|
Size: 5046
Comment:
|
Size: 5897
Comment:
|
| Deletions are marked like this. | Additions are marked like this. |
| Line 7: | Line 7: |
| When you create a new protocol, the program makes a copy of the ICBM152 or Colin27 anatomy and sets it as the default for the protocol. It means that you will be able to use this template brain as a substitute for the subjects without an individual MRI, or as the common brain for group analysis. | When you create a new protocol, the program makes a copy of the ICBM152 anatomy (previously Colin27) and sets it as the default for the protocol. It means that you will be able to use this template brain as a substitute for the subjects without an individual MRI, or as the common brain for group analysis. |
| Line 9: | Line 9: |
| Other sets of MRI+surfaces are available to replace the Colin27 anatomy. Right-click on ''(Default anatomy)'' > Use template. If a package is not currently available on your system, it will be downloaded from the Brainstorm website and saved in $HOME/.brainstorm/templates. | Other sets of MRI+surfaces are available to replace the ICBM152 anatomy. Right-click on ''(Default anatomy)'' > Use template. If a package is not currently available on your system, it will be downloaded from the Brainstorm website and saved in $HOME/.brainstorm/templates. |
| Line 22: | Line 22: |
| You can use either BrainSuite or FreeSurfer for processing the MRIs or your subjects, but you need to use a template that matches this choice in order to use the accurate registration methods. | You can use either '''BrainSuite''' or '''FreeSurfer''' for processing the MRIs or your subjects, but you need to use a template that matches this choice in order to use the accurate registration methods. |
| Line 28: | Line 28: |
| * '''ICBM152''': Non-linear average of 152 subjects, processed with FreeSurfer 5.3: [[http://www.bic.mni.mcgill.ca/ServicesAtlases/ICBM152NLin2009|more information]] | * '''ICBM152_2015''': Non-linear average of 152 subjects, FreeSurfer 5.3: [[http://www.bic.mni.mcgill.ca/ServicesAtlases/ICBM152NLin2009|more information]] |
| Line 35: | Line 35: |
| * Cortex surface: high-resolution (~300.000 vertices) and low-resolution (15.000 vertices) * Head surface: based on the head used for FSAverage in the MNE software * FreeSurfer spherical registration of each hemisphere, with which we can co-register the individual brains processed with FreeSurfer with the selected default anatomy |
* Cortex/white surface: high-resolution (~300.000 vertices) and low-resolution (15.000 vertices) * Head layers: scalp, outer skull, inner skull * FreeSurfer spherical registration of each hemisphere, for subject co-registration. |
| Line 39: | Line 39: |
| * ASEG sub-cortical atlas. | |
| Line 45: | Line 46: |
| * '''Colin27_BrainSuite''': Average of 27 scans, processed with BrainSuite 15b: [[http://www.bic.mni.mcgill.ca/ServicesAtlases/Colin27|more information]] * '''ICBM152_BrainSuite''': Non-linear average of 152 subjects, BrainSuite 15b: [[http://www.bic.mni.mcgill.ca/ServicesAtlases/ICBM152NLin2009|more information]] * '''BCI-DNI_BrainSuite''': Single subject atlas developed at USC, BrainSuite 15c: [[http://brainsuite.org/svreg_atlas_description/|more information]] They all include the following information: * T1 MRI volume * Cortex/white surfaces: high-resolution (~300.000 vertices) and low-resolution (15.000 vertices) * Head layers: scalp, outer skull, inner skull * BrainSuite square registration of each hemisphere, for subject co-registration. * BrainSuite surface-based atlas: SVReg For more information on the interactions between BrainSuite and Brainstorm: [[Tutorials/SegBrainSuite|read this tutorial]]. |
|
| Line 49: | Line 64: |
| * '''Infant7w''': 7-week infant brain with the antomical atlas presented in [[http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S105381191400411X|(Kabdebon et al. 2014)]]. | * '''Infant7w_2015b''': 7-week infant brain with the anatomical atlas from [[http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S105381191400411X|(Kabdebon et al. 2014)]]. |
| Line 53: | Line 68: |
| The fiducial points (Nasion, LPA, RPA) used in your recordings might not be the same as the ones used in the anatomy templates in Brainstorm (Colin27, ICBM152, FSAverage). By default, the LPA/RPA points are defined at the junction between the tragus and the helix, as represented with the red dot in the [[http://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/CoordinateSystems|Coordinates systems page]]. | The fiducial points (Nasion, LPA, RPA) used in your recordings might not be the same as the ones used in the anatomy templates in Brainstorm. By default, the LPA/RPA points are defined at the junction between the tragus and the helix, as represented with the red dot in the [[http://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/CoordinateSystems|Coordinates systems page]]. |
Using the anatomy templates
Author: Francois Tadel
Contents
Changing the default anatomy
When you create a new protocol, the program makes a copy of the ICBM152 anatomy (previously Colin27) and sets it as the default for the protocol. It means that you will be able to use this template brain as a substitute for the subjects without an individual MRI, or as the common brain for group analysis.
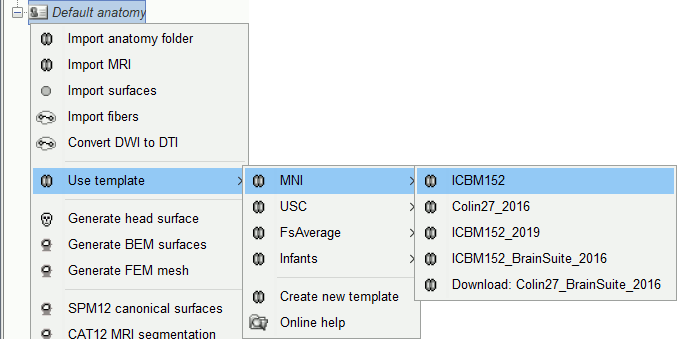
Other sets of MRI+surfaces are available to replace the ICBM152 anatomy. Right-click on (Default anatomy) > Use template. If a package is not currently available on your system, it will be downloaded from the Brainstorm website and saved in $HOME/.brainstorm/templates.
If you click on any of the download options, it downloads it into your $HOME/.brainstorm/templates folder, then the list of files in the (default anatomy) folder is replaced with the new template.
Group analysis
When performing a group analysis with multiple subjects for which you have the individual MRI scans, you need to project the sources estimated on each subject on a common template, as explained in this tutorial: Group analysis.
For accurate registration between different brains (from a subject to a template or between subjects), you need to use a template that was generated using the same program as the one you used for running the segmentation of all the subjects of your studies.
You can use either BrainSuite or FreeSurfer for processing the MRIs or your subjects, but you need to use a template that matches this choice in order to use the accurate registration methods.
FreeSurfer templates
Available options:
Colin27: Average of 27 scans of the same head, processed with FreeSurfer 5.3: more information
ICBM152_2015: Non-linear average of 152 subjects, FreeSurfer 5.3: more information
FSAverage: Average of 40 subjects using a spherical averaging described in (Fischl et al. 1999).
It is the default FreeSurfer brain: please register here if you are using it.
More images: http://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/LabelFreeSurfer#FSAverage_template
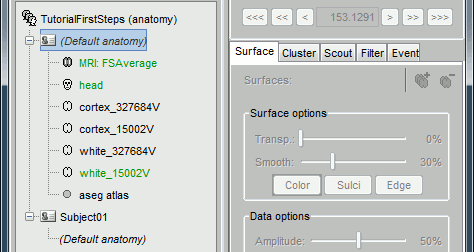
They all include the following information:
- T1 MRI volume
- Cortex/white surface: high-resolution (~300.000 vertices) and low-resolution (15.000 vertices)
- Head layers: scalp, outer skull, inner skull
FreeSurfer spherical registration of each hemisphere, for subject co-registration.
FreeSurfer surface-based atlases: Desikan-Killiany, Destrieux, Brodmann, Mindboggle
(plus Yeo2011 and PALS for FSAverage only)- ASEG sub-cortical atlas.
For more information on the interactions between FreeSurfer and Brainstorm: read this tutorial.
BrainSuite templates
Available options:
Colin27_BrainSuite: Average of 27 scans, processed with BrainSuite 15b: more information
ICBM152_BrainSuite: Non-linear average of 152 subjects, BrainSuite 15b: more information
BCI-DNI_BrainSuite: Single subject atlas developed at USC, BrainSuite 15c: more information
They all include the following information:
- T1 MRI volume
- Cortex/white surfaces: high-resolution (~300.000 vertices) and low-resolution (15.000 vertices)
- Head layers: scalp, outer skull, inner skull
BrainSuite square registration of each hemisphere, for subject co-registration.
BrainSuite surface-based atlas: SVReg
For more information on the interactions between BrainSuite and Brainstorm: read this tutorial.
BrainVISA templates
Note that the BrainVISA-based templates do not allow any accurate registration procedure.
Colin27_2012: Previous version of the default anatomy distributed with Brainstorm.
Infant7w_2015b: 7-week infant brain with the anatomical atlas from (Kabdebon et al. 2014).
Oreilly_1y: 1 year old infant brain with Tzourio-Mazoyer surface atlas (Li et al. 2015, Shi et al. 2011): http://neuroimage.usc.edu/forums/showthread.php?2123-Atlas-for-1-year-old-babies
Modify the default MRI fiducials
The fiducial points (Nasion, LPA, RPA) used in your recordings might not be the same as the ones used in the anatomy templates in Brainstorm. By default, the LPA/RPA points are defined at the junction between the tragus and the helix, as represented with the red dot in the Coordinates systems page.
If you want to use an anatomy template but you are using a different convention when digitizing the position of these points, you have to modify the default positions of the template with the MRI Viewer.
- Go to the anatomy view
In (default anatomy), right-click on the MRI > Edit MRI
- Modify the position of the fiducial points to match your own convention
- Click on [Save], it will update the surfaces to match the new coordinate system