|
Size: 31087
Comment:
|
Size: 29888
Comment:
|
| Deletions are marked like this. | Additions are marked like this. |
| Line 1: | Line 1: |
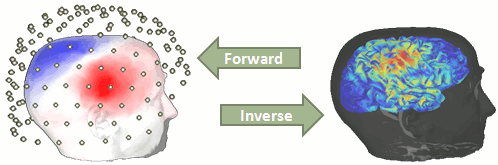
| = Tutorial 15: Source estimation = ''Authors: Francois Tadel, John C Mosher, Richard Leahy, Sylvain Baillet'' Now you have in your database a forward model matrix that explains how the cortical sources determine the values on the sensors. This is useful for simulations, but what we really need is to build the inverse information: how to estimate the sources when you have the recordings. Many solutions are described in the literature, some of them are implemented in Brainstorm, and only one is presented in this tutorial: the minimum-norm estimation. It is not really the most advanced solution, but it is one of the most robust. |
= Tutorial 22: Source estimation = '''[UNDER CONSTRUCTION]''' ''Authors: Francois Tadel, Elizabeth Bock, Rey R Ramirez, John C Mosher, Richard Leahy, Sylvain Baillet'' You have in your database a forward model matrix that explains how the cortical sources determine the values on the sensors. This is useful for simulations, but what we need is to build the inverse information: how to estimate the sources when we have the recordings. This tutorials introduces the tools available in Brainstorm for solving this inverse problem. |
| Line 8: | Line 10: |
| [[https://docs.google.com/document/d/1TsUVEu90--7AFxplxr76u9aEI9hNDhaOGx5Hdfdf1JI/edit?usp=sharing|Recent discussion about source modeling interface]] | == Ill-posed problem == Our goal is to estimate the activity of the 45,000 dipoles described by our forward model. However we only have a few hundreds of variables (the number of sensors). This inverse problem is ill-posed, there is an '''infinity of combinations''' of source activity that can generate exactly the same sensor topography. Inverting the forward problem directly is impossible, unless we add some strong priors in our model. Wikipedia says: "Inverse problems are some of the most important and well-studied mathematical problems in science and mathematics because they tell us about parameters that we cannot directly observe. They have wide application in optics, radar, acoustics, communication theory, signal processing, medical imaging, computer vision, geophysics, oceanography, astronomy, remote sensing, natural language processing, machine learning, nondestructive testing, and many other fields." . {{http://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/HeadModel?action=AttachFile&do=get&target=forward_inverse.gif|forward_inverse.gif|class="attachment"}} Many solutions have been proposed in the literature, based on different assumptions on the way the brain works and depending on the amount of information we already have on the effects we are studying. Among the hundreds of methods available, two classes of inverse models have been widely used in MEG/EEG source imaging in the past years: '''minimum-norm solutions''' and '''beamformers'''. Both approaches have the advantage of being '''linear''': the activity of the sources is a linear recombination of the MEG/EEG recordings. It is possible to solve the inverse problem independently of the recordings, making the data manipulation a lot easier and faster. Both are available in Brainstorm, so you can use the one the most adapted to your recordings or to your own personal expertise. Only the minimum norm estimates will be described in this tutorial, but the other solutions work exactly in the same way. == Source estimation options [TODO] == Before we start estimating the sources for the recordings available in our database, let's start with an overview of the options available. The screen capture below represents the basic options for the minimum norm estimates. The options for the other methods will be described in advanced tutorials. {{attachment:minnorm_options.gif}} === Method === * '''Minimum norm''': __Priors, justification, application case?__<<BR>> Require an estimation of the noise at the level of the sensors (noise covariance matrix). * '''Dipole modeling''': __?__ * '''LCMV beamformer''': __?__<<BR>>Require both a noise covariance matrix and a data covariance matrix (representation of the effect we are trying to localize in the brain, covariance of the latencies of interest). * __'''Recommended option'''__: Provided that we know at what latencies to look at, we can compute a correct data covariance matrix and may obtain a better spatial accuracy with a beamformer. However, in many cases we don't exactly know what we are looking at, the risks of misinterpretation of badly designed beamforming results are high. Brainstorm tends to favor minimum norm solutions, which have the advantage of needing less manual tuning for getting acceptable results. === Measure === The minimum norm estimates gives a measure of the current density flowing at the surface of the cortex. To visualize these results and compare them between subjects, we can normalize the MNE values to get a standardized level of activation with respect to the noise or baseline level (dSPM, sLORETA, MNp). * '''Current density map''': Whitened and depth-weigthed linear L2-minimum norm estimates algorithm inspired from Matti Hamalainen's MNE software. For a full description of this method, please refer to the [[http://www.nmr.mgh.harvard.edu/meg/manuals/MNE-manual-2.7.pdf|MNE manual]], section 6, "The current estimates". * '''dSPM''': Noise-normalized estimate (dynamical Statistical Parametric Mapping [Dale, 2000]). Its computation is based on the MNE solution. * '''sLORETA''': Noise-normalized estimate using the sLORETA approach (standardized LOw Resolution brain Electromagnetic TomogrAphy [Pasqual-Marqui, 2002]). sLORETA solutions have in general a smaller location bias than either the expected current (MNE) or the dSPM. * '''MNp''': ? * __'''Recommended option'''__: Discussed in the section "Source map normalization" === Source orientation === * '''Constrained: Normal to cortex''': Only one dipole at each vertex of the cortex surface, oriented normally to the surface. This is based on the anatomical observation that in the cortex, the neurons are mainly organized in macro-columns that are perpendicular to the cortex surface.<<BR>>Size of the inverse operator: [nVertices x nChannel]. * '''Constrained: Optimal orientation''': Only one dipole at each vertex of the cortex surface, oriented normally to the surface. This is based on the anatomical observation that in the cortex, the neurons are mainly organized in macro-columns that are perpendicular to the cortex surface.<<BR>>Size of the inverse operator: [nVertices x nChannel]. * '''Unconstrained''': At each vertex of the cortex surface, we define a base of three dipoles with orthogonal directions, then we estimate the sources for the three orientations independently. <<BR>>Size of the inverse operator: [3*nVertices x nChannel]. * '''Loose''': A version of the "unconstrained" option with a weak orientation constraint that emphasizes the importance of the sources with orientations that are close to the normal to the cortex. The value associated with this option set how "loose" should be the orientation constrain (recommended values in MNE are between 0.1 and 0.6, --loose option). <<BR>>Size of the inverse operator: [3*nVertices x nChannel]. * __'''Recommended option'''__: ?<<BR>>The constrained options use one dipole per orientation instead of three, therefore the source maps are smaller, faster to compute and display, and much more intuitive to process because we don't have to think about recombining the three values in one. However the normal orientation constraint is most of the time too strong and not realistic. <<BR>>Unconstrained sources look smoother and nicer but are not necessarily more accurate. |
| Line 11: | Line 51: |
| 1. Right-click on ''Subject01 / Right / ERF'' > ''Compute sources''.<<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:popupComputeSources.gif}} --- {{attachment:panelComputeSources.gif}} 1. With this window you can select the method you want to use to estimate the cortical currents, and the sensors you are going to use for this estimation. The default "Normal mode" only let you edit the following options:<<BR>> * '''Comment''': This field contains what is going to be displayed in the database explorer. * '''Method''': Please select wMNE. The other methods dSPM and sLORETA are also based on wMNE. They may give better and/or smoother results depending on the cases. * '''Sensors type''': Modalities that are used for the reconstruction. Here we only have one type of MEG sensors (axial gradiometers), so nothing to change. * '''Expert mode''': Show other options we do not care about right now. * Click on Run. 1. A new file is available in the database explorer.<<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:treeMinNorm.gif}} * It is displayed'' inside ''the recordings file ERF, because it is related to this file only. * Meaning of that weird filename: "MN" stands for "Minimum Norm", and "Constr" stands for "Constrained orientation" of the dipoles (the estimated dipoles orientations are constrained to be normal to the cortex). * You can have a look to the corresponding matrix file (right-click > File > View file contents). You would find all the options of forward and inverse modeling, and only one interesting field : '''ImagingKernel''', which contains the inversion kernel. It is a [nVertices x nChannels] matrix that has to be multiplied with the recordings matrix in order to get the activity for each source at all the time samples. * The minimum norm solution being a linear operation (the time series for each source is a linear combination of all the time series recorded by the sensors), we make this economy of saving only this linear operator instead of the full source matrix (nVertices x nTime)<<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:resultsMat.gif}} 1. Do the same for the ''Left / ERF'' file == Sources visualization == There are two main ways to display the sources: on the cortex surface and on the MRI slices. === Sources on cortex surface === 1. Double-click on recordings ''Right / ERF'', to display the time series (always nice to have a time reference). 1. Double-click on sources ''Right / ERF / MN: MEG''. <<BR>>Equivalent to right-click > Cortical activations > Display on cortex. 1. Go to the main peak around 46ms (by clicking on the times series figure)<<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:sources1.gif}} 1. Then you can manipulate the sources display exactly the same way as the surfaces and the 2D/3D recordings figures: rotation, zoom, ''Surface ''tab(smoothing, sulci, resection...), colormap, sensors, predefined orientations (keys from 0 to 7)... 1. Three new controls are available in the ''Surfaces ''tab, in panel ''Data options'': |
* In Run#01, right-click on the average response for the '''deviant''' stim > '''Compute sources [2015]'''.<<BR>>Select the options: Minimum norm imaging, Current density map, Constrained: Normal to cortex. <<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:minnorm_single.gif||height="462",width="492"}} * The other menu "Compute sources" brings the interface that was used previously in Brainstorm. We are going to keep maintaining the two implementations in parallel for a while for compatibility and cross-validation purposes. * The result of the computation is displayed as a dependent of the deviant average because it is related only to this file. In the file comment, "MN" stands minimum norm and "Constr" stands for "Constrained: normal orientation". <<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:minnorm_single_tree.gif}} == Display: Cortex surface == * Right-click on the sources for the deviant average > Cortical activations > '''Display on cortex'''.<<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:minnorm_single_popup.gif||height="167",width="380"}} * Double-click on the '''recordings '''for the deviant average to have time reference. <<BR>>In the filter tab, add a '''low-pass filter at 100Hz'''.<<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:display_cortex.gif||height="163",width="482"}} * Change the current time (click on the time series figure or use the keyboard arrows) and note it updates the source maps in the 3D figure. You can also use all the menus and shortcuts introduced in the anatomy tutorial (like setting the view with the keys from 0 to 6). * You can edit many display properties from the Surface tab: |
| Line 35: | Line 63: |
| * '''Min. size''': Hide all the small activated regions, ie. the connected color patches that contain a number of vertices smaller than this "min.size" value. | * '''Min. size''': Hide all the small activated regions, ie. the connected color patches that contain a number of vertices smaller than this "min size" value. |
| Line 37: | Line 65: |
| 1. Take a few minutes to understand what this threshold value represents.<<BR>> * The colorbar maximum depends on the way you configured your ''Sources ''colormap. In case the colormap is NOT normalized to current time frame, and the maximum is NOT set to a specific value, the colorbar maximum should be around 68 pA.m. * On the screenshot above, the threshold value was set to 35%. It means that only the sources that had a value over 0.35*68 = 23.8 pA.m were visible. * If you set the threshold to 0%, you display all the sources values on the cortex surface; and as most of the sources have values close to 0, the brain is mainly blue. * Move the slider and look for a threshold value that would give you a really focal source.The following figures represent the sources activations at t=46ms respectively with threshold at 0% and 90%.<<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:threshold0.gif}} {{attachment:threshold90.gif}} * The figure on the right shows the most active area of the cortex 46ms after an electric stimulation of the right thumb. As expected, it is localized in the left hemisphere, in the middle of post central gyrus (projection of the right hand in the primary somatosensory cortex). === Sources on MRI (3D) === 1. Close all the figures (''Close all'' button). Open the time series view for Right / ERF. 1. Right-click on Right / ERF / MN: MEG > Cortical activations > Display on MRI (3D). |
* Take a few minutes to understand what the '''amplitude threshold''' represents. * The colorbar maximum depends on the way you configured your ''Sources ''colormap. If the option "Maximum: Global" is selected, the maximum should be around 30 pA.m. This value is a rough estimate of the maximum amplitude, sometimes you may have to redefine it manually. * On the screen capture below, the threshold value is set to 90%. It means that only the sources that have a value over 0.90*30 = 27 pA.m are visible. <<BR>>The threshold level is indicated in the colorbar with a horizontal white line. * At the first response peak (91ms), the sources with high amplitudes are located around the primary somatosensory cortex, which is what we are expecting for an auditory stimulation. <<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:display_sliders.gif||height="225",width="478"}} == Display: MRI 3D == * Right-click on the source file > Cortical activations > Display on MRI (3D). |
| Line 51: | Line 77: |
| * '''Smooth level''': The sources values are smoothed after being re-interpolated in the volume. Those menus define the size of the smoothing kernel (fig2: smooth=2; fig3: smooth=5).<<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:mriMipAnat.gif||height="143px",width="176px"}} {{attachment:mriMipFunc.gif||height="142px",width="175px"}} {{attachment:mriSmooth.gif||height="141px",width="173px"}} 1. This view can be used to lots of different types of contact sheets: in time or in space, for each orientation. You can try all the menus. Example: Right-click on the figure > Snapshot > Volume contact sheet: axial: <<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:popupSnapshot.gif}} {{attachment:contactAxial.gif||height="288px",width="322px"}} === Sources on MRI (MRI Viewer) === |
* '''Smooth level''': The sources values are smoothed after being re-interpolated in the volume. These menus define the size of the smoothing kernel (fig2: smooth=2; fig3: smooth=5).<<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:mriMipAnat.gif||height="143px",width="176px"}} {{attachment:mriMipFunc.gif||height="142px",width="175px"}} {{attachment:mriSmooth.gif||height="141px",width="173px"}} == Display: MRI Viewer == |
| Line 58: | Line 83: |
| === Minimum norm values are not only positive === You should pay attention to a property of the current amplitudes that are given by the wMNE method: they can be positive of negative, and they oscillate around zero. It's not easy to figure out what is the exact meaning of a negative value respect with a positive value, and most of the time we are only interested in knowing what is activated at what time, and therefore we look only at the absolute values of the sources. In some other cases, mainly when doing frequency analysis, we need to pay attention to the sign of those values. Because we cannot do a frequency decomposition of the absolute values of the sources, we need to keep the sign all along our processes. Display again the sources for Right / ERF on the cortex surface (double-click on the source file), and uncheck the Absolute option for the colormap "Sources" (right-click on the figure > Colormap Sources > Absolute values). Decrease the threshold to observe the pattern of alternance between positive and negative values on the surface. Then double click on the colorbar to reset it to its default. |
== Display: Contact sheets and movies == * '''Standard:''' (Right-click on the 3D figures > Snapshot > Time contact sheet) . {{http://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/Auditory?action=AttachFile&do=get&target=average_source_standard_left.gif|average_source_standard_left.gif|height="263",width="486",class="attachment"}} * '''Deviant:''' . {{http://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/Auditory?action=AttachFile&do=get&target=average_source_deviant_left.gif|average_source_deviant_left.gif|height="263",width="486",class="attachment"}} * Contact sheets: in time or in space, for each orientation. You can try all the menus. Example: Right-click on the figure > Snapshot > Volume contact sheet: axial: <<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:popupSnapshot.gif}} {{attachment:contactAxial.gif||height="288px",width="322px"}} * '''Movies''': Right-click on any figure > Snapshot > '''Movie (time): All figures''' (click to download video) [[http://neuroimage.usc.edu/wikidocs/average_sources.avi|{{http://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/Auditory?action=AttachFile&do=get&target=average_source_video.gif|http://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/wikidocs/average_sources.avi|height="258",width="484",class="attachment"}}]] == Minimum norm values are not only positive == You should pay attention to a property of the current amplitudes that are given by the wMNE method: they can be positive of negative, and they oscillate around zero. It's not easy to figure out what is the exact meaning of a negative value respect with a positive value, and most of the time we are only interested in knowing what is activated at what time, and therefore we look only at the absolute values of the sources. In some other cases, mainly when doing frequency analysis, we need to pay attention to the sign of these values. Because we cannot do a frequency decomposition of the absolute values of the sources, we need to keep the sign all along our processes. Display again the sources for Right / ERF on the cortex surface (double-click on the source file), and uncheck the Absolute option for the colormap "Sources" (right-click on the figure > Colormap Sources > Absolute values). Decrease the threshold to observe the pattern of alternance between positive and negative values on the surface. Then double click on the colorbar to reset it to its default. |
| Line 67: | Line 100: |
| === Minimum norm units === For information about the units used to represent the minimum norm source activation, pA.m (pico Ampere meter), please refer to the following forum post: [[http://neuroimage.usc.edu/forums/showthread.php?1246-Doubt-about-current-density-units-pA.m-or-pA-m2|http://neuroimage.usc.edu/...Doubt-about-current-density-units-pA.m-or-pA-m2]] |
== Source map normalization == * MNp, dSPM, sLORETA * Z-score : baseline correction Typical recommendations: * Use non-normalized current density maps for shared kernels applied to single trials. Example cases: * Averaging across MEG runs, * Computing time-frequency decompositions or connectivity measures on the single trials. * Use normalized maps (dSPM, sLORETA, MNp, Z-score) for calculating sources for average responses: * Exploring visually the ERP/ERF at the source level, * Normalizing the subjects condition averages before a group analysis. * '''wMNE, Kernel only, Constrained '''(already computed) * Check the contents of the file (right-click > File > View file contents): The inverse operator is saved in the field ImagingKernel [nVertices x nSensors] * '''wMNE, Full results, Constrained''': * Check the contents of the file: The full results matrix is saved in the field ImageGridAmp [nVertices x nTime] * Open solutions #1 and #2 at the same time and check visually at different time points that the results are exactly the same * '''wMNE, Kernel only, Unconstrained''': * Check the contents of the file: The inverse operator contains now the information for three dipoles (three orientations) per vertex, [3*nVertices, nSensors] * Open solutions #1 and #3 at the same time, and observe that the unconstrained solution is much smoother * '''dSPM, Kernel only, Unconstrained''' * '''sLORETA, Kernel only, Unconstrained''' * Open solutions #3 (wMNE), #4 (dSPM) and #5 (sLORETA), all unconstrained. * Notice that the units are different: wMNE values are in pAm, dSPM and sLORETA are in arbitrary units (never try to compare these values to anything but the exact same type of inverse solution) * Observe around 46ms the respective behavior of these three solutions: * 3) wMNE tends to highlight the top of the gyri and the superficial sources, * 4) dSPM tends to correct that behavior and may give higher values in deeper areas, * 5) sLORETA produces a very smooth solution where all the potentially activated area of the brain (given to the low spatial resolution of the source localization with MEG/EEG) is shown as connected, regardless of the depth of the sources. wMNE: constrained (kernel and full), and unconstrained {{attachment:compMNEconstr.gif||height="173px",width="193px"}} {{attachment:compMNEconstr.gif||height="171px",width="190px"}} {{attachment:compMNE.gif||height="170px",width="189px"}} dSPM, sLORETA: {{attachment:compSPM.gif||height="173px",width="192px"}} {{attachment:compLORETA.gif||height="172px",width="191px"}} Now delete all these files when you're done, and keep only the initial solution: wMNE, Constrained. |
| Line 73: | Line 141: |
| The sources file we are observing was computed as an ''inversion kernel''. It means that we can apply it to any similar recordings file (same subject, same run, same positions of sensors). But in our TutorialCTF database, the ''MN: MEG'' node only appears in the the ''ERF ''file, not in the ''Std ''one. What is it necessary to share an inversion kernel between different recordings ? | '''UNCONSTRAINED MN''' The sources file we are observing was computed as an ''inversion kernel''. It means that we can apply it to any similar recordings file (same subject, same run, same positions of sensors). But in our TutorialCTF database, the ''MN: MEG'' node only appears in the the ''ERF ''file, not in the ''Std ''one. What is it necessary to share an inversion kernel between different recordings ? |
| Line 81: | Line 151: |
| 1. The actual inversion kernel you have just computed (1), contains the same information as the one from the previous section (Computing sources for a single data file). Note that you cannot do anything with this file: if you right-click on it, you can see that there are no ''Display ''menu for it. | 1. The actual inversion kernel you have just computed (1), contains the same information as the one from the previous section (Computing sources for a single data file). Note that you cannot do anything with this file: if you right-click on it, you can see that there are no ''Display ''menu for it. |
| Line 84: | Line 154: |
| * Those links are not saved as files but as specific strings in the database: "link|kernel_file|data_file". This means that to represent them, one should load the shared kernel, load the recordings, and multiply them. | * These links are not saved as files but as specific strings in the database: "link|kernel_file|data_file". This means that to represent them, one should load the shared kernel, load the recordings, and multiply them. |
| Line 89: | Line 159: |
| 1. You can estimate the sources for many subjects or conditions at once, as it was explained for the head models in previous tutorial: the ''Compute sources'' menu is available on all the subjects and conditions popup menus. 1. Delete the shared kernel (1), we don't need redundant and confusing information for the next steps. Observe that both links disappear at the same time. == Minimum norm options == Let's introduce briefly the other options offered for the source estimation. Right-click again on Right / ERF > Compute sources. Click on "Expert mode", you more options appearing in the window.If you click on Run, you have access to all the options of the wMNE algorithm. |
1. You can estimate the sources for many subjects or conditions at once, as it was explained for the head models in previous tutorial: the ''Compute sources'' menu is available on all the subjects and conditions popup menus. 1. Delete the shared kernel (1), we don't need redundant and confusing information for the next steps. Observe that both links disappear at the same time. == Average in source space == * Now we have the source maps available for all the trials, we average them in source space. * Select the folders for '''Run01 '''and '''Run02 '''and the ['''Process sources'''] button on the left. * Run process "'''Average > Average files'''": Select "'''By trial group (subject average)'''" . {{http://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/Auditory?action=AttachFile&do=get&target=process_average_results.gif|process_average_results.gif|height="376",width="425",class="attachment"}} * Double-click on the source averages to display them (standard=top, deviant=bottom). . {{http://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/Auditory?action=AttachFile&do=get&target=average_source.gif|average_source.gif|height="321",width="780",class="attachment"}} * Note that opening the source maps can be very long because of the online filters. Check in the Filter tab, you probably still have a '''100Hz low-pass filter''' applied for the visualization. In the case of averaged source maps, the 15000 source signals are filtered on the fly when you load a source file. This can take a significant amount of time. You may consider unchecking this option if the display is too slow on your computer. <<TAG(Advanced)>> == Advanced options == Let's introduce briefly the other options offered for the source estimation. Right-click again on Right / ERF > Compute sources. Click on "Expert mode", you see more options appearing in the window. If you click on Run, you have access to all the options of the wMNE algorithm. |
| Line 97: | Line 178: |
| === Method === * '''wMNE''': Whitened and depth-weigthed linear L2-minimum norm estimates algorithm inspired from Matti Hamalainen's MNE software. Introduced in Brainstorm 3.1 by Rey Ramirez. For a full description of this method, please refer to the MNE manual, section 6, "The current estimates". [[http://www.nmr.mgh.harvard.edu/meg/manuals/MNE-manual-2.7.pdf|Download MNE manual here]]. * '''dSPM''': Noise-normalized estimate (dynamical Statistical Parametric Mapping [Dale, 2000]). Its computation is based on the wMNE solution. <<BR>>Basically, the dSPM value at each location is equal to the wMNE value divided by the projection of the estimated noise covariance matrix onto each source point. After whitening, the operational noise covariance matrix is by definition the identity matrix, and hence the projection of the noise is equal to the L2 norm of the row of the row vector of the wMNE inverse operator (in the case of fixed dipole orientations). So, dSPM is what you get when the rows of the wMNE inverse operator all have unit norm (i.e., they all point in different directions but lie in a unit hyper-sphere). * '''sLORETA''': Noise-normalized estimate using the sLORETA approach (standardized LOw Resolution brain Electromagnetic TomogrAphy [Pasqual-Marqui, 2002]). sLORETA solutions have in general a smaller location bias than either the expected current (wMNE) or the dSPM. |
=== Beamformer options === === Dipole fitting options === |
| Line 104: | Line 182: |
| * '''Kernel only''': Saves only the ''Inversion kernel'', a matrix that describes how to compute the sources when you know the values at the sensor level. So its size is: number of sources (15000) x number of sensors (151). This is possible because those minimum norm methods are linear methods. | * '''Kernel only''': Saves only the ''Inversion kernel'', a matrix that describes how to compute the sources when you know the values at the sensor level. So its size is: number of sources (15000) x number of sensors (151). This is possible because these minimum norm methods are linear methods. |
| Line 111: | Line 189: |
| * The only reason that would make you chose the "''Full results''" options would be any interest in having the full matrix in one file, in case you want to process the sources values by yourself (filtering, statistics, display...). === Source orientation === * '''Constrained''': We consider that at each vertex of the cortex surface, there is only one dipole, and that its orientation is the normal to the cortex surface at this point. * The size of the inverse operator is [nVertices x nChannel]. * This is based on the anatomical observation that in the cortex, the neurons are mainly organized in macro-columns that are perpendicular to the cortex surface. But it's hard to know if we can really rely on it at this level, for this algorithm: Is it the case everywhere in the cortex? Are we supposed to use the inner (grey matter/white matter) or the outer (grey/CSF) surface of the cortex? Can we really be that precise in terms of MRI/MEG registration? Those are questions that do not have final answers yet. * A technical advantage of this method, it produces one value per vertex instead of three. As a consequence 1) the output size is smaller, 2) it's faster to compute and display, and 3) the results are much more intuitive to display because we don't have to think about how combining three values in one on a cortical map in a 3D figure * '''Unconstrained''': At each vertex of the cortex surface, we define a base of three dipoles with orthogonal directions, and then we estimate the sources for the three orientations independently.The size of the inverse operator is [3*nVertices x nChannel]. * '''Loose''': A version of the "unconstrained" method that integrates a weak orientation constraint. It generates an inverse operator that is the same size as the unconstrained one, but that emphasizes the importance of the sources that have an orientation that is close to the normal to the cortex. The value associated with this option set how "loose" should be the orientation constrain (recommended values in MNE are between 0.1 and 0.6, --loose option). This is the default in MNE software. * '''Truncated''':An SVD of the gain matrix for each source point is used to remove the dipole component with least variance, which for the single sphere head model, corresponds to the radial silent component. Only useful when combining a spherical head model and sLORETA. * '''Default''': At the present time, the default in Brainstorm is the "constrained" option, but we will probably switch to the unconstrained model soon. Because 1) we are not exactly sure that the orientation constraint is 100% correct, 2) the unconstrained sources look smoother and nicer, 3) the computation and storage capacities of the average computer increased a lot since the 1990s, so we can now afford to multiply by three the size of all the data. But right now, there are still some issues to fix in the processing pipeline of the unconstrained sources. |
* The only reason that would make you choose the "''Full results''" options would be any interest in having the full matrix in one file, in case you want to process the sources values by yourself (filtering, statistics, display...). |
| Line 133: | Line 201: |
| The minimum-norm estimates have a bias towards superficial currents. This tendency can be alleviated by adjusting those parameters. To understand how to set those parameters, please refer to the MNE manual (options --depth, --weightexp and --weightlimit). === Do it yourself === Typically, the only options you want to change is the type of estimator that is computed (wMNE, dSPM, sLORETA) and the orientation of the dipoles (constrained, unconstrained). Don't try to play with the other options if you are not really comfortable with what they represent. Now, compute and compare the following combinations of options for Right / ERF: 1. '''wMNE, Kernel only, Constrained '''(already computed) * Check the contents of the file (right-click > File > View file contents): The inverse operator is saved in the field ImagingKernel [nVertices x nSensors] 1. '''wMNE, Full results, Constrained''': * Check the contents of the file: The full results matrix is saved in the field ImageGridAmp [nVertices x nTime] * Open solutions #1 and #2 at the same time and check visually at different time points that the results are exactly the same 1. '''wMNE, Kernel only, Unconstrained''': * Check the contents of the file: The inverse operator contains now the information for three dipoles (three orientations) per vertex, [3*nVertices, nSensors] * Open solutions #1 and #3 at the same time, and observe that the unconstrained solution is much smoother 1. '''dSPM, Kernel only, Unconstrained''' 1. '''sLORETA, Kernel only, Unconstrained''' * Open solutions #3 (wMNE), #4 (dSPM) and #5 (sLORETA), all unconstrained. * Notice that the units are different: wMNE values are in pAm, dSPM and sLORETA are in arbitrary units (never try to compare those values to anything but the exact same type of inverse solution) * Observe around 46ms the respective behavior of those three solutions: * 3) wMNE tends to highlight the top of the gyri and the superficial sources, * 4) dSPM tends to correct that behavior and may give higher values in deeper areas, * 5) sLORETA produces a very smooth solution where all the potentially activated area of the brain (given to the low spatial resolution of the source localization with MEG/EEG) is shown as connected, regardless of the depth of the sources. wMNE: constrained (kernel and full), and unconstrained {{attachment:compMNEconstr.gif||height="173px",width="193px"}} {{attachment:compMNEconstr.gif||height="171px",width="190px"}} {{attachment:compMNE.gif||height="170px",width="189px"}} dSPM, sLORETA: {{attachment:compSPM.gif||height="173px",width="192px"}} {{attachment:compLORETA.gif||height="172px",width="191px"}} Now delete all those files when you're done, and keep only the initial solution: wMNE, Constrained. == Additional discussions on the forum == * Imaging resolution kernels: http://neuroimage.usc.edu/forums/showthread.php?1298 * Spatial smoothing of sources: http://neuroimage.usc.edu/forums/showthread.php?1409 * Units for dSPM and sLORETA: [[http://neuroimage.usc.edu/forums/showthread.php?1535-Dipole-strength-units-for-dSPM-and-sLORETA|http://neuroimage.usc.edu/forums/showthread.php?1535]] * EEG reference: http://neuroimage.usc.edu/forums/showthread.php?1525#post6718 * Sign of the MNE values: http://neuroimage.usc.edu/forums/showthread.php?1649#post7014 = From continuous tutorials = == Inverse model == Right-click on ''(Common files)'', on the head model or on the subject node, and select "'''Compute sources'''". A shared inversion kernel is created in ''(Common files)''; a link node is now visible for each recordings file, single trials and averages. For more information about what those links mean and the operations performed to display them, please refer to the [[http://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/TutSourceEstimation|tutorial #8 "Source estimation"]]. {{http://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/TutRawAvg?action=AttachFile&do=get&target=inverseDb.gif|inverseDb.gif|class="attachment"}} == Explore the sources == Right-click on the sources for the left average > Cortical activations > '''Display on cortex''', or simply double click on the file. Go to the main response peak at '''t = 30ms''', and increase the '''amplitude threshold''' to '''100%'''. You see a strong activity around the right primary somatosensory cortex, but there are still lots of brain areas that are shown in plain red (value >= 100% maximum of the colorbar ~= 280 pA.m). {{http://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/TutRawAvg?action=AttachFile&do=get&target=inverse100.gif|inverse100.gif|class="attachment"}} The colorbar maximum is set to an estimation of the maximum source amplitude over the time. This estimation is done by finding the time instant with the highest global field power on the sensors (green trace GFP), estimating the sources for this time only, and then taking the maximum source value at this time point. It is a very fast estimate, but not very reliable; we use it because calculating the full source matrix (all the time points x all the sources) just for finding the maximum value would be too long. In this case, the real maximum is probably higher than what is used by default. To redefine the colorbar maximum: right-click on the 3D figure > '''Colormap: sources > Set colorbar max value'''. Set the maximum to '''480 pA.m''', or any other value that would lead to see just one very focal point on the brain at 30ms. {{http://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/TutRawAvg?action=AttachFile&do=get&target=inverse480.gif|inverse480.gif|class="attachment"}} Go back to the first small peak at '''t=16ms''', and lower the threshold to '''10%'''. Then do what you did with at the sensor level: follow the information processing in the brain until 100ms, millisecond by millisecond, adapting the threshold and the camera position when needed: * '''16 ms''' (top-left): First response, primary somatosensory cortex (S1 right) * '''30 ms''' (top-right): S1 right * '''60 ms''' (bottom-left): Secondary somatosensory cortex (S2 right) * '''70 ms''' (bottom-right): Activity ipsilateral to the stimulus (S2 left + S2 right) {{http://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/TutRawAvg?action=AttachFile&do=get&target=sources16.gif|sources16.gif|class="attachment"}} {{http://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/TutRawAvg?action=AttachFile&do=get&target=sources30.gif|sources30.gif|class="attachment"}} {{http://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/TutRawAvg?action=AttachFile&do=get&target=sources60.gif|sources60.gif|class="attachment"}} {{http://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/TutRawAvg?action=AttachFile&do=get&target=sources70.gif|sources70.gif|class="attachment"}} = From auditory = === Inverse model === * Select the two imported folders at once, right-click > Compute sources . {{http://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/Auditory?action=AttachFile&do=get&target=inverse1.gif|inverse1.gif|height="192",width="282",class="attachment"}} * Select '''dSPM''' and keep all the default options. . {{http://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/Auditory?action=AttachFile&do=get&target=inverse2.gif|inverse2.gif|height="205",width="199",class="attachment"}} * Then you are asked to confirm the list of bad channels to use in the source estimation for each run. Just leave the defaults, which are the channels that we set as bad earlier. . {{http://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/Auditory?action=AttachFile&do=get&target=inverse_bad1.gif|inverse_bad1.gif|height="202",width="326",class="attachment"}} * One inverse operator is created in each condition, with one link per data file. . {{http://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/Auditory?action=AttachFile&do=get&target=inverse3.gif|inverse3.gif|height="240",width="202",class="attachment"}} * For more information: [[http://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/TutSourceEstimation|Source estimation tutorial]]. === Average in source space === * Now we have the source maps available for all the trials, we average them in source space. * Select the folders for '''Run01 '''and '''Run02 '''and the ['''Process sources'''] button on the left. * Run process "'''Average > Average files'''": Select "'''By trial group (subject average)'''" . {{http://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/Auditory?action=AttachFile&do=get&target=process_average_results.gif|process_average_results.gif|height="376",width="425",class="attachment"}} * Double-click on the source averages to display them (standard=top, deviant=bottom). . {{http://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/Auditory?action=AttachFile&do=get&target=average_source.gif|average_source.gif|height="321",width="780",class="attachment"}} * Note that opening the source maps can be very long because of the online filters. Check in the Filter tab, you probably still have a '''100Hz low-pass filter''' applied for the visualization. In the case of averaged source maps, the 15000 source signals are filtered on the fly when you load a source file. This can take a significant amount of time. You may consider unchecking this option if the display is too slow on your computer. * '''Standard:''' (Right-click on the 3D figures > Snapshot > Time contact sheet) . {{http://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/Auditory?action=AttachFile&do=get&target=average_source_standard_left.gif|average_source_standard_left.gif|height="263",width="486",class="attachment"}} {{http://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/Auditory?action=AttachFile&do=get&target=average_source_standard_right.gif|average_source_standard_right.gif|height="263",width="486",class="attachment"}} * '''Deviant:''' . {{http://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/Auditory?action=AttachFile&do=get&target=average_source_deviant_left.gif|average_source_deviant_left.gif|height="263",width="486",class="attachment"}} {{http://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/Auditory?action=AttachFile&do=get&target=average_source_deviant_right.gif|average_source_deviant_right.gif|height="263",width="486",class="attachment"}} * '''Movies''': Right-click on any figure > Snapshot > '''Movie (time): All figures''' (click to download video) [[http://neuroimage.usc.edu/wikidocs/average_sources.avi|{{http://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/Auditory?action=AttachFile&do=get&target=average_source_video.gif|http://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/wikidocs/average_sources.avi|height="258",width="484",class="attachment"}}]] |
The minimum-norm estimates have a bias towards superficial currents. This tendency can be alleviated by adjusting these parameters. To understand how to set these parameters, please refer to the MNE manual (options --depth, --weightexp and --weightlimit). <<TAG(Advanced)>> == Equations == TODO: John <<TAG(Advanced)>> |
| Line 231: | Line 215: |
| That is why sLORETA has zero localization bias for ALL point-spread functions, and why I always prefer sLORETA over dSPM, MNE, or any beamformer. This is all in the math .... but ..... just so that you know Fas Hsuan Lin's paper comparing sLORETA with dSPM, and MNE has a big mistake, the assumed source covariance matrix is not the identity matrix, and that violates the beauty of the math and results in non-zero localization bias. That's why in Brainstorm the prior source covariance matrix used for sLORETA automatically uses no depth bias compensation (identity matrix). sLORETA accomplishes depth bias compensation via the resolution matrix, NOT via the prior source covariance matrix. Trying to use a depth exponent of 0.7 or 0.8 like we do for MNE and dSPM will mess up sLORETA.You will not find this in a paper, but I checked it all out many years ago. This is critical.<<EmbedContent("http://neuroimage.usc.edu/bst/get_prevnext.php?prev=Tutorials/NoiseCovariance&next=Tutorials/Scouts")>> == What's in the source file == |
That is why sLORETA has zero localization bias for ALL point-spread functions, and why I always prefer sLORETA over dSPM, MNE, or any beamformer. This is all in the math .... but ..... just so that you know Fas Hsuan Lin's paper comparing sLORETA with dSPM, and MNE has a big mistake, the assumed source covariance matrix is not the identity matrix, and that violates the beauty of the math and results in non-zero localization bias. That's why in Brainstorm the prior source covariance matrix used for sLORETA automatically uses no depth bias compensation (identity matrix). sLORETA accomplishes depth bias compensation via the resolution matrix, NOT via the prior source covariance matrix. Trying to use a depth exponent of 0.7 or 0.8 like we do for MNE and dSPM will mess up sLORETA.You will not find this in a paper, but I checked it all out many years ago. This is critical. '''Explain sLORETA units (see email exchanges from Feb 2015) ''' <<TAG(Advanced)>> == Issues with dSPM average == Average(dSPM) is NOT equal to dSPM(Average). {{{ There is no problem for the MNE and sLORETA solutions, because the scaling of the noise covariance matrix doesn't impact the results. wMNE(Data, NoiseCov) = wMNE(Data, NoiseCov / N) So when we average we get: Average(wMNE(Trials, NoiseCov)) = wMNE(Average, NoiseCov) = wMNE(Average, NoiseCov / N) But for dSPM we have: dSPM(Data, NoiseCov) = dSPM(Data, NoiseCov / N) ./ sqrt(N) So when we average we get: Average(dSPM(Trials, NoiseCov)) = dSPM(Average, NoiseCov) = dSPM(Average, NoiseCov / N) ./ sqrt(N) }}} Rey: "Basically, the dSPM value at each location is equal to the wMNE value divided by the projection of the estimated noise covariance matrix onto each source point. After whitening, the operational noise covariance matrix is by definition the identity matrix, and hence the projection of the noise is equal to the L2 norm of the row vector of the wMNE inverse operator (in the case of fixed dipole orientations). So, dSPM is what you get when the rows of the wMNE inverse operator all have unit norm (i.e., they all point in different directions but lie in a unit hyper-sphere)." Rey: "dSPM is really a source mapping of SNR, not of activity. Hence, it's not all so surprising that the single trial SNR maps are smaller... "Rey: "Perhaps, dSPM should be used only for averaged data (i.e., ERF, ERP), at least until it's all figure out. In a way, dSPM is just MNE followed by the noise normalization. Thus, you could do all the single trial processing with the MNE algorithm, and only do the noise normalization when needed (e.g., after averaging or on single trials only if they are not going to be averaged)." == On the hard drive == |
| Line 236: | Line 244: |
| Document file structure Differences for kernel vs. sources Differences for constrained vs. unconstrained in_bst_results to get the full sources or apply any process * You can have a look to the corresponding matrix file (right-click > File > View file contents). You would find all the options of forward and inverse modeling, and only one interesting field : '''ImagingKernel''', which contains the inversion kernel. It is a [nVertices x nChannels] matrix that has to be multiplied with the recordings matrix in order to get the activity for each source at all the time samples. * The minimum norm solution being a linear operation (the time series for each source is a linear combination of all the time series recorded by the sensors), we make this economy of saving only this linear operator instead of the full source matrix (nVertices x nTime) == References == * Dale AM, Liu AK, Fischl BR, Buckner RL, Belliveau JW, Lewine JD, Halgren E<<BR>>[[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10798392|Dynamic statistical parametric mapping: combining fMRI and MEG for high-resolution imaging of cortical activity]]. Neuron 2000 Apr, 26(1):55-67 * Pascual-Marqui RD, [[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12575463|Standardized low-resolution brain electromagnetic tomography (sLORETA): technical details]], Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol 2002, 24 Suppl D:5-12 == Additional discussions on the forum == * Forum: Minimum norm units (pA.m): [[http://neuroimage.usc.edu/forums/showthread.php?1246-Doubt-about-current-density-units-pA.m-or-pA-m2|http://neuroimage.usc.edu/forums/showthread.php?1246]] * Forum: Imaging resolution kernels: http://neuroimage.usc.edu/forums/showthread.php?1298 * Forum: Spatial smoothing of sources: http://neuroimage.usc.edu/forums/showthread.php?1409 * Forum: Units for dSPM and sLORETA: [[http://neuroimage.usc.edu/forums/showthread.php?1535-Dipole-strength-units-for-dSPM-and-sLORETA|http://neuroimage.usc.edu/forums/showthread.php?1535]] * Forum: EEG reference: http://neuroimage.usc.edu/forums/showthread.php?1525#post6718 * Forum: Sign of the MNE values: http://neuroimage.usc.edu/forums/showthread.php?1649#post7014 * Forum: Combining magneto+gradiometers: http://neuroimage.usc.edu/forums/showthread.php?1900 * Forum: Residual ocular artifacts: http://neuroimage.usc.edu/forums/showthread.php?1272 <<HTML(<!-- END-PAGE -->)>> <<EmbedContent("http://neuroimage.usc.edu/bst/get_prevnext.php?prev=Tutorials/NoiseCovariance&next=Tutorials/Scouts")>> |
Tutorial 22: Source estimation
[UNDER CONSTRUCTION]
Authors: Francois Tadel, Elizabeth Bock, Rey R Ramirez, John C Mosher, Richard Leahy, Sylvain Baillet
You have in your database a forward model matrix that explains how the cortical sources determine the values on the sensors. This is useful for simulations, but what we need is to build the inverse information: how to estimate the sources when we have the recordings. This tutorials introduces the tools available in Brainstorm for solving this inverse problem.
Contents
- Ill-posed problem
- Source estimation options [TODO]
- Computing sources for a single data file
- Display: Cortex surface
- Display: MRI 3D
- Display: MRI Viewer
- Display: Contact sheets and movies
- Minimum norm values are not only positive
- Source map normalization
- Computing sources for multiple data files
- Average in source space
- Advanced options
- Equations
- Rey on sLORETA
- Issues with dSPM average
- On the hard drive
- References
- Additional discussions on the forum
Ill-posed problem
Our goal is to estimate the activity of the 45,000 dipoles described by our forward model. However we only have a few hundreds of variables (the number of sensors). This inverse problem is ill-posed, there is an infinity of combinations of source activity that can generate exactly the same sensor topography. Inverting the forward problem directly is impossible, unless we add some strong priors in our model.
Wikipedia says: "Inverse problems are some of the most important and well-studied mathematical problems in science and mathematics because they tell us about parameters that we cannot directly observe. They have wide application in optics, radar, acoustics, communication theory, signal processing, medical imaging, computer vision, geophysics, oceanography, astronomy, remote sensing, natural language processing, machine learning, nondestructive testing, and many other fields."
Many solutions have been proposed in the literature, based on different assumptions on the way the brain works and depending on the amount of information we already have on the effects we are studying. Among the hundreds of methods available, two classes of inverse models have been widely used in MEG/EEG source imaging in the past years: minimum-norm solutions and beamformers.
Both approaches have the advantage of being linear: the activity of the sources is a linear recombination of the MEG/EEG recordings. It is possible to solve the inverse problem independently of the recordings, making the data manipulation a lot easier and faster.
Both are available in Brainstorm, so you can use the one the most adapted to your recordings or to your own personal expertise. Only the minimum norm estimates will be described in this tutorial, but the other solutions work exactly in the same way.
Source estimation options [TODO]
Before we start estimating the sources for the recordings available in our database, let's start with an overview of the options available. The screen capture below represents the basic options for the minimum norm estimates. The options for the other methods will be described in advanced tutorials.
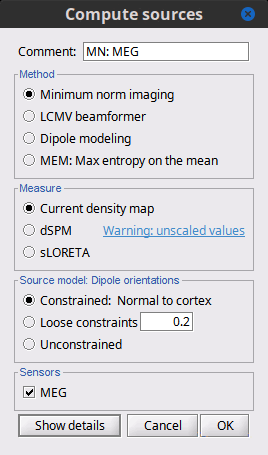
Method
Minimum norm: Priors, justification, application case?
Require an estimation of the noise at the level of the sensors (noise covariance matrix).Dipole modeling: ?
LCMV beamformer: ?
Require both a noise covariance matrix and a data covariance matrix (representation of the effect we are trying to localize in the brain, covariance of the latencies of interest).Recommended option: Provided that we know at what latencies to look at, we can compute a correct data covariance matrix and may obtain a better spatial accuracy with a beamformer. However, in many cases we don't exactly know what we are looking at, the risks of misinterpretation of badly designed beamforming results are high. Brainstorm tends to favor minimum norm solutions, which have the advantage of needing less manual tuning for getting acceptable results.
Measure
The minimum norm estimates gives a measure of the current density flowing at the surface of the cortex. To visualize these results and compare them between subjects, we can normalize the MNE values to get a standardized level of activation with respect to the noise or baseline level (dSPM, sLORETA, MNp).
Current density map: Whitened and depth-weigthed linear L2-minimum norm estimates algorithm inspired from Matti Hamalainen's MNE software. For a full description of this method, please refer to the MNE manual, section 6, "The current estimates".
dSPM: Noise-normalized estimate (dynamical Statistical Parametric Mapping [Dale, 2000]). Its computation is based on the MNE solution.
sLORETA: Noise-normalized estimate using the sLORETA approach (standardized LOw Resolution brain Electromagnetic TomogrAphy [Pasqual-Marqui, 2002]). sLORETA solutions have in general a smaller location bias than either the expected current (MNE) or the dSPM.
MNp: ?
Recommended option: Discussed in the section "Source map normalization"
Source orientation
Constrained: Normal to cortex: Only one dipole at each vertex of the cortex surface, oriented normally to the surface. This is based on the anatomical observation that in the cortex, the neurons are mainly organized in macro-columns that are perpendicular to the cortex surface.
Size of the inverse operator: [nVertices x nChannel].Constrained: Optimal orientation: Only one dipole at each vertex of the cortex surface, oriented normally to the surface. This is based on the anatomical observation that in the cortex, the neurons are mainly organized in macro-columns that are perpendicular to the cortex surface.
Size of the inverse operator: [nVertices x nChannel].Unconstrained: At each vertex of the cortex surface, we define a base of three dipoles with orthogonal directions, then we estimate the sources for the three orientations independently.
Size of the inverse operator: [3*nVertices x nChannel].Loose: A version of the "unconstrained" option with a weak orientation constraint that emphasizes the importance of the sources with orientations that are close to the normal to the cortex. The value associated with this option set how "loose" should be the orientation constrain (recommended values in MNE are between 0.1 and 0.6, --loose option).
Size of the inverse operator: [3*nVertices x nChannel].Recommended option: ?
The constrained options use one dipole per orientation instead of three, therefore the source maps are smaller, faster to compute and display, and much more intuitive to process because we don't have to think about recombining the three values in one. However the normal orientation constraint is most of the time too strong and not realistic.
Unconstrained sources look smoother and nicer but are not necessarily more accurate.
Computing sources for a single data file
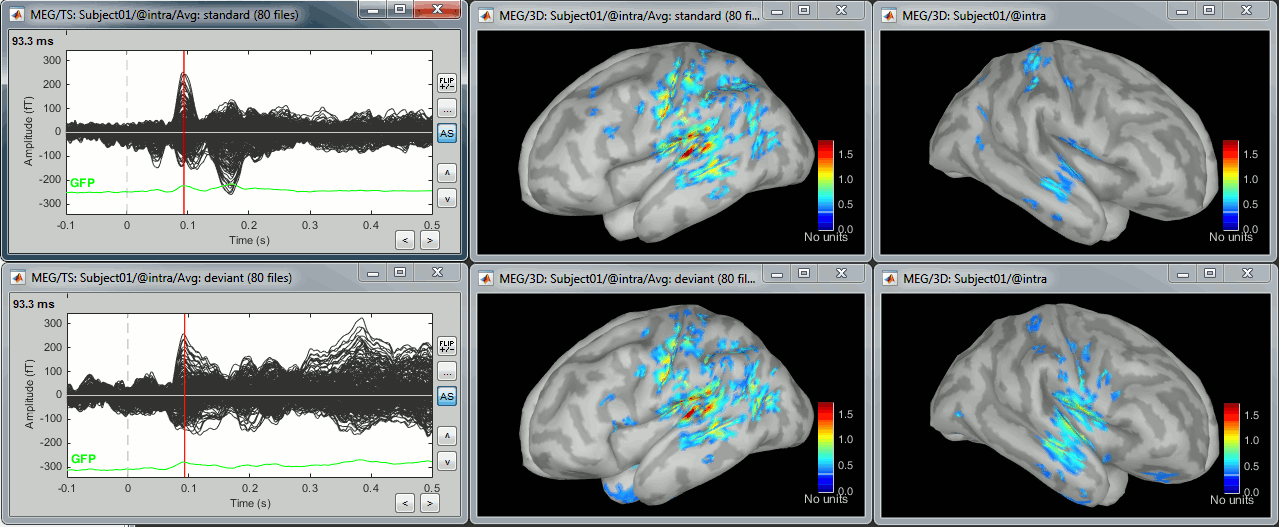
In Run#01, right-click on the average response for the deviant stim > Compute sources [2015].
Select the options: Minimum norm imaging, Current density map, Constrained: Normal to cortex.
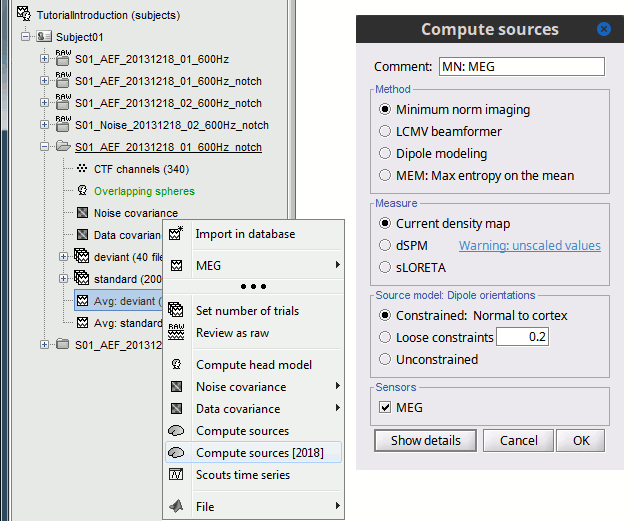
- The other menu "Compute sources" brings the interface that was used previously in Brainstorm. We are going to keep maintaining the two implementations in parallel for a while for compatibility and cross-validation purposes.
The result of the computation is displayed as a dependent of the deviant average because it is related only to this file. In the file comment, "MN" stands minimum norm and "Constr" stands for "Constrained: normal orientation".
Display: Cortex surface
Right-click on the sources for the deviant average > Cortical activations > Display on cortex.
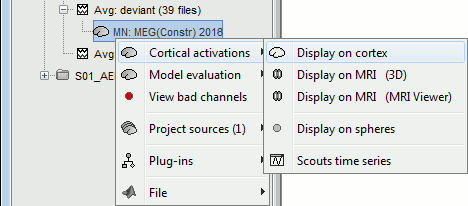
Double-click on the recordings for the deviant average to have time reference.
In the filter tab, add a low-pass filter at 100Hz.
- Change the current time (click on the time series figure or use the keyboard arrows) and note it updates the source maps in the 3D figure. You can also use all the menus and shortcuts introduced in the anatomy tutorial (like setting the view with the keys from 0 to 6).
- You can edit many display properties from the Surface tab:
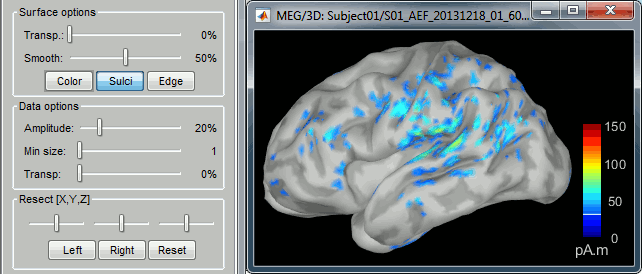
Amplitude: Only the sources that have a value superior than a given percentage of the colorbar maximum are displayed.
Min. size: Hide all the small activated regions, ie. the connected color patches that contain a number of vertices smaller than this "min size" value.
Transparency: Change the transparency of the sources on the cortex.
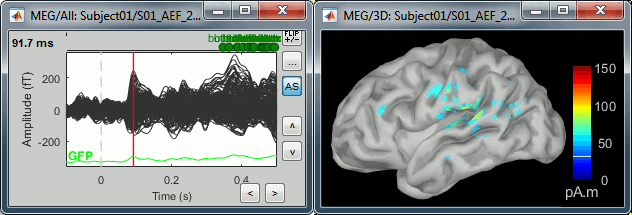
Take a few minutes to understand what the amplitude threshold represents.
The colorbar maximum depends on the way you configured your Sources colormap. If the option "Maximum: Global" is selected, the maximum should be around 30 pA.m. This value is a rough estimate of the maximum amplitude, sometimes you may have to redefine it manually.
On the screen capture below, the threshold value is set to 90%. It means that only the sources that have a value over 0.90*30 = 27 pA.m are visible.
The threshold level is indicated in the colorbar with a horizontal white line.
At the first response peak (91ms), the sources with high amplitudes are located around the primary somatosensory cortex, which is what we are expecting for an auditory stimulation.
Display: MRI 3D
Right-click on the source file > Cortical activations > Display on MRI (3D).
This view was also introduced in the tutorial about MRI and surface visualization. Try to rotate, zoom, move the slices, move in time, change the threshold.
![[ATTACH] [ATTACH]](/moin_static1911/brainstorm1/img/attach.png)
![[ATTACH] [ATTACH]](/moin_static1911/brainstorm1/img/attach.png)
- A new menu is available in the popup menu of this figure: MRI Display
MIP Anatomy: for each slice, display the maximum value over all the slices instead of the original value in the structural MRI (fig 1)
MIP Functional: same thing but with the layer of functional values (fig 2)
Smooth level: The sources values are smoothed after being re-interpolated in the volume. These menus define the size of the smoothing kernel (fig2: smooth=2; fig3: smooth=5).
![[ATTACH] [ATTACH]](/moin_static1911/brainstorm1/img/attach.png)
![[ATTACH] [ATTACH]](/moin_static1911/brainstorm1/img/attach.png)
![[ATTACH] [ATTACH]](/moin_static1911/brainstorm1/img/attach.png)
Display: MRI Viewer
Right-click on Right / ERF / MN: MEG > Cortical activations > Display on MRI (MRI Viewer).
This view was also introduced in the tutorial about MRI and surface visualization. Try to move the slices (sliders, mouse wheel, click on the views), move in time, change the threshold.
![[ATTACH] [ATTACH]](/moin_static1911/brainstorm1/img/attach.png)
Display: Contact sheets and movies
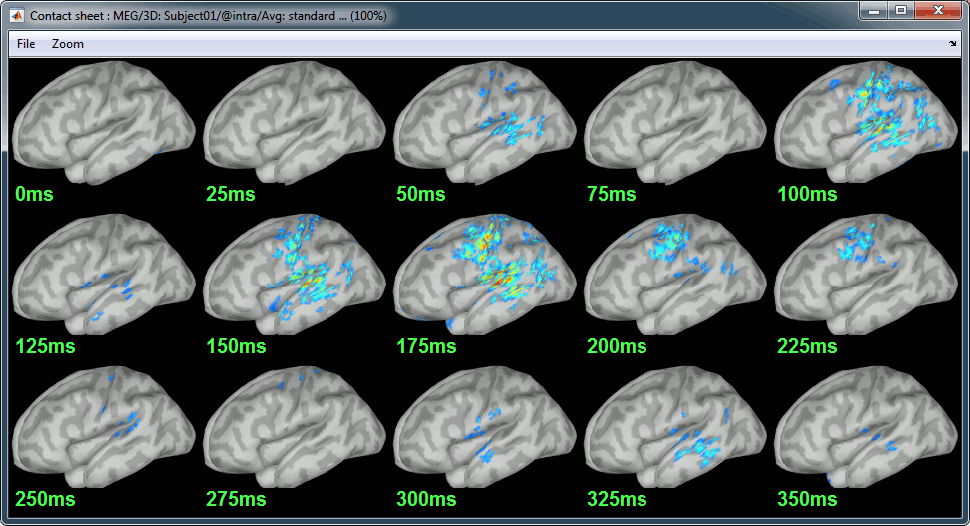
Standard: (Right-click on the 3D figures > Snapshot > Time contact sheet)
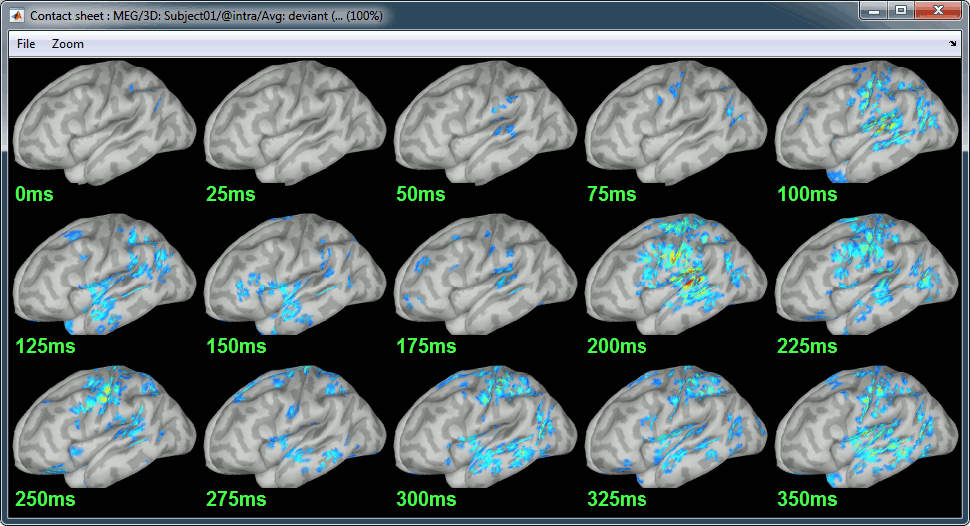
Deviant:
Contact sheets: in time or in space, for each orientation. You can try all the menus. Example: Right-click on the figure > Snapshot > Volume contact sheet: axial:
![[ATTACH] [ATTACH]](/moin_static1911/brainstorm1/img/attach.png)
![[ATTACH] [ATTACH]](/moin_static1911/brainstorm1/img/attach.png)
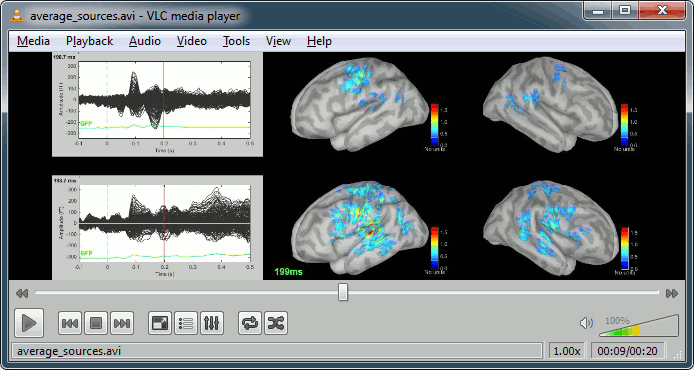
Movies: Right-click on any figure > Snapshot > Movie (time): All figures (click to download video)
Minimum norm values are not only positive
You should pay attention to a property of the current amplitudes that are given by the wMNE method: they can be positive of negative, and they oscillate around zero. It's not easy to figure out what is the exact meaning of a negative value respect with a positive value, and most of the time we are only interested in knowing what is activated at what time, and therefore we look only at the absolute values of the sources.
In some other cases, mainly when doing frequency analysis, we need to pay attention to the sign of these values. Because we cannot do a frequency decomposition of the absolute values of the sources, we need to keep the sign all along our processes.
Display again the sources for Right / ERF on the cortex surface (double-click on the source file), and uncheck the Absolute option for the colormap "Sources" (right-click on the figure > Colormap Sources > Absolute values). Decrease the threshold to observe the pattern of alternance between positive and negative values on the surface. Then double click on the colorbar to reset it to its default.
Source map normalization
- MNp, dSPM, sLORETA
- Z-score : baseline correction
Typical recommendations:
- Use non-normalized current density maps for shared kernels applied to single trials. Example cases:
- Averaging across MEG runs,
- Computing time-frequency decompositions or connectivity measures on the single trials.
- Use normalized maps (dSPM, sLORETA, MNp, Z-score) for calculating sources for average responses:
- Exploring visually the ERP/ERF at the source level,
- Normalizing the subjects condition averages before a group analysis.
wMNE, Kernel only, Constrained (already computed)
Check the contents of the file (right-click > File > View file contents): The inverse operator is saved in the field ImagingKernel [nVertices x nSensors]
wMNE, Full results, Constrained:
Check the contents of the file: The full results matrix is saved in the field ImageGridAmp [nVertices x nTime]
- Open solutions #1 and #2 at the same time and check visually at different time points that the results are exactly the same
wMNE, Kernel only, Unconstrained:
- Check the contents of the file: The inverse operator contains now the information for three dipoles (three orientations) per vertex, [3*nVertices, nSensors]
- Open solutions #1 and #3 at the same time, and observe that the unconstrained solution is much smoother
dSPM, Kernel only, Unconstrained
sLORETA, Kernel only, Unconstrained
- Open solutions #3 (wMNE), #4 (dSPM) and #5 (sLORETA), all unconstrained.
- Notice that the units are different: wMNE values are in pAm, dSPM and sLORETA are in arbitrary units (never try to compare these values to anything but the exact same type of inverse solution)
- Observe around 46ms the respective behavior of these three solutions:
- 3) wMNE tends to highlight the top of the gyri and the superficial sources,
- 4) dSPM tends to correct that behavior and may give higher values in deeper areas,
- 5) sLORETA produces a very smooth solution where all the potentially activated area of the brain (given to the low spatial resolution of the source localization with MEG/EEG) is shown as connected, regardless of the depth of the sources.
wMNE: constrained (kernel and full), and unconstrained
dSPM, sLORETA:
Now delete all these files when you're done, and keep only the initial solution: wMNE, Constrained.
Computing sources for multiple data files
UNCONSTRAINED MN
The sources file we are observing was computed as an inversion kernel. It means that we can apply it to any similar recordings file (same subject, same run, same positions of sensors). But in our TutorialCTF database, the MN: MEG node only appears in the the ERF file, not in the Std one. What is it necessary to share an inversion kernel between different recordings ?
Compute another source estimation: but instead of clicking on the Compute sources from the ERF recordings popup menu (which would mean that you only want sources for this particular recordings file), get this menu from the Right condition. This means that you want the inversion model to be applied to all the data in the condition.
- Select "Minimum Norm Imaging", click on Run.
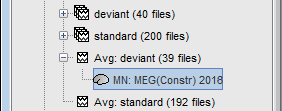
The actual inversion kernel you have just computed (1), contains the same information as the one from the previous section (Computing sources for a single data file). Note that you cannot do anything with this file: if you right-click on it, you can see that there are no Display menu for it.
Two links (2) that allow you apply this inversion kernel to the data files available in this condition (ERF and Std). In their popup menus, there are all the display options introduced in the previous section.
- These links are not saved as files but as specific strings in the database: "link|kernel_file|data_file". This means that to represent them, one should load the shared kernel, load the recordings, and multiply them.
The sources for the Std file do not have any meaning, do not even try to open it. It was just to illustrate the way a kernel is shared
Double-click on both sources files available for Right / ERF (link and non-link), and verify at many different times that the cortical maps are exactly the same in both cases.
You can estimate the sources for many subjects or conditions at once, as it was explained for the head models in previous tutorial: the Compute sources menu is available on all the subjects and conditions popup menus.
- Delete the shared kernel (1), we don't need redundant and confusing information for the next steps. Observe that both links disappear at the same time.
Average in source space
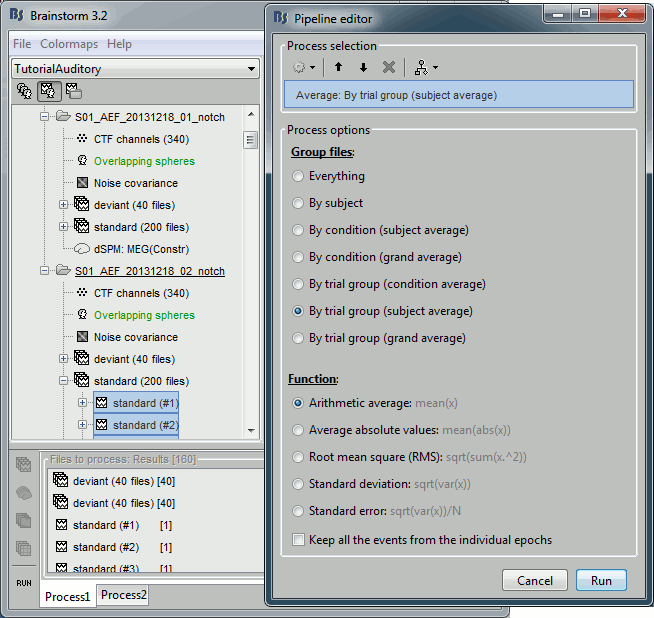
- Now we have the source maps available for all the trials, we average them in source space.
Select the folders for Run01 and Run02 and the [Process sources] button on the left.
Run process "Average > Average files": Select "By trial group (subject average)"
- Double-click on the source averages to display them (standard=top, deviant=bottom).
Note that opening the source maps can be very long because of the online filters. Check in the Filter tab, you probably still have a 100Hz low-pass filter applied for the visualization. In the case of averaged source maps, the 15000 source signals are filtered on the fly when you load a source file. This can take a significant amount of time. You may consider unchecking this option if the display is too slow on your computer.
Advanced options
Let's introduce briefly the other options offered for the source estimation. Right-click again on Right / ERF > Compute sources. Click on "Expert mode", you see more options appearing in the window. If you click on Run, you have access to all the options of the wMNE algorithm.
Beamformer options
Dipole fitting options
Output mode
Full results: Saves in one big matrix the values of all the sources (15000) for all the time samples (375). The size in memory of such a matrix is about 45Mb for 300ms of recordings. This is still reasonable, so you may use this option in this case. But if you need to process longer recordings, you may have some "Out of memory" errors in Matlab, or fill your hard drive quickly.
Kernel only: Saves only the Inversion kernel, a matrix that describes how to compute the sources when you know the values at the sensor level. So its size is: number of sources (15000) x number of sensors (151). This is possible because these minimum norm methods are linear methods.
- To get the sources time series, you just need to multiply this kernel by the MEG recordings.
Full results = Inversion kernel * Recordings
- The size of this matrix is about 18Mb. In this case, the difference is not very important because we only process 375 time samples. But this inversion kernel is independent from the recordings length, so you can easily scale its computation to much longer recordings.
Default ?
Probably "Kernel only", as it is faster and produces smaller files.
- All the following operations in Brainstorm will be exactly the same either way. Each time you access the sources values, the program has to do the multiplication Kernel * Recordings, but this is done in a totally transparent way.
The only reason that would make you choose the "Full results" options would be any interest in having the full matrix in one file, in case you want to process the sources values by yourself (filtering, statistics, display...).
Signal properties
Signal to noise ratio (SNR): An estimate of the amplitude SNR of the recordings, as defined in MNE (--snr option in MNE), used to compute the regularization parameter (lambda2 = 1/SNR2). The default value is SNR = 3. Automatic selection of the regularization parameter is currently not supported.
PCA Whitening: Parameter introduced by Rey Ramirez. For more information, see the code of bst_wmne function.
Noise covariance matrix
Full noise covariance: Use the full noise covariance matrix available in Brainstorm database. If the noise covariance file previously computed in is a diagonal matrix (as it is the case in this tutorial), this value is ignored, and the "diagonal noise covariance" option is used instead.
Diagonal noise covariance: Discard the off-diagonal elements of the noise covariance matrix (assuming heteroscedastic uncorrelated noise). Corresponds in MNE to the --diagnoise option.
Regularize noise covariance: Regularize the noise-covariance matrix by the given amount for each type of sensor individually (value is restricted to the range 0...1). For more information, please refer to the MNE manual, section 6.2.4 (options --magreg, --gradreg and --eegreg).
Depth weighting
The minimum-norm estimates have a bias towards superficial currents. This tendency can be alleviated by adjusting these parameters. To understand how to set these parameters, please refer to the MNE manual (options --depth, --weightexp and --weightlimit).
Equations
TODO: John
Rey on sLORETA
Yes in sLORETA the noise covariance is not used at all for the standardization process. It can be used modeling correlated noise and whitening, but that is optional.
I have noticed that a lot of folks are confused about this and I have seen many statements in papers spreading this awful confusion. The sLORETA is standardized by the resolution matrix (diagonal for dipole orientations constraints, or block diagonals for free orientations).
That is why sLORETA has zero localization bias for ALL point-spread functions, and why I always prefer sLORETA over dSPM, MNE, or any beamformer. This is all in the math .... but ..... just so that you know Fas Hsuan Lin's paper comparing sLORETA with dSPM, and MNE has a big mistake, the assumed source covariance matrix is not the identity matrix, and that violates the beauty of the math and results in non-zero localization bias. That's why in Brainstorm the prior source covariance matrix used for sLORETA automatically uses no depth bias compensation (identity matrix). sLORETA accomplishes depth bias compensation via the resolution matrix, NOT via the prior source covariance matrix. Trying to use a depth exponent of 0.7 or 0.8 like we do for MNE and dSPM will mess up sLORETA.You will not find this in a paper, but I checked it all out many years ago. This is critical.
Explain sLORETA units (see email exchanges from Feb 2015)
Issues with dSPM average
Average(dSPM) is NOT equal to dSPM(Average).
There is no problem for the MNE and sLORETA solutions, because the scaling of the noise covariance matrix doesn't impact the results.
wMNE(Data, NoiseCov) = wMNE(Data, NoiseCov / N)
So when we average we get:
Average(wMNE(Trials, NoiseCov)) = wMNE(Average, NoiseCov) = wMNE(Average, NoiseCov / N)
But for dSPM we have:
dSPM(Data, NoiseCov) = dSPM(Data, NoiseCov / N) ./ sqrt(N)
So when we average we get:
Average(dSPM(Trials, NoiseCov)) = dSPM(Average, NoiseCov) = dSPM(Average, NoiseCov / N) ./ sqrt(N)Rey: "Basically, the dSPM value at each location is equal to the wMNE value divided by the projection of the estimated noise covariance matrix onto each source point. After whitening, the operational noise covariance matrix is by definition the identity matrix, and hence the projection of the noise is equal to the L2 norm of the row vector of the wMNE inverse operator (in the case of fixed dipole orientations). So, dSPM is what you get when the rows of the wMNE inverse operator all have unit norm (i.e., they all point in different directions but lie in a unit hyper-sphere)."
Rey: "dSPM is really a source mapping of SNR, not of activity. Hence, it's not all so surprising that the single trial SNR maps are smaller...
"Rey: "Perhaps, dSPM should be used only for averaged data (i.e., ERF, ERP), at least until it's all figure out. In a way, dSPM is just MNE followed by the noise normalization. Thus, you could do all the single trial processing with the MNE algorithm, and only do the noise normalization when needed (e.g., after averaging or on single trials only if they are not going to be averaged)."
On the hard drive
Document file tags
Document file structure
Differences for kernel vs. sources
Differences for constrained vs. unconstrained
in_bst_results to get the full sources or apply any process
You can have a look to the corresponding matrix file (right-click > File > View file contents). You would find all the options of forward and inverse modeling, and only one interesting field : ImagingKernel, which contains the inversion kernel. It is a [nVertices x nChannels] matrix that has to be multiplied with the recordings matrix in order to get the activity for each source at all the time samples.
- The minimum norm solution being a linear operation (the time series for each source is a linear combination of all the time series recorded by the sensors), we make this economy of saving only this linear operator instead of the full source matrix (nVertices x nTime)
References
Dale AM, Liu AK, Fischl BR, Buckner RL, Belliveau JW, Lewine JD, Halgren E
Dynamic statistical parametric mapping: combining fMRI and MEG for high-resolution imaging of cortical activity. Neuron 2000 Apr, 26(1):55-67Pascual-Marqui RD, Standardized low-resolution brain electromagnetic tomography (sLORETA): technical details, Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol 2002, 24 Suppl D:5-12
Additional discussions on the forum
Forum: Minimum norm units (pA.m): http://neuroimage.usc.edu/forums/showthread.php?1246
Forum: Imaging resolution kernels: http://neuroimage.usc.edu/forums/showthread.php?1298
Forum: Spatial smoothing of sources: http://neuroimage.usc.edu/forums/showthread.php?1409
Forum: Units for dSPM and sLORETA: http://neuroimage.usc.edu/forums/showthread.php?1535
Forum: EEG reference: http://neuroimage.usc.edu/forums/showthread.php?1525#post6718
Forum: Sign of the MNE values: http://neuroimage.usc.edu/forums/showthread.php?1649#post7014
Forum: Combining magneto+gradiometers: http://neuroimage.usc.edu/forums/showthread.php?1900
Forum: Residual ocular artifacts: http://neuroimage.usc.edu/forums/showthread.php?1272