|
Size: 20664
Comment:
|
Size: 23426
Comment:
|
| Deletions are marked like this. | Additions are marked like this. |
| Line 31: | Line 31: |
| 1. Additional volume or surface parcellations can be computed at this stage. For details see section [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/LabelFreeSurfer#Cortical_parcellations|Cortical parcellations]] below. |
|
| Line 40: | Line 42: |
| 1. Select one the FreeSurfer import options and select the top folder of your subject <subject_id> (/.../data/freesurfer/subjects/subject_id) | 1. Select one of the FreeSurfer import options and select the top folder of your subject <subject_id> (/.../data/freesurfer/subjects/subject_id) |
| Line 43: | Line 45: |
| * '''FreeSurfer + Volume atlas + Thickenss''': Same as above, with the cortical thickness maps imported as source maps. | * '''FreeSurfer + Volume atlas + Thickness''': Same as above, with the cortical thickness maps imported as source maps. |
| Line 51: | Line 53: |
| * /mri/'''T1.mgz''' (T1 MRI volume) * /mri/'''aseg.mgz''' (segmentation of subcortical structures) |
* /mri/'''T1.mgz''' (T1 MRI volume) + optional /mri/'''T2.mgz''' * /mri/'''*aseg.mgz''' (volume parcellations) |
| Line 59: | Line 62: |
| The successive steps that are automatically performed by Brainstorm: |
The successive steps that are performed by Brainstorm: * Import the T1/T2 MRI * For "auto" import: Compute the linear MNI registration, otherwise asks for placing the fiducials |
| Line 63: | Line 68: |
| * Load the registered spheres for the the left and right hemispheres | * Load the registered spheres for the left and right hemispheres |
| Line 65: | Line 70: |
| * Compute the mid-surfaces (average of the pial + white surfaces vertex by vertex) | |
| Line 66: | Line 72: |
| * Delete all the unnecessary surfaces | |
| Line 68: | Line 73: |
| * Read the sub-cortical atlas aseg.mgz as a set of labelled surfaces * Read the cortical thickness maps The files you can see in the database explorer at the end: {{attachment:checkDb.gif}} * '''MRI''': The T1 MRI of the subject, imported from the MGH file format (.mgz) * '''head mask''' (10000,0,2): Scalp surface generated by Brainstorm. The numbers indicate the parameters that were automatically used for this head: vertices=10000, erode factor=0, fill holes=2 (these are detailed later) |
* Import the sub-cortical atlas *aseg.mgz as volume atlases and labelled surfaces * Import the cortical thickness maps The files you can see in the database explorer at the end (with Volume atlases + Thickness): * '''MRI''': The T1 MRI of the subject, imported from the MGH file format (T1.mgz) * '''Volume parcellations''': *aseg.mgz, see tutorial [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/ExploreAnatomy#Subcortical_regions:_Volume|Explore the anatomy]]. * '''head mask''': Scalp surface generated by Brainstorm. The numbers in the filename indicate the parameters that were used for this head: vertices=10000, erode factor=0, fill holes=2, background threshold=detected (these are detailed later) |
| Line 81: | Line 85: |
| * '''aseg atlas''': Atlas of subcortical regions | * '''mid_*V''': Mid-cortex surfaces (average of the pial + white surfaces vertex by vertex) * '''subcortical''': Atlas of subcortical regions imported as labelled surfaces {{attachment:checkDb.gif}} |
| Line 85: | Line 90: |
| It's hard to estimate what would be a good cortical reconstruction. What you are trying to spot at this level is mostly the obvious errors, like when the early stages of the brain extraction didn't perform well, just with a visual inspection. Play with the ''Smooth'' slider in the ''Surface ''tab. If it looks like a brain (two separate hemispheres) in both smooth and original views, it is probably ok. | It's hard to estimate what would be a good cortical reconstruction. Try to spot the most obvious errors, e.g. when the early stages of the brain extraction didn't perform well. Play with the ''Smooth'' slider in the ''Surface ''tab. If it looks like a brain (two separate hemispheres) in both smooth and original views, it is probably OK. |
| Line 94: | Line 99: |
| If after following these instructions you still don't manage to get good surfaces, you can try to run the automatic MRI segmentation from [[Tutorials/SegBrainVisa|BrainVISA]], [[Tutorials/SegBrainSuite|BrainSuite]] or [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/SegCAT12|CAT12]]. | If after following these instructions you still don't manage to get good surfaces, you can try to run the automatic MRI segmentation from [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/SegCAT12|CAT12]], [[Tutorials/SegBrainSuite|BrainSuite]] or [[Tutorials/SegBrainVisa|BrainVISA]]. |
| Line 99: | Line 104: |
| The head surface is important mainly for two reasons. First, for the alignment of the MEG sensors and the MRI, and second, for generating head models that incorporate the scalp surface (e.g. multi-layer BEM or FEM). If you digitized the head shape with a Polhemus device, you can automatically align the head surface (hence the MRI) with the MEG sensors (in the same referential as the Polhemus points). The quality of this automatic registrations depends on the quality of both surfaces: the Polhemus head shape (green points) and the head surface from the MRI (grey surface). If you placed lots of points on the nose but your head surface doesn't have a nose, these points are not going to help. {{attachment:checkAlignMeg.gif||width="298",height="243"}} If the default head surface looks bad, you can try generating another one: right-click on the subject folder > Generate head surface. The options are: |
The head surface is important mainly for two reasons. First, for the alignment of the MEG sensors and the MRI, and second, for generating head models that incorporate the scalp surface (e.g. multi-layer BEM or FEM). If you digitized the head shape with a Polhemus device, you can automatically align the head surface (hence the MRI) with the MEG sensors (in the same referential as the Polhemus points). The quality of this automatic registration depends on the quality of both surfaces: the Polhemus head shape (green points) and the head surface from the MRI (grey surface). If you digitized lots of points on the nose but your head surface doesn't have a nose, these points are not going to help. . {{attachment:checkAlignMeg.gif||width="298",height="243"}} If the default head surface looks bad, you can try generating another one: right-click on the subject folder > '''Generate head surface'''. The options are: |
| Line 110: | Line 115: |
| ==== Error in mne_read_surface.m ==== If you get an error message mentioning mne_read_surface.m, and the files pial.lh and pial.rh are only 2Kb, you probably had an issue with the transfer of symbolic links. See this forum post: https://neuroimage.usc.edu/forums/t/error-in-mne-read-surface-m/26418 |
|
| Line 111: | Line 119: |
| The default analysis pipeline in FreeSurfer implements an automatic parcellation of the cortical surface in anatomical regions. The description of this feature is available here:<<BR>>http://freesurfer.net/fswiki/CorticalParcellation With FreeSurfer >= 7, 5 atlases are available on all the individual brains: * '''Brodmann''' areas (?h.BA.annot and ?h.BA.thresh.annot): [[http://ftp.nmr.mgh.harvard.edu/fswiki/BrodmannAreaMaps|more information]] |
The default analysis pipeline in FreeSurfer computes several parcellations of the cortical surface in anatomical regions. The description of this feature is available here:<<BR>>http://freesurfer.net/fswiki/CorticalParcellation With FreeSurfer 7, the following parcellations are always available: * '''Brodmann''' areas (?h.BA*.annot and ?h.BA*.thresh.annot): [[http://ftp.nmr.mgh.harvard.edu/fswiki/BrodmannAreaMaps|more information]] |
| Line 118: | Line 126: |
| * '''Mindboggle''' (?h.aparc.DKTatlas40.annot): [[http://mindboggle.info/data.html|more information]] | * '''DKT / Mindboggle6''' (?h.aparc.DKTatlas.annot): [[http://mindboggle.info/data.html|more information]] |
| Line 121: | Line 130: |
| Additional 3rd-party atlases are loaded automatically by Brainstorm when available: | Additional parcellations can be computed from FreeSurfer with [[https://freesurfer.net/fswiki/mri_surf2surf|mri_surf2surf]] ([[https://github.com/ftadel/IntrAnat/issues/7#issuecomment-768996270|example]]): |
| Line 124: | Line 133: |
| * '''HCP-MMP1''' (?h.HCP-MMP1.annot): [[https://figshare.com/articles/dataset/HCP-MMP1_0_projected_on_fsaverage/3498446?file=5528837|more information]] * '''CHubs/OASIS''' (?h.oasis.chubs.annot): [[https://surfer.nmr.mgh.harvard.edu/fswiki/Chubs|more information]] |
|
| Line 125: | Line 136: |
| * '''Schaefer2018''' (?h.Schaefer2018_*Parcels_*Networks_order.annot): [[https://github.com/ThomasYeoLab/CBIG/tree/master/stable_projects/brain_parcellation/Schaefer2018_LocalGlobal/Parcellations/project_to_individual|more information]] | |
| Line 127: | Line 139: |
| * '''Retinotopy''' (?h.pRF.annot) These atlases are imported in Brainstorm as scouts (cortical regions of interest), and saved directly in the surface files. To check where they are saved: right-click on the low-resolution cortex file > File > View file contents. You can see that 4 structures "Atlas" are available, the first one that has Name='User scouts', and the second one Name='Destrieux'.<<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:viewMat.gif}} <<BR>><<BR>> To access them from the interface: Double-click on the cortex and go to the ''Scout'' tab, and click on the drop-down list to select another ''Atlas ''(ie group of scouts): {{attachment:scoutTab.gif}} |
These parcellations are imported in Brainstorm as [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/Scouts|scouts]] (cortical regions of interest). To access them from the interface: double-click on the cortex, go to the ''Scout'' tab, and click on the drop-down list to select another ''Atlas ''(ie group of scouts): {{attachment:scoutTab.png}} |
| Line 147: | Line 154: |
| The scouts are saved directly in the surface files. To check where they are saved: right-click on the low-resolution cortex file > File > View file contents. You can see that multiple "Atlas" structures are available, the first one that has Name='User scouts', and the second one Name='Brodmann'. {{attachment:viewMat.gif}} == Volume parcellations == All the volume parcellations available in the mri subfolder are imported when the option "FreeSurfer + Volumes atlases" is selected. This includes: * '''ASEG''': mri/aseg.mgz, subcortical structures only * '''Destrieux''': aparc.a2009s+aseg.mgz * '''Desikan-Killiany''': aparc.a2009s+aseg.mgz * '''DKT''': aparc.DKTatlas+aseg.mgz {{attachment:volatlas.gif}} |
|
| Line 150: | Line 171: |
| You can easily extract one structure (for example the brainstem or the cerebellum) by selecting the corresponding entries in the scouts list and selecting the menu Scout > Edit surface > Keep only selected scouts. It creates a new surface with only the selected regions. If you want to remove one or several structures, use the menu "Remove selected scouts" instead. | You can easily extract one structure (for example the brainstem or the cerebellum) by selecting the corresponding entries in the scouts list and selecting the menu Scout > Edit surface > Keep only selected scouts. It creates a new surface with only the selected regions. If you want to remove one or several structures, use the menu "Remove selected scouts" instead. [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/DeepAtlas#Select_deep_structures|More information]]. |
| Line 175: | Line 196: |
| To change the default, right-click on "(Default anatomy)" > Use template > FSAverage. If it is not available on your computer yet, it will be automatically downloaded from the server to your user folder: $HOME/.brainstorm/templates/anatomy. | To change the default, right-click on "(Default anatomy)" > Use template > FSAverage. If it is not available on your computer yet, it will be automatically downloaded from the server to your user folder: $HOME/.brainstorm/templates/anatomy. See tutorial: [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/DefaultAnatomy#Subject_configuration|Using the anatomy templates]]. |
| Line 192: | Line 213: |
| 1. Right-click on the subject folder > Import MRI > Select "mri/T1.mgz" 1. Set the 6 fiducial points, save 1. Right-click on the subject folder > Import surfaces > Select the FreeSurfer file format > Select simultaneously from the "surf" folder: lh.pial, lh.white, rh.pial, rh.white 1. Double-click on lh.pial toi display it. In the scout tab: Atlas > Load atlas > select all the lh.*.annot files available in the label folder. Close the figure. |
1. Right-click on the subject folder > Import MRI > Select "mri/T1.mgz". 1. Set the 6 fiducial points, or click on "Compute MNI normalization" (option maff8). Save. 1. Right-click on the subject folder > Import surfaces > Select the FreeSurfer file format > Select simultaneously from the "surf" folder: lh.pial, lh.white, rh.pial, rh.white. Question "Apply transformation?": NO. 1. Double-click on lh.pial to display it. In the scout tab: Atlas > Load atlas > select all the lh.*.annot files available in the label folder. Close the figure. |
| Line 200: | Line 221: |
| 1. Select lh.pial, rh.pial, right-click > Merge surfaces: Generates a surface cortex_250000V 1. Select lh.white, rh.white, right-click > Merge surfaces: Generates a surface white_250000V |
1. Select lh.pial + rh.pial, right-click > Merge surfaces: Generates a surface cortex_300000V 1. Select lh.white + rh.white, right-click > Merge surfaces: Generates a surface white_300000V |
| Line 206: | Line 227: |
| 1. Right-click on the subject folder > Import surfaces > Select the file format "Volume mask of atlas" > Select the file mri/aseg.mgz 1. Go to the functional view of the protocol, create a condition "FreeSurfer". Leave your mouse for a second over the new folder, an note the study index (iStudy). |
1. Right-click on the subject folder > Import surfaces > Select the file format "Volume mask or atlas (subject space)" > Select the file mri/aseg.mgz. Question "Apply transformation?": NO. 1. Right-click on the subject folder > Import MRI > Select the file format "Volume atlas (subject space)" > Select all the files mri/*aseg.mgz. * Question "Apply standard transformation?": NO * Question "Apply transformation?": YES * Question "How to register?": Ignore * Question "Reslice volume?": No 1. Go to the functional view of the protocol, create a folder "FreeSurfer". Leave your mouse for a second over the new folder, an note the study index (iStudy). |
Using FreeSurfer
Authors: Francois Tadel
The open-source software FreeSurfer can be used to extract the cortical envelope from a T1/T2 MRI and register it to an atlas. The process is fully automatic and the results can be imported in Brainstorm with just a few mouse clicks. If you are using FreeSurfer, please register on their website (registration page) and cite the appropriate references.
Contents
- Running FreeSurfer
- Importing the results in Brainstorm
- Files imported
- Handling errors
- Cortical parcellations
- Volume parcellations
- Subcortical structures: aseg atlas
- Registered spheres
- Mollweide projection
- Cortical thickness
- FSAverage template
- Running the folder import as a process
- Manual import of the anatomy
Running FreeSurfer
Downloading and installing FreeSurfer is easy but long (several Gb). Two options: you have a Linux system and you want to install FreeSurfer, or you don't and you want to run FreeSurfer in a Linux virtual machine. Just follow the instructions:
http://surfer.nmr.mgh.harvard.edu/fswiki/DownloadAndInstallSet up the FreeSurfer in a csh/tcsh environment: run the following lines, or add them at the end of your $HOME/.cshrc script for permanent change. If you're not sure what csh is: type "echo $SHELL" to know what is the name of the shell that you use. If it says "/bin/tcsh" or "/bin/csh", this is for you.
setenv FREESURFER_HOME /.../local/freesurfer setenv SUBJECTS_DIR /.../data/freesurfer/subjects setenv FUNCTIONALS_DIR /.../data/freesurfer/sessions source /.../local/freesurfer/FreeSurferEnv.csh
Set up the FreeSurfer environment in a bash environment (add these lines at the end of your $HOME/.bashrc script):
export FREESURFER_HOME=/.../local/freesurfer export SUBJECTS_DIR=/.../data/ftadel/freesurfer export FUNCTIONALS_DIR=/.../data/ftadel/freesurfer source $FREESURFER_HOME/FreeSurferEnv.sh
- Run the reconstruction (6-12 hours):
recon-all -i <mri_file> -subjid <subject_id> recon-all -all -subjid <subject_id>
If you have an additional T2 or FLAIR image, you can improve the cortex reconstruction: https://surfer.nmr.mgh.harvard.edu/fswiki/recon-all#UsingT2orFLAIRdatatoimprovepialsurfaces
Additional volume or surface parcellations can be computed at this stage. For details see section Cortical parcellations below.
Done. Everything is ready to be imported in Brainstorm. Because the process may occasionally fail, always check visually the final surfaces. The FreeSurfer wiki suggests that you check all the steps with FreeSurfer. We suggest instead that you load it all in Brainstorm and go back to the manual checking/editing only if it looks bad.
More instructions for setting up the environment and tuning the reconstruction here: http://surfer.nmr.mgh.harvard.edu/fswiki/RecommendedReconstruction
Importing the results in Brainstorm
- Switch to the anatomy view of the database explore.
- Create a new subject, set the default anatomy option to "No, use individual anatomy".
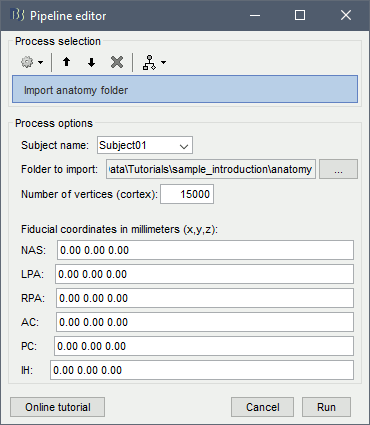
Right-click on the subject > Import anatomy folder.
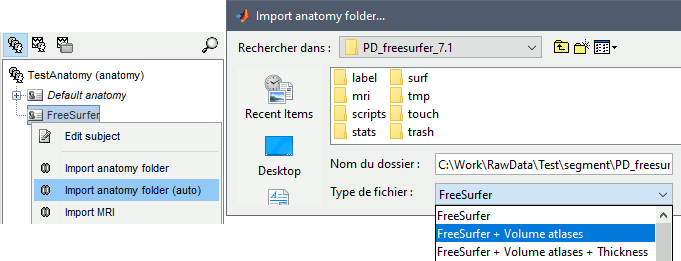
Import anatomy folder: Interactive import: asks for the number of vertices expected in the final cortex surfaces and for the location of the fiducials NAS/LPA/RPA. Select this option in the case of an MEG study, when you know exactly where the fiducials were digitized during the MEG acquisition. See tutorial MRI registration.
Import anatomy folder (auto): Automatic import: Computes the linear MNI normalization, uses default positions from the MNI atlas for the NAS/LPA/RPA fiducials, and uses 15000 vertices for the cortex downsampled surfaces.
Select one of the FreeSurfer import options and select the top folder of your subject <subject_id> (/.../data/freesurfer/subjects/subject_id)
FreeSurfer: Import the T1 MRI, pial and white cortex surfaces, surface parcellations, surface spherical registration, ASEG surface parcellation. Reconstruct the head surface.
FreeSurfer + Volume atlas: Same as above, with the following additions: Import the volume parcellations available in the mri subfolder; reconstruct the mid surfaces (intermediate between the pial and white surfaces).
FreeSurfer + Volume atlas + Thickness: Same as above, with the cortical thickness maps imported as source maps.
Manual import: You're prompted for the number of vertices you want in the final cortex surface. This will by extension define the number of dipoles to estimate during the source estimation process. By default we set this value to 15000 for the entire brain (it means 7500 for each hemisphere).
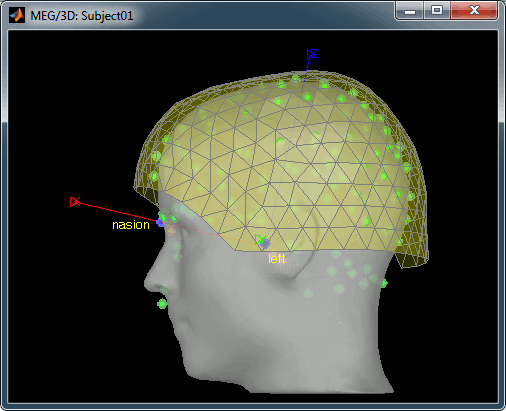
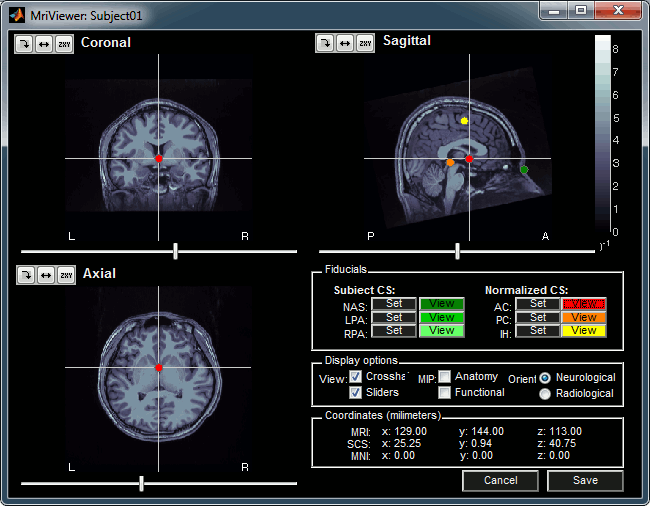
Manual import: The MRI Viewer appears for you to define the anatomical fiducials. See tutorial Import anatomy. Click on Save to keep your modifications, and the import will continue.
A figure is automatically shown at the end of the process, to check visually that the low-resolution cortex and head surfaces were properly generated and imported. If it doesn't look like the following picture, do not go any further in your source analysis, fix the anatomy first.
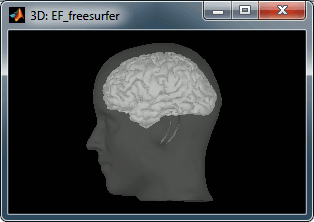
Files imported
The files that are imported from the subject_id folder are the following:
/mri/T1.mgz (T1 MRI volume) + optional /mri/T2.mgz
/mri/*aseg.mgz (volume parcellations)
/surf/?h.pial (grey/csf interface)
/surf/?h.white (grey/white matter interface)
/surf/?h.sphere.reg (registered parametrized sphere, for subject co-registration)
/label/?h.*.annot (cortical surface-based atlases)
/surf/?h.thickness (cortical thickness map)
The successive steps that are performed by Brainstorm:
- Import the T1/T2 MRI
- For "auto" import: Compute the linear MNI registration, otherwise asks for placing the fiducials
- Import all the surfaces (left/right, white/pial)
- Load all the atlases available for each surface (note that the .pial and .white surfaces are matching point-to-point, so the same annotation files are imported for both surface types)
- Load the registered spheres for the left and right hemispheres
- Downsample each hemisphere to the number specified in the options (by default 7500, half of the total default number 15000)
- Compute the mid-surfaces (average of the pial + white surfaces vertex by vertex)
- Merge left and right hemispheres for the two surface types: white matter and cortex envelope
- Generate a head surface from the MRI
- Import the sub-cortical atlas *aseg.mgz as volume atlases and labelled surfaces
- Import the cortical thickness maps
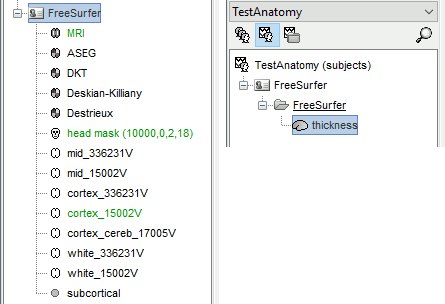
The files you can see in the database explorer at the end (with Volume atlases + Thickness):
MRI: The T1 MRI of the subject, imported from the MGH file format (T1.mgz)
Volume parcellations: *aseg.mgz, see tutorial Explore the anatomy.
head mask: Scalp surface generated by Brainstorm. The numbers in the filename indicate the parameters that were used for this head: vertices=10000, erode factor=0, fill holes=2, background threshold=detected (these are detailed later)
cortex_300000V: High-resolution cortex surface that was generated by FreeSurfer, that contains usually between 200,000 and 300,000 vertices.
cortex_15000V: Low-resolution cortex surface, downsampled using the reducepatch function from Matlab (it keeps a meaningful subset of vertices from the original surface). It appears in green in the database explorer, ie. it is going to be used as the default by the processes that require a cortex surface.
white_300000V: High-resolution white matter envelope from FreeSurfer
white_15000V: Low-resolution white matter, processed with reducepatch
mid_*V: Mid-cortex surfaces (average of the pial + white surfaces vertex by vertex)
subcortical: Atlas of subcortical regions imported as labelled surfaces
Handling errors
How to check the quality of the result
It's hard to estimate what would be a good cortical reconstruction. Try to spot the most obvious errors, e.g. when the early stages of the brain extraction didn't perform well. Play with the Smooth slider in the Surface tab. If it looks like a brain (two separate hemispheres) in both smooth and original views, it is probably OK.
Display the cortex surface on top of the MRI slices, to make sure that they are well aligned, that the surface follows well the folds, and that left and right were not flipped: right-click on the low-resolution cortex > MRI registration > Check MRI/surface registration...
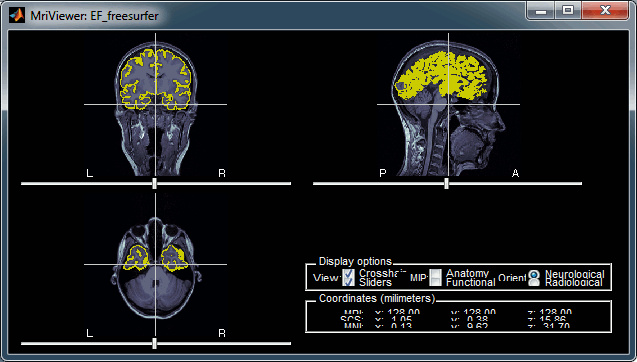
The cortex looks bad
It is critical to get a good cortex surface for source estimation. If the final cortex surface looks bad, it means that something didn't work well somewhere along the FreeSurfer pipeline. You can refer to the following page to fix the problems manually:
http://surfer.nmr.mgh.harvard.edu/fswiki/RecommendedReconstruction
If after following these instructions you still don't manage to get good surfaces, you can try to run the automatic MRI segmentation from CAT12, BrainSuite or BrainVISA.
The head surface looks bad
It is not mandatory to have a perfect head surface to use many Brainstorm features. (For anonymity, it may actually be necessary to distort or obscure the face in figures.)
The head surface is important mainly for two reasons. First, for the alignment of the MEG sensors and the MRI, and second, for generating head models that incorporate the scalp surface (e.g. multi-layer BEM or FEM). If you digitized the head shape with a Polhemus device, you can automatically align the head surface (hence the MRI) with the MEG sensors (in the same referential as the Polhemus points). The quality of this automatic registration depends on the quality of both surfaces: the Polhemus head shape (green points) and the head surface from the MRI (grey surface). If you digitized lots of points on the nose but your head surface doesn't have a nose, these points are not going to help.
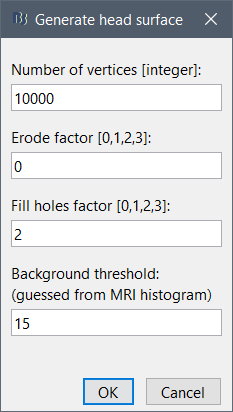
If the default head surface looks bad, you can try generating another one: right-click on the subject folder > Generate head surface. The options are:
Number of vertices: Number of points that are kept from the initial isosurface computed from the MRI. Increasing this number may increase the quality of the final surface.
Erode factor: Number of pixels to erode after the first binary threshold of the MRI. Increasing this number removes small components that are connected to the head.
Fill holes factor: Number of dimensions in which the holes should be identified and closed. Increasing this number removes more of the cavities of the head surface (0=no correction, 1=removes holes inside the surface, 3=closes all the features that make the surface non-convex)
Background threshold: Intensity below which most MRI voxels will be considered as background. This threshold is set automatically after analyzing the volume histogram, but this detection sometime fails. Redefining manually the background threshold may help obtaining a better head surface for noisy MRI scans. If the background was already removed and the background voxels set to zero, you should set this threshold to 1.
To help you define this threshold, you can get the intensity value of the selected voxel in the top-right corner of the MRI Viewer.
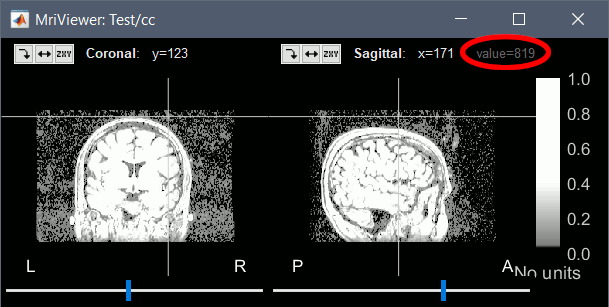
Error in mne_read_surface.m
If you get an error message mentioning mne_read_surface.m, and the files pial.lh and pial.rh are only 2Kb, you probably had an issue with the transfer of symbolic links. See this forum post: https://neuroimage.usc.edu/forums/t/error-in-mne-read-surface-m/26418
Cortical parcellations
The default analysis pipeline in FreeSurfer computes several parcellations of the cortical surface in anatomical regions. The description of this feature is available here:
http://freesurfer.net/fswiki/CorticalParcellation
With FreeSurfer 7, the following parcellations are always available:
Brodmann areas (?h.BA*.annot and ?h.BA*.thresh.annot): more information
Destrieux atlas (?h.aparc.a2009s.annot): more information
Desikan-Killiany atlas (?h.aparc.annot): more information
DKT / Mindboggle6 (?h.aparc.DKTatlas.annot): more information
VcAtlas (?h.mpm.vpnl.annot): more information
Additional parcellations can be computed from FreeSurfer with mri_surf2surf (example):
Brainnetome (?h.BN_Atlas.annot): more information | forum
HCP-MMP1 (?h.HCP-MMP1.annot): more information
CHubs/OASIS (?h.oasis.chubs.annot): more information
PALS-B12 (?h.PALS_B12_*.annot): more information
Schaefer2018 (?h.Schaefer2018_*Parcels_*Networks_order.annot): more information
Yeo2011 (?h.Yeo2011_7Networks_N1000, ?h.Yeo2011_17Networks_N1000): more information
Lausanne 2008 (?h.myaparc_*.annot): more information
These parcellations are imported in Brainstorm as scouts (cortical regions of interest). To access them from the interface: double-click on the cortex, go to the Scout tab, and click on the drop-down list to select another Atlas (ie group of scouts):
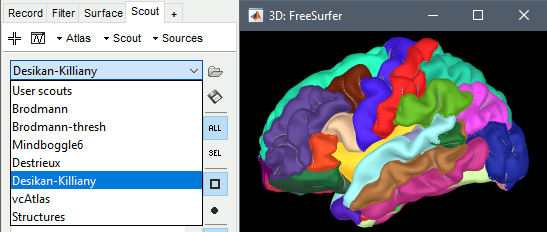
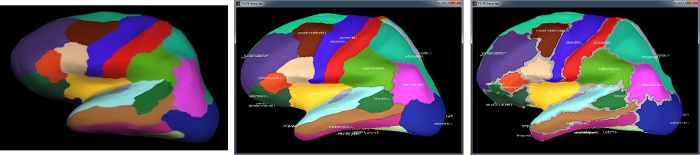
Desikan-Killiany atlas
Displayed respectively in: FreeSurfer, Brainstorm (high-resolution) and Brainstorm (15000 vertices)
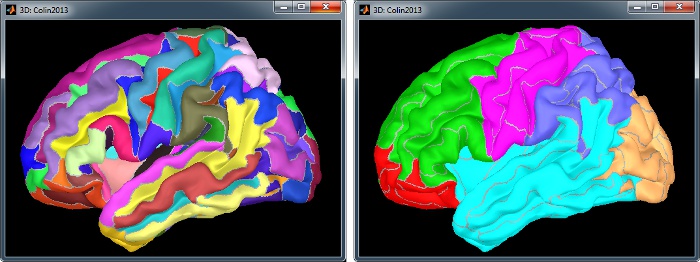
Destrieux atlas
Displayed in Brainstorm with the original scouts colors (left) or classified in 6 regions (right): pre-frontal, frontal, central, parietal, temporal, occipital, occipital. You can switch between the two views with the button "Identify regions with colors" in the toolbar on the right of the scouts list.
The scouts are saved directly in the surface files. To check where they are saved: right-click on the low-resolution cortex file > File > View file contents. You can see that multiple "Atlas" structures are available, the first one that has Name='User scouts', and the second one Name='Brodmann'.
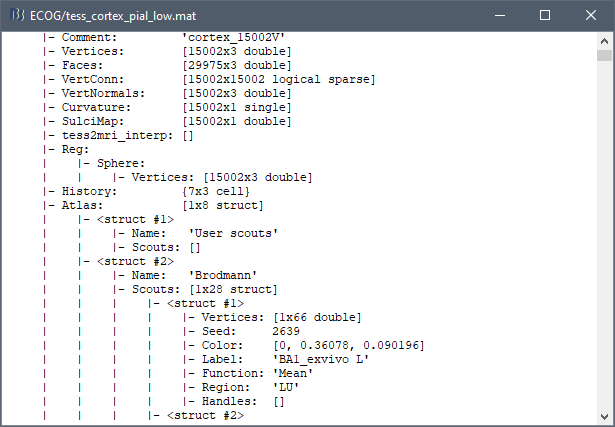
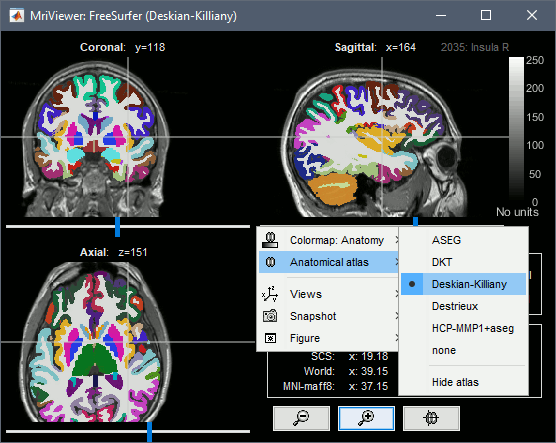
Volume parcellations
All the volume parcellations available in the mri subfolder are imported when the option "FreeSurfer + Volumes atlases" is selected. This includes:
ASEG: mri/aseg.mgz, subcortical structures only
Destrieux: aparc.a2009s+aseg.mgz
Desikan-Killiany: aparc.a2009s+aseg.mgz
DKT: aparc.DKTatlas+aseg.mgz
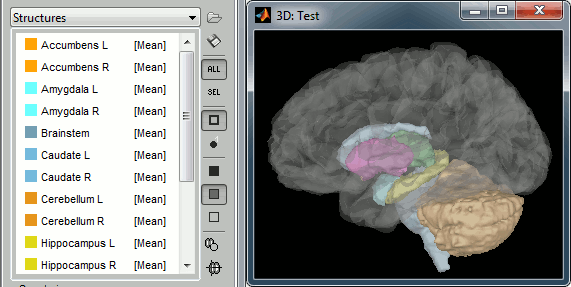
Subcortical structures: aseg atlas
The file aseg.mgz contains a volume atlas of 40 subcortical regions. Brainstorm reads these volume labels and tesselates some of these regions, groups all the meshes in a large surface file where the regions are identified in an atlas called "Structures". It identifies: 8 bialateral structures (accumbens, amygdala, caudate, hippocampus, pallidum, putamen, thalamus, cerebellum) and 1 central structure (brainstem).
You can easily extract one structure (for example the brainstem or the cerebellum) by selecting the corresponding entries in the scouts list and selecting the menu Scout > Edit surface > Keep only selected scouts. It creates a new surface with only the selected regions. If you want to remove one or several structures, use the menu "Remove selected scouts" instead. More information.
Read more about the FreeSurfer subcortical atlas on the software wiki:
http://ftp.nmr.mgh.harvard.edu/fswiki/SubcorticalSegmentation
Registered spheres
The registered spheres are saved in each surface file in the field Reg.Sphere.Vertices. There is nothing that can be done with this information at this point, but it will become helpful when projecting the source results from the individual brains to the default anatomy of the protocol, for a group analysis of the results: Subject coregistration.
Read more about the FreeSurfer registration process on the software wiki:
https://surfer.nmr.mgh.harvard.edu/fswiki/SurfaceRegAndTemplates
Mollweide projection
The FreeSurfer registered spheres can be used to compute a flat 2D projection of the cortex surface using the Mollweide projection, as described in this article: (Kang et al. 2019) Hemispherically-Unified Surface Maps of Human Cerebral Cortex: Reliability and Hemispheric Asymmetries.
Right-click on a cortex surface > MRI registration > 2D projection (Mollweide):
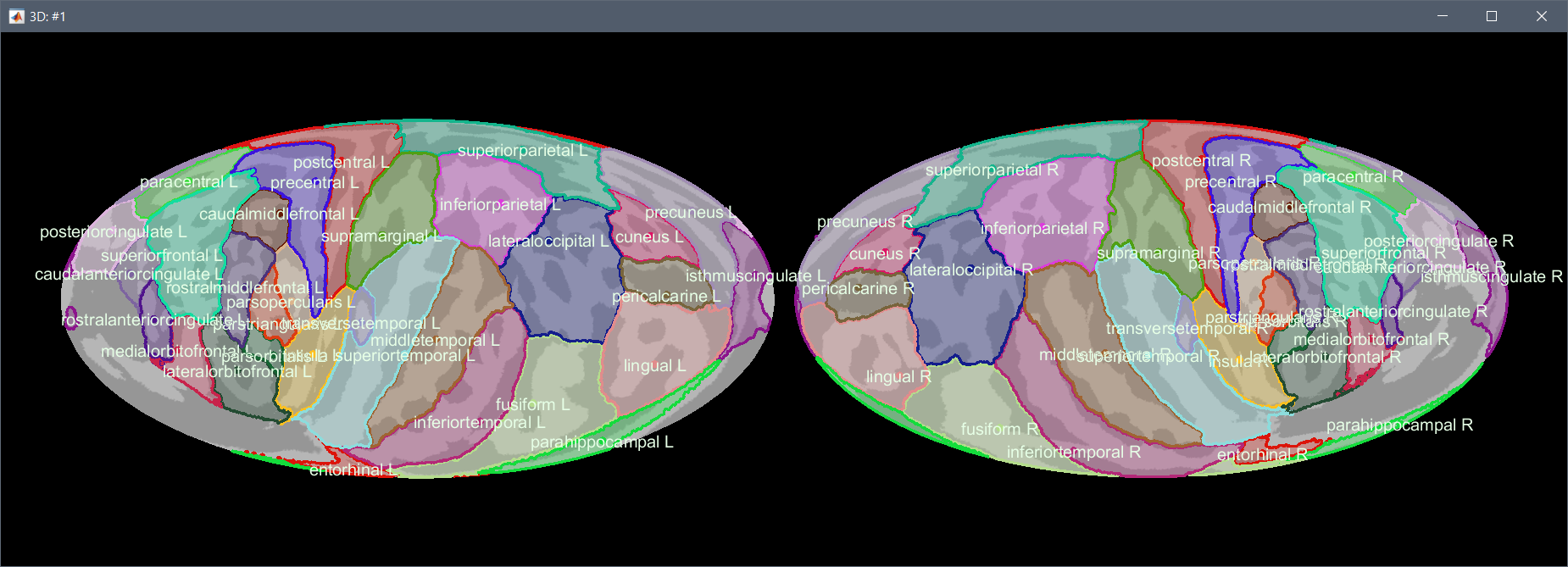
Right-click on a source file > Cortical activations > 2D projection (Mollweide):
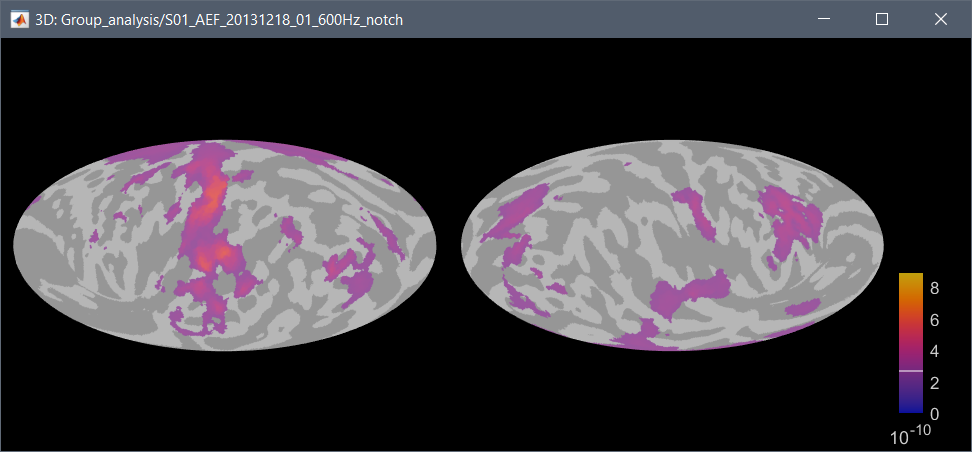
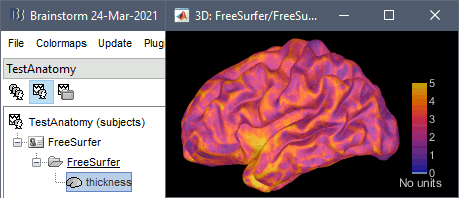
Cortical thickness
The cortical thickness can be saved as a cortical map in the database (a "results" file). This result is generated when using the file format "FreeSurfer folder + Thickness maps" in the Import anatomy folder selection.
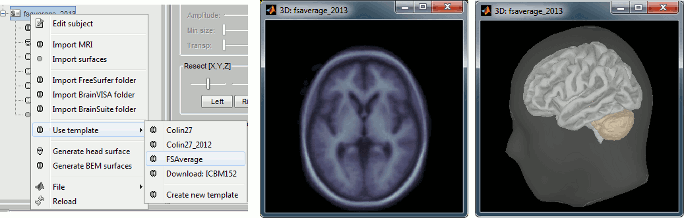
FSAverage template
Instead of the MNI ICBM152 brain, you can use the FreeSurfer average subject "FSAverage" as your default anatomy in Brainstorm. This template is an average of 40 subjects using a spherical averaging described in (Fischl et al. 1999).
To change the default, right-click on "(Default anatomy)" > Use template > FSAverage. If it is not available on your computer yet, it will be automatically downloaded from the server to your user folder: $HOME/.brainstorm/templates/anatomy. See tutorial: Using the anatomy templates.
If you are using the FSAverage template but not a regular user of FreeSurfer, please register on their website: registration page.
Running the folder import as a process
You can import the FreeSurfer folders from scripts, but you have to provide manually the position for all the fiducial points: process Import > Import anatomy > Import anatomy folder.
The corresponding process function is: brainstorm3/toolbox/process/functions/process_import_anatomy.m
Manual import of the anatomy
In case you need to import the MRI, surfaces and atlases separately instead of using the menu "Import anatomy folder", here is the sequence of operations to perform to get to the same result:
From the Anatomy side of the database explorer: create a subject.
Right-click on the subject folder > Import MRI > Select "mri/T1.mgz".
- Set the 6 fiducial points, or click on "Compute MNI normalization" (option maff8). Save.
Right-click on the subject folder > Import surfaces > Select the FreeSurfer file format > Select simultaneously from the "surf" folder: lh.pial, lh.white, rh.pial, rh.white. Question "Apply transformation?": NO.
Double-click on lh.pial to display it. In the scout tab: Atlas > Load atlas > select all the lh.*.annot files available in the label folder. Close the figure.
- Repeat for the other surfaces: lh.white, rh.pial, rh.white
Right-click on lh.pial > MRI registration > Load FreeSurfer sphere > Select "surf/lh.sphere.reg"
- Repeat with the other surfaces (use rh.sphere.reg for the right hemisphere, white and pial surfaces)
Select all the surfaces, right-click > Less vertices > 7500 vertices > Select the first option "Matlab reducepatch"
Select lh.pial + rh.pial, right-click > Merge surfaces: Generates a surface cortex_300000V
Select lh.white + rh.white, right-click > Merge surfaces: Generates a surface white_300000V
Select lh.pial_7500V, rh.pial_7500V, right-click > Merge surfaces: Generates a surface cortex_15000V
Select lh.white_7500V, rh.white_7500V, right-click > Merge surfaces: Generates a surface white_15000V
- Delete all the separate hemispheres: ?h.pial, ?h.white
- Double-click on cortex_15000V to set it as the default cortex
Right-click on the subject folder > Import surfaces > Select the file format "Volume mask or atlas (subject space)" > Select the file mri/aseg.mgz. Question "Apply transformation?": NO.
Right-click on the subject folder > Import MRI > Select the file format "Volume atlas (subject space)" > Select all the files mri/*aseg.mgz.
- Question "Apply standard transformation?": NO
- Question "Apply transformation?": YES
- Question "How to register?": Ignore
- Question "Reslice volume?": No
Go to the functional view of the protocol, create a folder "FreeSurfer". Leave your mouse for a second over the new folder, an note the study index (iStudy).
- From the Matlab command window, you can import the thickness maps with the following call:
ThickFile = import_sources(iStudy, CortexHiFile, ThickLhFile, ThickRhFile, 'FS');
CortexHiFile = full path to the high-res cortex file (right-click > File > Copy file path to clipboard)
ThickLhFile = full path to the surf/lh.thickness file
ThickRhFile = full path to the surf/rh.thickness file