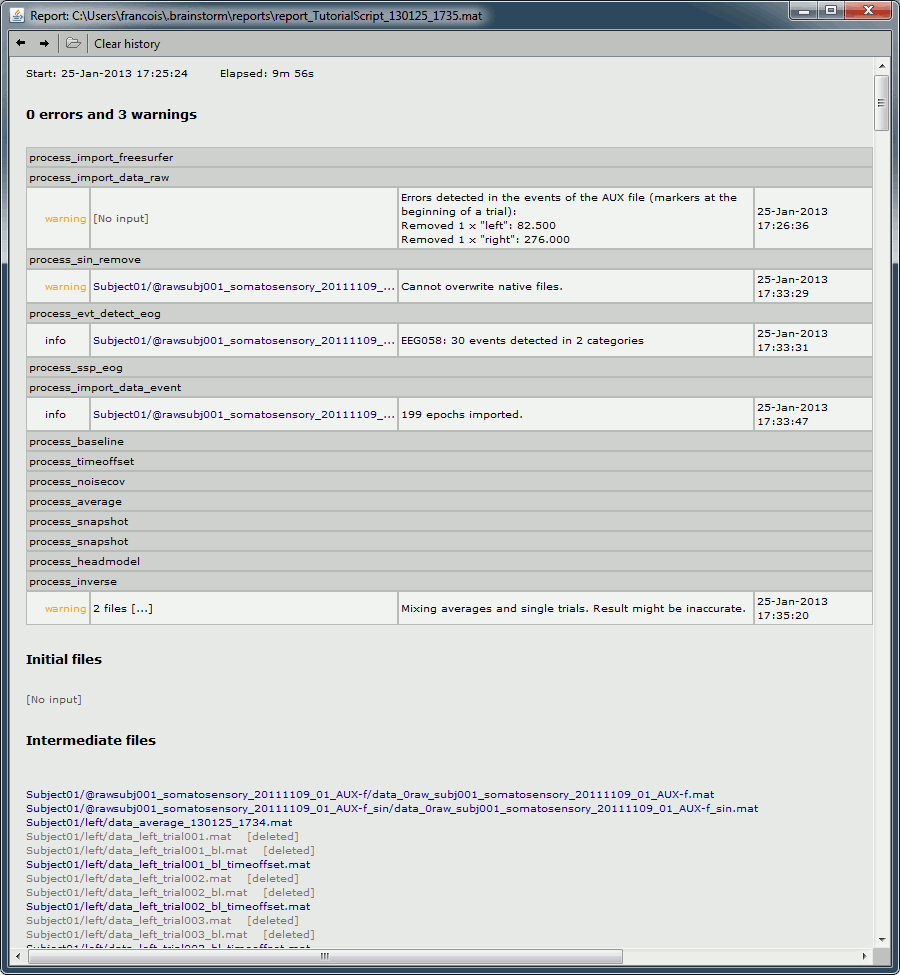
Report viewer
Click on Run to start the script.
As this process is taking screen captures, do not use your computer for something else at the same time: if another window covers the Brainstorm figures, it will not capture the right images.
At the end, the report viewer is opened to show the status of all the processes, the information messages, the list of input and output files, and the screen captures. The report is saved in your home folder ($home/.brainstorm/reports). If you close this window, you can get it back with the menu File > Report viewer.