|
Size: 44
Comment:
|
Size: 14564
Comment:
|
| Deletions are marked like this. | Additions are marked like this. |
| Line 2: | Line 2: |
| ''Authors: Francois Tadel '' {{attachment:CAT.gif||align="right",width="195px"}} [[http://www.neuro.uni-jena.de/cat/|CAT]] is a SPM12 toolbox that is fully interfaced with Brainstorm. It can replace efficiently FreeSurfer for generating the cortical surface from any T1 MRI. It runs on '''any OS''' in '''about 1 hour''', instead of the typical 24hr FreeSurfer recon-all processing. The surfaces are registered to the templates with the FreeSurfer spheres, and include many surface and volume parcellations. You can either install and run the CAT segmentation from Brainstorm, or run it separately and import its outputs as you would do with FreeSurfer. <<TableOfContents(2,2)>> == Install CAT12 == CAT12 requires the prior installation of SPM12. Both are Matlab-based programs that be installed automatically as [[Tutorials/Plugins|Brainstorm plugins]]: * Plugins > spm12 > Install * Plugins > Anatomy > spm12 > Install<<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:install.gif}} If you want to use your own installation of SPM12/CAT12 instead, refer to the [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/Plugins#Example:_How_to_set_up_FieldTrip|plugins tutorial]]. * SPM12 download: https://www.fil.ion.ucl.ac.uk/spm/software/download/ * CAT12 download: http://www.neuro.uni-jena.de/cat/index.html#DOWNLOAD == Cite CAT12 == If you use CAT from Brainstorm for MRI segmentation, please cite the following article in your publications: Gaser C, Dahnke R, Kurth F, Luders E<<BR>>CAT - A Computational Anatomy Toolbox for the Analysis of Structural MRI Data<<BR>>'''NeuroImage''', in review == Run CAT from Brainstorm == * Switch to the anatomy side of the database explorer. * Create a new subject, set the default anatomy option to "No, use individual anatomy". * Import the T1 MRI for this subject. * Set the [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/ImportAnatomy#Fiducial_points|fiducial points]] manually (NAS/LPA/RPA) or [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/ImportAnatomy#MNI_normalization|compute the MNI normalization]]. * Right-click on the MRI > '''MRI segmentation > CAT12'''. Two options can be selected interactively: the number of final vertices in the cortex surface, and the computation additional volume parcellations. <<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:segmentMenu.gif}} * Alternatively, use the process: '''Import anatomy > Segment MRI with SPM12/CAT12'''. <<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:segmentProcess.gif}} * With the process version, you have access to more options: * '''TPM atlas''': Location of the template tissue probabilistic maps. If empty, it uses by default the standard TPM.nii available in SPM12 (usually downloaded automatically in the folder $HOME/.brainstorm/defaults/spm/TPM.nii). It can be interesting to replace it with a probabilistic atlas better adapted to specific population, eg. the children atlas from CAT12 (spm12/toolbox/cat12/templates_volumes/TPM_Age11.5.nii) * '''Use spherical registration''': Call CAT12 with the highest possible accuracy, which includes the [[http://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/LabelFreeSurfer#Registered_sphere|spherical registration]] to the FSAverage template. Enabling this option takes much longer, but is necessary for importing all the FreeSurfer atlases, projecting the sources maps to a common template in the case of group analysis, and computing accurate cortical thickness maps. * '''Compute volume parcellations''': Compute and import all the volume parcellations that are available in CAT12: AAL3, CoBrALab, Hammers, IBSR, JulichBrain v2, LPBA40, Mori, Schaefer2018 * '''Import cortical thickness maps''': Enable this option to import the cortical thickness computed by CAT12 as source files. See section [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/SegCAT12#Cortical_thickness|Cortical thickness]]. * Brainstorm saves the MRI to process in a temporary folder, then calls CAT as a SPM batch:<<BR>>$HOME/.brainstorm/tmp/cat12/spm_cat12.nii * All the output from CAT is saved in the same temporary folder. At the end, Brainstorm imports the output folder as the anatomy for the selected subject. If the process crashes, you can inspect the contents of this folder for indices on how to solve the problem. If the segmentation and the import is successful, the temporary folder is deleted. * A report is displayed by CAT, and saved as an image and a PDF file in tmp/cat12/report. <<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:catreportj_spm_cat12.jpg||width="600",height="844"}} == Troubleshooting == * Error about a missing function '''spm_ov_mesh.m''': you need to update SPM12, from the Brainstorm plugins menu, or run "spm_update" from the Matlab command line. See [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/forums/t/cat12-segmentation-error-in-linux-and-windows/13409/2|forum post]]. * Search the [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/forums/tag/cat12|Brainstorm forum]] or create a new topic. * Search the [[https://www.jiscmail.ac.uk/cgi-bin/wa-jisc.exe?A0=SPM|SPM mailing list archive]] or send an email to this list. == Importing the results in Brainstorm == If you run the segmentation process from Brainstorm, the import will be done automatically. Otherwise, if you need to import an existing CAT segmentation, here is the following procedure. * Right-click on the subject > '''Import anatomy folder'''.<<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:importSelect.gif}} * '''Import anatomy folder''': Interactive import: asks for the number of vertices expected in the final cortex surfaces, for the volume atlases, and for the location of the fiducials NAS/LPA/RPA. Select this option in the case of an MEG study, when you know exactly where the fiducials were digitized during the MEG acquisition. See tutorial [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/ChannelFile#Automatic_registration|MRI registration]]. * '''Import anatomy folder (auto)''': Automatic import: Computes the [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/CoordinateSystems#MNI_coordinates|linear MNI normalization]], uses default positions from the MNI atlas for the NAS/LPA/RPA fiducials, uses 15000 vertices for the cortex downsampled surfaces, and imports all the volume atlases. * Select one the CAT12 import options and select the top folder of the CAT12 segmentation: * '''CAT12''': Import the T1 MRI, pial and white cortex surfaces, surface parcellations, surface spherical registration, surface and volume parcellations. Reconstruct the head surface. * '''CAT12 + ''''''Thickness''':Same as above, with the cortical thickness maps imported as source maps. * A figure is automatically shown at the end of the process, to check visually that the low-resolution cortex and head surfaces were properly generated and imported. If it doesn't look like the following picture, do not go any further in your source analysis, [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/LabelFreeSurfer#Handling_errors|fix the anatomy]] first. <<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:checkDb.gif}} == Files imported == The files that are imported from the segmentation output folder are the following: * /'''*.nii''' (T1 MRI volume - only one .nii file allowed in the top-level folder) * /surf/'''?h.central.*.gii''' (left/right hemisphere of the central surface) * /surf/'''?h.sphere.reg.*.gii''' (left/right [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/LabelFreeSurfer#Registered_sphere|FreeSurfer registered spheres]]) * /surf/'''?h.*.annot''' (cortical surface-based atlases) * /surf/'''?h.thickness'''.* (texture with the cortical thickness at each vertex) * /mri/'''p*.nii''' (tissue probability maps, used to create the tissue segmentation volume) * /mri_atlas/'''*.nii''' (volume parcellations) The '''central surfaces''' generated by CAT are meshes half-way between the grey-white interface and the external pial surface. The files you can see in the database explorer at the end: * '''MRI''': The T1 MRI of the subject, imported from the .nii file at the top-level folder. * '''head mask''' (10000,0,2): Scalp surface generated by Brainstorm. The numbers indicate the parameters that were automatically used for this head: vertices=10000, erode factor=0, fill holes=2. * '''cortex_250000V''': High-resolution cortex surface that was generated by CAT. * '''cortex_15000V''': Low-resolution cortex surface, downsampled using the reducepatch function from Matlab (it keeps a meaningful subset of vertices from the original surface). It appears in green in the database explorer, ie. it is going to be used as the default by the processes that require a cortex surface. == Cortical parcellations == FreeSurfer's FSAverage subject includes parcellations of the cortical surface in anatomical or functional regions. The description of this feature is available here:<<BR>>http://freesurfer.net/fswiki/CorticalParcellation Using CAT12 from Brainstorm, you have access to 15 atlases on all the individual brains: * '''Destrieux''' atlas (atlases_surfaces/?h.aparc_a2009s.freesurfer.annot): [[http://ftp.nmr.mgh.harvard.edu/fswiki/CorticalParcellation|more info]] * '''Desikan-Killiany''' atlas (atlases_surfaces/?h.aparc_DK40.freesurfer.annot): [[http://ftp.nmr.mgh.harvard.edu/fswiki/CorticalParcellation|more info]] * '''HCP MMP1''' atlas (atlases_surfaces/?h.aparc_HCP_MMP1.freesurfer.annot): [[https://cjneurolab.org/2016/11/22/hcp-mmp1-0-volumetric-nifti-masks-in-native-structural-space/|more info]] * '''Schaefer 2018''' atlases (atlases_surfaces_32k/?h.Schaefer2018_*.annot): [[https://www.biorxiv.org/content/biorxiv/early/2017/07/16/135632.full.pdf|more info]] These atlases are imported in Brainstorm as scouts (cortical regions of interest), and saved directly in the surface files. To check where they are saved: right-click on the low-resolution cortex file > File > View file contents. You can see that 17 structures "Atlas" are available, the first one that has Name='User scouts', and the second one Name='Destrieux'. {{attachment:viewMat.gif||width="430",height="404"}} To access them from the interface: Double-click on the cortex and go to the ''Scout'' tab, and click on the drop-down list to select another ''Atlas ''(ie group of scouts): {{attachment:scoutTab.gif||width="187",height="180"}} {{attachment:atlasDestrieux.gif||width="227",height="180"}} {{attachment:atlasDK.gif||width="229",height="180"}} {{attachment:atlasHCP.gif||width="224",height="180"}} {{attachment:atlasSchaefer7.gif||width="225",height="180"}} {{attachment:atlasSchaefer17.gif||width="225",height="180"}} == Cortical thickness == The cortical thickness can be saved as a cortical map in the database (a "results" file). This result is generated when using the file format "'''CAT12 folder + Thickness maps'''" in the Import anatomy folder selection. {{attachment:thicknessFile.gif}} {{attachment:thicknessMap.gif||width="300",height="203"}} == SPM batch == The CAT segmentation is executed with the following SPM12 batch: {{{ matlabbatch{1}.spm.tools.cat.estwrite.data = {[NiiFile ',1']}; matlabbatch{1}.spm.tools.cat.estwrite.data_wmh = {''}; matlabbatch{1}.spm.tools.cat.estwrite.useprior = ''; matlabbatch{1}.spm.tools.cat.estwrite.nproc = 0; % Blocking call to CAT12 matlabbatch{1}.spm.tools.cat.estwrite.opts.tpm = {TpmNii}; % User-defined TPM atlas matlabbatch{1}.spm.tools.cat.estwrite.output.bias.warped = 0; matlabbatch{1}.spm.tools.cat.estwrite.output.GM.native = 1; % GM tissue maps matlabbatch{1}.spm.tools.cat.estwrite.output.GM.warped = 0; matlabbatch{1}.spm.tools.cat.estwrite.output.GM.mod = 0; matlabbatch{1}.spm.tools.cat.estwrite.output.GM.dartel = 0; matlabbatch{1}.spm.tools.cat.estwrite.output.WM.native = 1; % WM tissue maps matlabbatch{1}.spm.tools.cat.estwrite.output.WM.warped = 0; matlabbatch{1}.spm.tools.cat.estwrite.output.WM.mod = 0; matlabbatch{1}.spm.tools.cat.estwrite.output.WM.dartel = 0; matlabbatch{1}.spm.tools.cat.estwrite.output.TPMC.native = 1; % Tissue classes 4-6 matlabbatch{1}.spm.tools.cat.estwrite.output.TPMC.warped = 0; matlabbatch{1}.spm.tools.cat.estwrite.output.TPMC.mod = 0; matlabbatch{1}.spm.tools.cat.estwrite.output.TPMC.dartel = 0; matlabbatch{1}.spm.tools.cat.estwrite.output.CSF.native = 1; % CSF tissue maps matlabbatch{1}.spm.tools.cat.estwrite.output.CSF.warped = 0; matlabbatch{1}.spm.tools.cat.estwrite.output.CSF.mod = 0; matlabbatch{1}.spm.tools.cat.estwrite.output.CSF.dartel = 0; matlabbatch{1}.spm.tools.cat.estwrite.output.label.native = 1; % CSF=1,GM=2,WM=3,WMH=4 matlabbatch{1}.spm.tools.cat.estwrite.output.label.warped = 0; matlabbatch{1}.spm.tools.cat.estwrite.output.label.dartel = 0; matlabbatch{1}.spm.tools.cat.estwrite.output.surface = 1; % 1: lh+rh, sph registration % Volume atlases if isVolumeAtlases matlabbatch{1}.spm.tools.cat.estwrite.output.warps = [1 1]; matlabbatch{1}.spm.tools.cat.estwrite.output.ROI = 1; matlabbatch{1}.spm.tools.cat.estwrite.output.ROImenu.atlases.neuromorphometrics = 1; matlabbatch{1}.spm.tools.cat.estwrite.output.ROImenu.atlases.lpba40 = 1; matlabbatch{1}.spm.tools.cat.estwrite.output.ROImenu.atlases.cobra = 1; matlabbatch{1}.spm.tools.cat.estwrite.output.ROImenu.atlases.hammers = 1; matlabbatch{1}.spm.tools.cat.estwrite.output.atlas.native = 1; else matlabbatch{1}.spm.tools.cat.estwrite.output.warps = [0 0]; matlabbatch{1}.spm.tools.cat.estwrite.output.ROI = 0; matlabbatch{1}.spm.tools.cat.estwrite.output.ROImenu.noROI = struct([]); matlabbatch{1}.spm.tools.cat.estwrite.output.ROImenu.atlases.neuromorphometrics = 0; matlabbatch{1}.spm.tools.cat.estwrite.output.ROImenu.atlases.lpba40 = 0; matlabbatch{1}.spm.tools.cat.estwrite.output.ROImenu.atlases.cobra = 0; matlabbatch{1}.spm.tools.cat.estwrite.output.ROImenu.atlases.hammers = 0; end % Run SPM batch spm_jobman('initcfg'); spm_jobman('run',matlabbatch); }}} == Additional documentation == * Forum: [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/forums/t/various-cat12-errors-with-different-versions-of-matlab-operating-systems/13435/5|Debugging CAT12 integration in Brainstorm]] * Forum: [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/forums/t/cat12-missing-files/23121/3|CAT12 Missing Files + ICBM152 segmentation]] * Git issue: [[https://github.com/brainstorm-tools/brainstorm3/issues/352|Bugs CAT12 v1728]] |
T1-MRI Segmentation with SPM12 / CAT12
Authors: Francois Tadel
 CAT is a SPM12 toolbox that is fully interfaced with Brainstorm. It can replace efficiently FreeSurfer for generating the cortical surface from any T1 MRI. It runs on any OS in about 1 hour, instead of the typical 24hr FreeSurfer recon-all processing. The surfaces are registered to the templates with the FreeSurfer spheres, and include many surface and volume parcellations. You can either install and run the CAT segmentation from Brainstorm, or run it separately and import its outputs as you would do with FreeSurfer.
CAT is a SPM12 toolbox that is fully interfaced with Brainstorm. It can replace efficiently FreeSurfer for generating the cortical surface from any T1 MRI. It runs on any OS in about 1 hour, instead of the typical 24hr FreeSurfer recon-all processing. The surfaces are registered to the templates with the FreeSurfer spheres, and include many surface and volume parcellations. You can either install and run the CAT segmentation from Brainstorm, or run it separately and import its outputs as you would do with FreeSurfer.
Contents
Install CAT12
CAT12 requires the prior installation of SPM12. Both are Matlab-based programs that be installed automatically as Brainstorm plugins:
Plugins > spm12 > Install
Plugins > Anatomy > spm12 > Install
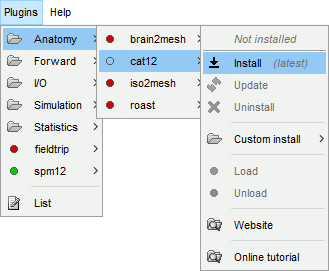
If you want to use your own installation of SPM12/CAT12 instead, refer to the plugins tutorial.
SPM12 download: https://www.fil.ion.ucl.ac.uk/spm/software/download/
CAT12 download: http://www.neuro.uni-jena.de/cat/index.html#DOWNLOAD
Cite CAT12
If you use CAT from Brainstorm for MRI segmentation, please cite the following article in your publications:
Gaser C, Dahnke R, Kurth F, Luders E
CAT - A Computational Anatomy Toolbox for the Analysis of Structural MRI Data
NeuroImage, in review
Run CAT from Brainstorm
- Switch to the anatomy side of the database explorer.
- Create a new subject, set the default anatomy option to "No, use individual anatomy".
- Import the T1 MRI for this subject.
Set the fiducial points manually (NAS/LPA/RPA) or compute the MNI normalization.
Right-click on the MRI > MRI segmentation > CAT12. Two options can be selected interactively: the number of final vertices in the cortex surface, and the computation additional volume parcellations.
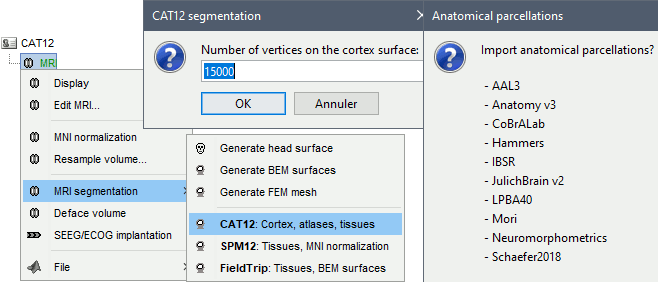
Alternatively, use the process: Import anatomy > Segment MRI with SPM12/CAT12.
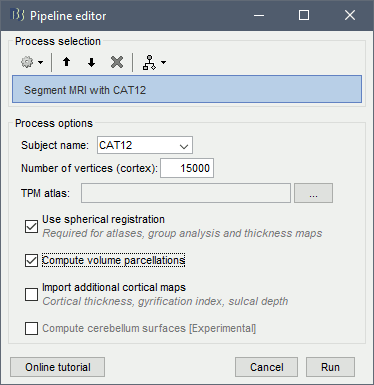
- With the process version, you have access to more options:
TPM atlas: Location of the template tissue probabilistic maps. If empty, it uses by default the standard TPM.nii available in SPM12 (usually downloaded automatically in the folder $HOME/.brainstorm/defaults/spm/TPM.nii). It can be interesting to replace it with a probabilistic atlas better adapted to specific population, eg. the children atlas from CAT12 (spm12/toolbox/cat12/templates_volumes/TPM_Age11.5.nii)
Use spherical registration: Call CAT12 with the highest possible accuracy, which includes the spherical registration to the FSAverage template. Enabling this option takes much longer, but is necessary for importing all the FreeSurfer atlases, projecting the sources maps to a common template in the case of group analysis, and computing accurate cortical thickness maps.
Compute volume parcellations: Compute and import all the volume parcellations that are available in CAT12: AAL3, CoBrALab, Hammers, IBSR, JulichBrain v2, LPBA40, Mori, Schaefer2018
Import cortical thickness maps: Enable this option to import the cortical thickness computed by CAT12 as source files. See section Cortical thickness.
Brainstorm saves the MRI to process in a temporary folder, then calls CAT as a SPM batch:
$HOME/.brainstorm/tmp/cat12/spm_cat12.nii- All the output from CAT is saved in the same temporary folder. At the end, Brainstorm imports the output folder as the anatomy for the selected subject. If the process crashes, you can inspect the contents of this folder for indices on how to solve the problem. If the segmentation and the import is successful, the temporary folder is deleted.
A report is displayed by CAT, and saved as an image and a PDF file in tmp/cat12/report.
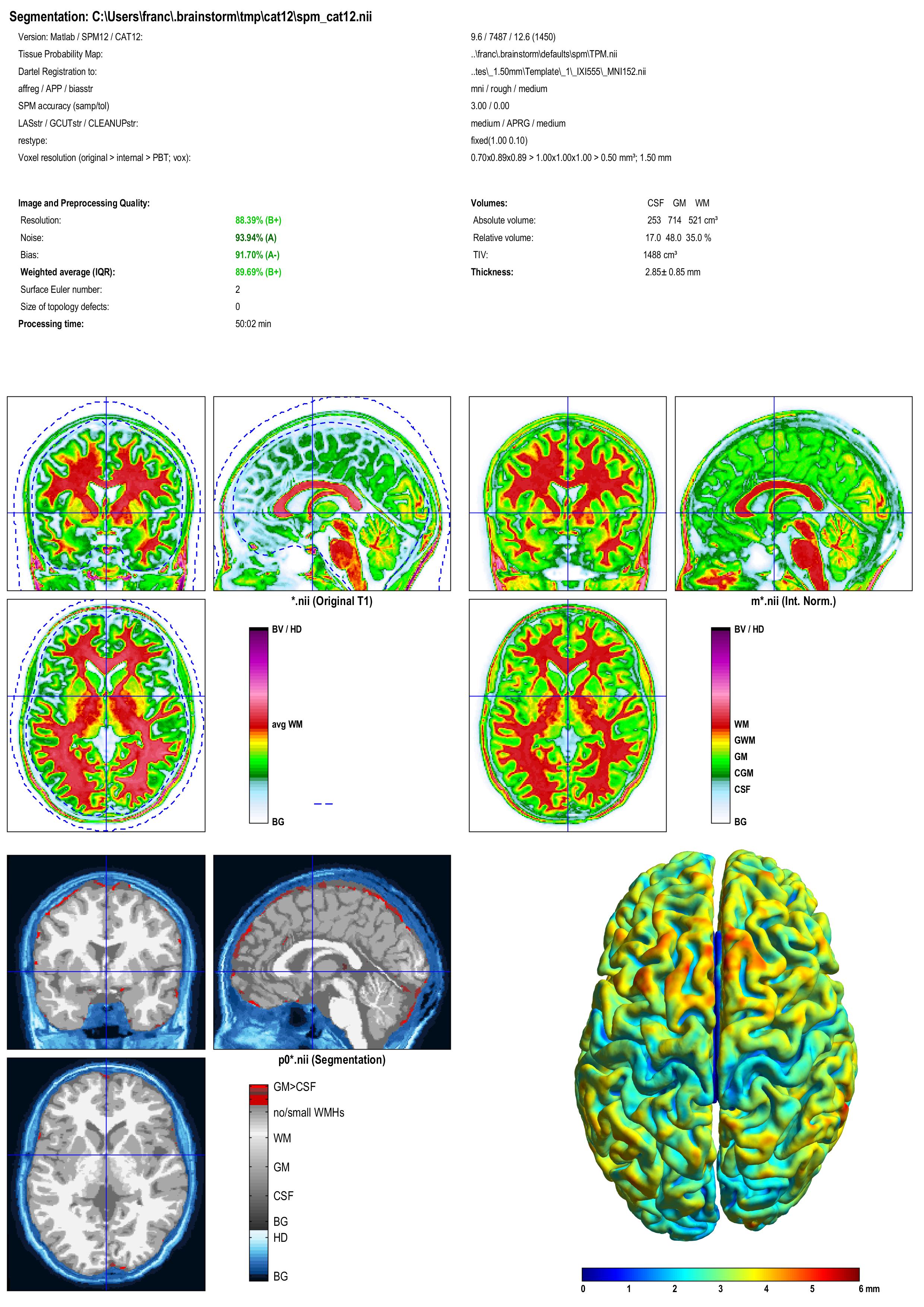
Troubleshooting
Error about a missing function spm_ov_mesh.m: you need to update SPM12, from the Brainstorm plugins menu, or run "spm_update" from the Matlab command line. See forum post.
Search the Brainstorm forum or create a new topic.
Search the SPM mailing list archive or send an email to this list.
Importing the results in Brainstorm
If you run the segmentation process from Brainstorm, the import will be done automatically. Otherwise, if you need to import an existing CAT segmentation, here is the following procedure.
Right-click on the subject > Import anatomy folder.
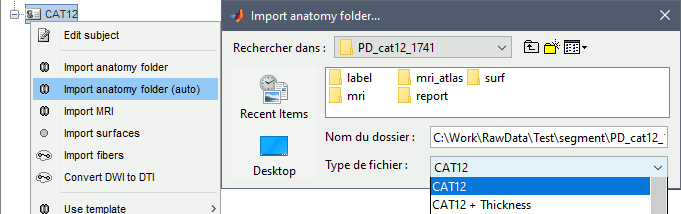
Import anatomy folder: Interactive import: asks for the number of vertices expected in the final cortex surfaces, for the volume atlases, and for the location of the fiducials NAS/LPA/RPA. Select this option in the case of an MEG study, when you know exactly where the fiducials were digitized during the MEG acquisition. See tutorial MRI registration.
Import anatomy folder (auto): Automatic import: Computes the linear MNI normalization, uses default positions from the MNI atlas for the NAS/LPA/RPA fiducials, uses 15000 vertices for the cortex downsampled surfaces, and imports all the volume atlases.
- Select one the CAT12 import options and select the top folder of the CAT12 segmentation:
CAT12: Import the T1 MRI, pial and white cortex surfaces, surface parcellations, surface spherical registration, surface and volume parcellations. Reconstruct the head surface.
CAT12 + Thickness:Same as above, with the cortical thickness maps imported as source maps.
A figure is automatically shown at the end of the process, to check visually that the low-resolution cortex and head surfaces were properly generated and imported. If it doesn't look like the following picture, do not go any further in your source analysis, fix the anatomy first.
Files imported
The files that are imported from the segmentation output folder are the following:
/*.nii (T1 MRI volume - only one .nii file allowed in the top-level folder)
/surf/?h.central.*.gii (left/right hemisphere of the central surface)
/surf/?h.sphere.reg.*.gii (left/right FreeSurfer registered spheres)
/surf/?h.*.annot (cortical surface-based atlases)
/surf/?h.thickness.* (texture with the cortical thickness at each vertex)
/mri/p*.nii (tissue probability maps, used to create the tissue segmentation volume)
/mri_atlas/*.nii (volume parcellations)
The central surfaces generated by CAT are meshes half-way between the grey-white interface and the external pial surface.
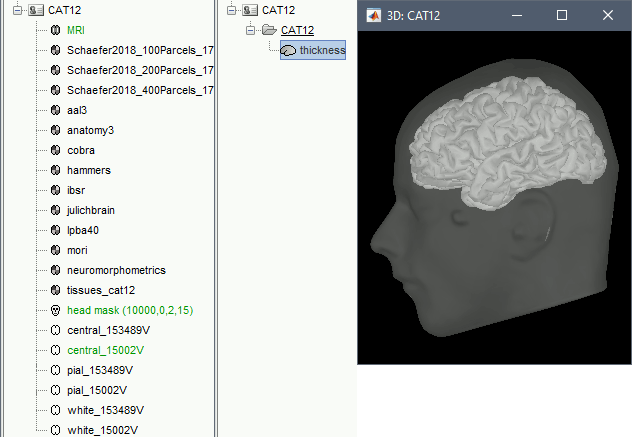
The files you can see in the database explorer at the end:
MRI: The T1 MRI of the subject, imported from the .nii file at the top-level folder.
head mask (10000,0,2): Scalp surface generated by Brainstorm. The numbers indicate the parameters that were automatically used for this head: vertices=10000, erode factor=0, fill holes=2.
cortex_250000V: High-resolution cortex surface that was generated by CAT.
cortex_15000V: Low-resolution cortex surface, downsampled using the reducepatch function from Matlab (it keeps a meaningful subset of vertices from the original surface). It appears in green in the database explorer, ie. it is going to be used as the default by the processes that require a cortex surface.
Cortical parcellations
FreeSurfer's FSAverage subject includes parcellations of the cortical surface in anatomical or functional regions. The description of this feature is available here:
http://freesurfer.net/fswiki/CorticalParcellation
Using CAT12 from Brainstorm, you have access to 15 atlases on all the individual brains:
Destrieux atlas (atlases_surfaces/?h.aparc_a2009s.freesurfer.annot): more info
Desikan-Killiany atlas (atlases_surfaces/?h.aparc_DK40.freesurfer.annot): more info
HCP MMP1 atlas (atlases_surfaces/?h.aparc_HCP_MMP1.freesurfer.annot): more info
Schaefer 2018 atlases (atlases_surfaces_32k/?h.Schaefer2018_*.annot): more info
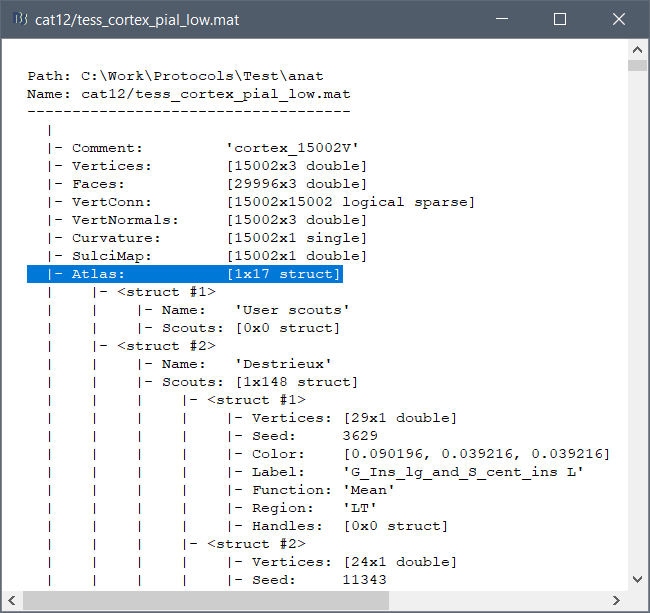
These atlases are imported in Brainstorm as scouts (cortical regions of interest), and saved directly in the surface files. To check where they are saved: right-click on the low-resolution cortex file > File > View file contents. You can see that 17 structures "Atlas" are available, the first one that has Name='User scouts', and the second one Name='Destrieux'.
To access them from the interface: Double-click on the cortex and go to the Scout tab, and click on the drop-down list to select another Atlas (ie group of scouts):
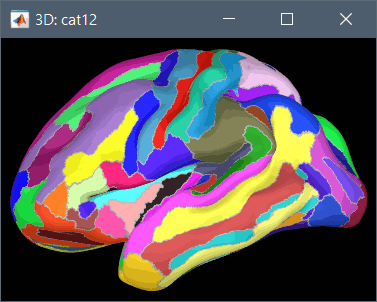
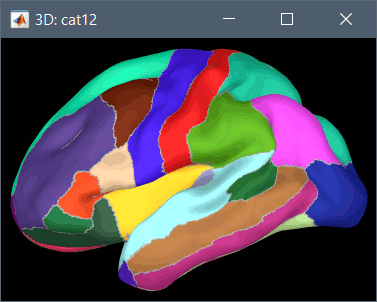
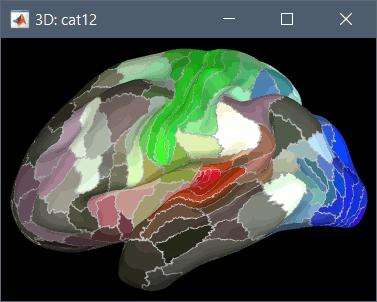
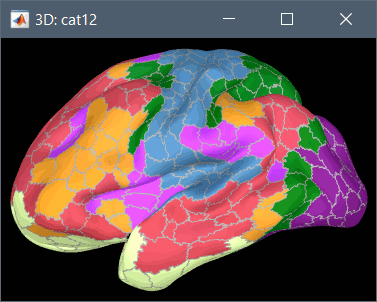
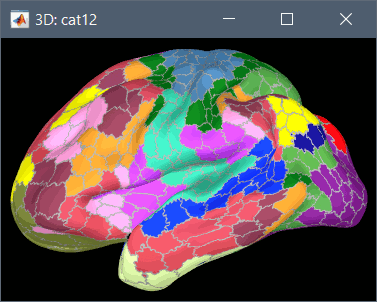
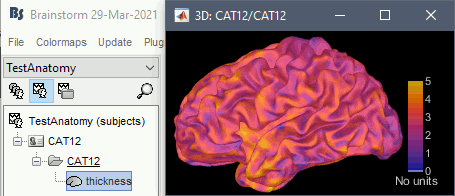
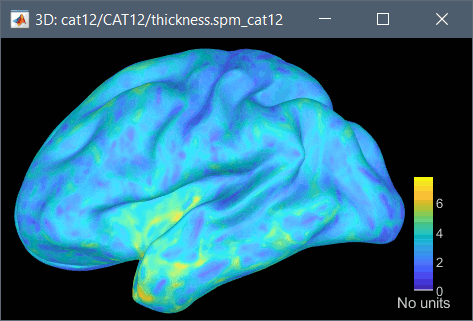
Cortical thickness
The cortical thickness can be saved as a cortical map in the database (a "results" file). This result is generated when using the file format "CAT12 folder + Thickness maps" in the Import anatomy folder selection.
SPM batch
The CAT segmentation is executed with the following SPM12 batch:
matlabbatch{1}.spm.tools.cat.estwrite.data = {[NiiFile ',1']};
matlabbatch{1}.spm.tools.cat.estwrite.data_wmh = {''};
matlabbatch{1}.spm.tools.cat.estwrite.useprior = '';
matlabbatch{1}.spm.tools.cat.estwrite.nproc = 0; % Blocking call to CAT12
matlabbatch{1}.spm.tools.cat.estwrite.opts.tpm = {TpmNii}; % User-defined TPM atlas
matlabbatch{1}.spm.tools.cat.estwrite.output.bias.warped = 0;
matlabbatch{1}.spm.tools.cat.estwrite.output.GM.native = 1; % GM tissue maps
matlabbatch{1}.spm.tools.cat.estwrite.output.GM.warped = 0;
matlabbatch{1}.spm.tools.cat.estwrite.output.GM.mod = 0;
matlabbatch{1}.spm.tools.cat.estwrite.output.GM.dartel = 0;
matlabbatch{1}.spm.tools.cat.estwrite.output.WM.native = 1; % WM tissue maps
matlabbatch{1}.spm.tools.cat.estwrite.output.WM.warped = 0;
matlabbatch{1}.spm.tools.cat.estwrite.output.WM.mod = 0;
matlabbatch{1}.spm.tools.cat.estwrite.output.WM.dartel = 0;
matlabbatch{1}.spm.tools.cat.estwrite.output.TPMC.native = 1; % Tissue classes 4-6
matlabbatch{1}.spm.tools.cat.estwrite.output.TPMC.warped = 0;
matlabbatch{1}.spm.tools.cat.estwrite.output.TPMC.mod = 0;
matlabbatch{1}.spm.tools.cat.estwrite.output.TPMC.dartel = 0;
matlabbatch{1}.spm.tools.cat.estwrite.output.CSF.native = 1; % CSF tissue maps
matlabbatch{1}.spm.tools.cat.estwrite.output.CSF.warped = 0;
matlabbatch{1}.spm.tools.cat.estwrite.output.CSF.mod = 0;
matlabbatch{1}.spm.tools.cat.estwrite.output.CSF.dartel = 0;
matlabbatch{1}.spm.tools.cat.estwrite.output.label.native = 1; % CSF=1,GM=2,WM=3,WMH=4
matlabbatch{1}.spm.tools.cat.estwrite.output.label.warped = 0;
matlabbatch{1}.spm.tools.cat.estwrite.output.label.dartel = 0;
matlabbatch{1}.spm.tools.cat.estwrite.output.surface = 1; % 1: lh+rh, sph registration
% Volume atlases
if isVolumeAtlases
matlabbatch{1}.spm.tools.cat.estwrite.output.warps = [1 1];
matlabbatch{1}.spm.tools.cat.estwrite.output.ROI = 1;
matlabbatch{1}.spm.tools.cat.estwrite.output.ROImenu.atlases.neuromorphometrics = 1;
matlabbatch{1}.spm.tools.cat.estwrite.output.ROImenu.atlases.lpba40 = 1;
matlabbatch{1}.spm.tools.cat.estwrite.output.ROImenu.atlases.cobra = 1;
matlabbatch{1}.spm.tools.cat.estwrite.output.ROImenu.atlases.hammers = 1;
matlabbatch{1}.spm.tools.cat.estwrite.output.atlas.native = 1;
else
matlabbatch{1}.spm.tools.cat.estwrite.output.warps = [0 0];
matlabbatch{1}.spm.tools.cat.estwrite.output.ROI = 0;
matlabbatch{1}.spm.tools.cat.estwrite.output.ROImenu.noROI = struct([]);
matlabbatch{1}.spm.tools.cat.estwrite.output.ROImenu.atlases.neuromorphometrics = 0;
matlabbatch{1}.spm.tools.cat.estwrite.output.ROImenu.atlases.lpba40 = 0;
matlabbatch{1}.spm.tools.cat.estwrite.output.ROImenu.atlases.cobra = 0;
matlabbatch{1}.spm.tools.cat.estwrite.output.ROImenu.atlases.hammers = 0;
end
% Run SPM batch
spm_jobman('initcfg');
spm_jobman('run',matlabbatch);
Additional documentation
Git issue: Bugs CAT12 v1728
