|
Size: 12319
Comment:
|
Size: 15983
Comment:
|
| Deletions are marked like this. | Additions are marked like this. |
| Line 1: | Line 1: |
| = Realistic head model: FEM mesh generation = '''[TUTORIAL UNDER DEVELOPMENT: NOT READY FOR PUBLIC USE]''' |
'''[TUTORIAL UNDER CONSTRUCTION: NOT READY FOR PUBLIC USE]''' |
| Line 4: | Line 3: |
| ''Authors: Takfarinas Medani '' | ---- |
| Line 6: | Line 5: |
| <<TableOfContents(2,2)>> | = FEM mesh generation = ''Authors: [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/AboutUs/tmedani#preview|Takfarinas Medani]], Francois Tadel'' |
| Line 8: | Line 8: |
| == Introduction == This tutorial present the different method integrated to brainstorm used to generate the FEM mesh. |
FEM forward modeling requires the construction of a 3D model of the head tissues. The volume of the head is divided in small geometrical elements with 4 faces (tetrahedrons) or 6 faces (hexahedrons). Each element is associated with a type of biological tissue (e.g. white matter, gray matter, CSF, skull, skin) and electrical conductivity properties. |
| Line 11: | Line 10: |
| In order to use the finite element method to compute either the EEG/MEG forward problem or the simulate TMS od TDSC stimulation, the mesh of the head model is required. | This page lists the methods integrated with Brainstorm to generate 3D meshes of the head. For a generic introduction to FEM in Brainstorm, refer to the tutorials: [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/Duneuro|Realistic head model: FEM with DUNEuro]] and [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/FemMedianNerve|FEM median nerve example]]. |
| Line 13: | Line 12: |
| In this tutorial, we present the different methods available with brainstorm to generate the FEM mesh and how to use them. | <<TableOfContents(3,2)>> |
| Line 15: | Line 14: |
| == FEM Mesh generation methods == The most modern software that are used to generate the volume mesh head model are integrated within brainstorm with an easy graphical interface to use call these tools. |
== Generate FEM mesh == FEM meshes can be computed from surfaces (as the ones generated for the [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/TutBem#BEM_surfaces|BEM models]]) or from MRI volumes (T1w and/or T2w). The methods that are available when using the popup menu '''Generate FEM mesh''' depend on the selected inputs. |
| Line 18: | Line 17: |
| "Iso2mesh" : This option merges the brainstorm surfaces available on the subject and then generarte the tetrahedral mesh. | === Surfaces === Select a list of surfaces representing the separation between different tissues (holding the CTRL or SHIFT key), then right-click on any of them. The software [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/FemMesh#Iso2mesh|Iso2mesh]] can create a tetrahedral mesh to represent the tissues between these different layers. |
| Line 20: | Line 20: |
| "Brain2Mesh" : This options uses the MRIs available on the subjects, then it calls the SPM segmentation of the volume into 5 tissus (white, gray, scf, skull and skin). After that it converts into a tetrahedral mesh. | {{attachment:callSurf.gif}} |
| Line 22: | Line 22: |
| "SimNibs" : The recommended option, it calls the headreco {ref} and generate a FEM head model | === T1 MRI === Right-click on a T1 MRI available in the databas. Typically, this is the default MRI volume displayed in green in the subject folder. Methods available: [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/FemMesh#Brain2mesh|Brain2mesh]], [[http://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/FemMesh#SimNIBS|SimNIBS]], [[http://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/FemMesh#ROAST|ROAST]], [[http://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/FemMesh#FieldTrip|FieldTrip]]. |
| Line 24: | Line 25: |
| "FieldTrip" : (in progress) "Roast" : (in progress) | {{attachment:callT1.gif}} |
| Line 26: | Line 27: |
| "headreco" : | === T1+T2 MRI === Select the T1+T2 volumes, then right-click on any of them. The different files are identified based on the tags "T1" and "T2" the file names (as displayed in the Brainstorm database explorer). If these identification tags are not found in the file names, the default MRI (in green) is used as the T1, the other as the T2. If none of the is the default MRI, the first selected file is used as the T1, the second is used as the T2. Methods available: [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/FemMesh#Brain2mesh|Brain2mesh]], [[http://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/FemMesh#SimNIBS|SimNIBS]], [[http://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/FemMesh#ROAST|ROAST]]. |
| Line 28: | Line 30: |
| https://simnibs.github.io/simnibs/build/html/documentation/command_line/headreco.html | {{attachment:callT1T2.gif}} |
| Line 30: | Line 32: |
| This function is part of the SimNibs software: | === Anatomy folder === If you right-click on the subject folder > Generate FEM mesh, then Brainstorm offers all the possible options, even the ones that are not applicable to this specific subject. |
| Line 32: | Line 35: |
| Brainstorm integrated a list of the open-source tools that are commonly used by the FEM community to generate either tetra or hexahedra mesh head model either from surface mesh or from MRI. Here is the list of the available methods in brainstorm: | * '''Volume ''''''method''': If using a method based on MRI volumes, the T1 and T2 volumes are detected among all the volumes available based on the tags "T1" and "T2" in the file names (make sure only one file as each of these tags), otherwise use only the default MRI (in green) as the T1. * '''Surface method''': If using a method based on surfaces, the default surfaces (in green) from three categories as selected: the inner skull, the outer skull and the head surfaces. |
| Line 34: | Line 38: |
| - [[http://iso2mesh.sourceforge.net/cgi-bin/index.cgi?Doc/FunctionList|iso2mesh]] | {{attachment:callAnat.gif}} |
| Line 36: | Line 40: |
| - [[http://mcx.space/brain2mesh/|Brain2mesh]] | == Iso2mesh == [[http://iso2mesh.sourceforge.net|Iso2mesh]] is a Matlab/Octave-based mesh generation and processing toolbox, available as a [[https://Tutorials/Plugins|Brainstorm plugin]]. |
| Line 38: | Line 43: |
| - [[https://simnibs.github.io/simnibs/build/html/index.html|SimNibs]] | Brainstorm uses it to generate a FEM tetrahedral mesh from a set of '''nested surfaces''' representing the separation between different tissues of the head. For example, these surfaces can be the ones generated for the computation of a [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/TutBem#BEM_surfaces|BEM forward model]]. A full example is available in the tutorial [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/Duneuro#FEM_mesh|Realistic head model: FEM with DUNEuro]]. |
| Line 40: | Line 45: |
| - [[http://www.fieldtriptoolbox.org/|Fieldtrip]] | {{attachment:iso2meshOptions.gif}} |
| Line 42: | Line 47: |
| You can display the full list and a short description by right click on the MRI of the subject and then click the item "Generate FEM Mesh" | ==== Options ==== * '''MergeMesh''': Simply concatenates the input surfaces without any intersection checks. Default option (faster). * '''MergeSurf''': Concatenates and checks for intersections, split intersecting elements. Advanced option (slower). * '''Max tetrahedral volume''': Maximum volume of the tetrahedral element in the mesh. * From our tests, a DUNEuro FEM head model with a value of 0.1 achieves similar results as the OpenMeeg head model computed from the same surfaces. We have also noticed that the result with v = 0,001 is almost similar to v = 0,01. * Increasing the mesh resolution requires more time to generate the mesh, more time and memory to perform the FEM computation and more storage space in the database. * '''Percentage of elements kept''': Parameter between 0-100%, used to keep or not the original input surface nodes. |
| Line 44: | Line 55: |
| {{attachment:meshMethods.JPG||height="400",width="350"}} | ==== Examples ==== * FEM mesh with different values of "Max volume": [10, 1, 0.1, 0.01] - Kept ratio=100%.<<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:iso2meshMaxvol.gif}} * FEM meshes with only two compartments: This could be useful for investigating the influence of a specific tissue on the EEG/MEG forward solution or on the source localization, or for analyzing SEEG only within the brain volume. On the left: head and outer skull; On the right: inner and outer skull. <<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:iso2Mesh2layer.gif}} |
| Line 46: | Line 59: |
| === iso2mesh === iso2mesh is a matlab /octave-based mesh generation and processing toolbox. It can [[http://iso2mesh.sourceforge.net/cgi-bin/index.cgi?Doc/Workflow|create 3D tetrahedral finite element (FE) mesh from surfaces, 3D binary and gray-scale volumetric images]] such as segmented MRI/CT scans. |
==== Troubleshooting ==== * '''Tetget failed''': If intersections are present on the surfaces mesh, the iso2mesh FEM mesh generation fails (tetgen). You may need regenerate new surfaces from the MRI. ''' ''' * Alternatively: You may try with the MergSurf option, this option can correct the intersection and create new nodes and elements. However, we do not recommend to use these models for EEG/MEG forward head computations: this is a research topic and it's still under investigation by the FEM communities. |
| Line 49: | Line 63: |
| '''Requirement ''' | == Brain2mesh == [[http://mcx.space/brain2mesh/|Brain2mesh]] is a MATLAB/Octave based 3D mesh generation toolbox dedicated to the creation of high-quality multi-layered brain mesh models. This software is developed by the same team developing Iso2mesh and relies heavily on it. Both are available as a [[https://Tutorials/Plugins|Brainstorm plugins]]. |
| Line 51: | Line 66: |
| it If iso2mesh is not installed in your computer, Brainstrom will download the last release from this [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/http://iso2mesh.sourceforge.net/cgi-bin/index.cgi?Download|webpage]] and install it when it'is needed. However, you can also download the iso2mesh from the [[https://github.com/fangq/iso2mesh|github]] and add it to your matlab path. | Brainstorm runs the '''SPM12 '''segmentation routine on the '''T1 '''or '''T1+T2 MRI''' volumes to obtain a 5-tissue classifcation (white matter, gray matter, CSF, skull and skin), which is then passed to Brain2mesh for 3D meshing. A full example is available in the tutorial [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/FemTensors#FEM_mesh|FEM tensors estimation]]. This option runs fast, but does not generate good quality cortex surfaces, which are needed for the full cortically-constrained source estimation pipeline in Brainstorm. |
| Line 53: | Line 68: |
| '''When and how to use it''' | At the moment, Brainstorm can only use the default parameters of Brain2mesh. If you need more options to be available from the interface, please contact us on the user forum. |
| Line 55: | Line 70: |
| iso2mesh is used as the basic option by brainstorm to generate FEM mesh from surfaces mesh. | {{attachment:brain2meshCall.gif}} |
| Line 57: | Line 72: |
| Assuming the situation where you have surfaces mesh of your subject available and you have already computed the [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/TutBem?highlight=(bem)|OpenMeeg]]forward problem. If you want to use the duneuro FEM to compute the forward model, you need to generate the FEM mesh from a similar surface used by OpenMeeg Here is the way to do it : | {{attachment:brain2meshMesh.gif}} |
| Line 59: | Line 74: |
| 1. Richt click on the subject : In this way, brainstorm will load the inner, outer and the head from the subject data. if any of these surfaces is missing, an error will be displayed. 1. Select the 'Generate FEM mesh' item, 1. Select the iso2mesh option, 1. Set the iso2mesh parameters, |
==== Troubleshooting ==== * '''SPM-related errors''': If you've been trying multiple methods successively, errors mentioning a spm_*.m function could be due to incompatible versions of SPM12 functions in the Matlab path. Brain2mesh, FieldTrip and ROAST all run different versions of SPM12 from the same instance of Matlab. Solution: '''Restart Matlab''' to get a fresh workspace. |
| Line 64: | Line 77: |
| 1. These options are used by the surf2mesh function. Select either '''MergeMesh''' or '''MergeSurf.''' 1. '''Max tetrahedral volum''' : is the maximum volume of the tetrahedral element in the mesh. '''Pourcentage of the element to keep''': parameter between 0-100%, it used to keep or not the original input surface nodes. |
== SimNIBS == [[https://simnibs.github.io/simnibs|SimNIBS]] software was developed to calculate the electric fields caused by Transcranial Electrical Stimulation (TES) and Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS). All its software dependencies (CAT12, Netgen, Gmsh, MeshFix) are embedded in the SimNIBS installation, which ensures a high stability and portability. However, it cannot be managed automatically as a plugin by Brainstorm, and needs to be installed manually. See: [[https://simnibs.github.io/simnibs/build/html/installation/simnibs_installer.html|Download and install SimNIBS]]. |
| Line 68: | Line 80: |
| Also, a full example is explained in this [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Duneuro?highlight=(duneuro)|page]]. | In Brainstorm, we use the [[https://simnibs.github.io/simnibs/build/html/documentation/command_line/headreco.html|headreco]] pipeline to process '''T1''' or '''T1+T2 MRI''' volumes (T1 is required, [[https://simnibs.github.io/simnibs/build/html/tutorial/head_meshing.html|T2 is highly recommended]]). This pipeline generates the highest-quality tetrahedral FEM mesh we can get from Brainstorm. It calls internally [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/SegCAT12|CAT12]] for tissue segmentation (white matter, gray matter, CSF, skull and scalp), and therefore gives us access to high-quality cortex surfaces and surface-based atlases. The tetrahedral mesh generation is done with Gmsh, Netgen and MeshFix. Depending on your computer performances, this process will take between 2 to 5 hours. |
| Line 70: | Line 82: |
| . | Given the high quality and exhaustivity of its outputs, SimNIBS/headreco is the recommended method for FEM mesh generation in Brainstorm. A full example is available in the tutorial: [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/FemMedianNerve#FEM_mesh_with_SimNIBS|FEM median nerve example]]. |
| Line 72: | Line 84: |
| {{attachment:iso2meshProcess.JPG||height="380",width="720"}} | {{attachment:simnibs.gif}} |
| Line 74: | Line 86: |
| Here is a view of mesh obtained with different values of the Max volume = [10, 1, 0.1, 0.01] with a keep ratio = 100%. | {{attachment:simnibs2.gif}} |
| Line 76: | Line 88: |
| {{attachment:IcbmMeshModels.jpg||height="420",width="700"}} | {{attachment:simnibs3.gif}} |
| Line 78: | Line 90: |
| From our experience, a value of 0,1 for the tetrahedral volume achieves similar results as the OpenMeeg computed from the same surfaces. And we have noticed that the result with v = 0,001 is almost similar to v = 0,01. Increasing the mesh resolution needs more time to generate the mesh, more time to perform the FEM computation and of course more memory to store the mesh in the disc. | ==== Options ==== * '''Vertex density''': Number of node per mm2 of the surface mesh. * '''Number of vertices''': This is not an input parameter of SimNIBS, but a parameter to control how much to downsample the cortex surface generated by CAT12 when importing it into the Brainstorm database. See the [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/ImportAnatomy#Import_the_anatomy|introduction tutorials]]. |
| Line 80: | Line 94: |
| If intersections are present on the surfaces mesh, the iso2mesh FEM mesh generation fails (tetgen) and an error will be displayed on the screen. If you face this problem, you need to check the surfaces and/or regenerate new surfaces from the MRI. | ==== Troubleshooting ==== * SimNIBS help: https://simnibs.github.io/simnibs/build/html/installation/throubleshooting.html |
| Line 82: | Line 97: |
| ==== other use ==== You can also select any surface mesh, or multiple surfaces (with Shift key), on the brainstorm anatomy windows and then generate tetrahedral mesh y following the same steps above. |
== ROAST == [[https://www.parralab.org/roast/|ROAST]] is a fully automated, Realistic, vOlumetric Approach to Simulate Transcranial electric stimulation. Open-source and Matlab-based, it is available as a [[https://Tutorials/Plugins|Brainstorm plugin]]. It calls internally SPM8 for tissue segmentation of the '''T1 '''or '''T1+T2 MRI''' volumes to obtain a 5-tissue classifcation (white matter, gray matter, CSF, skull and skin). Then it relies mostly on iso2mesh for generating a tetrahedral mesh. |
| Line 85: | Line 100: |
| Here are some examples using only some 2 tissues. This option could be useful for investigation of tissue influence on the EEG/MEG source localization or analyzing only SEEG within brain volume ... | This option runs fast, but does not generate good quality cortex surfaces, which are needed for the full cortically-constrained source estimation pipeline in Brainstorm. |
| Line 87: | Line 102: |
| {{attachment:otherMesh.JPG||height="320",width="600"}} | {{attachment:roast1.gif}} |
| Line 89: | Line 104: |
| In this part you can generate your FEM mesh from surfaces that you can get fron the segmentation software (brainSuite, FreeSurfer ....). | {{attachment:roast2.gif}} |
| Line 91: | Line 106: |
| This process will | ==== Troubleshooting ==== * '''SPM-related errors''': If you've been trying multiple methods successively, errors mentioning a spm_*.m function could be due to incompatible versions of SPM12 functions in the Matlab path. Brain2mesh, FieldTrip and ROAST all run different versions of SPM12 from the same instance of Matlab. Solution: '''Restart Matlab''' to get a fresh workspace. |
| Line 93: | Line 109: |
| - merge the surfaces, | == Fieldtrip == [[http://www.fieldtriptoolbox.org/|FieldTrip]] is an open-source Matlab-based toolbox that includes a pipeline dedicated to the generation of [[http://www.fieldtriptoolbox.org/tutorial/headmodel_eeg_fem/|hexahedral FEM mesh]]. It is available as a [[https://Tutorials/Plugins|Brainstorm plugin]]. |
| Line 95: | Line 112: |
| - check the self intersecting | Brainstorm calls the function [[https://github.com/fieldtrip/fieldtrip/blob/release/ft_volumesegment.m|ft_volumesegment]] on the '''T1 MRI''' volume to obtain a tissue segmentation with 5 layers (white matter, gray matter, CSF, skull and skin), then [[https://github.com/fieldtrip/fieldtrip/blob/release/ft_prepare_mesh.m|ft_prepare_mesh_hexa]] to create a hexahedral mesh. |
| Line 97: | Line 114: |
| - fixe the size of the mesh | The mesh generation with the method is simple and fast: it downsamples the tissue classification volume, then converts all the voxels to a hexahedral mesh. The quality of the output is relatively poor: the regular meshing of the voxels makes it inefficient for providing a good representation of the tissues geometry with a limited number of elements. |
| Line 99: | Line 116: |
| - generate the volum mesh | {{attachment:fieldtrip1.gif}} |
| Line 101: | Line 118: |
| - visual checking ... | {{attachment:fieldtrip2.gif}} |
| Line 103: | Line 120: |
| === brain2mesh === Brain2Mesh is a MATLAB/Octave based 3D mesh generation toolbox dedicated to the creation of high-quality multi-layered brain mesh models. |
Options |
| Line 106: | Line 122: |
| '''Requirement''' | |
| Line 108: | Line 123: |
| Brain2Mesh is developed by the same team that developed the iso2mesh toolbox. Therefore iso2mesh is required. So if these toolboxes are not available on your computer, Brainstorm will download the last release and install it when it's needed. | |
| Line 110: | Line 124: |
| You may also need the SPM12 toolbox. Brain2mesh is used only to generate tetrahedral mesh from the segmentation output. Therefore a segmentation of the MRI will be performed by SPM when this option is called. | |
| Line 112: | Line 125: |
| More parameters will be added in the next version. If you are using this method you can request our support to help you or to add these parameters asap. | |
| Line 114: | Line 126: |
| '''When and how to use it''' This option is used when you have the individual MRI of the subject either T1 or T1 and T2. As said before, the SPM toolbox is required. The time required for this option is around 1 hour. here is the view of the obtained mesh from a T1 MRI | The option "Downsamp volume before meshing" will reduce the number of voxel by this factor. |
| Line 116: | Line 128: |
| {{attachment:brain2meshModel.JPG||height="450",width="600"}} | The "Shift node" option calls the adaptative mesh generation. The process moves the nodes located on the interface either inward or outward in order to fit the geometry as explained [[http://www.fieldtriptoolbox.org/tutorial/headmodel_eeg_fem/|here]]. This figure shows an example (from Fieldtrip webpage), left the unshifted and on the right the shifted. |
| Line 118: | Line 130: |
| More details will be added to this part door. | {{attachment:nodeShiftFigure.JPG||width="500",height="200"}} |
| Line 120: | Line 132: |
| === Fieldtrip === This option call the process of segmentation and hexa mesh generation of simbio. |
This method is fast compare to the previous options, the following figures show examples of the mesh obtained with fieldtrip option from the ICBM model. |
| Line 123: | Line 134: |
| This method calls the function ft_volumesegment then the ft_meshprepare of the field trip. | {{attachment:fieldTripMeshICBM.JPG||width="700",height="300"}} |
| Line 125: | Line 136: |
| The mesh generation process is faster. It converts all the voxels to hexahedral mesh. | === Troubleshooting === '''SPM-related errors''': If you've been trying multiple methods successively, errors mentioning a spm_*.m function could be due to incompatible versions of SPM12 functions in the Matlab path. Brain2mesh, FieldTrip and ROAST all run different versions of SPM12 from the same instance of Matlab. Solution: '''Restart Matlab''' to get a fresh workspace. |
| Line 127: | Line 139: |
| Requirement | == BrainSuite == [[http://brainsuite.org/|BrainSuite]] is a collection of open source software tools that enable largely automated processing of magnetic resonance images (MRI) of the human brain. |
| Line 129: | Line 142: |
| The fielstrip toolbox and spm. | Brainstorm calls BrainSuite tools in order to compute the diffusion tensors from the diffusion wiethed inaging (DWI) data. The diffusion tensor are then converted to conductivity tensors by the linear transformation described by David Tuch et al (ref). |
| Line 131: | Line 144: |
| Adaptative hexahedral mesh | The conductivity tensors are are associated with the FEM mesh of the head model. Where ecah mesh element have it's own tensors. |
| Line 133: | Line 146: |
| view of the mesh | The tensors are used to represnet the anisotropic conductivity of a tissue. The anisotropy means the change on the conductivity by changing the direction. For more information regarding tensors please refers to this page (add link). |
| Line 135: | Line 148: |
| {{attachment:ernieFieldtrip.JPG||height="450",width="450"}} | === Requirement === BrainSuite is an independant softeware, Brainstoem calls its functions from the core source code, therefore the installation of BrainSuite is required. |
| Line 137: | Line 151: |
| === SimNIBS === ==== Installation ==== Please follow the instructions on this [[https://simnibs.github.io/simnibs/build/html/installation/simnibs_installer.html|webapge]]''__ (new brainstorm page that explains how to generate the head model is under development)__'' |
Please follow the instructions as explained in [[http://forums.brainsuite.org/download/|this webpage]]. |
| Line 141: | Line 153: |
| in order to do the SimNibs software should be installed on your computer. | Once the instalation is completed, The BrainSuite installation folder must be informed in the Brainstorm preferences (From the Brainsuitrom interface, click on 'File' and then 'Edite preferences'). |
| Line 143: | Line 155: |
| ==== FEM Head model generation with SimNibs ==== This method used the SimNibs software. So to call this process, you need to download and install the SimNibs software, the process of the installation is explained in the SimNibs webpage : https://simnibs.github.io/simnibs/build/html/installation/simnibs_installer.html. |
{{https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/6920058/81406567-1c785400-913a-11ea-9048-28c7459af7da.png|image}} |
| Line 146: | Line 157: |
| When you have installed SimNibs, Brainstorm can call the main function used for the mesh generation frm the main graphical interface. Depemding on your computer performances, this process will take between 2 to 5 hours. We highly recommend to close all other running process and application on our computer in order to speed this process. | === When and how to use it === [For this version June 2020, only the tetra mesh are supported and tested.] |
| Line 148: | Line 160: |
| 1- Create new subject within the current protocole | The BrainSuite pipline is used to estimate the anisotropy of the brain tissues. This process is associated with the [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/Duneuro?highlight=(duneuro)|DUNEuro FEM computation]]. The conductivity tensors will be assigned to each mesh elements. |
| Line 150: | Line 162: |
| 2- Load the T1 of the subject to the brainstorm database. | In order to use this functionnality the DWI data are required. The Niftii files and the assocaited bvec and bval are required. Further more we assume that you have already generated the FEM mesh from the MRI as explained in the previous sections. |
| Line 152: | Line 164: |
| 3- Associate a T2 mri to the subject if it's available (this is better for csf/skull/scalp segmentation) 4- Right click on the subject, select the "Generate FEM mesh" . Select "SIMNIBS", and choose "Tetrahedral element" and keep the other options to the default value. The headreco function is fully integrated to brainstorm. With this option, brainstorm can reconstructs a tetrahedral head mesh from T1- and T2-weighted structural MR images. It runs also with only a T1w image, but it will achieve more reliable skull segmentations when a T2w image is supplied. == Tissue anisotropy estimation == ==== Brainsuite Installation [TODO] ==== == Volume generation from surface files == |
=== Tissue anisotropy estimation === |
| Line 165: | Line 167: |
| === Volume generation from T1/T2 MRI data === You can also generate your own FEM head model and then load it to brainstorm. However the automatic head model generation from from imaging techniques are not accurate and most of the time visual checking are needed and manual correction are required. |
From Brainstorm, BrainSuite is used for the skull stripping, bias field correction and then the diffusion pipline is used to compute the diffusion tensors. |
| Line 168: | Line 169: |
| ==> this depends lagely on the quality of the T1/T2 MRI image(https://simnibs.github.io/simnibs/build/html/tutorial/head_meshing.html). | ref to the maon function : likToGit |
| Line 170: | Line 171: |
| This step is based on the "roast" toolbox (link to roast : https://github.com/andypotatohy/roast | == On the hard drive == Right-click on a FEM mesh > File > View file contents: |
| Line 172: | Line 174: |
| ) that we adapted for the MEEG forward computation. If you want to generate your own FEM head model from an MRI, you will need to download these file (link), then run the bst process as explained here. | {{attachment:femMesh2.gif}} |
| Line 174: | Line 176: |
| * If there is a MRI file with the string "T2" in the subject anatomy folder, it will use it * Otherwise, if you select explicitly two MRI files with CTRL+Click, it will use the first one as the T1 and the second one as the T2 (this needs to be documented in the tutorial) === FEM Head model template === - Load the FEM volumic mesh (template created from ICBM T1 MRI using SimNibs) - Load the surface mesh (template created also from ICBM using ICBM ) and then generates the volume mesh (either tetra or hexa) by calling the tetgen process cia iso2mesh toolbox (if hexa are desired, the tetra mesh will be converted to hexa ... ) https://github.com/brainstorm-tools/brainstorm3/issues/185#issuecomment-576749612 === Head model based on the level set approach === TODO and Validate == Errors == <<BR>>'''<<TAG(Advanced)>>''' <<BR>> == FEM computation and interface to DUNEuro == === Head model === Number of layers, conductivity value, isotropy/anisotropy/ mesh resolution/ === Electrode model === Check the position of the electrodes and align to the head model (projection if needed) === Source model === Similarly to the spherical and BEM head model, the source position are defined on the cortex surface vertices. We can either define a constrained or not constrained orientation. However, for the FEM model, more paramters could be tuned for the source model. Choice of the source model : PI, Venant, Subtraction, Whitney Panel of the options choice that the user can select. (other wise we will set to default ) '''<<TAG(Advanced)>>''' === Advanced paramaters === - Solver parameters - Electrodes projection - maybe explain here the relevant option of the mini file ?? == Additional documentation == refer to : http://duneuro.org/ https://www.dune-project.org/ https://simnibs.github.io/simnibs/build/html/index.html == Reported Errors & alternative solution == '''<<TAG(Advanced)>>''' simnibs pblm : https://simnibs.github.io/simnibs/build/html/installation/throubleshooting.html == The MEEG forward problem with the FEM == == License == == Reference == == Additional documentation == https://github.com/brainstorm-tools/bst-duneuro/issues/1 https://github.com/brainstorm-tools/brainstorm3/issues/242 |
TODO |
[TUTORIAL UNDER CONSTRUCTION: NOT READY FOR PUBLIC USE]
FEM mesh generation
Authors: Takfarinas Medani, Francois Tadel
FEM forward modeling requires the construction of a 3D model of the head tissues. The volume of the head is divided in small geometrical elements with 4 faces (tetrahedrons) or 6 faces (hexahedrons). Each element is associated with a type of biological tissue (e.g. white matter, gray matter, CSF, skull, skin) and electrical conductivity properties.
This page lists the methods integrated with Brainstorm to generate 3D meshes of the head. For a generic introduction to FEM in Brainstorm, refer to the tutorials: Realistic head model: FEM with DUNEuro and FEM median nerve example.
Contents
Generate FEM mesh
FEM meshes can be computed from surfaces (as the ones generated for the BEM models) or from MRI volumes (T1w and/or T2w). The methods that are available when using the popup menu Generate FEM mesh depend on the selected inputs.
Surfaces
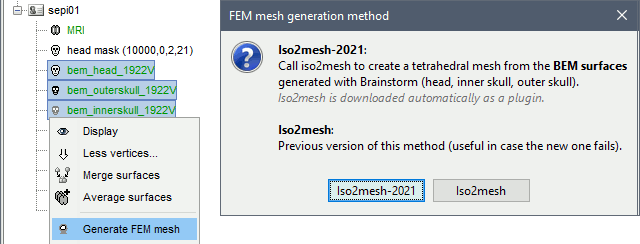
Select a list of surfaces representing the separation between different tissues (holding the CTRL or SHIFT key), then right-click on any of them. The software Iso2mesh can create a tetrahedral mesh to represent the tissues between these different layers.
T1 MRI
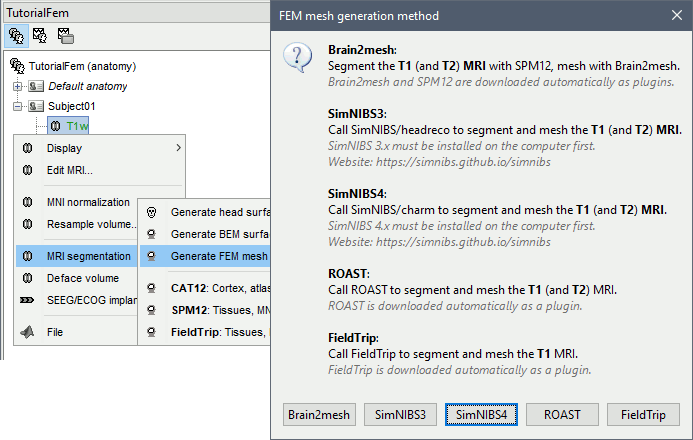
Right-click on a T1 MRI available in the databas. Typically, this is the default MRI volume displayed in green in the subject folder. Methods available: Brain2mesh, SimNIBS, ROAST, FieldTrip.
T1+T2 MRI
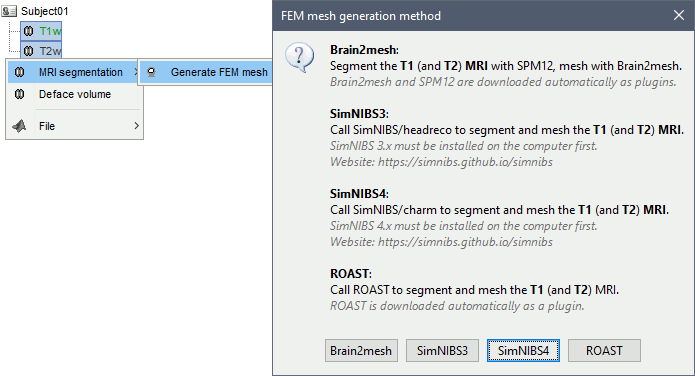
Select the T1+T2 volumes, then right-click on any of them. The different files are identified based on the tags "T1" and "T2" the file names (as displayed in the Brainstorm database explorer). If these identification tags are not found in the file names, the default MRI (in green) is used as the T1, the other as the T2. If none of the is the default MRI, the first selected file is used as the T1, the second is used as the T2. Methods available: Brain2mesh, SimNIBS, ROAST.
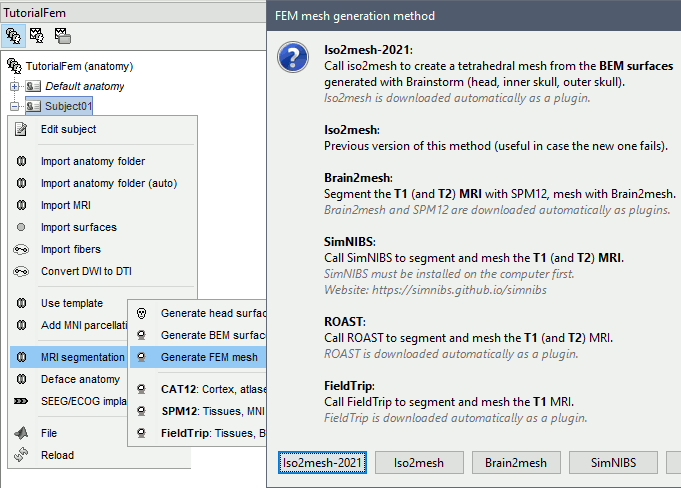
Anatomy folder
If you right-click on the subject folder > Generate FEM mesh, then Brainstorm offers all the possible options, even the ones that are not applicable to this specific subject.
Volume method: If using a method based on MRI volumes, the T1 and T2 volumes are detected among all the volumes available based on the tags "T1" and "T2" in the file names (make sure only one file as each of these tags), otherwise use only the default MRI (in green) as the T1.
Surface method: If using a method based on surfaces, the default surfaces (in green) from three categories as selected: the inner skull, the outer skull and the head surfaces.
Iso2mesh
Iso2mesh is a Matlab/Octave-based mesh generation and processing toolbox, available as a Brainstorm plugin.
Brainstorm uses it to generate a FEM tetrahedral mesh from a set of nested surfaces representing the separation between different tissues of the head. For example, these surfaces can be the ones generated for the computation of a BEM forward model. A full example is available in the tutorial Realistic head model: FEM with DUNEuro.
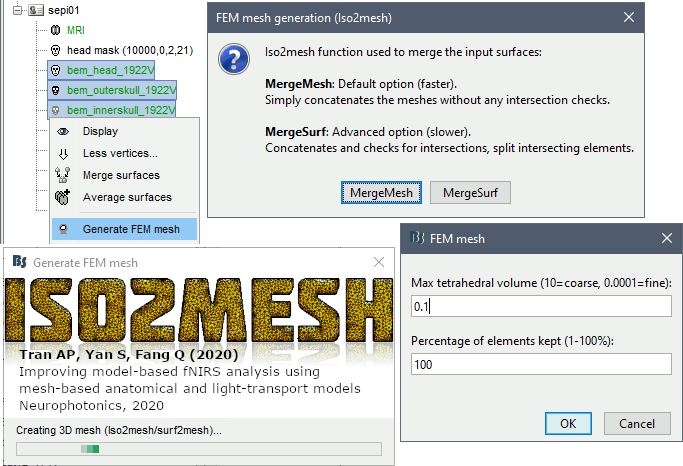
Options
MergeMesh: Simply concatenates the input surfaces without any intersection checks. Default option (faster).
MergeSurf: Concatenates and checks for intersections, split intersecting elements. Advanced option (slower).
Max tetrahedral volume: Maximum volume of the tetrahedral element in the mesh.
From our tests, a DUNEuro FEM head model with a value of 0.1 achieves similar results as the OpenMeeg head model computed from the same surfaces. We have also noticed that the result with v = 0,001 is almost similar to v = 0,01.
- Increasing the mesh resolution requires more time to generate the mesh, more time and memory to perform the FEM computation and more storage space in the database.
Percentage of elements kept: Parameter between 0-100%, used to keep or not the original input surface nodes.
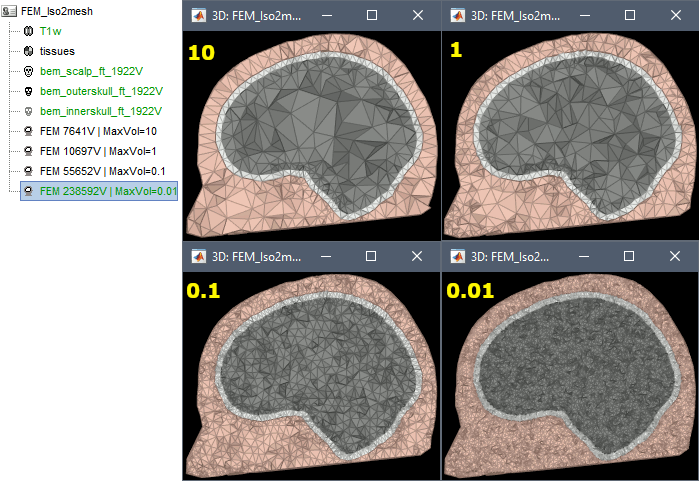
Examples
FEM mesh with different values of "Max volume": [10, 1, 0.1, 0.01] - Kept ratio=100%.
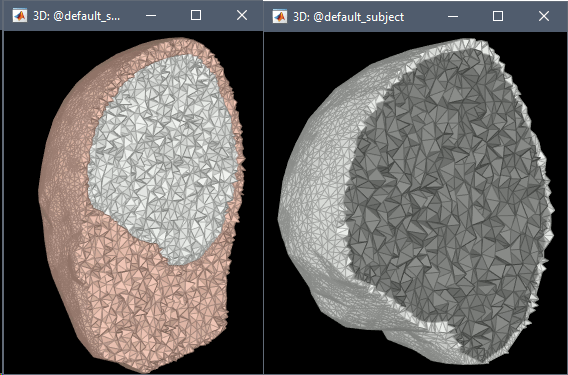
FEM meshes with only two compartments: This could be useful for investigating the influence of a specific tissue on the EEG/MEG forward solution or on the source localization, or for analyzing SEEG only within the brain volume. On the left: head and outer skull; On the right: inner and outer skull.
Troubleshooting
Tetget failed: If intersections are present on the surfaces mesh, the iso2mesh FEM mesh generation fails (tetgen). You may need regenerate new surfaces from the MRI.
Alternatively: You may try with the MergSurf option, this option can correct the intersection and create new nodes and elements. However, we do not recommend to use these models for EEG/MEG forward head computations: this is a research topic and it's still under investigation by the FEM communities.
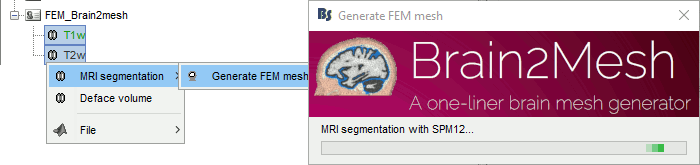
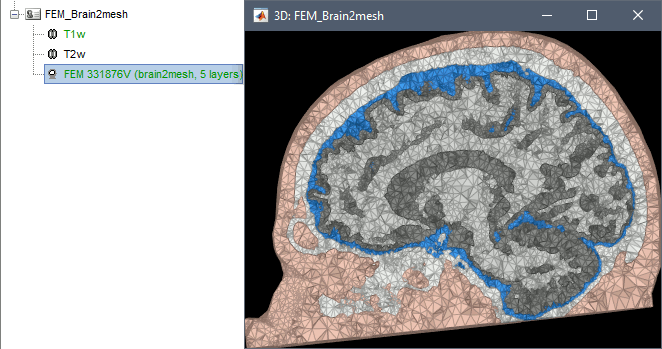
Brain2mesh
Brain2mesh is a MATLAB/Octave based 3D mesh generation toolbox dedicated to the creation of high-quality multi-layered brain mesh models. This software is developed by the same team developing Iso2mesh and relies heavily on it. Both are available as a Brainstorm plugins.
Brainstorm runs the SPM12 segmentation routine on the T1 or T1+T2 MRI volumes to obtain a 5-tissue classifcation (white matter, gray matter, CSF, skull and skin), which is then passed to Brain2mesh for 3D meshing. A full example is available in the tutorial FEM tensors estimation. This option runs fast, but does not generate good quality cortex surfaces, which are needed for the full cortically-constrained source estimation pipeline in Brainstorm.
At the moment, Brainstorm can only use the default parameters of Brain2mesh. If you need more options to be available from the interface, please contact us on the user forum.
Troubleshooting
SPM-related errors: If you've been trying multiple methods successively, errors mentioning a spm_*.m function could be due to incompatible versions of SPM12 functions in the Matlab path. Brain2mesh, FieldTrip and ROAST all run different versions of SPM12 from the same instance of Matlab. Solution: Restart Matlab to get a fresh workspace.
SimNIBS
SimNIBS software was developed to calculate the electric fields caused by Transcranial Electrical Stimulation (TES) and Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS). All its software dependencies (CAT12, Netgen, Gmsh, MeshFix) are embedded in the SimNIBS installation, which ensures a high stability and portability. However, it cannot be managed automatically as a plugin by Brainstorm, and needs to be installed manually. See: Download and install SimNIBS.
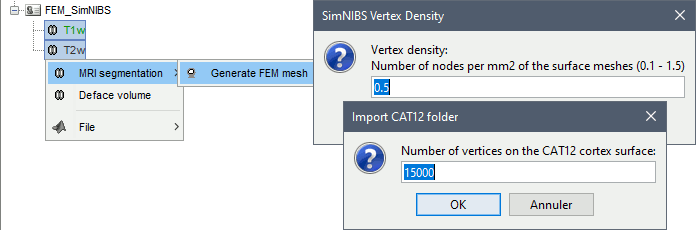
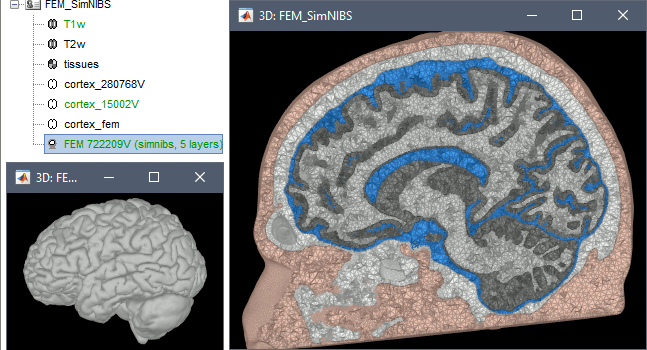
In Brainstorm, we use the headreco pipeline to process T1 or T1+T2 MRI volumes (T1 is required, T2 is highly recommended). This pipeline generates the highest-quality tetrahedral FEM mesh we can get from Brainstorm. It calls internally CAT12 for tissue segmentation (white matter, gray matter, CSF, skull and scalp), and therefore gives us access to high-quality cortex surfaces and surface-based atlases. The tetrahedral mesh generation is done with Gmsh, Netgen and MeshFix. Depending on your computer performances, this process will take between 2 to 5 hours.
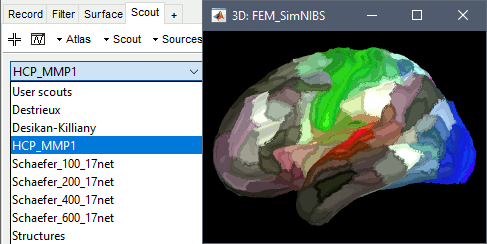
Given the high quality and exhaustivity of its outputs, SimNIBS/headreco is the recommended method for FEM mesh generation in Brainstorm. A full example is available in the tutorial: FEM median nerve example.
Options
Vertex density: Number of node per mm2 of the surface mesh.
Number of vertices: This is not an input parameter of SimNIBS, but a parameter to control how much to downsample the cortex surface generated by CAT12 when importing it into the Brainstorm database. See the introduction tutorials.
Troubleshooting
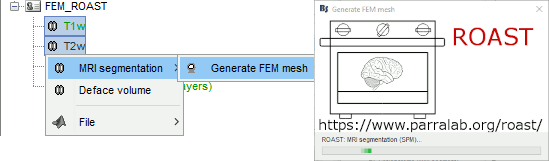
ROAST
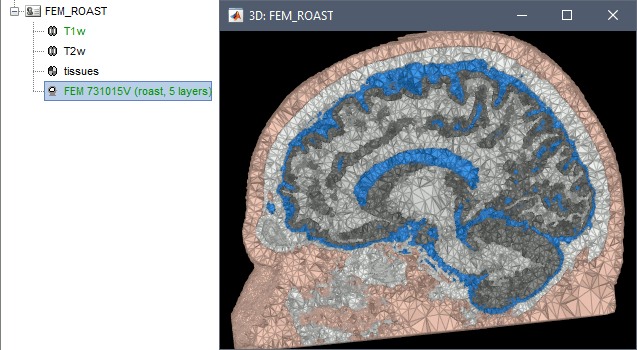
ROAST is a fully automated, Realistic, vOlumetric Approach to Simulate Transcranial electric stimulation. Open-source and Matlab-based, it is available as a Brainstorm plugin. It calls internally SPM8 for tissue segmentation of the T1 or T1+T2 MRI volumes to obtain a 5-tissue classifcation (white matter, gray matter, CSF, skull and skin). Then it relies mostly on iso2mesh for generating a tetrahedral mesh.
This option runs fast, but does not generate good quality cortex surfaces, which are needed for the full cortically-constrained source estimation pipeline in Brainstorm.
Troubleshooting
SPM-related errors: If you've been trying multiple methods successively, errors mentioning a spm_*.m function could be due to incompatible versions of SPM12 functions in the Matlab path. Brain2mesh, FieldTrip and ROAST all run different versions of SPM12 from the same instance of Matlab. Solution: Restart Matlab to get a fresh workspace.
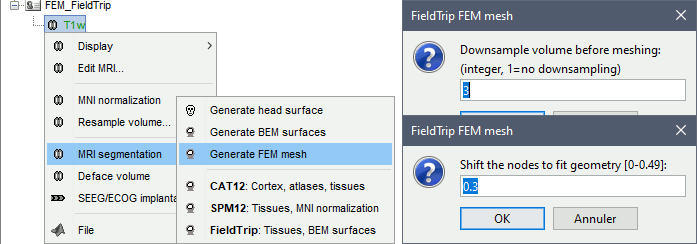
Fieldtrip
FieldTrip is an open-source Matlab-based toolbox that includes a pipeline dedicated to the generation of hexahedral FEM mesh. It is available as a Brainstorm plugin.
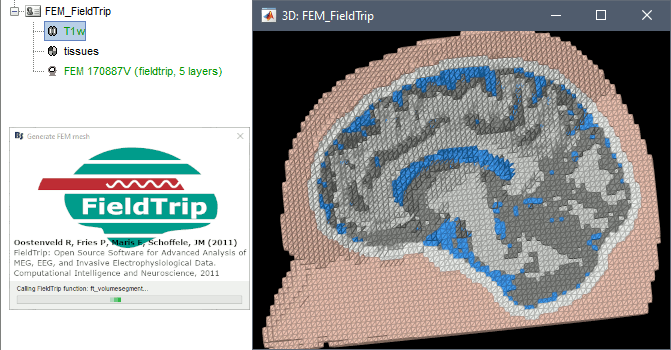
Brainstorm calls the function ft_volumesegment on the T1 MRI volume to obtain a tissue segmentation with 5 layers (white matter, gray matter, CSF, skull and skin), then ft_prepare_mesh_hexa to create a hexahedral mesh.
The mesh generation with the method is simple and fast: it downsamples the tissue classification volume, then converts all the voxels to a hexahedral mesh. The quality of the output is relatively poor: the regular meshing of the voxels makes it inefficient for providing a good representation of the tissues geometry with a limited number of elements.
Options
The option "Downsamp volume before meshing" will reduce the number of voxel by this factor.
The "Shift node" option calls the adaptative mesh generation. The process moves the nodes located on the interface either inward or outward in order to fit the geometry as explained here. This figure shows an example (from Fieldtrip webpage), left the unshifted and on the right the shifted.
This method is fast compare to the previous options, the following figures show examples of the mesh obtained with fieldtrip option from the ICBM model.
Troubleshooting
SPM-related errors: If you've been trying multiple methods successively, errors mentioning a spm_*.m function could be due to incompatible versions of SPM12 functions in the Matlab path. Brain2mesh, FieldTrip and ROAST all run different versions of SPM12 from the same instance of Matlab. Solution: Restart Matlab to get a fresh workspace.
BrainSuite
BrainSuite is a collection of open source software tools that enable largely automated processing of magnetic resonance images (MRI) of the human brain.
Brainstorm calls BrainSuite tools in order to compute the diffusion tensors from the diffusion wiethed inaging (DWI) data. The diffusion tensor are then converted to conductivity tensors by the linear transformation described by David Tuch et al (ref).
The conductivity tensors are are associated with the FEM mesh of the head model. Where ecah mesh element have it's own tensors.
The tensors are used to represnet the anisotropic conductivity of a tissue. The anisotropy means the change on the conductivity by changing the direction. For more information regarding tensors please refers to this page (add link).
Requirement
BrainSuite is an independant softeware, Brainstoem calls its functions from the core source code, therefore the installation of BrainSuite is required.
Please follow the instructions as explained in this webpage.
Once the instalation is completed, The BrainSuite installation folder must be informed in the Brainstorm preferences (From the Brainsuitrom interface, click on 'File' and then 'Edite preferences').

When and how to use it
[For this version June 2020, only the tetra mesh are supported and tested.]
The BrainSuite pipline is used to estimate the anisotropy of the brain tissues. This process is associated with the DUNEuro FEM computation. The conductivity tensors will be assigned to each mesh elements.
In order to use this functionnality the DWI data are required. The Niftii files and the assocaited bvec and bval are required. Further more we assume that you have already generated the FEM mesh from the MRI as explained in the previous sections.
Tissue anisotropy estimation
From Brainstorm, BrainSuite is used for the skull stripping, bias field correction and then the diffusion pipline is used to compute the diffusion tensors.
ref to the maon function : likToGit
On the hard drive
Right-click on a FEM mesh > File > View file contents:
TODO
