|
Size: 15983
Comment:
|
Size: 15462
Comment:
|
| Deletions are marked like this. | Additions are marked like this. |
| Line 1: | Line 1: |
| '''[TUTORIAL UNDER CONSTRUCTION: NOT READY FOR PUBLIC USE]''' | |
| Line 3: | Line 2: |
| ---- | |
| Line 120: | Line 118: |
| Options | ==== Options ==== * '''Downsample volume before meshing''': When processing the tissue classification volume, reduce the number of voxels along each dimension by this factor. * '''Shift nodes to fit geometry''': The option calls the adaptative mesh generation. The process moves the nodes located on the interface either inward or outward in order to fit the geometry as explained in the [[http://www.fieldtriptoolbox.org/tutorial/headmodel_eeg_fem/|FieldTrip tutorial]]. Below, the example from the FieldTrip website, left=original, right=shifted.<<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:nodeShiftFigure.JPG||width="500",height="200"}} ==== Troubleshooting ==== * '''SPM-related errors''': If you've been trying multiple methods successively, errors mentioning a spm_*.m function could be due to incompatible versions of SPM12 functions in the Matlab path. Brain2mesh, FieldTrip and ROAST all run different versions of SPM12 from the same instance of Matlab. Solution: '''Restart Matlab''' to get a fresh workspace. |
| Line 123: | Line 126: |
The option "Downsamp volume before meshing" will reduce the number of voxel by this factor. The "Shift node" option calls the adaptative mesh generation. The process moves the nodes located on the interface either inward or outward in order to fit the geometry as explained [[http://www.fieldtriptoolbox.org/tutorial/headmodel_eeg_fem/|here]]. This figure shows an example (from Fieldtrip webpage), left the unshifted and on the right the shifted. {{attachment:nodeShiftFigure.JPG||width="500",height="200"}} This method is fast compare to the previous options, the following figures show examples of the mesh obtained with fieldtrip option from the ICBM model. {{attachment:fieldTripMeshICBM.JPG||width="700",height="300"}} === Troubleshooting === '''SPM-related errors''': If you've been trying multiple methods successively, errors mentioning a spm_*.m function could be due to incompatible versions of SPM12 functions in the Matlab path. Brain2mesh, FieldTrip and ROAST all run different versions of SPM12 from the same instance of Matlab. Solution: '''Restart Matlab''' to get a fresh workspace. == BrainSuite == [[http://brainsuite.org/|BrainSuite]] is a collection of open source software tools that enable largely automated processing of magnetic resonance images (MRI) of the human brain. Brainstorm calls BrainSuite tools in order to compute the diffusion tensors from the diffusion wiethed inaging (DWI) data. The diffusion tensor are then converted to conductivity tensors by the linear transformation described by David Tuch et al (ref). The conductivity tensors are are associated with the FEM mesh of the head model. Where ecah mesh element have it's own tensors. The tensors are used to represnet the anisotropic conductivity of a tissue. The anisotropy means the change on the conductivity by changing the direction. For more information regarding tensors please refers to this page (add link). === Requirement === BrainSuite is an independant softeware, Brainstoem calls its functions from the core source code, therefore the installation of BrainSuite is required. Please follow the instructions as explained in [[http://forums.brainsuite.org/download/|this webpage]]. Once the instalation is completed, The BrainSuite installation folder must be informed in the Brainstorm preferences (From the Brainsuitrom interface, click on 'File' and then 'Edite preferences'). {{https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/6920058/81406567-1c785400-913a-11ea-9048-28c7459af7da.png|image}} === When and how to use it === [For this version June 2020, only the tetra mesh are supported and tested.] The BrainSuite pipline is used to estimate the anisotropy of the brain tissues. This process is associated with the [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/Duneuro?highlight=(duneuro)|DUNEuro FEM computation]]. The conductivity tensors will be assigned to each mesh elements. In order to use this functionnality the DWI data are required. The Niftii files and the assocaited bvec and bval are required. Further more we assume that you have already generated the FEM mesh from the MRI as explained in the previous sections. === Tissue anisotropy estimation === '''<<TAG(Advanced)>>''' From Brainstorm, BrainSuite is used for the skull stripping, bias field correction and then the diffusion pipline is used to compute the diffusion tensors. ref to the maon function : likToGit |
|
| Line 174: | Line 130: |
| {{attachment:femMesh2.gif}} | {{attachment:femContents.gif}} |
| Line 176: | Line 132: |
| TODO | ==== Structure of the FEM mesh files: tess_fem_*.mat ==== * '''Atlas''': Array of structures, each entry is one menu in the drop-down list in the Scout tab. * '''Name''': Label of the atlas (reserved names: "User scouts", "Structures", "Source model") * '''Scouts''': List of regions of interest in this atlas, see the [[http://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/Scouts#On_the_hard_drive|Scout tutorial]]. * '''Comment''': String displayed in the database explorer to represent the file. '' '' * '''Curvature''': [Nvertices x 1], curvature value at each point. * '''Faces''': [Nfaces x 3], triangles constituting the surface mesh. * '''History''': List of operations performed on this file (menu File > View file history). * '''iAtlas''': Index of the atlas that is currently selected for this surface. * '''Reg''': Structure with registration information, used to interpolate the subject's maps on a template. * '''Sphere.Vertices''': Location of the surface vertices on the [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/CoregisterSubjects|FreeSurfer registered spheres]]. * '''Square.Vertices''': Location of the surface vertices in the [[http://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/CoregisterSubjects#Registration_with_BrainSuite|BrainSuite atlas]]. * '''AtlasSquare.Vertices''': Corresponding vertices in the high-resolution [[http://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/CoregisterSubjects#Registration_with_BrainSuite|BrainSuite atlas]]. * '''SulciMap''': [Nvertices x 1], binary mask marking the botton of the sulci (1=displayed as darker). * '''tess2mri_interp''': [Nvoxels x Nvertices] sparse interpolation matrix MRI<=>surface. * '''VertConn''': [Nvertices x Nvertices] Sparse adjacency matrix, VertConn(i,j)=1 if i and j are neighbors. * '''Vertices''': [Nvertices x 3], coordinates (x,y,z) of all the points of the surface, in SCS coordinates. * '''VertNormals''': [Nvertices x 3], direction (x,y,z) of the normal to the surface at each vertex. |
FEM mesh generation
Authors: Takfarinas Medani, Francois Tadel
FEM forward modeling requires the construction of a 3D model of the head tissues. The volume of the head is divided in small geometrical elements with 4 faces (tetrahedrons) or 6 faces (hexahedrons). Each element is associated with a type of biological tissue (e.g. white matter, gray matter, CSF, skull, skin) and electrical conductivity properties.
This page lists the methods integrated with Brainstorm to generate 3D meshes of the head. For a generic introduction to FEM in Brainstorm, refer to the tutorials: Realistic head model: FEM with DUNEuro and FEM median nerve example.
Contents
Generate FEM mesh
FEM meshes can be computed from surfaces (as the ones generated for the BEM models) or from MRI volumes (T1w and/or T2w). The methods that are available when using the popup menu Generate FEM mesh depend on the selected inputs.
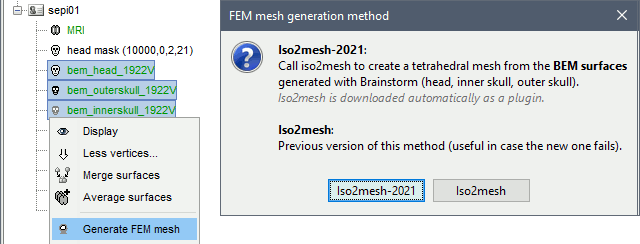
Surfaces
Select a list of surfaces representing the separation between different tissues (holding the CTRL or SHIFT key), then right-click on any of them. The software Iso2mesh can create a tetrahedral mesh to represent the tissues between these different layers.
T1 MRI
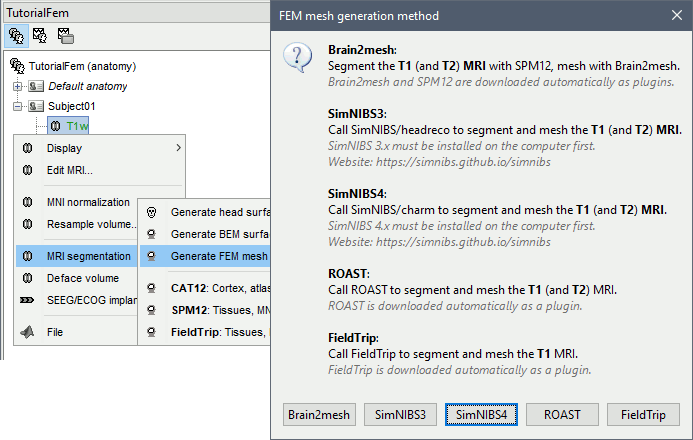
Right-click on a T1 MRI available in the databas. Typically, this is the default MRI volume displayed in green in the subject folder. Methods available: Brain2mesh, SimNIBS, ROAST, FieldTrip.
T1+T2 MRI
Select the T1+T2 volumes, then right-click on any of them. The different files are identified based on the tags "T1" and "T2" the file names (as displayed in the Brainstorm database explorer). If these identification tags are not found in the file names, the default MRI (in green) is used as the T1, the other as the T2. If none of the is the default MRI, the first selected file is used as the T1, the second is used as the T2. Methods available: Brain2mesh, SimNIBS, ROAST.
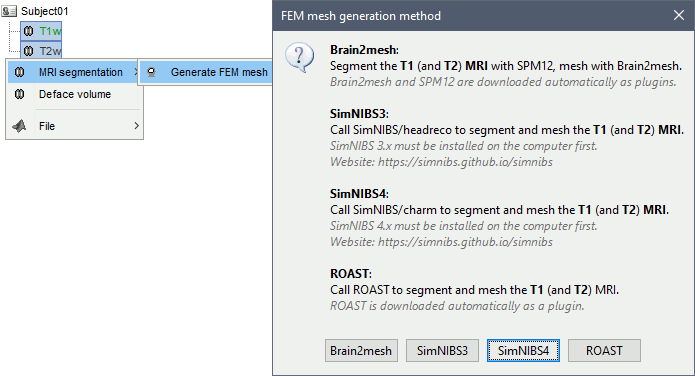
Anatomy folder
If you right-click on the subject folder > Generate FEM mesh, then Brainstorm offers all the possible options, even the ones that are not applicable to this specific subject.
Volume method: If using a method based on MRI volumes, the T1 and T2 volumes are detected among all the volumes available based on the tags "T1" and "T2" in the file names (make sure only one file as each of these tags), otherwise use only the default MRI (in green) as the T1.
Surface method: If using a method based on surfaces, the default surfaces (in green) from three categories as selected: the inner skull, the outer skull and the head surfaces.
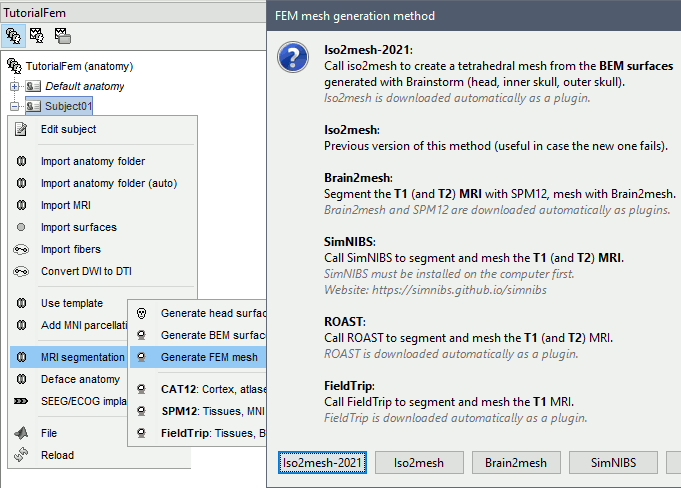
Iso2mesh
Iso2mesh is a Matlab/Octave-based mesh generation and processing toolbox, available as a Brainstorm plugin.
Brainstorm uses it to generate a FEM tetrahedral mesh from a set of nested surfaces representing the separation between different tissues of the head. For example, these surfaces can be the ones generated for the computation of a BEM forward model. A full example is available in the tutorial Realistic head model: FEM with DUNEuro.
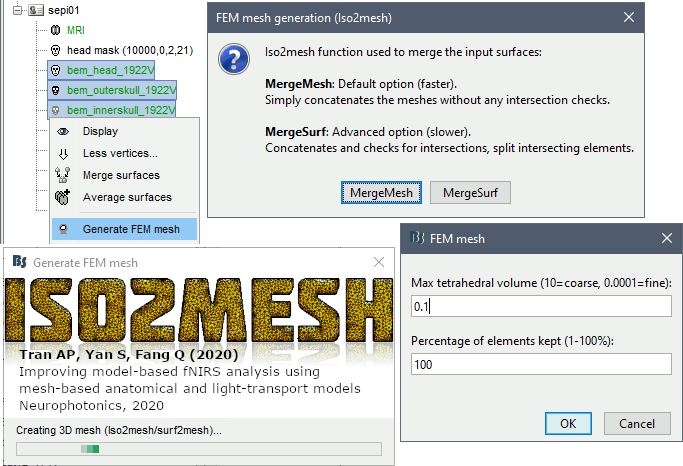
Options
MergeMesh: Simply concatenates the input surfaces without any intersection checks. Default option (faster).
MergeSurf: Concatenates and checks for intersections, split intersecting elements. Advanced option (slower).
Max tetrahedral volume: Maximum volume of the tetrahedral element in the mesh.
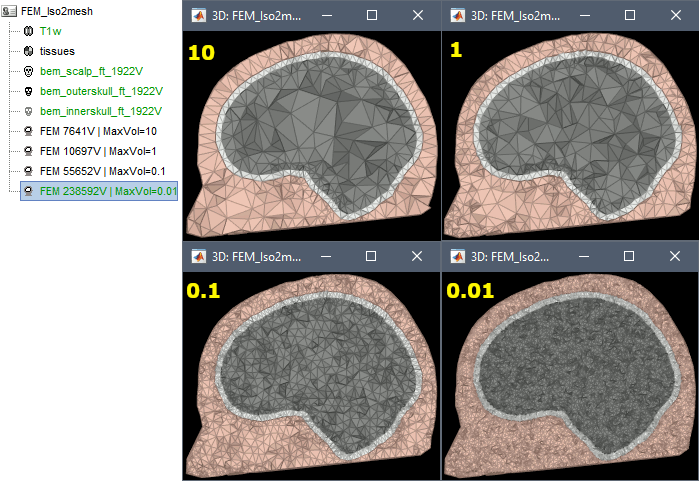
From our tests, a DUNEuro FEM head model with a value of 0.1 achieves similar results as the OpenMeeg head model computed from the same surfaces. We have also noticed that the result with v = 0,001 is almost similar to v = 0,01.
- Increasing the mesh resolution requires more time to generate the mesh, more time and memory to perform the FEM computation and more storage space in the database.
Percentage of elements kept: Parameter between 0-100%, used to keep or not the original input surface nodes.
Examples
FEM mesh with different values of "Max volume": [10, 1, 0.1, 0.01] - Kept ratio=100%.
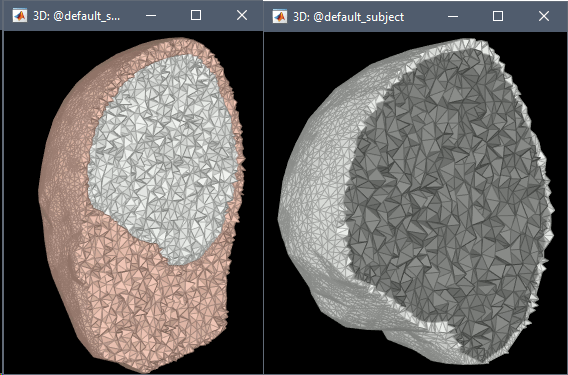
FEM meshes with only two compartments: This could be useful for investigating the influence of a specific tissue on the EEG/MEG forward solution or on the source localization, or for analyzing SEEG only within the brain volume. On the left: head and outer skull; On the right: inner and outer skull.
Troubleshooting
Tetget failed: If intersections are present on the surfaces mesh, the iso2mesh FEM mesh generation fails (tetgen). You may need regenerate new surfaces from the MRI.
Alternatively: You may try with the MergSurf option, this option can correct the intersection and create new nodes and elements. However, we do not recommend to use these models for EEG/MEG forward head computations: this is a research topic and it's still under investigation by the FEM communities.
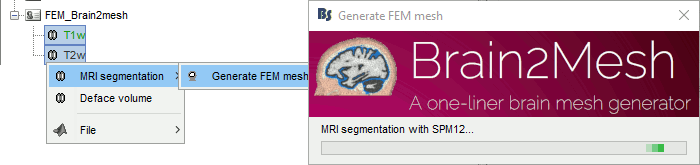
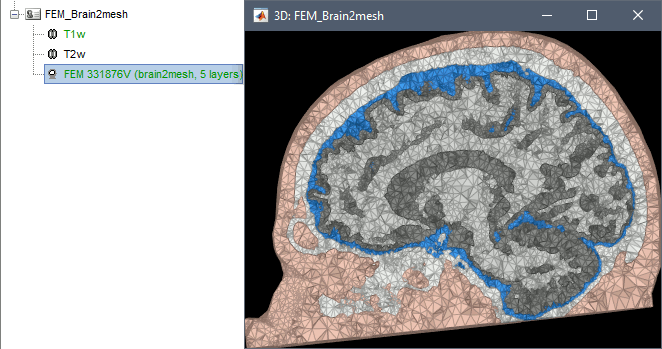
Brain2mesh
Brain2mesh is a MATLAB/Octave based 3D mesh generation toolbox dedicated to the creation of high-quality multi-layered brain mesh models. This software is developed by the same team developing Iso2mesh and relies heavily on it. Both are available as a Brainstorm plugins.
Brainstorm runs the SPM12 segmentation routine on the T1 or T1+T2 MRI volumes to obtain a 5-tissue classifcation (white matter, gray matter, CSF, skull and skin), which is then passed to Brain2mesh for 3D meshing. A full example is available in the tutorial FEM tensors estimation. This option runs fast, but does not generate good quality cortex surfaces, which are needed for the full cortically-constrained source estimation pipeline in Brainstorm.
At the moment, Brainstorm can only use the default parameters of Brain2mesh. If you need more options to be available from the interface, please contact us on the user forum.
Troubleshooting
SPM-related errors: If you've been trying multiple methods successively, errors mentioning a spm_*.m function could be due to incompatible versions of SPM12 functions in the Matlab path. Brain2mesh, FieldTrip and ROAST all run different versions of SPM12 from the same instance of Matlab. Solution: Restart Matlab to get a fresh workspace.
SimNIBS
SimNIBS software was developed to calculate the electric fields caused by Transcranial Electrical Stimulation (TES) and Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS). All its software dependencies (CAT12, Netgen, Gmsh, MeshFix) are embedded in the SimNIBS installation, which ensures a high stability and portability. However, it cannot be managed automatically as a plugin by Brainstorm, and needs to be installed manually. See: Download and install SimNIBS.
In Brainstorm, we use the headreco pipeline to process T1 or T1+T2 MRI volumes (T1 is required, T2 is highly recommended). This pipeline generates the highest-quality tetrahedral FEM mesh we can get from Brainstorm. It calls internally CAT12 for tissue segmentation (white matter, gray matter, CSF, skull and scalp), and therefore gives us access to high-quality cortex surfaces and surface-based atlases. The tetrahedral mesh generation is done with Gmsh, Netgen and MeshFix. Depending on your computer performances, this process will take between 2 to 5 hours.
Given the high quality and exhaustivity of its outputs, SimNIBS/headreco is the recommended method for FEM mesh generation in Brainstorm. A full example is available in the tutorial: FEM median nerve example.
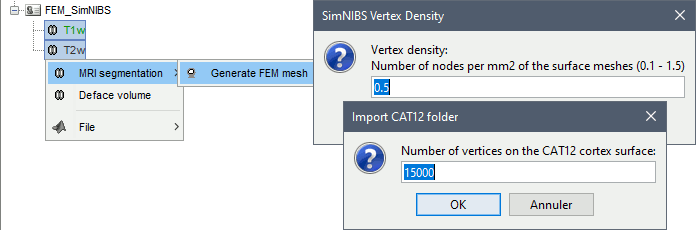
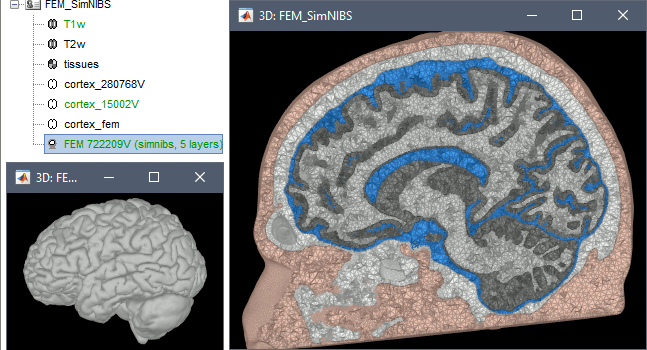
Options
Vertex density: Number of node per mm2 of the surface mesh.
Number of vertices: This is not an input parameter of SimNIBS, but a parameter to control how much to downsample the cortex surface generated by CAT12 when importing it into the Brainstorm database. See the introduction tutorials.
Troubleshooting
ROAST
ROAST is a fully automated, Realistic, vOlumetric Approach to Simulate Transcranial electric stimulation. Open-source and Matlab-based, it is available as a Brainstorm plugin. It calls internally SPM8 for tissue segmentation of the T1 or T1+T2 MRI volumes to obtain a 5-tissue classifcation (white matter, gray matter, CSF, skull and skin). Then it relies mostly on iso2mesh for generating a tetrahedral mesh.
This option runs fast, but does not generate good quality cortex surfaces, which are needed for the full cortically-constrained source estimation pipeline in Brainstorm.
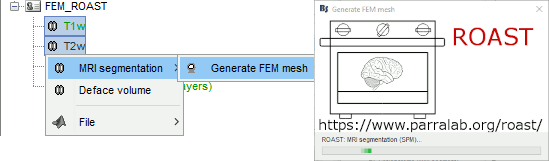
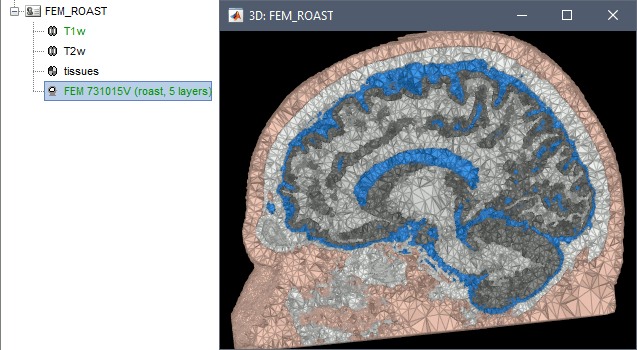
Troubleshooting
SPM-related errors: If you've been trying multiple methods successively, errors mentioning a spm_*.m function could be due to incompatible versions of SPM12 functions in the Matlab path. Brain2mesh, FieldTrip and ROAST all run different versions of SPM12 from the same instance of Matlab. Solution: Restart Matlab to get a fresh workspace.
Fieldtrip
FieldTrip is an open-source Matlab-based toolbox that includes a pipeline dedicated to the generation of hexahedral FEM mesh. It is available as a Brainstorm plugin.
Brainstorm calls the function ft_volumesegment on the T1 MRI volume to obtain a tissue segmentation with 5 layers (white matter, gray matter, CSF, skull and skin), then ft_prepare_mesh_hexa to create a hexahedral mesh.
The mesh generation with the method is simple and fast: it downsamples the tissue classification volume, then converts all the voxels to a hexahedral mesh. The quality of the output is relatively poor: the regular meshing of the voxels makes it inefficient for providing a good representation of the tissues geometry with a limited number of elements.
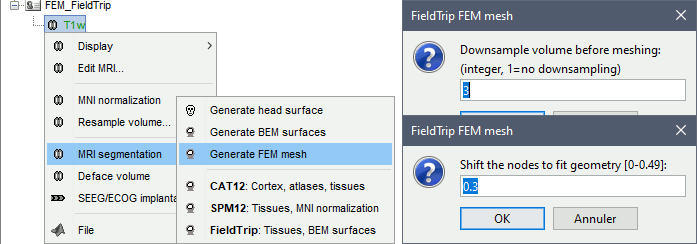
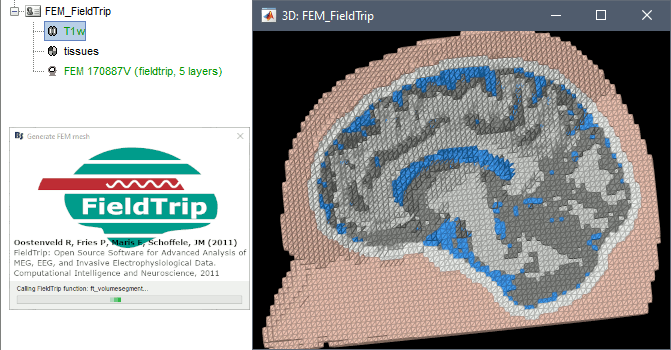
Options
Downsample volume before meshing: When processing the tissue classification volume, reduce the number of voxels along each dimension by this factor.
Shift nodes to fit geometry: The option calls the adaptative mesh generation. The process moves the nodes located on the interface either inward or outward in order to fit the geometry as explained in the FieldTrip tutorial. Below, the example from the FieldTrip website, left=original, right=shifted.
Troubleshooting
SPM-related errors: If you've been trying multiple methods successively, errors mentioning a spm_*.m function could be due to incompatible versions of SPM12 functions in the Matlab path. Brain2mesh, FieldTrip and ROAST all run different versions of SPM12 from the same instance of Matlab. Solution: Restart Matlab to get a fresh workspace.
On the hard drive
Right-click on a FEM mesh > File > View file contents:
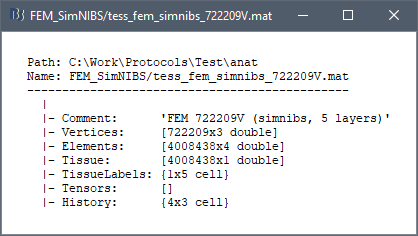
Structure of the FEM mesh files: tess_fem_*.mat
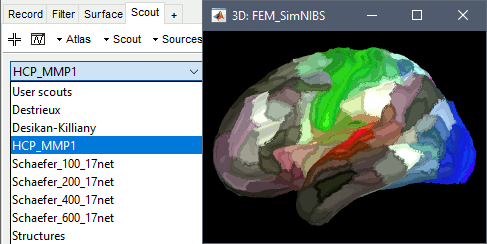
Atlas: Array of structures, each entry is one menu in the drop-down list in the Scout tab.
Name: Label of the atlas (reserved names: "User scouts", "Structures", "Source model")
Scouts: List of regions of interest in this atlas, see the Scout tutorial.
Comment: String displayed in the database explorer to represent the file.
Curvature: [Nvertices x 1], curvature value at each point.
Faces: [Nfaces x 3], triangles constituting the surface mesh.
History: List of operations performed on this file (menu File > View file history).
iAtlas: Index of the atlas that is currently selected for this surface.
Reg: Structure with registration information, used to interpolate the subject's maps on a template.
Sphere.Vertices: Location of the surface vertices on the FreeSurfer registered spheres.
Square.Vertices: Location of the surface vertices in the BrainSuite atlas.
AtlasSquare.Vertices: Corresponding vertices in the high-resolution BrainSuite atlas.
SulciMap: [Nvertices x 1], binary mask marking the botton of the sulci (1=displayed as darker).
tess2mri_interp: [Nvoxels x Nvertices] sparse interpolation matrix MRI<=>surface.
VertConn: [Nvertices x Nvertices] Sparse adjacency matrix, VertConn(i,j)=1 if i and j are neighbors.
Vertices: [Nvertices x 3], coordinates (x,y,z) of all the points of the surface, in SCS coordinates.
VertNormals: [Nvertices x 3], direction (x,y,z) of the normal to the surface at each vertex.
