|
Size: 124294
Comment:
|
Size: 141961
Comment:
|
| Deletions are marked like this. | Additions are marked like this. |
| Line 2: | Line 2: |
| Brainstorm is in a very active development state: small or major bug fixes and improvements are issued almost everyday. To update your version of the software easily: [[http://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Installation#Updates|Install and update]].<<BR>>See also the full list of updates: [[Updates|brainstorm3/doc/updates.txt]] | [[https://github.com/brainstorm-tools/brainstorm3/commits/master|All github commit]] | Brainstorm is in a very active development state: small or major bug fixes and improvements are issued almost everyday. To update your version of the software easily: [[http://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Installation#Updates|Install and update]].<<BR>>See also the full list of updates: [[Updates|brainstorm3/doc/updates.txt]] | [[https://github.com/brainstorm-tools/brainstorm3/commits/master|All GitHub commits]] == January 2024 == === Input / output === * Import channel-wise events from BrainVision BrainAmp == December 2023 == === Software distribution === * Basic support Apple silicon (OsType 'mac64arm') === Input / output === * Add process '''Export to file''' to export or or multple '''data'', '''sources''', '''timefreq''' and '''matrix''' files. {{attachment:process_file_export.gif||width=240}} == November 2023 == === CT to MRI co-registration === * The method [[https://github.com/ajoshiusc/USCCleveland/tree/master/ct2mrireg|CT2MRI]] was added as an option to co-register CT and MRI volumes. CT2MRI plugin and BrainSuite are required. * CT2MRI co-registration offers the option of skull stripping for the registered CT. {{attachment:ct2mri_1.gif||width="100%"}} === Plugins === * Remove EASYH5 and JSNIRF code from Brainstorm, add them as plugins === Input / output === * Always Export EDF+ with UTF-8 encoding (bugfix) * Support export to `.xlsx` files for Matlab >= R2019a * Export EEG data as Brainsight format == October 2023 == === iEEG electrode models === * Save, Load, Export and Import electrode models {{attachment:save_ieeg_models.gif||width=240}} === Software distribution === * Compilation with Matlab 2023a/2023b == September 2023 == === Anatomy === * Import resection mask from BrainSuite SVReg. See [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/SegBrainSuite#Resection_labeling|tutorial]] <<HTML(<img class="attachment" src="/brainstorm/Tutorials/SegBrainSuite?action=AttachFile&do=get&target=resection_labeling3.png" style="width:80%">)>> === Input / output === * Export raw data as FieldTrip structure == August 2023 == === Brainstorm ChatBot === <<HTML(<div style="float: right; clear: left; margin: 20px 20px 0px 20px;">)>> {{attachment:bst_chatbot.gif||width=240}} <<HTML(</div>)>> Users can now interact with the ChatBrainstorm3 a chatbot based on the '''ChatGPT 3.5'''. ChatBrainstorm3 is fine tuned using ~11M characters, from [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Introduction?action=sitemap|all the Brainstorm website pages]], from all the [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/forums/|forum's discussions]] and from the [[https://github.com/brainstorm-tools/brainstorm3|Brainstorm GitHub repo]]. This ChatBot is available both on the Brainstorm webpages and on the forum. You can find it on the bottom right on your screen. Click on the 🗨️ icon and start your discussion with it :) === Interface === * Display anatomical atlases on 3D orthogonal slices view. {{attachment:anat_atlas_3d_slices.gif||width=240}} === Connectivity === * Improve across-trials average of phase metrics * Reorganize connectivity metrics {{attachment:pipeline_connect_processes.gif||width=200}} == March 2023 == === Temporary files === The [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/CreateProtocol#Changing_the_temporary_folder|temporary files]] in Brainstorm are saved by default in the user home folder ($HOME/.brainstorm/tmp). Previsouly, all the files were always with the same name, directly in the tmp folder. Now, each process saving temporary files creates a sub-folder with a timestamp. This avoids conflicts between multiple Brainstorm sessions and enables '''parallel computing''' for some processes ([[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/Scripting#Parallel_processing|more information]]). For example, when epoching MEG/EEG recordings, Brainstorm would first create a temporary folder '''import_yymmdd_hhmmss''', store all the epochs in it, then move them to the database when the epoching process is completed. The name of the temporary folder indicates its creation time (year/month/day_hour_minutes_seconds). At the end of the process, all the temporary files should be deleted automatically. If the process crashes or is killed before it returns, the files remain in the tmp folder and need to be explicitly deleted, either with a [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/Scripting#Temporary_files|function call]] or from the Brainstorm preferences. When starting the Brainstorm interface, users are now prompted to delete files in the temporary folder. They can be safely deleted if they result from a previous unfinished process, but must be kept if in use from a different instance of Matlab/Brainstorm. {{attachment:tmp_delete.gif||height="191",width="262"}} === Database === * '''Events''': Update storage of [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/EventMarkers#On_the_hard_drive|events structures]]: The fields "channels" and "notes" are now allowed to be empty. This can save Gb of storage and long minutes of loading when working with recordings including hundreds of thousands of events (e.g. single neuron spiking activity). * '''Channel clusters''': The [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/ChannelClusters|clusters of channels]] are now saved in the channel files, while there were previously available only temporarily in the graphic interface. The Cluster tab is now opened automatically when loading recordings for which clusters have been defined. Associated function '''db_set_clusters.m''' and process '''Import clusters of channels'''. == February 2023 == === FEM anatomy === * FEM mesh generation with [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/FemMesh#SimNIBS_4:_charm|SimNIBS4/CHARM]]<<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:fem_charm.png||height="210",width="338"}} * Merge/rename/delete FEM layers: [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/FemMedianNerveCharm#Merge_tissues|new popup menu]] * Compute FEM mesh statistics<<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:fem_stat.gif||height="230",width="445"}} === Statistics === * Non-parametric tests: Added FieldTrip threshold-free cluster enhancement (TFCE) * Fixed error in data covariance computation: The baseline was not removed when the baseline time window was not included in data time window. See [[https://github.com/brainstorm-tools/brainstorm3/issues/602|issue #602]]. === Input / output === * Export matrix files as EDF+ == January 2023 == === Anatomy === * New MNI template: [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/DefaultAnatomy#FreeSurfer_templates|ICBM152 2023]] * Project scouts between hemispheres using the anatomy template * Removed selection of fiducials when setting anatomy template === Software distribution === * Brainstorm is now compiled with Matlab 2022b: [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Installation#Requirements|Installation instructions]] * The compilation is now supported on Linux and MacOS: [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/Scripting#How_to_compile_Brainstorm|How to compile]] === Interface === * Display scouts on source-level PSD as PSD figures == November 2022 == === Leadfield sensitivity === The leadfield for each MEG sensor, or each pair of EEG/SEEG electrode/reference, can now be displayed as vectors, or as sensitivity maps: on the cortex surface, in the the MRI volume, or as an isosurface at a specific sensitivity value. {{attachment:leadfield_sensitivity.gif}} === BIDS import === * Support for ACPC and CapTrak coordinate systems * Support for NIRS extension * Support for AssociatedEmptyRoom + automatic computation of noise covariance === MNI normalization === * New MNI template: [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/DefaultAnatomy#FreeSurfer_templates|ICBM152 2022]] * EEG: Project channel files between subjects * EEG: When using menu menu "Add EEG positions", convert from MNI space to subject space * Project dipoles files between subjects == September 2022 == === ICA analysis === The interface of the ICA process has been improved and two new popular and efficient methods have been added: [[https://github.com/pierreablin/picard|PICARD]] and [[https://research.ics.aalto.fi/ica/fastica/|FastICA]]. Picard is now the default option for ICA analysis in Brainstorm. [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/Epilepsy#Artifact_cleaning_with_ICA|More information]]. {{attachment:ica_compare_small.gif}} === Coregistration === '''Color-coded distance''': When checking visually the registration between the sensors and the anatomy, a new option allows to color the digitized head points based on the distance to the scalp surface. This can help identify and fix manually coregistration issues. [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/LabelFreeSurfer#Contralateral_registration|More information]]. {{attachment:refine_dist.png||height="162",width="326"}} '''Fiducials on head surface''': It is now possible to position the anatomical fiducials (NAS, LPA, RPA) on the surface instead of the slices in the MRI Viewer. [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/ImportAnatomy#Using_the_MRI_Viewer|More information]]. {{attachment:head_fiducials.gif||height="163",width="206"}} === Input / output === * Support for BCI2000 .dat recordings * Support for BIOPAC AcqKnowledge .acq recordings * Support for XDF EEG recordings * Updated Nicolet EEG reader == June 2022 == === Connectivity graph === It is now possible to apply a threshold based on the '''percentile''' of the distribution of the connectivity values. This option is available both interactively and from a new process "Threshold by percentile". [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/ConnectivityGraph#Filtering_options|More information]]. {{attachment:thresh_percentile.gif}} === Anatomy === The [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/LabelFreeSurfer#Contralateral_registration|contralateral registration]] from FreeSurfer is now supported in Brainstorm and allows the projection of scouts between hemispheres. [[http://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/LabelFreeSurfer#Contralateral_registration|More information]]. {{attachment:project_contra.gif||height="241",width="371"}} === BIDS === * Import: Added support for IntendedFor in _coordsystem.json * Import: Added support for anatomical landmarks (_t1w.json and _coordsystem.json) * Export _electrodes.tsv, with the choice of the reference MRI == April 2022 == === Electrophysiology === Major update of the electrophysiology toolbox: new features, many bug fixes, and improved documentation. Explore the [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials#Electrophysiology|new tutorials]]. {{attachment:ephys_update.png}} === Input / output === * Support for Neuroelectrics EEG with EEGLAB plugin (.easy, .nedf) * Updated Plexon reader * Export events in AnyWave .mrk format * Import channel from ASCII files now expect mm instead of cm == February 2022 == === Connectivity === * New tutorial: [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/Connectivity|Functional connectivity]] (methods) * New tutorial: [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/CorticomuscularCoherence|Corticomuscular coherence]] (practice with FieldTrip tutorial dataset) * New measures: [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/Connectivity#Phase_locking_value|wPLI and ciPLV]] * Updated process: [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/Connectivity#Simulated_data|Simulate AR signals]] * Computation: Removed the p-values thresholding from all connectivity metrics * Removed JAVA3D/JOGL support and the older connectivity graph display === Anatomy === * Extract head with FSL/BET: Right-click on MRI > MRI segmentation. * FreeSurfer: Added support for InfantFS / infant_recon_all == January 2022 == === SPRiNT: Time-resolved spectral parameterization === New tutorial and process for decomposing and parameterizing spectral components over time: <<BR>>[[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/SPRiNT|Spectral Parameterization Resolved in Time (SPRiNT)]] {{attachment:SPRiNT_schematic.png||height="300",width="1050"}} === Plugins === * SimMEEG: New [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/Simulations#SimMEEG|video tutorials]]. * New menu: Update > Reproducibility > Export software environment: <<BR>>Archives the software environment in one zip file, including installed plugins and templates. * Track software versions: Save GitHub commit SHA and installation date for each plugin. === Statistics === * New process: [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/forums/t/common-source-activation-across-subjects-and-conditions/1152|Conjunction inference]] == December 2021 == === Input / output === * Support for Tobii Pro Glasses export .tsv * Support for FieldTrip trialinfo field * Updated York Instrument MEGSCAN reader (.meghdf5) == November 2021 == === MRI segmentation === Brainstorm is now fully interfaced with new programs for MRI processing and segmentation: * [[Tutorials/SegFastSurfer|MRI segmentation with FastSurfer]] (T1 only) * [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/LabelFreeSurfer#Run_FreeSurfer_from_Brainstorm|MRI segmentation with FreeSurfer]] (T1+T2) * [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/SegBrainSuite#Run_BrainSuite_from_Brainstorm|MRI segmentation with BrainSuite]] (T1 only) * Import BIDS: Add support for CAT12, BrainSuite and BrainVISA === New plugins === * '''MIA''': Group statistics on SEEG data, see the [[http://www.neurotrack.fr/mia/|website]]. * '''DeriveLFP''': Part of the e-phys toolbox, available in the compiled distribution. * '''Download statistics''' are now accessible for each plugin. See tutorial: [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/Plugins#Interactive_management|Plugins]]. === Automatic registration === The automatic MEG/sensors registration using digitized head points has been improved. It now includes an new parameter to exclude outlier digitized points, and a report of the distance between the digitized head points and the scalp surface. See tutorial: [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/ChannelFile#Automatic_registration|MRI registration]]. {{attachment:refine_newstat.gif}} === Send reports by email === When running some long computation on a distant server, you can now receive an email when the processing is over. See tutorial: [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/Scripting#Send_report_by_email|Scripting]]. == October 2021 == === Major bug fix: PCA === The computation of the first mode of the PCA from multiple time series has been fixed. It now restores the mean of the signal after the computation of the PCA. See [[https://github.com/brainstorm-tools/brainstorm3/commit/621735880ca829df64d29ae83c192031895bdd73|GitHub commit]]. The output of the following functions and processes are affected by this modification: * Interactive display of the scouts time series, with scout function PCA. * Process: Extract > Scout time series, with scout function PCA. * Process: Sources > Unconstrained to flat maps, option PCA. === Brainstorm compilation === We updated the deployment and compilation scripts of Brainstorm. Now everybody with the Matlab Compiler toolbox can recompile the Brainstorm standalone package, including additional personal scripts of modified versions of the code. See tutorial: [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/Scripting#How_to_compile_Brainstorm|Scripting]]. |
| Line 5: | Line 240: |
| SEEG/ECOG contact labelling from volume and surface atlases | === iEEG anatomical labels === New automatic SEEG/ECOG contact labelling from volume and surface parcellations. See tutorials: [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/Epileptogenicity#Anatomical_labelling|SEEG epileptogenicity maps]] and [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/ECoG#Anatomical_labelling|ECoG+sEEG epilepsy]]. {{attachment:seeg_labels.gif}} |
| Line 9: | Line 247: |
| The FEM tools in Brainstorm are now documented in new tutorials: [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/FemMesh|FEM mesh generation]], [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/FemTensors|FEM tensors estimation]], [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/FemMedianNerve|FEM median nerve example]], [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/Duneuro|Realistic head model: FEM with DUNEuro]]. |
The FEM tools in Brainstorm are now documented in new tutorials: [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/FemMesh|FEM mesh generation]], [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/FemTensors|FEM tensors estimation]], [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/FemMedianNerveCharm|FEM median nerve example]], [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/Duneuro|Realistic head model: FEM with DUNEuro]]. {{attachment:fem_tuto.png}} |
| Line 22: | Line 260: |
| {{attachment:dics.png||width="491",height="135"}} | {{attachment:dics.png||height="135",width="491"}} |
| Line 28: | Line 266: |
| {{attachment:connect_graphs.png||width="475",height="180"}} | {{attachment:connect_graphs.png||height="180",width="475"}} |
| Line 50: | Line 288: |
| {{attachment:plugin_manager.gif||width="359",height="189"}} | {{attachment:plugin_manager.gif||height="189",width="359"}} |
| Line 64: | Line 302: |
| * Import all volume parcellations from FreeSurfer, CAT, BrainVISA, BrainSuite<<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:volatlas.gif||width="436",height="324"}} | * Import all volume parcellations from FreeSurfer, CAT, BrainVISA, BrainSuite<<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:volatlas.gif||height="324",width="436"}} |
| Line 77: | Line 315: |
| * SSS/tSSS process = Wrapper for mne.preprocessing.maxwell_filter<<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:mne_python_maxwell.gif||width="537",height="162"}} | * SSS/tSSS process = Wrapper for mne.preprocessing.maxwell_filter<<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:mne_python_maxwell.gif||height="162",width="537"}} |
| Line 93: | Line 331: |
| {{attachment:simvol_resultsx.png||width="459",height="134"}} | {{attachment:simvol_resultsx.png||height="134",width="459"}} |
| Line 98: | Line 336: |
| {{attachment:FOOOF_schematic.png||width="408",height="256"}} | {{attachment:FOOOF_schematic.png||height="256",width="408"}} |
| Line 146: | Line 384: |
| . {{attachment:forward_disp.gif||width="679",height="180"}} | . {{attachment:forward_disp.gif||height="180",width="679"}} |
| Line 189: | Line 427: |
| * '''Zoom''' on selected time/frequency segments with '''shift+click''' (time series and spectrum) <<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:review_timesel.gif||width="408",height="110"}} | * '''Zoom''' on selected time/frequency segments with '''shift+click''' (time series and spectrum) <<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:review_timesel.gif||height="110",width="408"}} |
| Line 199: | Line 437: |
| * Computation of FEM meshes with ROAST and iso2mesh: see [[https://github.com/brainstorm-tools/brainstorm3/issues/185|GitHub discussion]] <<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:fem_display.gif||width="425",height="196"}} | * Computation of FEM meshes with ROAST and iso2mesh: see [[https://github.com/brainstorm-tools/brainstorm3/issues/185|GitHub discussion]] <<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:fem_display.gif||height="196",width="425"}} |
| Line 214: | Line 452: |
| {{attachment:cat12_atlases.gif||width="474",height="208"}} | {{attachment:cat12_atlases.gif||height="208",width="474"}} |
| Line 222: | Line 460: |
| {{attachment:dspm_scale.gif||width="464",height="261"}} | {{attachment:dspm_scale.gif||height="261",width="464"}} |
| Line 228: | Line 466: |
| {{attachment:marsAtlas.gif||width="438",height="174"}} | {{attachment:marsAtlas.gif||height="174",width="438"}} |
| Line 241: | Line 479: |
| {{attachment:events_lines.gif||width="504",height="156"}} | {{attachment:events_lines.gif||height="156",width="504"}} |
| Line 246: | Line 484: |
| {{attachment:events_shortcuts.gif||width="377",height="244"}} | {{attachment:events_shortcuts.gif||height="244",width="377"}} |
| Line 276: | Line 514: |
| * Deface MRI with [[https://surfer.nmr.mgh.harvard.edu/fswiki/mri_deface|FreeSurfer]] or [[https://github.com/neurodebian/spm12/blob/master/spm_deface.m|SPM]].<<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:defacing_figure.gif||width="502",height="154"}} | * Deface MRI with [[https://surfer.nmr.mgh.harvard.edu/fswiki/mri_deface|FreeSurfer]] or [[https://github.com/neurodebian/spm12/blob/master/spm_deface.m|SPM]].<<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:defacing_figure.gif||height="154",width="502"}} |
| Line 332: | Line 570: |
| {{attachment:multi2dlayout.gif||width="581",height="159"}} | {{attachment:multi2dlayout.gif||height="159",width="581"}} |
| Line 423: | Line 661: |
| * New options for [[http://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/Epileptogenicity#Volume_coregistration|volume coregistration]] of multiple scans of the same subject (MRI/MRI or MRI/CT)<<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:mri_coreg.gif||width="607",height="167"}} * New interface for [[http://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/Epileptogenicity#Edit_the_contacts_positions|placing SEEG/ECOG contacts]] in the MRI Viewer <<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:seeg_edit.gif||width="609",height="171"}} |
* New options for [[http://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/Epileptogenicity#Volume_coregistration|volume coregistration]] of multiple scans of the same subject (MRI/MRI or MRI/CT)<<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:mri_coreg.gif||height="167",width="607"}} * New interface for [[http://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/Epileptogenicity#Edit_the_contacts_positions|placing SEEG/ECOG contacts]] in the MRI Viewer <<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:seeg_edit.gif||height="171",width="609"}} |
| Line 432: | Line 670: |
| * Add event markers on the signals when the event names match the channel names<<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:raw_chanevt.gif||width="444",height="119"}} * New tab [[http://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/Epileptogenicity#Guidelines_panel|Guidelines]] for computing epileptogenicity maps<<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:guidelines.gif||width="599",height="181"}} |
* Add event markers on the signals when the event names match the channel names<<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:raw_chanevt.gif||height="119",width="444"}} * New tab [[http://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/Epileptogenicity#Guidelines_panel|Guidelines]] for computing epileptogenicity maps<<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:guidelines.gif||height="181",width="599"}} |
| Line 465: | Line 703: |
| * Computation of SPM canonical surfaces (alternative to FreeSurfer/BrainSuite/BrainVISA)<<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:spm_canonical.gif||width="546",height="147"}} * New anatomy template: [[http://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/DefaultAnatomy#BrainSuite_templates|USCBrain]] <<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:USCBrain.gif||width="594",height="79"}} |
* Computation of SPM canonical surfaces (alternative to FreeSurfer/BrainSuite/BrainVISA)<<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:spm_canonical.gif||height="147",width="546"}} * New anatomy template: [[http://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/DefaultAnatomy#BrainSuite_templates|USCBrain]] <<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:USCBrain.gif||height="79",width="594"}} |
| Line 483: | Line 721: |
| . {{attachment:preferences.gif||width="395",height="250"}} | . {{attachment:preferences.gif||height="250",width="395"}} |
| Line 504: | Line 742: |
| {{attachment:newdisp_seeg.gif||width="569",height="188"}} {{attachment:newdisp_ecog.gif||width="567",height="135"}} |
{{attachment:newdisp_seeg.gif||height="188",width="569"}} {{attachment:newdisp_ecog.gif||height="135",width="567"}} |
| Line 529: | Line 767: |
| {{attachment:hcp_tutorial.gif||width="657",height="153"}} | {{attachment:hcp_tutorial.gif||height="153",width="657"}} |
| Line 535: | Line 773: |
| {{attachment:psd_sources_left.gif||width="378",height="167"}} {{attachment:psd_sources_top.gif||width="264",height="167"}} | {{attachment:psd_sources_left.gif||height="167",width="378"}} {{attachment:psd_sources_top.gif||height="167",width="264"}} |
| Line 549: | Line 787: |
| * Import as '''volume''': Import the aseg.mgz file as a new MRI in the subject anatomy folder, then display it with the MRI viewer. New colormaps are available for representing labelled atlases. <<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:volume_atlas_aseg.gif||width="428",height="198"}} {{attachment:volume_atlas_aseg2.gif||width="169",height="200"}} | * Import as '''volume''': Import the aseg.mgz file as a new MRI in the subject anatomy folder, then display it with the MRI viewer. New colormaps are available for representing labelled atlases. <<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:volume_atlas_aseg.gif||height="198",width="428"}} {{attachment:volume_atlas_aseg2.gif||height="200",width="169"}} |
| Line 560: | Line 798: |
| * To get the labels of the atlas displayed correctly, a .txt file with the same name should be present in the folder. Each line in this file must include the index of the label ("label_index label_name"), such as the atlases distributed as part of the [[http://people.cas.sc.edu/rorden/mricron/install.html|MRIcron software]].<<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:aal_scouts.gif||width="335",height="188"}} {{attachment:aal_volume.gif||width="154",height="188"}} {{attachment:aal_surfaces.gif||width="151",height="188"}} | * To get the labels of the atlas displayed correctly, a .txt file with the same name should be present in the folder. Each line in this file must include the index of the label ("label_index label_name"), such as the atlases distributed as part of the [[http://people.cas.sc.edu/rorden/mricron/install.html|MRIcron software]].<<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:aal_scouts.gif||height="188",width="335"}} {{attachment:aal_volume.gif||height="188",width="154"}} {{attachment:aal_surfaces.gif||height="188",width="151"}} |
| Line 565: | Line 803: |
| {{attachment:ct_mri.gif||width="280",height="171"}} | {{attachment:ct_mri.gif||height="171",width="280"}} |
| Line 570: | Line 808: |
| {{attachment:grid_fullhead.gif||width="219",height="302"}} {{attachment:psd_volume_delta.gif||width="219",height="215"}} {{attachment:psd_volume_gamma.gif||width="217",height="215"}} | {{attachment:grid_fullhead.gif||height="302",width="219"}} {{attachment:psd_volume_delta.gif||height="215",width="219"}} {{attachment:psd_volume_gamma.gif||height="215",width="217"}} |
| Line 574: | Line 812: |
| {{attachment:import_cerebellum.gif||width="311",height="158"}} | {{attachment:import_cerebellum.gif||height="158",width="311"}} |
| Line 620: | Line 858: |
| {{attachment:specs_bandpass.gif||width="574",height="290"}} | {{attachment:specs_bandpass.gif||height="290",width="574"}} |
| Line 624: | Line 862: |
| {{attachment:bandpass_transient.gif||width="432",height="131"}} | {{attachment:bandpass_transient.gif||height="131",width="432"}} |
| Line 643: | Line 881: |
| {{attachment:new_topo.gif||width="596",height="170"}} | {{attachment:new_topo.gif||height="170",width="596"}} |
| Line 651: | Line 889: |
| * New [[http://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/DeepAtlas#Source_estimation|exploded view]] to visualize all the subcortical regions on the same view. <<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:resect_struct.gif||width="386",height="167"}} | * New [[http://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/DeepAtlas#Source_estimation|exploded view]] to visualize all the subcortical regions on the same view. <<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:resect_struct.gif||height="167",width="386"}} |
| Line 660: | Line 898: |
| * These two options are offered when importing additional volumes in the subject anatomy, if their dimensions or resolution do not match the initial structural MRI. <<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:resample_mri.gif||width="529",height="164"}} | * These two options are offered when importing additional volumes in the subject anatomy, if their dimensions or resolution do not match the initial structural MRI. <<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:resample_mri.gif||height="164",width="529"}} |
| Line 664: | Line 902: |
| * When you have a secondary volume imported in your subject, you can display it as an overlay on the original MRI and configure the threshold and transparency from the Surface tab. <<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:mri_overlay.gif||width="490",height="214"}} | * When you have a secondary volume imported in your subject, you can display it as an overlay on the original MRI and configure the threshold and transparency from the Surface tab. <<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:mri_overlay.gif||height="214",width="490"}} |
| Line 697: | Line 935: |
| {{attachment:group_tutorial.gif||width="615",height="104"}} | {{attachment:group_tutorial.gif||height="104",width="615"}} |
| Line 702: | Line 940: |
| {{attachment:generate_script.gif||width="467",height="188"}} | {{attachment:generate_script.gif||height="188",width="467"}} |
| Line 707: | Line 945: |
| * Implementation of volume scouts: [[http://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/TutVolSource#Volume_scouts|Volume source estimation tutorial]]. <<BR>> {{attachment:scouts_3d.gif||width="345",height="167"}} * Projection on an anatomy template for group analysis: [[http://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/CoregisterSubjects#Volume_source_models|Subjects coregistration tutorial]]. <<BR>> {{attachment:volume_display.gif||width="345",height="180"}} |
* Implementation of volume scouts: [[http://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/TutVolSource#Volume_scouts|Volume source estimation tutorial]]. <<BR>> {{attachment:scouts_3d.gif||height="167",width="345"}} * Projection on an anatomy template for group analysis: [[http://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/CoregisterSubjects#Volume_source_models|Subjects coregistration tutorial]]. <<BR>> {{attachment:volume_display.gif||height="180",width="345"}} |
| Line 751: | Line 989: |
| * Organized the default electrode positions by manufacturer. <<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:default_eeg.gif||width="445",height="94"}} | * Organized the default electrode positions by manufacturer. <<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:default_eeg.gif||height="94",width="445"}} |
| Line 757: | Line 995: |
| {{attachment:news_nirs.gif||width="665",height="163"}} | {{attachment:news_nirs.gif||height="163",width="665"}} |
| Line 762: | Line 1000: |
| {{attachment:elekta_phantom.gif||width="481",height="168"}} | {{attachment:elekta_phantom.gif||height="168",width="481"}} |
| Line 767: | Line 1005: |
| * New recommendations for the normalization of source maps (never use an absolute value):<<BR>> [[http://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/SourceEstimation#Source_map_normalization|Source estimation tutorial (normalization)]]. | * New recommendations for the normalization of source maps (never use an absolute value):<<BR>> [[https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/SourceEstimation#Standardization_of_source_maps|Source estimation tutorial (normalization)]]. |
| Line 772: | Line 1010: |
| * '''Min/max''': You can now quickly get the minimum and maximum values in the recordings by simply selecting a time segment. If some channels are selected, it shows the extrema only for them. <<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:viewer_max.gif||width="540",height="176"}} | * '''Min/max''': You can now quickly get the minimum and maximum values in the recordings by simply selecting a time segment. If some channels are selected, it shows the extrema only for them. <<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:viewer_max.gif||height="176",width="540"}} |
| Line 776: | Line 1014: |
| * '''Color''': The montage editor now allows the direct definition of a color for specific channels: Use the specific syntax for the display name: "NAME|RRGGBB" (hexadecimal notation). <<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:montage_overlay.gif||width="522",height="230"}} | * '''Color''': The montage editor now allows the direct definition of a color for specific channels: Use the specific syntax for the display name: "NAME|RRGGBB" (hexadecimal notation). <<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:montage_overlay.gif||height="230",width="522"}} |
| Line 847: | Line 1085: |
| * New Process2: File > Select uniform number of files: Selects the same number of files in A and B <<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:stat_feb2016.gif||width="538",height="371"}} | * New Process2: File > Select uniform number of files: Selects the same number of files in A and B <<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:stat_feb2016.gif||height="371",width="538"}} |
| Line 851: | Line 1089: |
| * '''[Trials x Time]''' Right-click on a group of trials > Display as image: Raster plot for the values of one sensor across the trials. Change the channel from the Display tab (or up/down arrow key). <<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:rasterplot.gif||width="548",height="159"}} * '''[Channels x Time]''' Right-click on one single file > MEG/EEG > Display as image: <<BR>>Shows the same information as the "time series" view, but with colors instead of lines. <<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:displayimage.gif||width="547",height="150"}} |
* '''[Trials x Time]''' Right-click on a group of trials > Display as image: Raster plot for the values of one sensor across the trials. Change the channel from the Display tab (or up/down arrow key). <<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:rasterplot.gif||height="159",width="548"}} * '''[Channels x Time]''' Right-click on one single file > MEG/EEG > Display as image: <<BR>>Shows the same information as the "time series" view, but with colors instead of lines. <<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:displayimage.gif||height="150",width="547"}} |
| Line 862: | Line 1100: |
| * New button [Online tutorial] in the pipeline editor, to jump instantly to the corresponding tutorial. <<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:online_help.gif||width="230",height="129"}} | * New button [Online tutorial] in the pipeline editor, to jump instantly to the corresponding tutorial. <<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:online_help.gif||height="129",width="230"}} |
| Line 886: | Line 1124: |
| * Display of value histograms for all the files in the database (right-click > File > View histogram) <<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:histograms.gif||width="330",height="155"}} | * Display of value histograms for all the files in the database (right-click > File > View histogram) <<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:histograms.gif||height="155",width="330"}} |
| Line 924: | Line 1162: |
| * New displays for exploring significant clusters <<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:ft_cluster_display1.gif||width="418",height="145"}} | * New displays for exploring significant clusters <<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:ft_cluster_display1.gif||height="145",width="418"}} |
| Line 963: | Line 1201: |
| . {{attachment:stddev.gif||width="394",height="132"}} | . {{attachment:stddev.gif||height="132",width="394"}} |
| Line 968: | Line 1206: |
| . {{attachment:syncvid.gif||width="405",height="143"}} | . {{attachment:syncvid.gif||height="143",width="405"}} |
| Line 1016: | Line 1254: |
| {{attachment:ica_test.gif||width="696",height="205"}} | {{attachment:ica_test.gif||height="205",width="696"}} |
| Line 1022: | Line 1260: |
| * Mixing channels from different modalities in the same montage. This is useful for re-referencing the EEG with an electrode that is not classified as "EEG" in the channel file. It allows also to review multiple types of signals in the same figure: EEG, EOG, ECG, EMG, etc.<<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:montage_linkref.gif||width="335",height="238"}} | * Mixing channels from different modalities in the same montage. This is useful for re-referencing the EEG with an electrode that is not classified as "EEG" in the channel file. It allows also to review multiple types of signals in the same figure: EEG, EOG, ECG, EMG, etc.<<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:montage_linkref.gif||height="238",width="335"}} |
| Line 1035: | Line 1273: |
| * New display mode: 3D Electrodes<<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:intra_3delectrodes.gif||width="453",height="196"}} * Edit the position of the contact positions using the MRI Viewer.<<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:intra_setpos.gif||width="508",height="147"}} * Grouping contacts using the new field "Group" in the channel file. Use the channel file editor to modify these groups if they haven't been identified correctly (right-click > Edit channel file).<<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:intra_setgroup.gif||width="463",height="169"}} * Set of temporary bipolar montages automatically created when loading SEEG/ECOG recordings.<<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:intra_montages.gif||width="211",height="220"}} * Computation of the forward model for ECOG and SEEG concacts using the OpenMEEG BEM model. <<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:intra_forward.gif||width="201",height="81"}} |
* New display mode: 3D Electrodes<<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:intra_3delectrodes.gif||height="196",width="453"}} * Edit the position of the contact positions using the MRI Viewer.<<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:intra_setpos.gif||height="147",width="508"}} * Grouping contacts using the new field "Group" in the channel file. Use the channel file editor to modify these groups if they haven't been identified correctly (right-click > Edit channel file).<<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:intra_setgroup.gif||height="169",width="463"}} * Set of temporary bipolar montages automatically created when loading SEEG/ECOG recordings.<<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:intra_montages.gif||height="220",width="211"}} * Computation of the forward model for ECOG and SEEG concacts using the OpenMEEG BEM model. <<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:intra_forward.gif||height="81",width="201"}} |
| Line 1087: | Line 1325: |
| {{attachment:infant7w.gif||width="371",height="113"}} | {{attachment:infant7w.gif||height="113",width="371"}} |
| Line 1092: | Line 1330: |
| {{attachment:add_positions.gif||width="408",height="94"}} | {{attachment:add_positions.gif||height="94",width="408"}} |
| Line 1097: | Line 1335: |
| {{attachment:new_best.gif||width="371",height="231"}} | {{attachment:new_best.gif||height="231",width="371"}} |
| Line 1119: | Line 1357: |
| {{attachment:average_source.gif||width="373",height="153"}} | {{attachment:average_source.gif||height="153",width="373"}} |
| Line 1144: | Line 1382: |
| {{attachment:resting_meg.gif||width="508",height="265"}} | {{attachment:resting_meg.gif||height="265",width="508"}} |
| Line 1186: | Line 1424: |
| {{attachment:newEpilepsy.gif||width="477",height="159"}} | {{attachment:newEpilepsy.gif||height="159",width="477"}} |
| Line 1194: | Line 1432: |
| {{attachment:newMontages.gif||width="492",height="228"}} | {{attachment:newMontages.gif||height="228",width="492"}} |
| Line 1203: | Line 1441: |
| {{attachment:newAvgref.gif||width="478",height="143"}} | {{attachment:newAvgref.gif||height="143",width="478"}} |
| Line 1219: | Line 1457: |
| {{attachment:toolbarWindows.gif||width="277",height="219"}} | {{attachment:toolbarWindows.gif||height="219",width="277"}} |
| Line 1224: | Line 1462: |
| {{attachment:newColormap.gif||width="381",height="246"}} | {{attachment:newColormap.gif||height="246",width="381"}} |
| Line 1230: | Line 1468: |
| {{attachment:allFiles.gif||width="352",height="122"}} | {{attachment:allFiles.gif||height="122",width="352"}} |
| Line 1274: | Line 1512: |
| . {{attachment:spmResults.gif||width="222",height="333"}} | . {{attachment:spmResults.gif||height="333",width="222"}} |
| Line 1288: | Line 1526: |
| {{attachment:aseg.gif||width="408",height="205"}} | {{attachment:aseg.gif||height="205",width="408"}} |
| Line 1301: | Line 1539: |
| {{attachment:fsaverage.gif||width="553",height="176"}} | {{attachment:fsaverage.gif||height="176",width="553"}} |
| Line 1379: | Line 1617: |
| {{attachment:iEEG.gif||width="417",height="168"}} | {{attachment:iEEG.gif||height="168",width="417"}} |
| Line 1391: | Line 1629: |
| {{attachment:layout.gif||width="336",height="172"}} | {{attachment:layout.gif||height="172",width="336"}} |
| Line 1396: | Line 1634: |
| {{attachment:saveSurface.gif||width="429",height="286"}} | {{attachment:saveSurface.gif||height="286",width="429"}} |
| Line 1445: | Line 1683: |
| {{attachment:import1.gif||width="150",height="185"}} | {{attachment:import1.gif||height="185",width="150"}} |
| Line 1462: | Line 1700: |
| {{attachment:newTopo.gif||width="411",height="170"}} | {{attachment:newTopo.gif||height="170",width="411"}} |
| Line 1482: | Line 1720: |
| {{attachment:figureCortex.gif||width="472",height="181"}} | {{attachment:figureCortex.gif||height="181",width="472"}} |
| Line 1487: | Line 1725: |
| {{attachment:downsampleAtlas.gif||width="388",height="147"}} | {{attachment:downsampleAtlas.gif||height="147",width="388"}} |
| Line 1549: | Line 1787: |
| . {{attachment:eventShortcuts.gif||width="484px",height="400px"}} | . {{attachment:eventShortcuts.gif||height="400px",width="484px"}} |
| Line 1555: | Line 1793: |
| {{attachment:sspExample.gif||width="624px",height="328px"}} | {{attachment:sspExample.gif||height="328px",width="624px"}} |
| Line 1560: | Line 1798: |
| . {{attachment:megReg.gif||width="349px",height="189px"}} | . {{attachment:megReg.gif||height="189px",width="349px"}} |
| Line 1614: | Line 1852: |
| {{attachment:warp.jpg||width="377px",height="128px"}} | {{attachment:warp.jpg||height="128px",width="377px"}} |
| Line 1627: | Line 1865: |
| {{attachment:openmeeg.gif||width="248px",height="67px"}} | {{attachment:openmeeg.gif||height="67px",width="248px"}} |
| Line 1632: | Line 1870: |
| {{attachment:grid.jpg||width="191px",height="163px"}} {{attachment:sourcevol.jpg||width="178px",height="162px"}} {{attachment:mriviewer_vol.jpg||height="162px",width="157px",class="hoverZoomLink"}} | {{attachment:grid.jpg||height="163px",width="191px"}} {{attachment:sourcevol.jpg||height="162px",width="178px"}} {{attachment:mriviewer_vol.jpg||height="162px",width="157px",class="hoverZoomLink"}} |
| Line 1697: | Line 1935: |
| {{/brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm/None%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent?action=content|None|width="100%"}} {{/brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm/None%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent?action=content|None|width="100%"}} | {{/brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm/None%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent?action=content|None|width="100%"}} {{/brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm//brainstorm/None%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent%3Faction%3Dcontent?action=content|None|width="100%"}} |
What's new
Brainstorm is in a very active development state: small or major bug fixes and improvements are issued almost everyday. To update your version of the software easily: Install and update.
See also the full list of updates: brainstorm3/doc/updates.txt | All GitHub commits
January 2024
Input / output
Import channel-wise events from BrainVision BrainAmp
December 2023
Software distribution
Basic support Apple silicon (OsType 'mac64arm')
Input / output
Add process Export to file to export or or multple data, sources, timefreq and matrix files.
November 2023
CT to MRI co-registration
The method CT2MRI was added as an option to co-register CT and MRI volumes. CT2MRI plugin and BrainSuite are required.
- CT2MRI co-registration offers the option of skull stripping for the registered CT.
Plugins
- Remove EASYH5 and JSNIRF code from Brainstorm, add them as plugins
Input / output
- Always Export EDF+ with UTF-8 encoding (bugfix)
Support export to .xlsx files for Matlab >= R2019a
- Export EEG data as Brainsight format
October 2023
iEEG electrode models
- Save, Load, Export and Import electrode models
Software distribution
- Compilation with Matlab 2023a/2023b
September 2023
Anatomy
Import resection mask from BrainSuite SVReg. See tutorial
Input / output
Export raw data as FieldTrip structure
August 2023
Brainstorm ChatBot
Users can now interact with the ChatBrainstorm3 a chatbot based on the ChatGPT 3.5. ChatBrainstorm3 is fine tuned using ~11M characters, from all the Brainstorm website pages, from all the forum's discussions and from the Brainstorm GitHub repo. This ChatBot is available both on the Brainstorm webpages and on the forum. You can find it on the bottom right on your screen. Click on the 🗨️ icon and start your discussion with it
The temporary files in Brainstorm are saved by default in the user home folder ($HOME/.brainstorm/tmp). Previsouly, all the files were always with the same name, directly in the tmp folder. Now, each process saving temporary files creates a sub-folder with a timestamp. This avoids conflicts between multiple Brainstorm sessions and enables For example, when epoching MEG/EEG recordings, Brainstorm would first create a temporary folder When starting the Brainstorm interface, users are now prompted to delete files in the temporary folder. They can be safely deleted if they result from a previous unfinished process, but must be kept if in use from a different instance of Matlab/Brainstorm.
FEM mesh generation with SimNIBS4/CHARM Merge/rename/delete FEM layers: new popup menu Compute FEM mesh statistics
Non-parametric tests: Added FieldTrip threshold-free cluster enhancement (TFCE) Fixed error in data covariance computation: The baseline was not removed when the baseline time window was not included in data time window. See issue #602.
New MNI template: ICBM152 2023
Brainstorm is now compiled with Matlab 2022b: Installation instructions The compilation is now supported on Linux and MacOS: How to compile
The leadfield for each MEG sensor, or each pair of EEG/SEEG electrode/reference, can now be displayed as vectors, or as sensitivity maps: on the cortex surface, in the the MRI volume, or as an isosurface at a specific sensitivity value.
Support for ACPC and CapTrak coordinate systems Support for AssociatedEmptyRoom + automatic computation of noise covariance
New MNI template: ICBM152 2022
The interface of the ICA process has been improved and two new popular and efficient methods have been added: PICARD and FastICA. Picard is now the default option for ICA analysis in Brainstorm. More information.
Support for BIOPAC AcqKnowledge .acq recordings
It is now possible to apply a threshold based on the
The contralateral registration from FreeSurfer is now supported in Brainstorm and allows the projection of scouts between hemispheres. More information.
Import: Added support for IntendedFor in _coordsystem.json
Major update of the electrophysiology toolbox: new features, many bug fixes, and improved documentation. Explore the new tutorials.
Export events in AnyWave .mrk format
New tutorial: Functional connectivity (methods) New tutorial: Corticomuscular coherence (practice with FieldTrip tutorial dataset) New measures: wPLI and ciPLV Updated process: Simulate AR signals
Extract head with FSL/BET: Right-click on MRI > MRI segmentation. FreeSurfer: Added support for InfantFS / infant_recon_all
New tutorial and process for decomposing and parameterizing spectral components over time:
SimMEEG: New video tutorials. New menu: Update > Reproducibility > Export software environment: Track software versions: Save GitHub commit SHA and installation date for each plugin.
New process: Conjunction inference
Support for FieldTrip trialinfo field
Brainstorm is now fully interfaced with new programs for MRI processing and segmentation: MRI segmentation with FastSurfer (T1 only) MRI segmentation with FreeSurfer (T1+T2) MRI segmentation with BrainSuite (T1 only) Import BIDS: Add support for CAT12, BrainSuite and BrainVISA
The automatic MEG/sensors registration using digitized head points has been improved. It now includes an new parameter to exclude outlier digitized points, and a report of the distance between the digitized head points and the scalp surface. See tutorial: MRI registration.
When running some long computation on a distant server, you can now receive an email when the processing is over. See tutorial: Scripting.
The computation of the first mode of the PCA from multiple time series has been fixed. It now restores the mean of the signal after the computation of the PCA. See GitHub commit. The output of the following functions and processes are affected by this modification: Process: Extract > Scout time series, with scout function PCA. Process: Sources > Unconstrained to flat maps, option PCA.
We updated the deployment and compilation scripts of Brainstorm. Now everybody with the Matlab Compiler toolbox can recompile the Brainstorm standalone package, including additional personal scripts of modified versions of the code. See tutorial: Scripting.
New automatic SEEG/ECOG contact labelling from volume and surface parcellations. See tutorials: SEEG epileptogenicity maps and ECoG+sEEG epilepsy.
The FEM tools in Brainstorm are now documented in new tutorials: FEM mesh generation, FEM tensors estimation, FEM median nerve example, Realistic head model: FEM with DUNEuro.
The computation of the coherence has been revisited: new formula for the Imaginary Coherence, online averaging of the cross-spectra, estimator window length as a duration. See GitHub PR.
The FieldTrip DICS method is now available as a process function, thanks to the contribution of Vahab Youssof Zadeh: GitHub PR, Tutorial.
The display of connectivity graphs has been revisited. This new version is now fully written in native Matlab code, not dependent anymore on the JOGL library. See the new tutorial: Connectivity graphs, GitHub PR.
A fresh compiled distribution of Brainstorm is now available, including many of the new Brainstorm plugins. Without a MATLAB license, you can now use functions from plugins: SPM12, FieldTrip, Iso2mesh, Brain2mesh, OpenMEEG, DUNEuro and libSVM. Because the size of the full pacakge binary + sources increased a lot, we now recommend to download either the
A new plugin manager now allows an easy management of all the software packages related with Brainstorm. See the Plugins tutorial.
Support for ADInstruments LabChart EEG (.adicht)
Import and reslices MNI atlases using linear/nonlinear normalization
Support for volume parcellations in the database and the MRI viewer (volatlas) Import all volume parcellations from FreeSurfer, CAT, BrainVISA, BrainSuite Standard MNI atlases available for download, applicable both with the linear and the non-linear MNI normalization: AAL2, AAL3, AICHA, Brainnetome, Hammers, Neuromorphometrics, Julich-Brain, Schaefer2018.
FreeSurfer import now loads all the .annot files in /label New automated import, with no user interaction: using 15000 vertices, MNI fiducials
SSS/tSSS process = Wrapper for mne.preprocessing.maxwell_filter
Compiled version: Now includes NIRSTORM, Brain2Mesh and Iso2Mesh
New tutorial and processes for simulating signals, and simulating EEG/MEG recordings from dipoles. See the Simulations tutorial.
New tutorial and process for modeling and analyzing the power spectra:
Display cortical surfaces and source maps as flat 2D maps using the Mollweide projection, The FreeSurfer registered spheres can now be used to compute a flat 2D projection of the cortex surface using the
New process Connectivity >
Thanks to Christian O'Reilly, we can now distribute 13 anatomical models for infants between zero and 24 months of age (O'Reilly et al. 2020), available as FreeSurfer templates.
Computation of DTI tensors from DWI images with BrainSuite, display on tetrahedral meshes.
The MIT MEG lab presents new processes for MEG/EEG decoding (a type of multivariate pattern analysis / MVPA) using support vector machines (SVM): Machine learning: Decoding / MVPA.
Support for fNIRS format .snirf
The state-of-the-art library for
Select one or multiple forward models in the database explorer >
BEM surface generation with FieldTrip / ft_volumesegment: Use custom background threshold for head surface generation: allows fixing some cases where the automatic analysis of the MRI histogram fails. Updated FSAverave template, including the new Braintomme atlas.
Preparation Java/Swing-free Matlab: deprecated JavaFrame and javacomponent
The database explorer now offers advanced and scriptable search tools: see tutorial.
Mesh generation using iso2mesh, Brain2mesh, SimNIBS/headreco, ROAST and FieldTrip. Optimized 3D tetrahedral mesh display
Computation of FEM meshes with ROAST and iso2mesh: see GitHub discussion
Conversion functions from/to
CAT is a SPM12 toolbox that is now fully interfaced with Brainstorm. It can replace efficiently FreeSurfer for generating the cortical surface from any T1 MRI. It runs on See new tutorial: T1-MRI Segmentation with SPM12 / CAT12
A new variable
Since July 2018, the dSPM maps have been saved without any scaling. As a consequence, the values obtained for averages (ERP/ERF) are much lower than expected. To obtain correctly scaled values, one can now run the process Sources > Scale averaged dSPM.
The default analysis pipeline in BrainVISA implements an automatic parcellation of the cortical surface in anatomical regions. The MarsAtlas model is now imported automatically by Brainstorm.
Three display modes are now available for the event markers:
New shortcuts have been added to the signals viewer to allow tagging entire pages of recordings:
It is now possible to run the decoding processes with more than 2 conditions by grouping your trials in condition folders, and dragging them in the process box rather than the process2 box.
A new surface type was added to Brainstorm: fibers. One can use this to visualize connectivity results by displaying fibers connecting regions of interest and thresholding by connectivity value.
The colormaps "jet" or "rbw", used by default in Brainstorm for many years, lack important attributes of good colormaps: they dont’t have linear lightness and are not perceptually uniform. This can either cause details in the visualization to be hidden or create features that don’t exist in the underlying data, which results in a distortion of the perceived pattern. New colormaps were added to better represent the data: the three colormaps below were created, and the viridis and magma were taken from mpl colormaps. For more information about these new colormaps: colormap_optimization.pdf
The tutorial ECoG+sEEG epilepsy illustrates all the new features related with SEEG/ECOG: coregistration of MRI and CT scans, placement of depth electrodes in the post-implantation scans, SEEG bipolar montages, display and processing of intracranial recordings, computation of epileptogenicity maps.
Important for users who edit Brainstorm structures manually: The field Additionnally, the fields
Deface MRI with FreeSurfer or SPM. World coordinates now available in the MRI viewer. More details.
Support for synchronized EEG-video. Review of synchronized EEG-video with VLC ActiveX plugin.
New display modes for ECoG and sEEG:
New filters: The default frequency filters (band-pass, band-stop, notch) were modified to follow the new Shahabi/Leahy 2019 specifications. New process: Standardize > Interpolate time
Compiled distribution now includes all SPM and FieldTrip dependencies Compiled distribution can execute custom scripts (GUI and command line)
Export EEG to BrainVision BrainAmp format (.eeg) for iEEG-BIDS Bug fix: Fixed coil orientations when reading CTF .ds folders including a .pos file (McGIll MEG system): https://neuroimage.usc.edu/brainstorm/Tutorials/CtfCoilOrientBugFix
Management of multiple screens for Matlab>2015b
A new toolbox featuring basic electrophysiology tools is now included in Brainstorm, and documented in a brand new series of tutorial pages on Invasive Neurophysiology. The toolbox includes both unsupervised and supervised neuron spike sorting, extraction of local field potentials (LFPs), spike field coherence, spike triggered average, noise correlation, and basic visualizations such as tuning curves and raster plots.
Compare easily averages between experimental conditions: Select multiple files in the database explorer, right-click on any of them > 2DLayout.
Major modification in "Compute sources [2018]":
New montage: "Average reference (L -> R)" for 10-20 EEG caps
BrainSuite: Now reading subcortical structures from the SVReg atlas. See details. FreeSurfer: Added labels for volume atlases: aparc+aseg, aparc.a2009s, aparc.DKTatlas
Changed reconstruction method: (Winv_good * W_good) => (eye() - Winv_bad * W_bad)
FreeSurfer: Import the vox2ras matrix from the .mgz MRI files (ignored until now) FreeSurfer: Correct registration of additional .nii files with full FreeSurfer anatomy folders
Documentation: Source estimation tutorial
Support for the new Improved BIDS-MEG importer: derivatives folder (FreeSurfer, MaxFilter), acquisition info (_scans.tsv) Keep acquisition dates in the database (DateOfStudy of the brainstormstudy.at files)
The tutorial SEEG epileptogenicity maps illustrates all the new features related with SEEG/ECOG: coregistration of MRI and CT scans, placement of depth electrodes in the post-implantation scans, SEEG bipolar montages, display and processing of intracranial recordings, computation of epileptogenicity maps.
New options for volume coregistration of multiple scans of the same subject (MRI/MRI or MRI/CT) New interface for placing SEEG/ECOG contacts in the MRI Viewer
Add event markers on the signals when the event names match the channel names New tab Guidelines for computing epileptogenicity maps
New Export figures to Plotly: See tutorial Import channel files in .tsv format (IntrAnat)
Epilepsy > Epileptogenicity maps: See tutorial Frequency > Time-resolved phase amplitude coupling (tPAC): See tutorial Frequency > FieldTrip: ft_mtmconvol (Multitaper) Connectivity > Phase transfer entropy Artifacts > Undo 4D/CTF noise compensation
SEEG/ECOG: New option to import sensor positions in Computation of SPM canonical surfaces (alternative to FreeSurfer/BrainSuite/BrainVISA) New anatomy template: USCBrain
Resize the display page with the red square at the bottom of the figure
If you have a high-resolution screen, the text and icons in the Brainstorm window may not scale properly, leading the interface to be impossible to use. Select the menu
Many new options are available to render sEEG/ECoG recordings or power: interpolations on the cortex surface, in the MRI volume, or 2D displays of the time series.
When using the digitized head shape for aligning the MEG/EEG sensors on the MRI, the fiducial points NAS/LPA/RPA do not need to be placed very precisely as they are used only as a first approximation. Computing the MNI transformation for the MRI now sets default positions for the NAS/LPA/RPA fiducial points, you can use these if the accurracy of their location is sufficient. This option allows a fully automatic import of the anatomy+recordings.
New process: Connectivity > Amplitude envelope correlation
The tutorial Human Connectome Project: Resting-state MEG explains how to download MEG recordings from the Human Connectome Project (HCP) ConnectomeDB database and process them into Brainstorm.
The Open MEG Archive (OMEGA) offers for download a large database of resting state MEG recordings. The tutorial MEG resting state & OMEGA database describes how to access this database, download a few subjects and process them in Brainstorm.
The Brain Imaging Data Structure (BIDS) standard for neuroimaging data organization was first established for MRI and fMRI (Gorgolewski, 2016). It is based on simple file formats and folder structures that can readily expand to additional data modalities. An extension of the BIDS for MEG datasets is currently under review. One objective is that analysis pipelines designed with major analysis tools (such as Brainstorm, FieldTrip, MNE, SPM and others) can be readily applied without requiring software or pipeline redevelopments. We have implemented functions that load automatically into a Brainstorm database any dataset following the BIDS specification. This prototype is illustrated in the tutorial MEG resting state & OMEGA database.
Volume atlases in subject space (eg. FreeSurfer's Aseg atlas) can be used in various ways: Import as Import as
Volumes in MNI space can be imported and transformed to the subject space. This allows the new features described above also for standard volume atlases, such as the AAL atlas. You just need to make sure you select the file format " Import MNI volume atlases as Import MNI volume atlases as a Import MNI volume atlases as To get the labels of the atlas displayed correctly, a .txt file with the same name should be present in the folder. Each line in this file must include the index of the label ("label_index label_name"), such as the atlases distributed as part of the MRIcron software.
The volume registration functions allow to import a CT scan in the anatomy folder of the subject, and then to overlay it with the MRI to mark
Many new FieldTrip functions are now supported, especially for forward and inverse modeling: Previously made available: Most data types can be converted easily between Brainstorm and FieldTrip structures (MRI, surfaces, sensors, recordings, head models, source maps, time-frequency results): Right-click on any file > File > toolbox/io/ toolbox/io/
We moved all the code of Brainstorm to a public GitHub repository. You're welcome to join! https://github.com/brainstorm-tools/brainstorm3
The frequency filters have been notably improved. They have been completely redesigned and are now fully documented in the tutorial Frequency filters. From the process "Pre-process > Band-pass filter", you can display the filter response in frequency and time domain, together with all its properties. After filtering signals, new events indicate the transient durations to consider. This represents an absolute minimum, if possible always exclude the full filter length, documented in the filter response window. This modification has some impact in many processes using the band-pass filters: the SSP computation, the Hilbert transform, the visualization. These new filters are slightly slower but much more accurate. If reproducibility is a concern, use can select "Use old implementation" in the process options.
New process: Events > Detect cHPI activity (Elekta) Volume scouts: Can be exported as volume masks (menu Scouts > Export as MRI mask)
The projection of the EEG/MEG recordings on 2D maps have been updated. The new functions are more stable and the figures will be easier to integrate directly in your publications.
The basic source reconstruction limits the source space to the left and right hemispheres of the brain. The mixed head models allow to include the cerebellum and various subcortical regions to the estimation and the visualization of the source activity. Their support has been extended to include new features: New exploded view to visualize all the subcortical regions on the same view.
You may be interested in importing multiple volumes (MRI, fMRI, CT, PET, etc) in the anatomy folder of a subject. You can overlay volumes and compare the results obtained with different imaging modalities or at various stages of a surgical procedure, or use fMRI results in an ROI analysis of you MEG/EEG recordings. However these various volumes usually have different orientations or spatial resolutions, and in order to be displayed in the MRI Viewer in Brainstorm, the files must have the same size and same orientation. We added some functions to help you coregister these volumes. New menu " New menu " These two options are offered when importing additional volumes in the subject anatomy, if their dimensions or resolution do not match the initial structural MRI. The computation of the When you have a secondary volume imported in your subject, you can display it as an overlay on the original MRI and configure the threshold and transparency from the Surface tab.
Many of the advanced tutorials were outdated, they have all been updated to include the latest advances in cleaning procedures, workflow management and display. EEG/Epilepsy: Includes a new section about ICA decomposition. Elekta-Neuromag median nerve: Reference for processing Elekta MEG recordings. Yokogawa/KIT median nerve: Reference for processing Yokogawa/KIT/Ricoh MEG recordings. CTF median nerve tutorial: Dataset used in the previous version of the introduction tutorials. Other advanced tutorials that have been improved recently:
This new tutorial reproduces in the Brainstorm environment the analysis described in the SPM tutorial "Multimodal, Multisubject data fusion". The data processed here consists of simultaneous MEG/EEG recordings from 19 participants performing a simple visual recognition task from presentations of famous, unfamiliar and scrambled faces. The analysis is split in two tutorial pages: the analysis of a single subject and the group analysis. This is part of a new effort in cross-validating the various academic programs for EEG/MEG analysis (EEGLAB, FieldTrip, SPM, MNE). The results will be presented at a satellite meeting at the Biomag conference, held in Seoul on October 2nd.
Advanced users who want to go beyond the limits of the graphic interface, script large studies or add their own routines to the software now have access to an introduction to the Brainstorm API. The tutorial Scripting explains how to interact with the software from the Matlab command line or a .m script.
The support for volume source models has been improved and now includes new features: Implementation of volume scouts: Volume source estimation tutorial. Projection on an anatomy template for group analysis: Subjects coregistration tutorial.
We propose a new pipeline for processing and importing the anatomy for multiple subjects. This is described in this section of the Scripting tutorial: How to process an entire study. New menu "File > Batch MRI fiducials": Sets the anatomical landmarks for all the subjects.
New popup menu "File > New menu "File > Export protocol > Continuous files can now be resampled with the process "Pre-process > New menu "File > Load protocol > Change database folder": Changes the folder in which the new protocols are created, but does not have any impact on the existing protocols.
Redesign of all the functions related with statistic testing. See the new Statistics tutorial. New process(2): Test > Parametric test: Paired/Independent New process(2): Test > Permutation test: Paired/Independent New process(1): Test > Parametric test against zero New process(1): Test > Parametric test against baseline New process: Extract > Find maximum in time New process: Extract > Find maximum in frequency
Added support for BioSemi caps with electrodes named "A1" instead of "A01". Organized the default electrode positions by manufacturer.
Many new tools are available for importing manipulating fNIRS recordings in Brainstorm. This is explained in a new online tutorial (work in progress): NIRS finger tapping.
A new tutorial explains how to import and process Elekta-Neuromag current phantom recordings. The framework presented on this page is designed to be used for the quality control of an Elekta MEG system (after a maintenance for instance) and for evaluating dipole modeling techniques.
New process " New recommendations for the normalization of source maps (never use an absolute value):
Make a database portable: New menu "Export protocol > Copy raw files to database". Make a database portable: New popup menu for raw files "File > Copy to database".
The gain of the channels in some BrainVision files (BrainAmp or V-Amp) was not read correctly. The files impacted are the ones for which the gains are specified in the .vhdr/.ahdr files, in section [Channel Infos], field <Resolution in microvolts>.
Major modification in the computation of the scouts time series (constrained orientations only). Previously, the sign flip of sources with opposite directions was applied only if it increased the average scout amplitude. Therefore the procedure was dependent on the data, making it difficult to compare across conditions and subjects. Now the sign flip is always applied. To disable completely the sign flip: Use the process "Extract > Extract scouts time series".
Major update of the new inverse interface (Compute sources [2016]).
Support for FieldTrip raw data file (trials) Convert imported files to continuous files: Right-click > Review as raw Copy external raw files to the database: Right-click > File > Copy to database Make the entire protocol portable: File > Export protocol > Copy raw files to database
Bug fix: The geometry of the CTF MEG reference sensors was not imported correctly. The forward model was not as accurate as expected, especially with a very high signal-to-noise ratio. Bug identified: Similarly, the 4D MEG reference gradiometers may not be modeled properly New tutorial to investigate this problem: CTF current phantom Channel file: New menu "Display sensors > CTF coils (ALL)" to represent the CTF reference sensors.
New template BCI-DNI_BrainSuite: Description of the atlas | Brainstorm documentation Replaced the default template Colin27 with ICBM152: Brainstorm documentation Process "Sources > Spatial smoothing": Replaced with a function from the SurfStat toolbox
New Process2: File > Select uniform number of files: Selects the same number of files in A and B
A new tutorial from Martin Völker explains how to import the eye movements detected by an eye tracking device into an EEG/MEG file. The new generic process "
New introduction tutorials: Difference and Statistics New button [Online tutorial] in the pipeline editor, to jump instantly to the corresponding tutorial.
Support for EyeLink eye tracker recordings (.edf)
A new external plugin for microstate segmentation developed at John Cacioppo's lab (UChicago) has been made available publicly in Brainstorm. See the CENA website and the corresponding online tutorial.
Standardize > Scalp current density (FieldTrip: ft_scalpcurrentdensity) Standardize > Concatenate signals Extract > Extract values: Generic process for extracting and concatenating blocks of files File > Select uniform number of trials
Display of value histograms for all the files in the database (right-click > File > View histogram)
We completely re-organized the tutorials page. A new set of introduction tutorials is now available for beginners to learn the basics and for expert users to find references and technical details. We added a lot of material to describe the improvements we brought to the software in the past five years. We encourage advanced user to have a look at them to learn about the new features and the new best practice guidelines we came up with over the years.
Support for MEGA NeurOne file format (.bin) Support for Blackrock NeuroPort file format (.nsX, .nev) Support for BrainVision channel files (.bvct, .bvef) Import FieldTrip structures: data_timelocked saved as .mat files Export FieldTrip structures: source files, time-frequency maps and head models
New process: Source > Dipole fitting (FieldTrip: process_ft_dipolefitting)
BrainSuite now provides an accurate registration method to the BrainStorm anatomy templates (ICBM152, Colin27). See the BrainSuite tutorial.
Some FieldTrip functions can be called from the pipeline editor in Brainstorm, this brings a lot of long-awaited tools for statistical analysis. See the Statistics tutorial. This is done with direct calls to FieldTrip functions: New displays for exploring significant clusters
Christian O'Reilly proposes a new anatomical atlas for one year old babies, described in this forum post: http://neuroimage.usc.edu/forums/showthread.php?2123-Atlas-for-1-year-old-babies To use this template: create a new subject using an individual anatomy, right-click on the subject >
A simple yet very powerful tool is now available to project a region of interest between surfaces: from different surfaces of a subject, or between a subject and a template. When using surfaces generated with FreeSurfer, this projection uses the accurate registration described in the coregistration tutorial.
You can now start a scout from anatomical positions specified in MNI coordinates.
Modifications were made to the Z-score process, specially for handling the normalization of sources:
New functions are now available for solving the MEG/EEG inverse problems. Not all the options are publicly available yet, but they will be soon. See the new tutorial: Source estimation.
A new process is available for helping with the detection of non-standard artifacts in MEG/EEG recordings:
The recent work from Oliva's lab at MIT on decoding experimental conditions with MEG is now available as a process in Brainstorm. It allows to run support vector machine (SVM) and linear discriminant analysis (LDA) classification on MEG data across time. It is documented in the tutorial Decoding conditions. Cichy RM, Pantazis D, Oliva A (2014)
Custom colormaps can be saved in the user preferences, edited and re-used easily. This is documented in the new colormap tutorial.
Two new options are available in the proces "Average files", to compute the standard deviant or the standard error together with the average. This additional information is stored in the field Std of the average files, and is displayed as a bounded line around the signals when available.
You can attach synchronized videos to the continuous file viewer. Right-click on the "link to raw file"
The The new values are multiplied on the fly by a fixed factor: sqrt(nAvg) This issue is documented in the source estimation tutorial.
It is now possible to use MNI coordinates to navigate in the original individual MRI volumes. We estimate the affine transformation from the subject space to the MNI ICBM152 template using the SPM12 software (spm_maff8 ©J Ashburner). The general approach is described in the following article: To compute the linear transformation matrix between the individual MRI and the ICBM152 template, click on New functions are also available for converting between coordinate systems: cs_convert and cs_compute.
FieldTrip > ft_channelrepair Standardize > Interpolate bad electrodes Standardize > Normalized difference (A-B)/(A+B) Standardize > ERDS with two inputs Events > Detect multiple responses Events > Detect movement Test > Student's t-test against zero
Export data files to FieldTrip structures (out_fieldtrip_data)
Many EEG users are familiar with the Independent Component Analysis (ICA) for identifying and correcting artifacts such as eye movements, muscle activity or 60Hz. We added methods implemented initially in EEGLAB for calculating ICA decompositions of MEG and EEG signals. The methods available for now are Infomax and JADE. We will add soon other methods widely used in the EEG community: SOBI and AMICA. The ICA decomposition is available for continuous files only and can be found next to the SSP menus, either in the pipeline editor or in the Artifacts menu of the Record tab. The SSP interface has been extended to select interactively the ICA components and display their spatial topography and time series.
Improved flexibility of the montage editor, for supporting some common operations in EEG analysis: Mixing channels from different modalities in the same montage. This is useful for re-referencing the EEG with an electrode that is not classified as "EEG" in the channel file. It allows also to review multiple types of signals in the same figure: EEG, EOG, ECG, EMG, etc.
EEG recordings can be re-referenced using projectors, similar to the ICA or SSP projectors. This allows to change permanently the reference without having to create a montage and explicitly apply it to the recordings. This feature is available in two ways: Process: Standardize > Re-reference EEG Record tab: menu Artifacts > Re-reference EEG
New options are available to display and process invasive recordings, sEEG (depth electrodes) and ECoG (grids of strips of subdural electrodes), developed in collaboration with the Cleveland Clinic and the Freiburg University Hospital. New display mode: 3D Electrodes Edit the position of the contact positions using the MRI Viewer. Grouping contacts using the new field "Group" in the channel file. Use the channel file editor to modify these groups if they haven't been identified correctly (right-click > Edit channel file). Set of temporary bipolar montages automatically created when loading SEEG/ECOG recordings. Computation of the forward model for ECOG and SEEG concacts using the OpenMEEG BEM model.
EEG: Compumedics ProFusion Sleep 4 file format
Connectivity > Time-resolved correlation and coherence Events > Convert to simple event Events > Convert to extended event
We made some important modifications to the way the scouts where handled in the processes. Now it is possible to select the atlas directly in the options of the process, and to process at the same time scouts from different subjects with different list of vertices. The new process function for extracting scouts is This will affect all the processes that use scouts: time-frequency decompositions, power spectrum estimates, connectivity and PAC metrics. We tried to keep all the processes compatible with the previous input format, but there might be some modifications to do in personal scripts. If you have processes that use scouts structures in input, you might need to edit them to accept this new format. You can look at how it is done in process_canoltymap.m, or contact us through the user forum for help with updating your scripts.
The anatomical atlas presented in Kabdebon's article Anatomical correlations of the international 10–20 sensor placement system in infants is made available as a template in Brainstorm. To use this anatomy: create a new subject using an individual anatomy, right-click on the subject >
It is now easier to manage the 3D positions of the EEG electrodes. To add electrodes positions to an existing channel file: right-click on the channel file > Add EEG positions. You can import the points from a file or from one of the default sets of positions available in Brainstorm.
A tutorial is available online to introduce a new Brainstorm plug-in BEst: Brain Entropy in space and time which offers three new source localization approaches for EEG and MEG data, based on the framework of the
All the files in the Brainstorm database can now be exported as
Major modifications were made to the way the continuous files are handled: The continuous files saved by Brainstorm when applying a filter to a native file are now saved in a new file format ( All the frequency filters can now be applied to To revert to the previous behavior (saving to native CTF or FIF files, in the database folder), use the menu File > Edit preferences > options "Store continuous files in original folder" and "Save continuous files in original format".
A new tutorial proposes a standard pipeline for the complete analysis of a simple oddball paradigm in MEG: MEG auditory tutorial. It presents the workflow in the Brainstorm environment, the equivalent documentation for the FieldTrip environment will be available on the FieldTrip website.
File > Select files: Get all the files from a specific folder with a process
New figure popup menu: Snapshots > Open as figure
Two new tutorial are available online to explore the cross-frequency coupling in MEG resting state recordings: Resting state MEG and Phase-amplitude coupling They will allow you to reproduce step-by-step the analysis and the results illustrated in this article:
A updated version of the Elekta-Neuromag tutorial is finally available: click here.
New developements allow more flexible configurations of source models. Now, different brain regions (cortical or subcortical) can be modeled using different constraints. From the Scout tab, select the menu Atlas > New atlas > Source model option. All the scouts present in this atlas can be associated with different source constraints (surface/volume, constrained/free orientation). Then, when computing the head model, select the option "Custom source model". This work will be soon part of a detailed tutorial showing how to use efficiently sub-cortical atlases for estimating sources in the deeper regions of the brain.
Scouts may now be defined on 3D source grids. Display the volume-based source results in 3D, then use the Scout tab exactly the way you would do it for surface maps.
A new online tutorial teaches Brainstorm users how to import and process Yokogawa MEG recordings:
Many features have been added for displaying and processing clinical EEG and invasive measurement data (ECoG and LFPs). These tools are illustrated in a new online tutorial EEG and epilepsy. It is based on a clinical case from the Epilepsy Center at the University Hospital of Freiburg, Germany. The anonymized dataset can be downloaded directly from the Brainstorm download page.
The "channel selection" menu and the "EEG average reference" button have been replaced with a more flexible interface to edit montages. Montages can be used to simply select a list of sensors, re-order them in the display or to do more complex operations. The term refers mainly to EEG, to define the referencing system used to display the values recorded on the electrodes: bipolar montages, custom reference electrodes, average reference. See tutorial: Exploring the recordings Some EEG montages recommended by the American Clinical Neurophysiology Society have been added to the distribution: longitudinal bipolar, transversal bipolar and referential. They are saved in .mon files in the folder brainstorm3/toolbox/sensors/private.
The average reference is now offered in the the list of available montages for EEG, SEEG and ECoG recordings. By default, the average is calculated from all the electrodes and the same value is subtracted everywhere. In some cases, you may be interested in calculating different averages from different subgroups of electrodes: multiple cortical grids or electrodes stripes. To do this, you have two options: Create a montage manually that defines exactly what are the operations to perform. For instance, if you have 4 electrodes E1..E4 you want to group together, enter four lines, one for each electrode, with this structure: E1: 0.75*E1, -0.25*E2, -0.25*E3, -0.25*E4 Set the comment of the electrodes to define the groups. Right-click on the channel file > Edit channel file. Select the electrodes of group #1, right-click > Set channel comment. The electrodes with the same comment would be averaged together.
Setting manually time and amplitude resolutions: right-click > Figure >
Dealing with multiple figures can be annoying when you review lots of recordings.
The management of the colormaps has been revamped to include non-symmetrical colormaps. You can now set independently the minimum and the maximum of the figure colorbar. A white marker has also been added to the colorbar when displaying source maps, to indicate the level of the amplitude threshold.
A new filter text box can help you select easily files in the Process1 and Process2 tabs.
Electrophysiology: NeuroScope / Klusters (.eeg/.dat)
Simulate > Auto-regressive and custom signals Simulate > Simulate recordings from scouts (transform matrix files into source files) Extract > Apply statistic threshold (export stat file with a specific static threshold) Extract > Unconstrained to flat map (convert unconstrained sources to flat cortical maps) File > Add tag File > Select files with tag Events > Detect analog triggers
Brainstorm offers a flexible plug-in structure. If you are interested in running your own code from the Brainstorm interface and benefit from the powerful database and visualization systems, the best option is probably for you to create your own process functions. You would be able to exchange code easily with your collaborators and the methods you develop could immediately reach thousands of users. Once your functions are stable, we can integrate them in the main Brainstorm distribution and maintain the code for you to ensure it stays compatible with the future releases of the software. Tutorial: How to write your own process
It is now very easy to pre-process your recordings and estimate sources in Brainstorm, and do you statistics in SPM8 and SPM12. This powerful combination is illustrated in the following tutorials:
The FreeSurfer software registers all the subjects to the FSAverage atlas using a spherical representation of the cortex. Each hemisphere of the subject's brain is inflated to a sphere, which is then deformed to match the curvature map of the equivalent sphere in the FSAverage subject. In the case of a group study, these results are now used by default in Brainstorm to register all the subjects on the same default anatomy. For more information, read the group analysis tutorial.
Many news on the FreeSurfer import side. Now Brainstorm imports the subcortical atlas aseg.mgz as a set of surfaces. The cortical thickness results can also be saved in the database and explored easily. More information on the FreeSurfer tutorial page.
New models are available to replace the previous Colin27 default anatomy in your Brainstorm protocols. Right-click on (Default anatomy) > Use template. If a package is not available on your system, it will be downloaded from the Brainstorm website and saved in $HOME/.brainstorm/templates. The options available in this menu are:
The results of the CIVET anatomical segmentation pipeline, developed at the MNI, can be automatically imported in Brainstorm (surfaces and cortical thickness maps). Right-click on a subject > Import anatomy folder > Select "CIVET folder". More information: CIVET website and CIVET tutorial.
A new section of the website dedicated to usage statistics and exchange between users: User community.
A new fantastic feature to create movies: the "
The results of the BrainSuite anatomical segmentation can be automatically imported in Brainstorm (surfaces and atlases). See: BrainSuite website and BrainSuite tutorial.
Standardize > Concatenate recordings Test>StudentT-test: Now available on time-frequency maps Standardize>Uniform row names: Re-order the signals in a set of files to make them compatible. Average>Average rows: Average the different signals in a time-frequency file. Pre-process>Band-pass filter: Now available on source maps Standardize>Event related perturbation Events > Add time offset
All the time markers available in the continuous recordings are now preserved when importing epochs in the database. It is also possible to add new markers to segment of recordings imported in the database, and to generate new epochs based on them. A new option of the averaging process allows all the events from all the individual epochs to be combined. It can be a quick way to check that an event of interest (for instance the eye blinks) is not time-locked to the stimulus.
The Z-score operation, ie. the normalization of the signals by the level of noise calculated over a baseline, now exists in two forms. The process previously called "Compute Z-score" is now available as " The new process " This has almost no impact for the sensor data, but is a great improvement for the source files for which only the inversion kernel is saved. The static Z-score process would rebuild and save the full source matrix [Nsources x Ntime], while the dynamic version can keep the compact formulation of the linear inverse operator [Nsources x Nsensors]. The resulting files are much smaller and faster to open and review.
The process " Canolty RT, Edwards E, Dalal SS, Soltani M, Nagarajan SS, Kirsch HE, Berger MS, Barbaro NM, Knight RT, The process "
Two or more MRI volumes can be imported for the same subject, if they have the same size and are properly co-registered. Only the first volume is used as a reference for placing the fiducial points, the additional ones are there for visualization purpose only. This feature can be useful for grouping different sequences (T1/T2), pre-op and post-op scans, regions of interest from fMRI results, or volume-based anatomical atlases.
The process "Pre-process > Run Matlab command" is very simple but very powerful. It loads the files in input and run the signals through a piece of Matlab code that you can edit freely. It can extend a lot the flexibility of the Brainstorm pipeline manager, providing an easy access to any Matlab function or script.
Dipoles localizations from the CTF DipoleFit and Neuromag Xfit software can be imported in the Brainstorm database and displayed on the same figures as cortical maps. See tutorial: Import and visualize dipoles.
The last version of the OpenMEEG software includes the ability to calculate forward models for cortical grids and intra-cortical electrodes. We integrated these changes to allow the calculation of sources for these two types of implanted electrodes. To be available in the forward and inverse model options, you need to change manually the type of the channels to respectively "
The The events have to be processed manually: link the continuous file to your subject, then run the process "Events > read from channel" on the "Link to raw file". Select the options TTL or RTTL, and type the names of the channels to use as stim channels (example: " null045, null046").
We are adding some more flexibility to the way the figures are automatically arranged on the screen. You can explore the different options available in the Layout menu. More features to come, including the ability to save custom layouts for the different types of figures.
You can now create a new surface from the one that is displayed in a 3D figure. The exported surface would include all the current modifications: smoothness and resections. Right click on the figure > Snapshot > Save surface.
Many new step-by-step tutorials are now available, covering the processing and epoching of continuous files, the artifact rejection and the graphical scripting:
A report is generated each time an operation is executed from the Process1 or Process2 tabs, and automatically saved in the user folder ($HOME/.brainstorm/reports). You can browse through all the previous reports for the current protocol using the Report Viewer (File > Report viewer). The reports can be reloaded easily: the menu "
Some important pre-processing operations are now available directly on continuous recordings in FIF format (usually Elekta-Neuromag MEG/EEG recordings). The new available processes include: the band-pass filter, the sinusoid removal (notch filter) and the baseline correction. To process a continuous FIF file: link it to the Brainstorm database (right-click on the subject > Review RAW file), then drag and drop the "Link to raw file" in the Process1 box. Select a process in the Pre-process category. In output, it would create a new native continuous FIF file in the same folder, and also link it into the Brainstorm database. This feature is also available for CTF recordings, and is one of the key elements of our recommended pre-processing pipeline, as illustrated in the tutorial ?Detect and remove artifacts.
As explained in the tutorial ?Noise covariance, the best way to estimate the sensors noise for MEG source reconstruction is to use empty room measurements. This implies that you have to import the noise measurements, calculate the noise covariance matrix, and copy it to the other acquisition runs or subjects. You can use the popup menus "
The co-registration of the MEG/Polhemus positions with the anatomy of the subject (MRI+surfaces) is not an easy task. We offer three approaches that should be combined to get the best possible results: a first approximation based on three fiducial points (NAS/LPA/RPA), the automatic fit of the Polhemus head shape on the head surface from the MRI, and an rich interface for refining the results manually. The problem of the automatic method is its strong dependance to the initial conditions. The new button "Refine using head points" in the edition window allows you to fix iteratively the registration: change the position manually, the run the automatic fit again. This solution can help you getting better registration results while we are working on an improved version of the automatic registration that would be less sensitive to the initial alignment.
The FreeSurfer atlases are now automatically imported in Brainstorm. They provide a good starting point for subdividing the cortex surface into anatomical regions, but the corresponding scouts can be too large for many functional applications. Averaging the time series from 600 different sources is likely to blur too much our data, we might lose the effects of interest. We are working subdividing efficiently the regions of these atlases. The first functions developed in this direction are the menus
Improvements were made for handling FreeSurfer and BrainVISA segmentations. Both software packages generate a tree of folders that contain all the intermediate steps of the reconstruction, the top folder being the subject name or id. It is now possible to import the entire segmentation folders with just one click. Additionally, new menus are available to generate head surfaces from the MRI.
By "MRI masks", we refer to MRI volumes that contain either only 0 and 1 (binary mask) or integer values (labelled atlas). Both type of MRI masks can be imported directly: as surfaces: Right-click on subject > Import surfaces > Select the file type "Volume mask (all MRI files)". The tesselation is automatically generated by Brainstorm. This works well only in the case of convex envelopes, it is not recommended for complex objects as scouts: In the Scout tab, menu Atlas > Load atlas > Select the file type "Volume mask (all MRI files)". For each label in the volume, a scout is created, containing all the vertices that are in this region.
The rendering of the 2D topography plots is slightly improved, with a new option to set the number of contour lines.
Standardize > Uniform epoch time: Sets the same time vector for all the input files Pre-process > Scale values: Multiply the values of one or several sensors by a fixed factor Average > Average frequency bands: Average values across frequency bands Extract > Measure from complex values: Apply a function to complex values (typically Morlet or Hilbert coefficients)
The scouts interface has been redesigned to integrated the logic of atlases, and the classification of each scout in an anatomical region. You are welcome to visit the following tutorials for more information:
One of the main problems when dealing with source time series is the size of files. A new process lets you reduce the dimension of your sources by keeping only one value for each scout instead of one value for each vertex: Source > Downsample to atlas. It works well in the case of a set of scouts covering the entire cortex surface, either with a FreeSurfer atlas, or with a random clustering of the surface (menu Atlas>Surface clustering in the Scout tab).
Brainstorm can now import and review native BDF/BDF+ files from Biosemi.
Brainstorm can now import and review native MANSCAN EEG files (SAM Technology, Microamp amplifiers): .mbi/.mb2
For accurate source localization in MEG and EEG with registration to anatomical MRI image volume and efficient head localization in MEG, a 3D digitization solution such as the Polhemus-Fastrak is required. This new, simple Brainstorm feature will help you save time and is efficient for error-checking while digitizing sensor positions and the subject's head shape. See the Digitize tutorial for more information.
All the features available from the Brainstorm interface are now also available as "processes", including the import of the data, the artifact cleaning and the source estimation. A full analysis pipeline, starting from the raw continuous file, can be edited graphically and saved as a Matlab script, easy to read an edit. These scripts can now run on distant servers without any user interaction. The status of all the computations and the information messages that are generated during the execution of an batch script are now saved in detailed reports that can be reviewed as HTML pages, including screen captures of the data for quality control. See the two tutorials: ?Processes and Automated processing.
The compiled version of Brainstorm is now based on Matlab 2012a. It provides more stability and fixes some issues with the Signal Processing Toolbox. However, if you were previously running the stand-alone version of Brainstorm, you may have to install a newer version of the Matlab Compiler Runtime. See the Installation page.
Compute the variance s and average m of the baseline from files A, Center on m and divide by s all the files B
The interface for computing and displaying spectrum and time-frequency information has been largely improved. Two new types of windows are available, allowing the display of the time-frequency matrices as [time x amplitude] or [frequency x amplitude] graphs, for one given frequency or time. Four new processes are available, in the Frequency menu: All these processes can run on any type of time series: recordings, sources, scouts.They all generate complex values, on which we need to apply a function to extract values that can be represented easily. This function can be changed easily after the computation, as a display parameter:
The SSP projectors are now saved in a more sophisticated way, allowing a dynamic selection of the projectors to apply on the recordings.
One of the problems related with the MEG analysis is that the subject's head can move with respect with the sensors during the acquisition. Hence, for the same subject, the position of a given sensor is different for two different runs or two different days of acquisition. We added a process ( Another issue with the data acquisition is the sensors selection: depending on the acquisition system or the day of acquisition, one may end up having lists of channels that do not match across runs or subjects. For instance: there were more auxiliary channels recorded for a few files, or different EEG amplifiers listed the electrodes in a different order. In these cases, it is very difficult to average or compare the information at the sensor level. The new process "
FreeSurfer is one of the many great academic software applications available to perform MRI image analysis. Brainstorm users can now use FreeSurfer to generate surface envelopes of head tissues to generate a model of MEG or EEG sources. Brainstorm now features the possibility to import the labels for regions of the cortex generated by FreeSurfer's analysis, which correspond to the regions of the Desikan-Killiany and Destrieux cortical parcellation atlases. The corresponding surface areas can subsequently be treated as scouts in Brainstorm, and therefore be used as anatomical ROIs to guide the exploration of MEG/EEG source maps. See tutorial: Use FreeSurfer cortical parcellation
We have added the possibility to import compressed Nifti MR images directly into Brainstorm's MRI Viewer and export MR volumes as Nifti.
We have added new, convenient features to navigate through trials, time samples and files in your Brainstorm database. Buttons have been added to the main Brainstorm panel and also into the figure window that display time series: navigate through complex data structures with just a click! You can also adjust the amplitude gain using buttons now, or readily set the scale of time-series displays. As always, feedback is always welcome through our forum.
'Like Us' on Facebook to stay in touch:
1) Specific channels can be scanned for automatic detection of ocular and cardiac artifacts from continuous recordings; this feature works best with dedicated control channels (i.e. ECG and EOG), 2) Artifact modeling and attenuation using a signal space projection (SSP) approach.
We introduced a new packaging logic for the distribution of Brainstorm executable (i.e., which does require the user to run a Matlab license). The entire set of application files (Matlab scripts and compiled executable) are now integrated in the same unique archive. The executable is now platform (OS) independent as it has been reduced to a single .jar file created with Matlab's JavaBuilder, that runs on any platform supporting Matlab. To run the stand-alone version of Brainstorm, you just need to install the free, Matlab Compiler Runtime (version 7.16) foryour operating system. Read more on the Installation page.
Part of the Brainstorm development team has moved to theMcConnell Brain Imaging Center at McGill University's Montreal Neurological Institute, in Montreal, Canada. At this occasion, a full-day training session with 70 participants from across Canada has been organized for new users, back-to-back with the first MEG training workshop of the Canada MEG Consortium (see pictures here). For more training opportunities, visit our Training pages.
Publication of a special issue of the journal Tadel F, Baillet S, Mosher JC, Pantazis D, Leahy RM (2011) Brainstorm: A User-Friendly Application for MEG/EEG Analysis,
The file manager has been extended to support drag-and-drop and copy-paste operations. Users can now move or copy easily files from a condition or subject entry to another using the mouse, keyboard shortcuts [CTRL+C (copy), CTRL+X (cut) and CTRL+V (paste)], or the File section from the contextual menus from the GUI.
No worries: Brainstorm can adjust a template anatomy to individual scalp points (MEG) / electrode locations (EEG). It is now possible to generate pseudo-individual anatomies from a template, for participants for whom the anatomical MRI volume is not available. This operation is possible if digitized head (scalp) points were acquired using a tracking system (e.g., Polhemus Isotrak), which is commonplace in most MEG labs. The default anatomy (volume and surface envelopes) distributed with Brainstorm (MNI/Colin27) can be transformed (warped) to match the subject's scalp points. This is a great cost-saving alternative when individual anatomy is not accessible to investigators (not recommended for accurate, local mapping of the loci of activity though). See tutorial: Warping default anatomy.
When importing MEG recordings, the registration between the MRI volume and the MEG was formerly based only on three fiducial points only (nasion, left ear, right ear). This approach is known be potentially of poor accuracy. If multiple (>60, typically) scalp points were digitized, the transformation between the MEG's and the MRI's referential can be refined by minimizing the average distance between the scalp surface obtained from MRI and the actual digitized head points. See tutorial: Review raw recordings.
A new feature has been made available for a more accurate computation of EEG forward models with realistic geometry (strongly recommended). OpenMEEG generates forward models using a symmetric boundary element method that was developed by the INRIA team ATHENA. It considers three realistic layers (scalp, inner skull, outer skull), which can all be generated from the MRI volume using Brainstorm. See tutorial: BEM head model.
Source models computed in Brainstorm were until now restricted to the cortical surface. To extend the range of analyses made possible with Brainstorm, and to compare Brainstorm's source estimates with these obtained using other software, source models based on dipole grids sampling the entire brain volume can be obtained and reviewed, using the same efficient tools featured in Brainstorm. See tutorial: Volume source estimation.
The approach to combine concurrent MEG and EEG recordings to obtain a joint source model has been substantially improved.
Added multiple options to review and visualize source maps using contact sheets and volume smoothing of activity maps. 1) source maps are spatially smoothed after interpolation in the MRI voxels. The size of the smoothing kernel can be configured: right-click on the figure > MRI display; 2) the resulting volumes can be used to create contact sheets along all viewing directions, either in time or across the volume. See tutorial: ?Source estimation.
When displaying the outcome of a t-test, there is now a new tab "stat" that is shown in the main window, which allows to adjust dynamically the type of correction applied to multiple comparisons and the p-value of the test.
A brand new version of the "Process" tab is available. Processing pipelines can now be elaborated in a convivial way, in just a few clicks! You can also save and export your pipeline as Matlab scripts. The processes available are now written as plug-ins: you can contribute your own process and it will automatically list to your menu of available tasks that can be performed on data. See tutorial: ?Processes.
Brainstorm can now be used to visualize and process full length continuous/raw files in native format. See tutorial: ?Review raw recordings and edit markers.
New process available to detect bad trials or bad trials based on peak-to-peak values. The peak-to-peak threshold can be set by channel type.
The interface that computes the noise covariance matrix can be called on continuous recordings. Right-click on link to raw file > Noise covariance.
New menus to help users exchange data easily. A full protocol can be exported as a single zip file (menu File > Export protocol), and then imported in another database (menu File > Load protocol > Load from .zip file). Same thing for a single subject: right-click on the subject > File > Export subject. The subject .zip file is actually a full protocol zip file with only the exported subject, hence it should be loaded as a protocol.
Computation and visualization of time-frequency decompositions of MEG/EEG and source signals using Morlet wavelets. See tutorial: ?Time-frequency.
Two lists of scouts have been created for the default anatomy (MNI/Colin27), inspired from the atlases of Tzourio-Mazoyer and Brodmann. To access these files: display the cortex surface of the default anatomy, then in the "Scout" tab click on the "Load scouts" button, on the right of the scouts list.
The 2D Layout display for recordings has been re-writen to include many tools: sensors selection, interactive gain change, zoom in time and space... See tutorial: ?Exploring the recordings.
Dipoles localizations from the Neuromag Xfit software can be imported in Brainstorm database and displayed on the same figures as Brainstorm cortical maps. See tutorial: ?Import and visualize dipoles.
Integration of a new minimum norm solution, with more and better tuned parameters. This algorithm is now similar to the one implemented in MNE software.
Any source file estimated for a given surface can be re-projected on another surface. This allows to project sources of individual subjects on the default anatomy to compare subjects. See tutorial: Project sources on default anatomy.
The time series can be displayed in columns. The displayed sensors can be edited with an interface similar to the selection editor in MNE software.
Brainstorm is now self-updating. It tests at each startup if your version is older than a month; if so, it downloads a new version. The software can also be updated manually very easily (menu Help > Update Brainstorm). ![]()
Interface
Connectivity
March 2023
Temporary files
Database
Events: Update storage of events structures: The fields "channels" and "notes" are now allowed to be empty. This can save Gb of storage and long minutes of loading when working with recordings including hundreds of thousands of events (e.g. single neuron spiking activity). February 2023
FEM anatomy
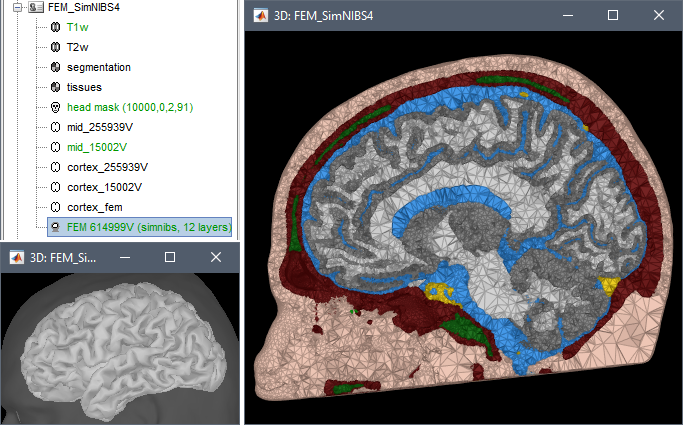
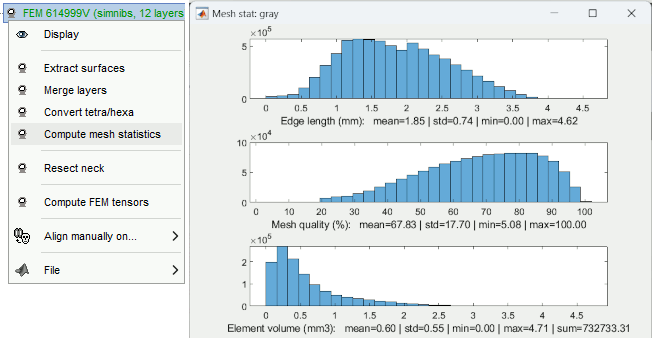
Statistics
Input / output
January 2023
Anatomy
Software distribution
Interface
November 2022
Leadfield sensitivity
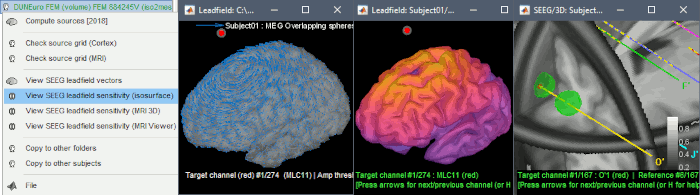
BIDS import
MNI normalization
September 2022
ICA analysis
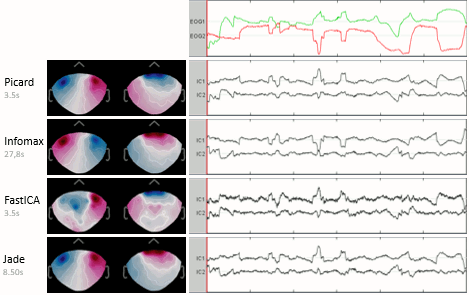
Coregistration
Color-coded distance: When checking visually the registration between the sensors and the anatomy, a new option allows to color the digitized head points based on the distance to the scalp surface. This can help identify and fix manually coregistration issues. More information. 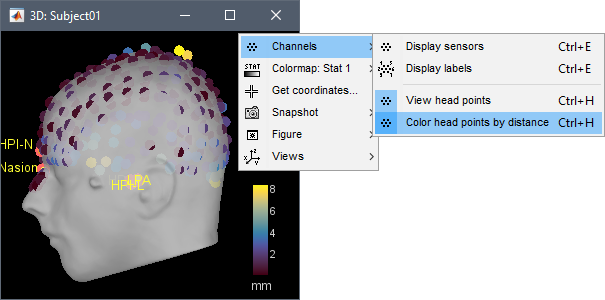
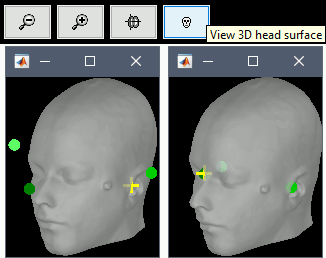
Input / output
June 2022
Connectivity graph
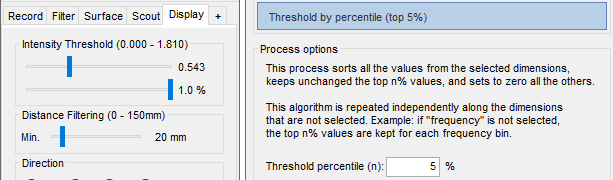
Anatomy
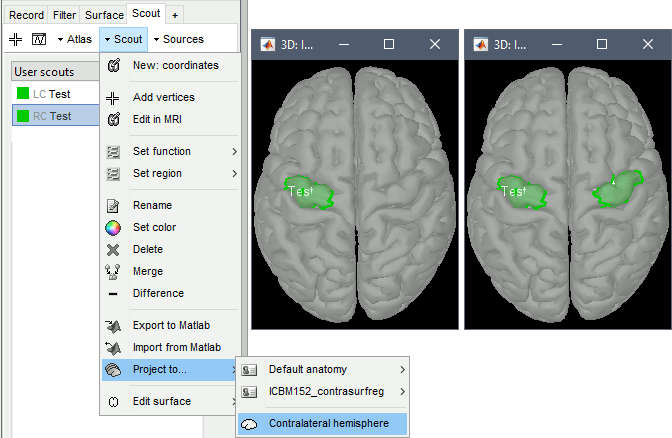
BIDS
April 2022
Electrophysiology
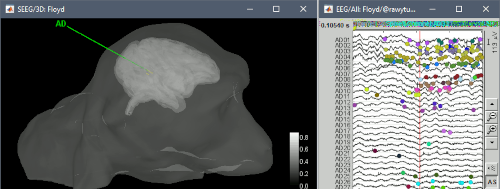
Input / output
February 2022
Connectivity
Anatomy
January 2022
SPRiNT: Time-resolved spectral parameterization
Spectral Parameterization Resolved in Time (SPRiNT) 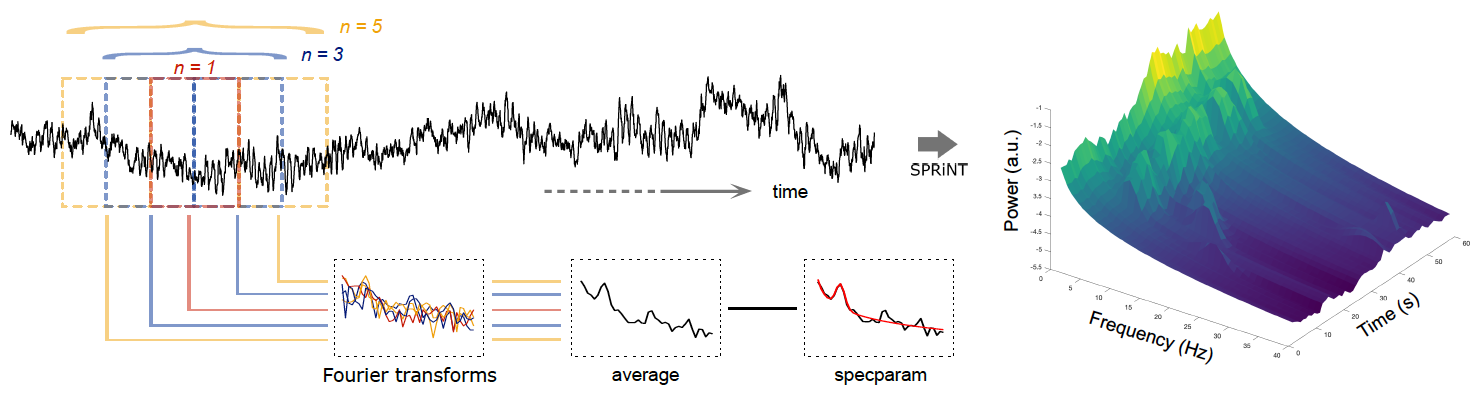
Plugins
Archives the software environment in one zip file, including installed plugins and templates. Statistics
December 2021
Input / output
November 2021
MRI segmentation
New plugins
MIA: Group statistics on SEEG data, see the website. Automatic registration
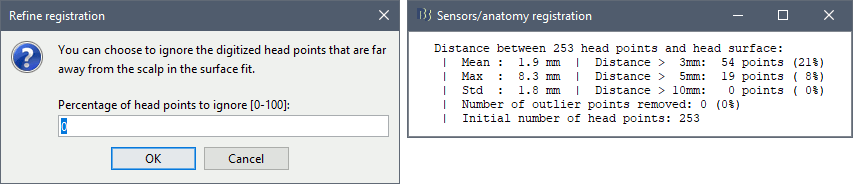
Send reports by email
October 2021
Major bug fix: PCA
Brainstorm compilation
September 2021
iEEG anatomical labels
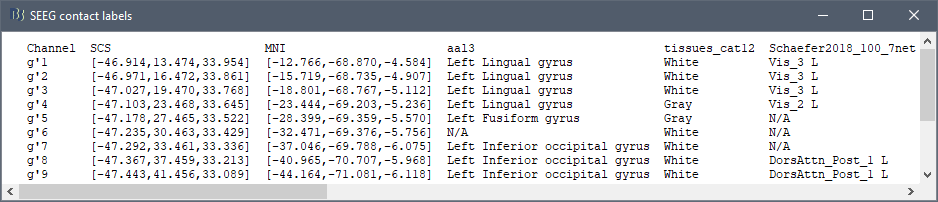
August 2021
FEM tutorials

July 2021
Coherence
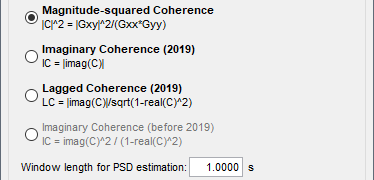
Inverse: FieldTrip DICS
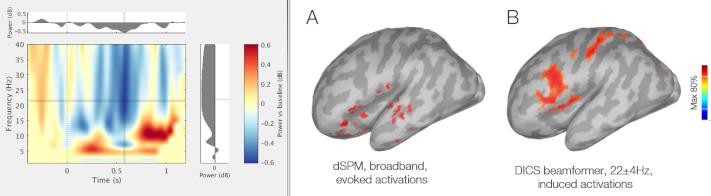
June 2021
Connectivity graphs
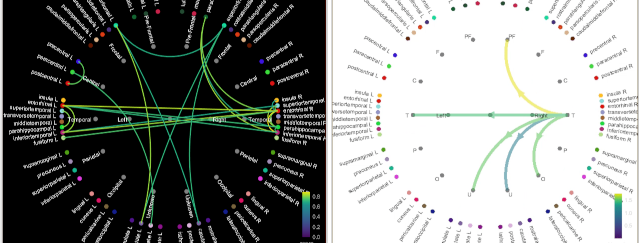
May 2021
Anatomy
Input / output
March 2021
Compiled distribution
February 2021
Plugin manager
Input / output
December 2020
MNI normalization
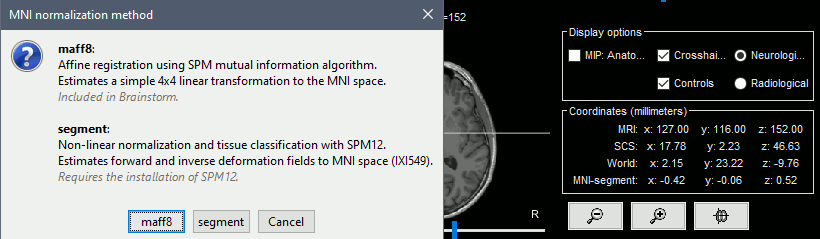
Volume parcellations
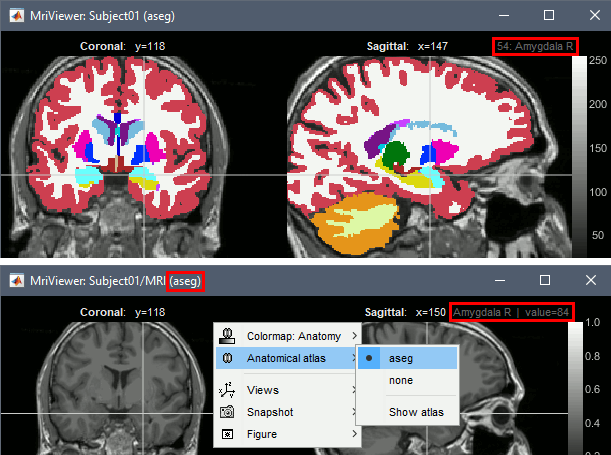
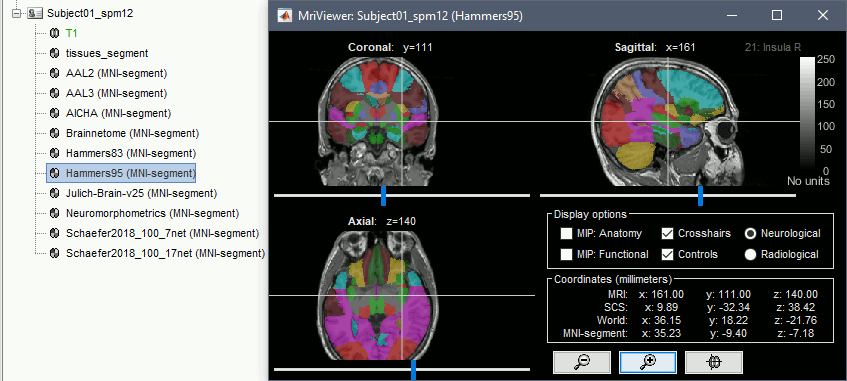
Anatomy
November 2020
MNE-Python
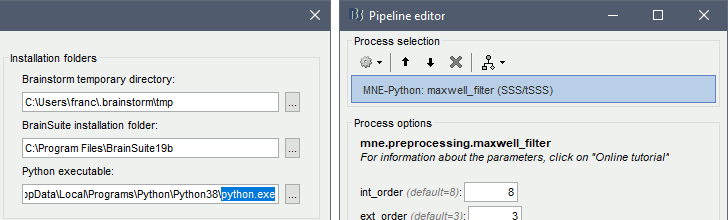
Extensions
October 2020
Major change: Power spectrum computation (PSD)
September 2020
Simulations
Spectrum analysis
Fitting oscillations and one-over-f (FOOOF) 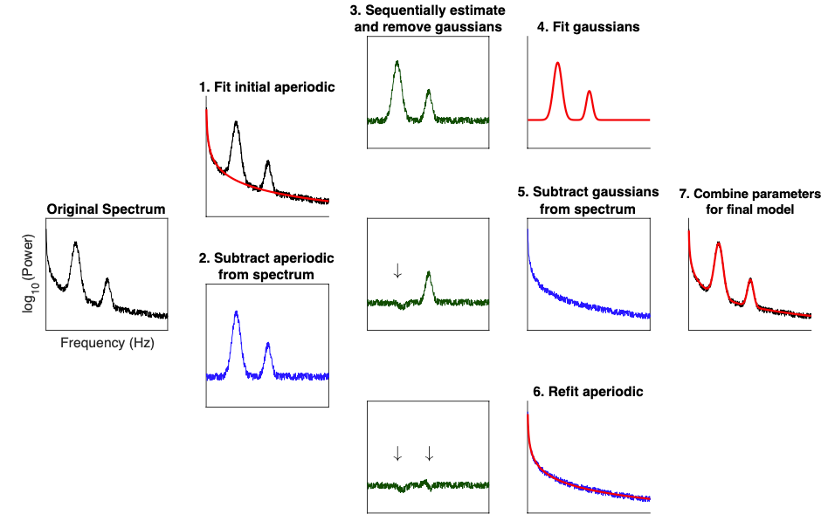
August 2020
2D surface projection
Connectivity
Envelope correlation. It will be document as part of the new Connectivity tutorial, which is still under construction for the moment. Input / output
July 2020
Infant anatomy templates
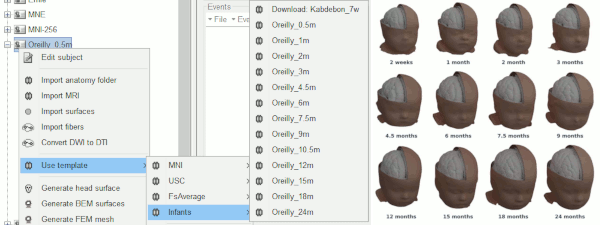
FEM: Use of conductivity tensors
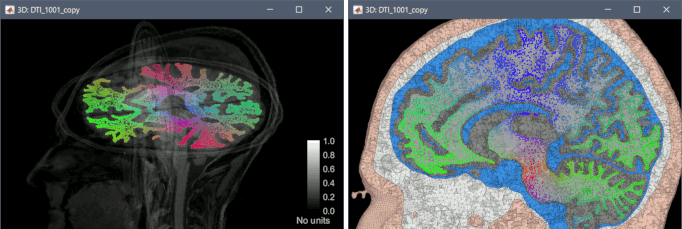
May 2020
Machine learning / Decoding
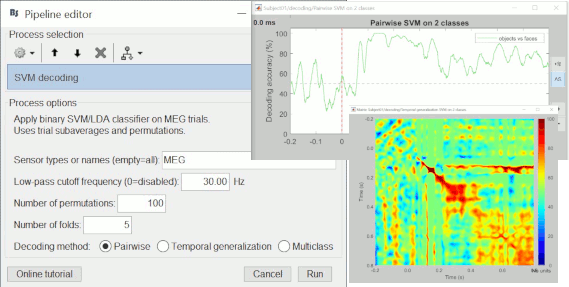
Input / output
April 2020
FEM forward modelling with DUNEuro
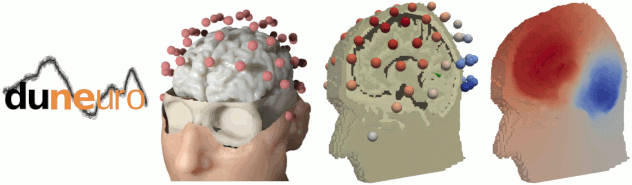
View leadfield vectors
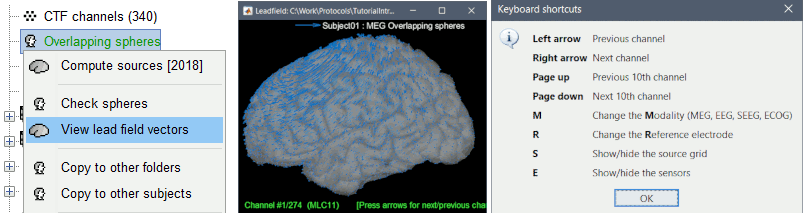
March 2020
Anatomy
Distribution
January 2020
Database search interface
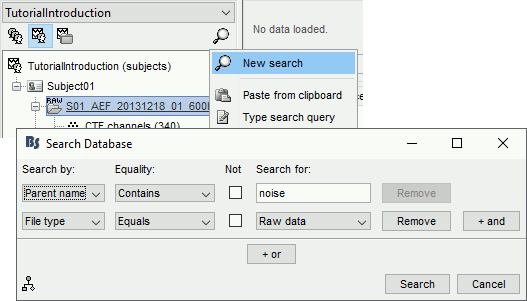
3D mesh generation for FEM
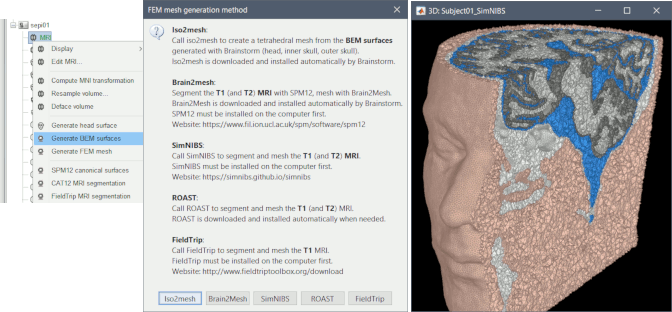
Input / output
October 2019
Recordings
Montage editor: New option to filter each signal in a specific frequency band: see tutorial
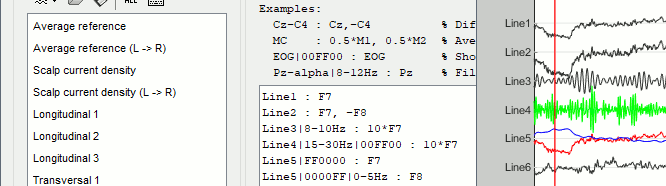
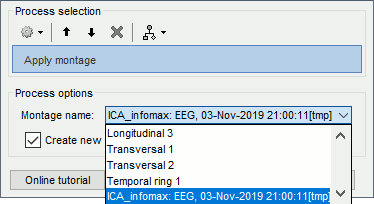
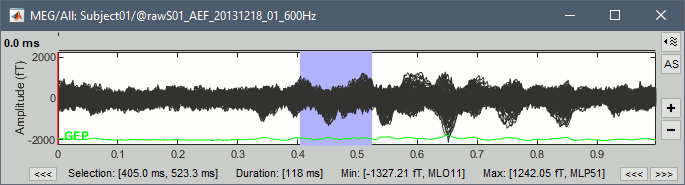
Interface
September 2019
Anatomy
Input / output
MNE-Python objects (Raw, Epoched, Evoked) July 2019
MRI segmentation with CAT12
Averaging: API modification
dSPM averages: Scaling with number of averages
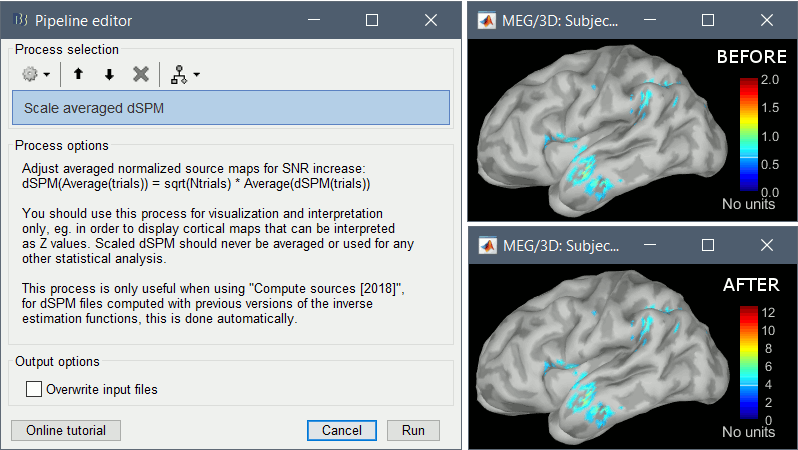
June 2019
BrainVISA: MarsAtlas parcellation
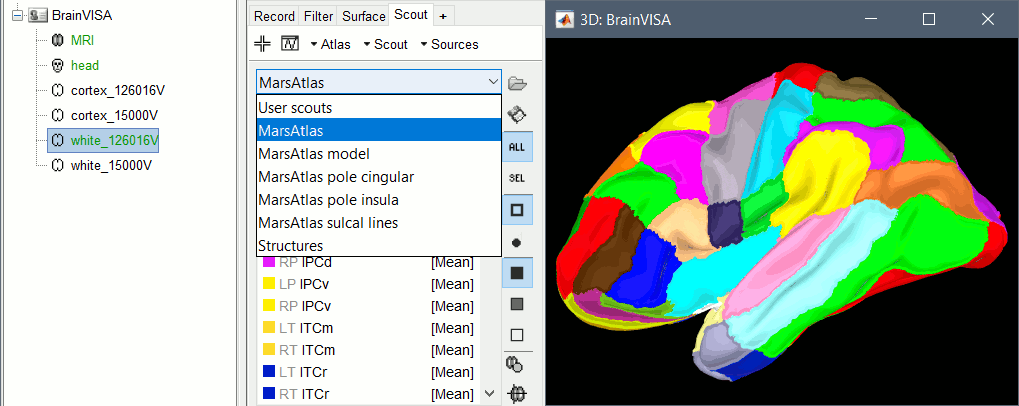
Input / output
May 2019
Events display
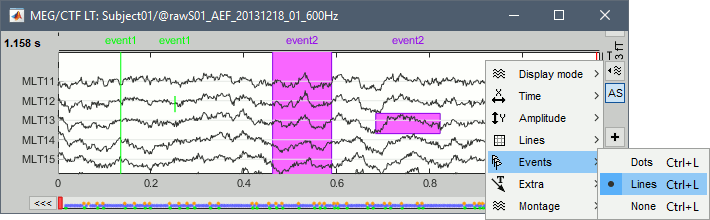
Events shortcuts for sleep staging
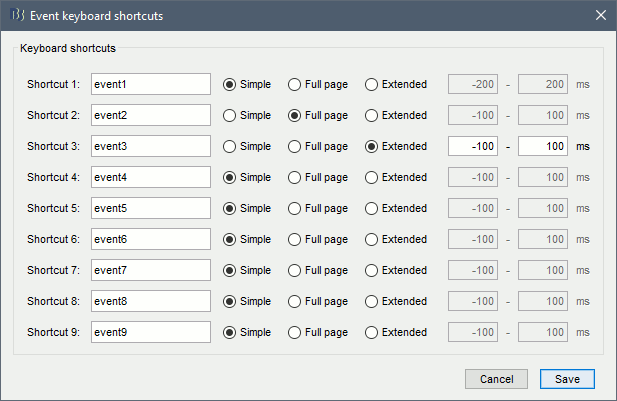
Decoding processes for more than 2 conditions
Fiber viewer for connectivity visualization
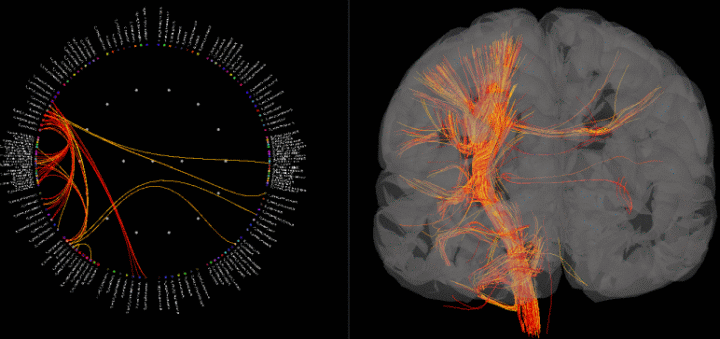
April 2019
New default colormaps

New ECoG/sEEG tutorial
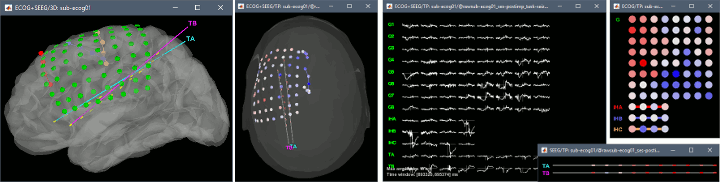
Programming: Field "samples" removed
March 2019
Anatomy

Video-EEG
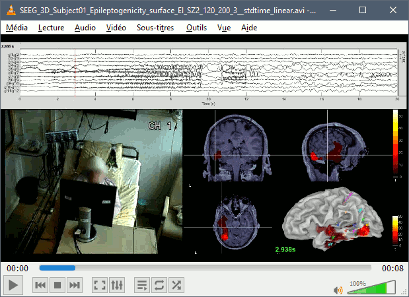
EEG and iEEG
2DLayout and 2DElectrode
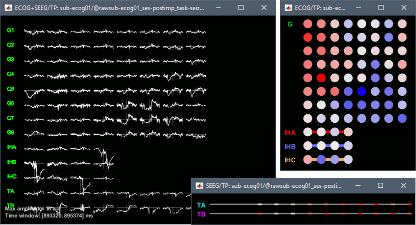
February 2019
Processes
Input/output
Distribution
January 2019
Input/output
Interface
November 2018
New Invasive Neurophysiology toolbox
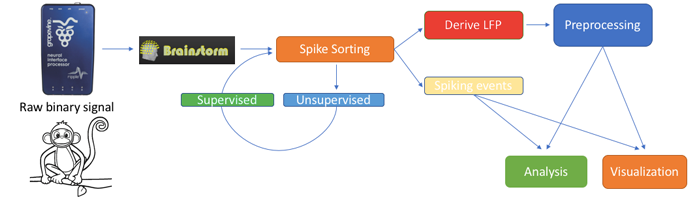
Display multiple files with 2DLayout
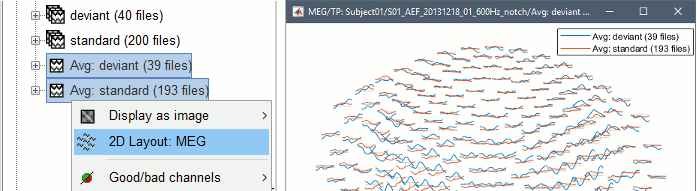
September 2018
Input/output
July 2018
Updated dSPM 2018
dSPM values are no longer scaled by number of trials. See source tutorial. Interface
Headless mode: Brainstorm now runs without any rendering capability, allowing the execution of scripts on distant servers and computation clusters that do not have any display attached to them. Adding snapshots to the execution reports is still possible. Start your script with "brainstorm server". Anatomy
April 2018
Input/output
ICA cleaning
March 2018
SEEG/ECOG
Bug fixes
February 2018
Anatomy
Source modeling 2018
January 2018
Input/output
RICOH MEG file format Processes
November 2017
New tutorial: SEEG epileptogenicity maps
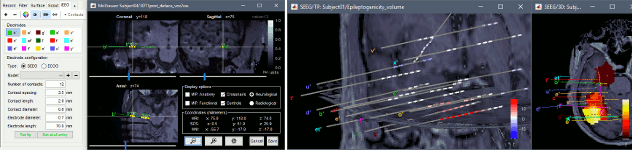
Bug fixes
October 2017
Anatomy
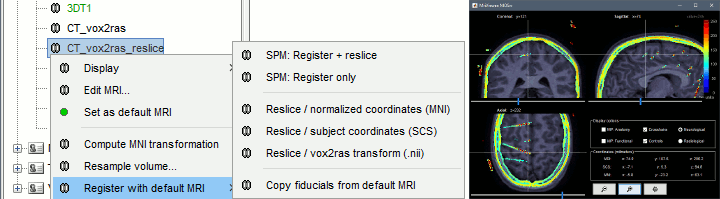
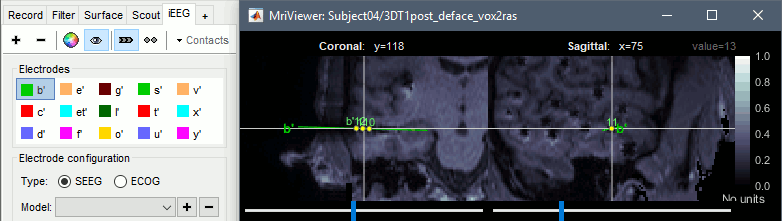
SEEG/ECOG
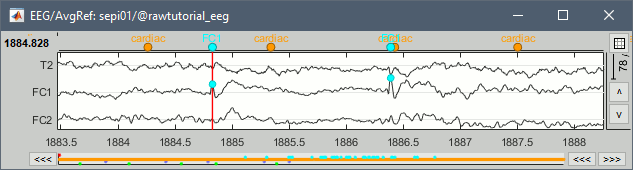
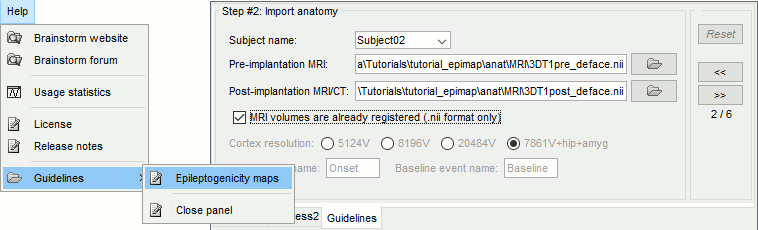
September 2017
Elekta: Major workflow changes
Input/output
DICOM converter (SPM-based): Use menu "Import MRI" and select file format "MRI: DICOM" August 2017
New processes
July 2017
Anatomy
subject or MNI coordinates
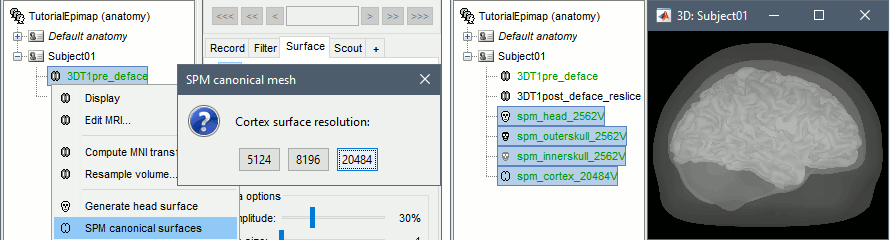
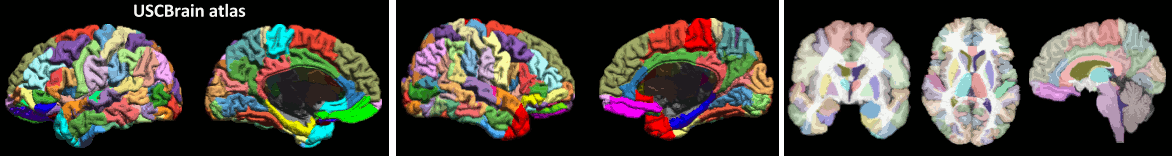
Recordings viewer
Support for high-resolution screens
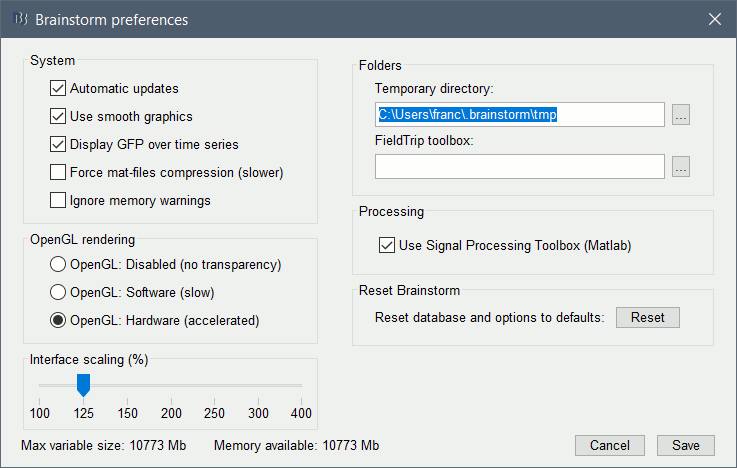
May 2017
New file formats
Major bug fixes
April 2017
New display for ECoG and sEEG
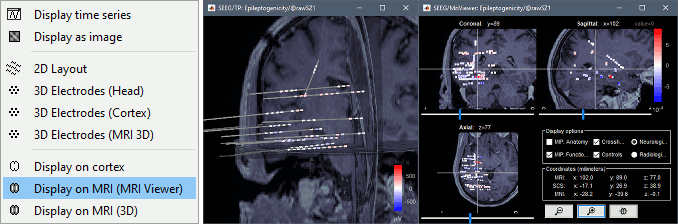
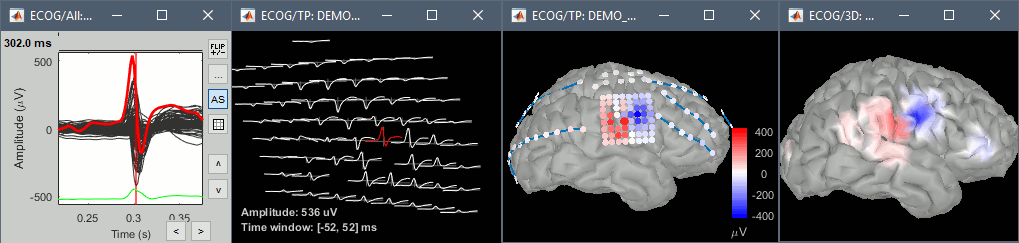
Default fiducials from MNI template
March 2017
New file formats
Other improvements
January 2017
New tutorial: Human Connectome Project (MEG)
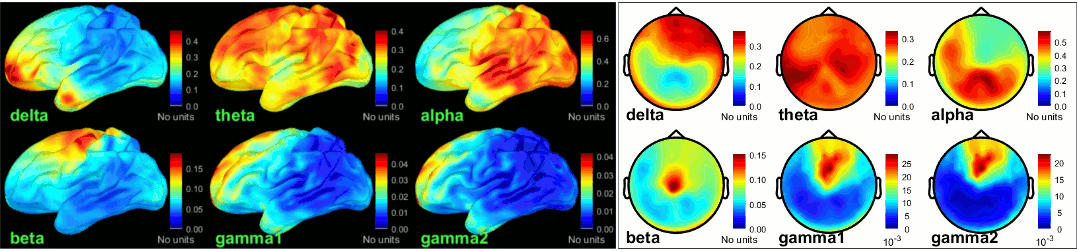
November 2016
New tutorial: OMEGA database & resting state (MEG)
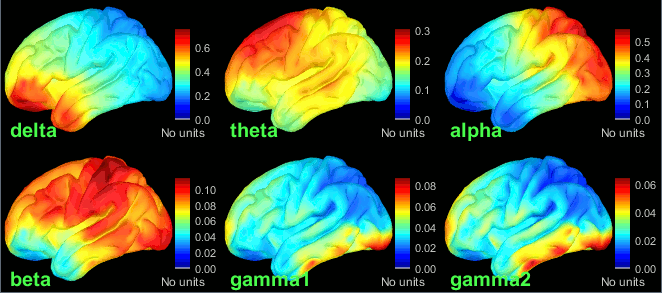
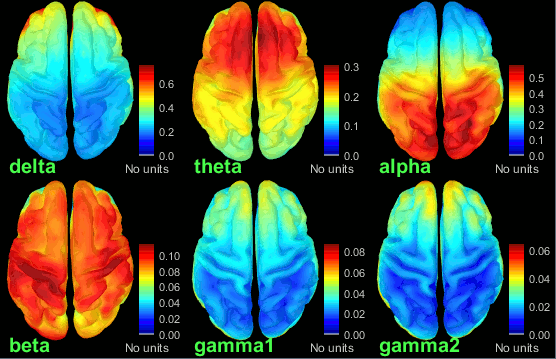
BIDS specification
Volume atlases
scouts for volume source models: See Volume source estimation.
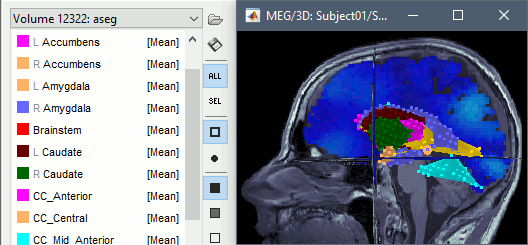
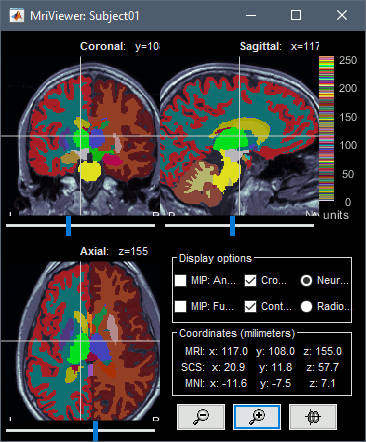
Volumes in MNI space
scouts for volume source models.
CT-MRI coregistration
Extended source space
Head grid: The source space can be extended to the full head volume, this can help decide whether some sources are brain signals or artifacts (eg. eye movements or neck muscles, as illustrated below). 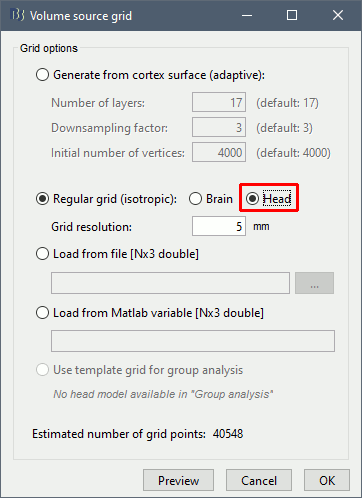
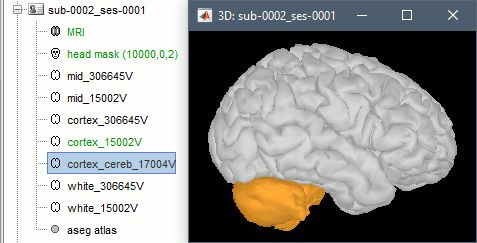
FieldTrip: Improved support
ft_volumesegment: MRI volume segmentation (scalp, skull, brain)
ft_dipolefitting: Dipole fitting for MEG and EEG recordings
Export to file > Look for the FieldTrip option in the file formats. October 2016
Brainstorm on GitHub
New band-pass filters
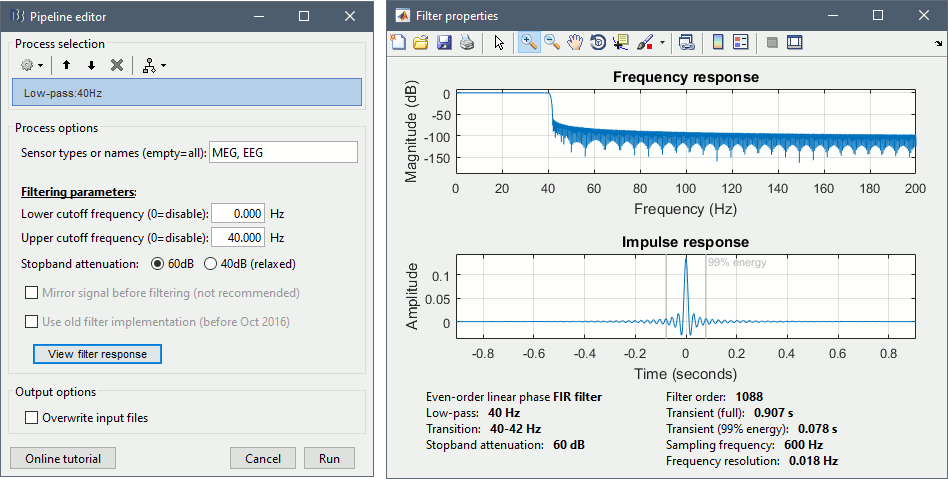
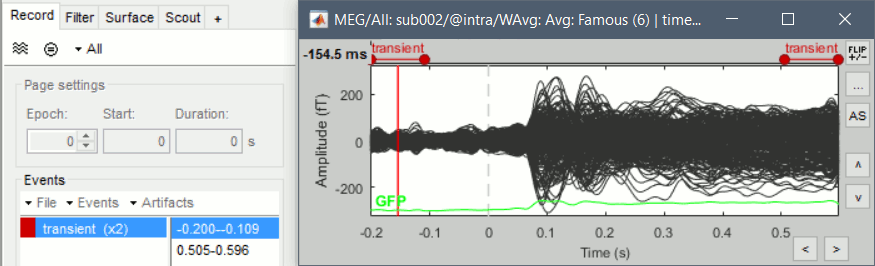
Other improvements
August 2016
2D topography plots
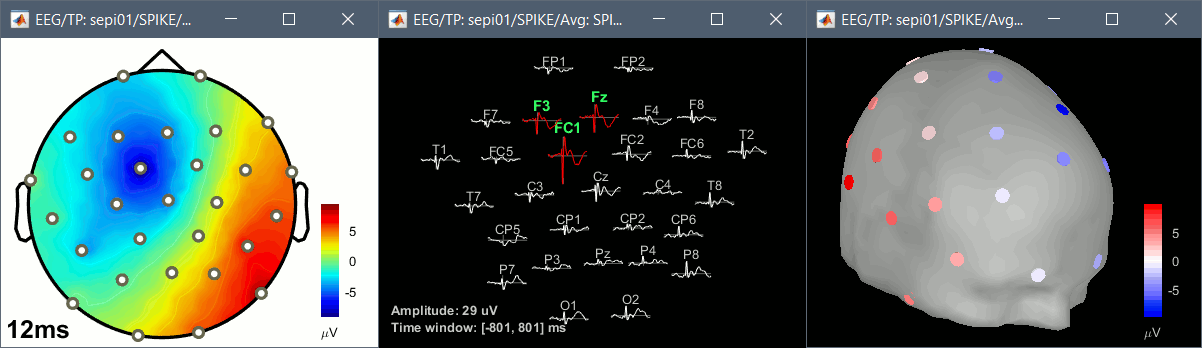
Mixed head models
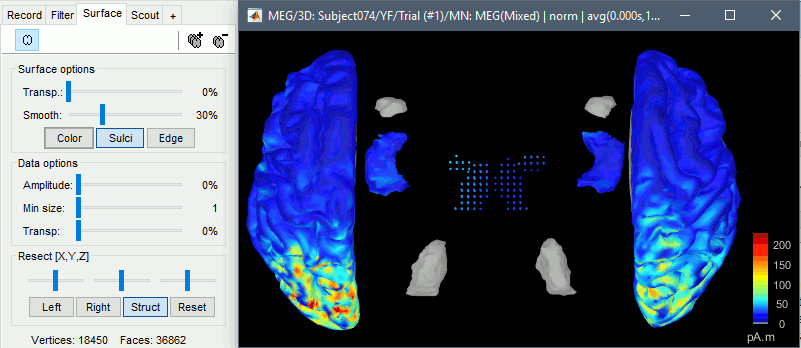
MRI coregistration
Resample MRI" to reslice any MRI volume.
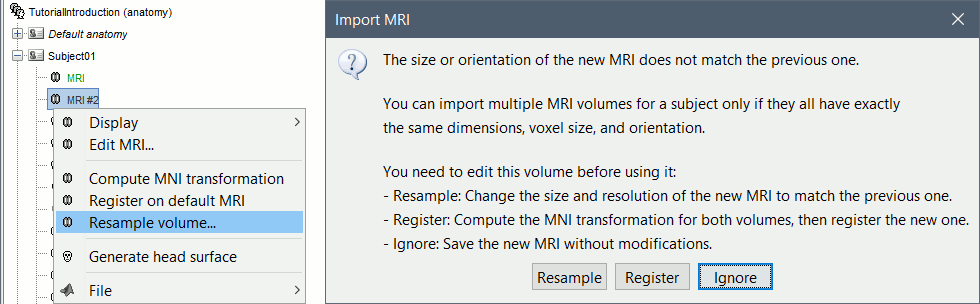
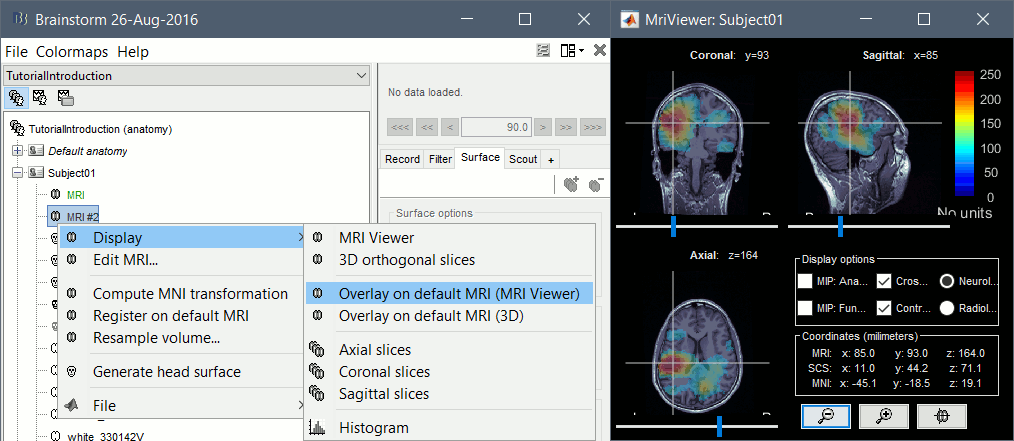
Updated advanced tutorials
July 2016
New tutorial: Group analysis
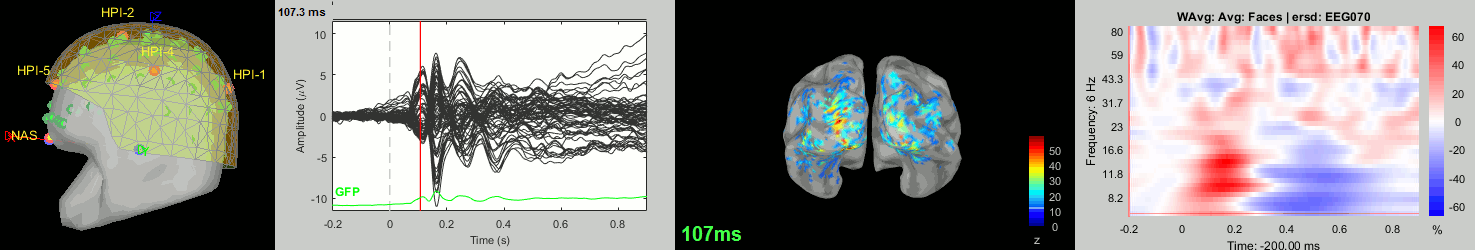
New tutorial: Scripting
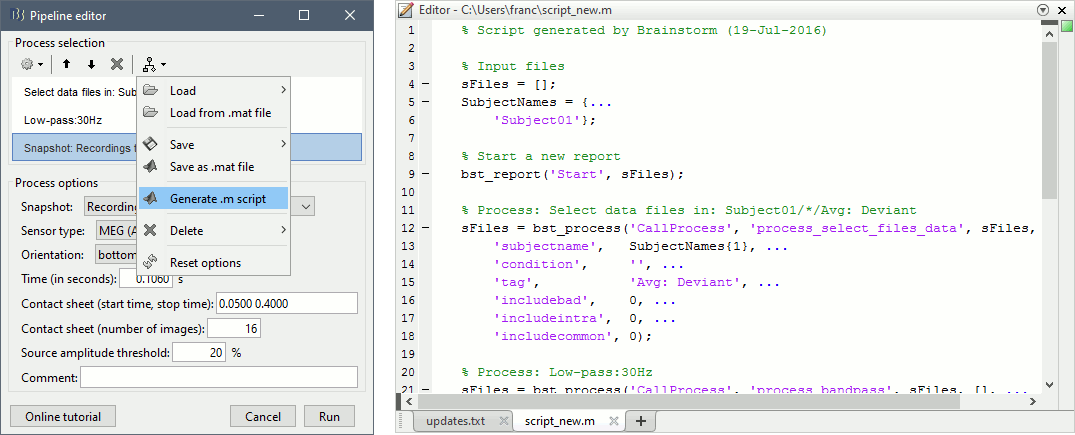
Volume sources
Anatomy: Defining the fiducials
June 2016
Continuous recordings
Copy to database": Copies a native continuous file to the protocol folder, in order to make the database portable between computers. Statistics
Default EEG caps
May 2016
New tutorial: fNIRS
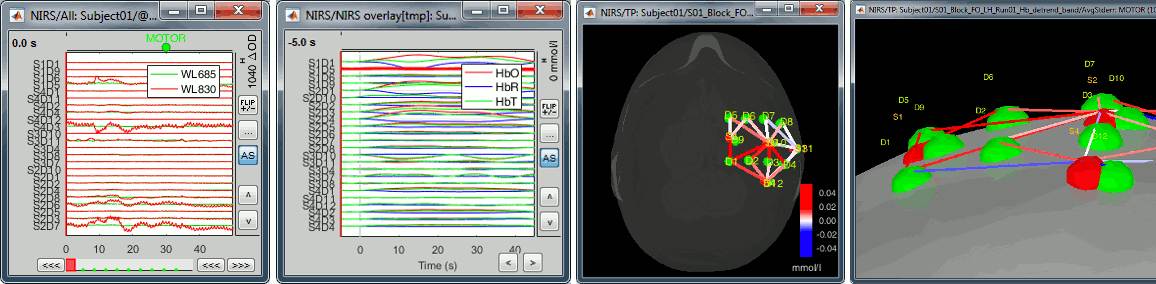
New tutorial: Elekta phantom
MEG current phantom (Elekta) 
Baseline normalization
Standardize > Baseline normalization" that replaces two existing processes: "Z-score normalization" and "Event-related perturbation (ERS/ERD)"
Source estimation tutorial (normalization). Recordings viewer
Min/max: You can now quickly get the minimum and maximum values in the recordings by simply selecting a time segment. If some channels are selected, it shows the extrema only for them.
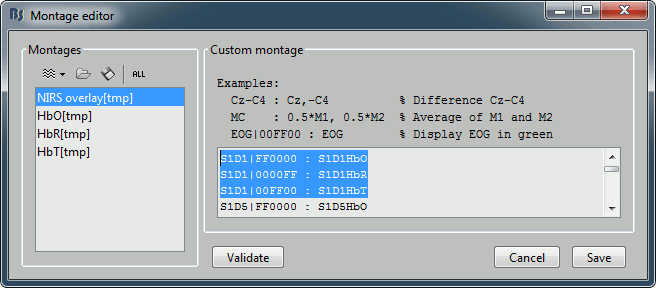
Time-frequency
April 2016
Major bug fix: BrainAmp
Scouts: Sign flip
Source modeling
Save whitened recordings: New menu available when right-clicking on source files in the database explorer. It shows how the recordings are actually used in the minimum norm source estimation, after the pre-whitening computed based on the noise-covariance matrix. If this doesn't look correct, you might think about changing the options for the noise covariance regularization (increasing or decreasing the amount of regularization. Dipoles
March 2016
Input / output
Distribution
February 2016
Major bug fix: MEG reference sensors
For more accurate results, re-import the recordings and compute a new forward model.
(waiting for tests from any site with a 4D system)
Similar menus available for 4D and Elekta-Neuromag systems.
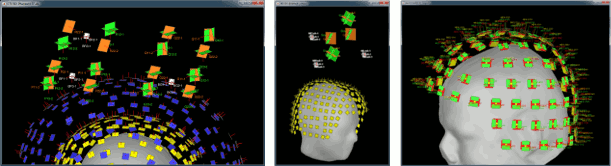
Anatomy
Parametric statistics
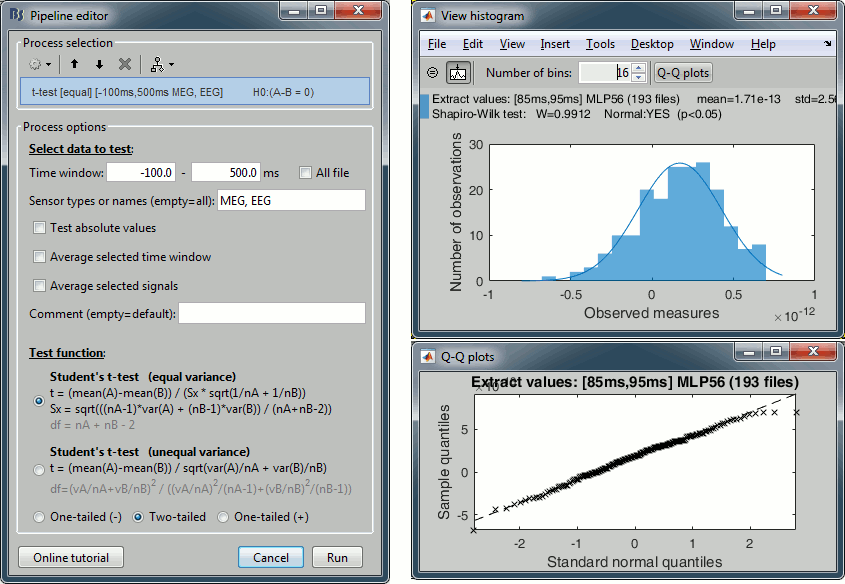
January 2016
Display as image
[Trials x Time] Right-click on a group of trials > Display as image: Raster plot for the values of one sensor across the trials. Change the channel from the Display tab (or up/down arrow key).
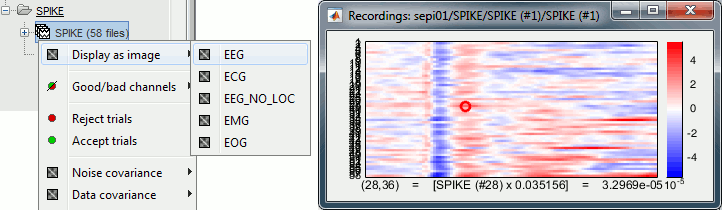
Shows the same information as the "time series" view, but with colors instead of lines.
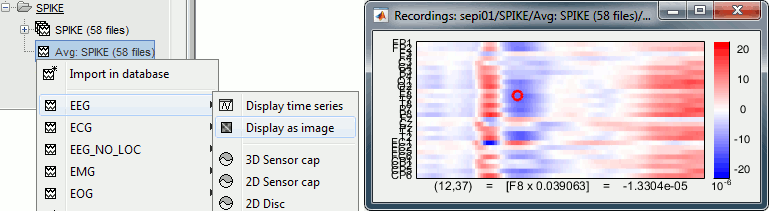
Synchronization with an eye tracker
See tutorial: Synchronization with eye tracker. November 2015
Documentation
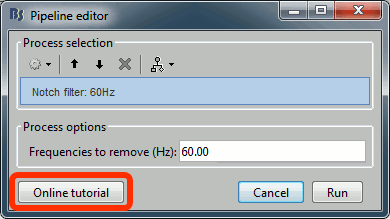
Input / output
Microstate segmentation
October 2015
New processes
Histograms
September 2015
New introduction tutorials
Input / output
Source modeling
Anatomical registration with BrainSuite
August 2015
FieldTrip statistics
ft_timelockstatistics, ft_sourcestatistics, ft_freqstatistics
New anatomy template: One year old infant
Use template > Download: Oreilly_1y. Project scouts between subjects
In the Scout tab, this is available in the menu Scouts from MNI coordinates
In the Scout tab, this is available in the menu Z-score normalization
July 2015
New inverse functions
Artifact detection
Decoding and MVPA
Resolving human object recognition in space and time, Nature Neuroscience, 17:455–462. Custom colormaps
June 2015
Standard deviation/error
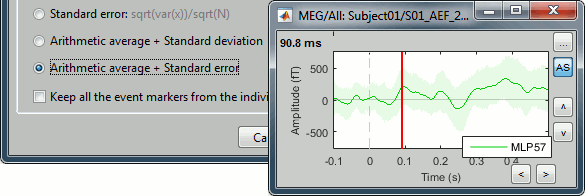
Synchronized videos
> File > 
April 2015
Major bug fix: dSPM
where nAvg is the number epochs that are were averaged to compute the average. MNI coordinates
Ashburner J, Friston KJ, Unified segmentation, NeuroImage 2005 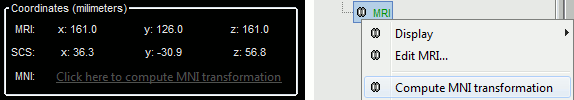
New processes
Input / output
March 2015
EEG: Artifact cleaning with ICA
EEG: Montage editor

EEG: Permanent re-referencing
February 2015
Intra-cranial recordings
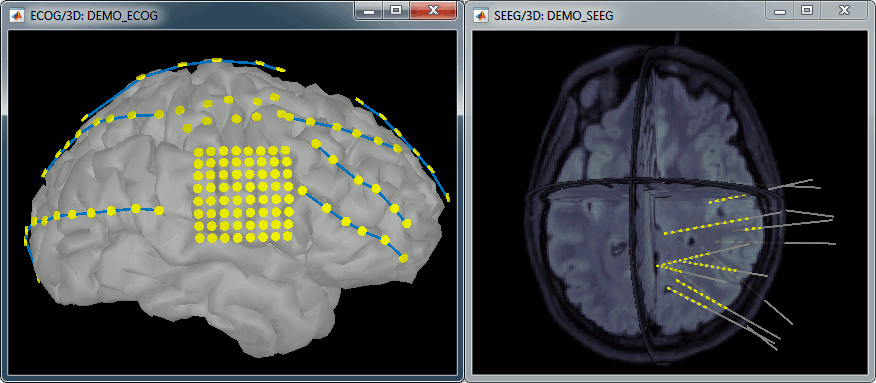
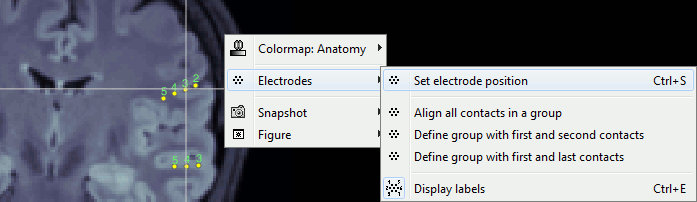
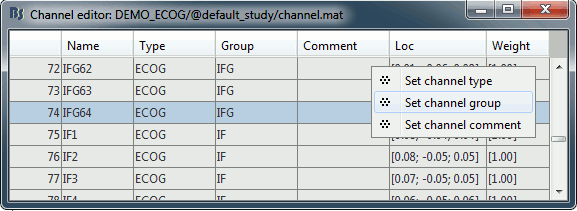

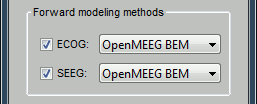
January 2015
Major bug fixes
New supported file formats
New processes
December 2014
New processes
Standardize > Spectrum normalization: Corrects for 1/f decrease in power in TF and PSD results. November 2014
Changes in scout processing
October 2014
New anatomy template: Infant 7 weeks
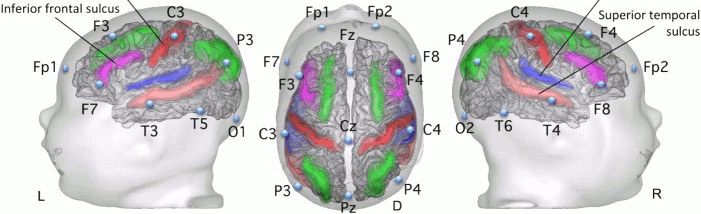
EEG electrodes positions
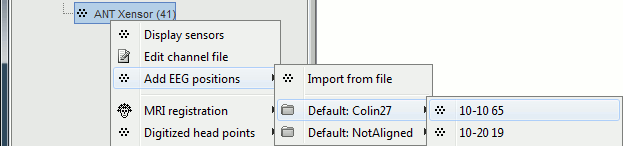
Brain Entropy in space and time
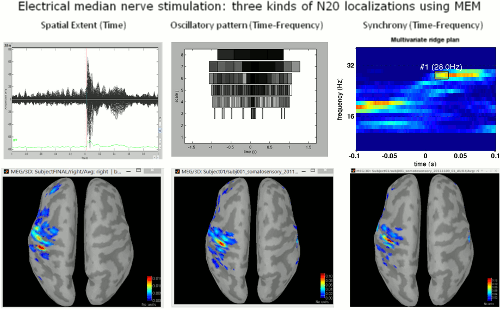
Data export
September 2014
Filtering continuous files
Brainstorm binary, extension .bst), regardless of the original file format. The values in this file are saved in floating point double precision to avoid the re-conversion to integer 16bit needed to save CTF of FIF files, which cause significant loss of data quality. August 2014
MEG auditory tutorial
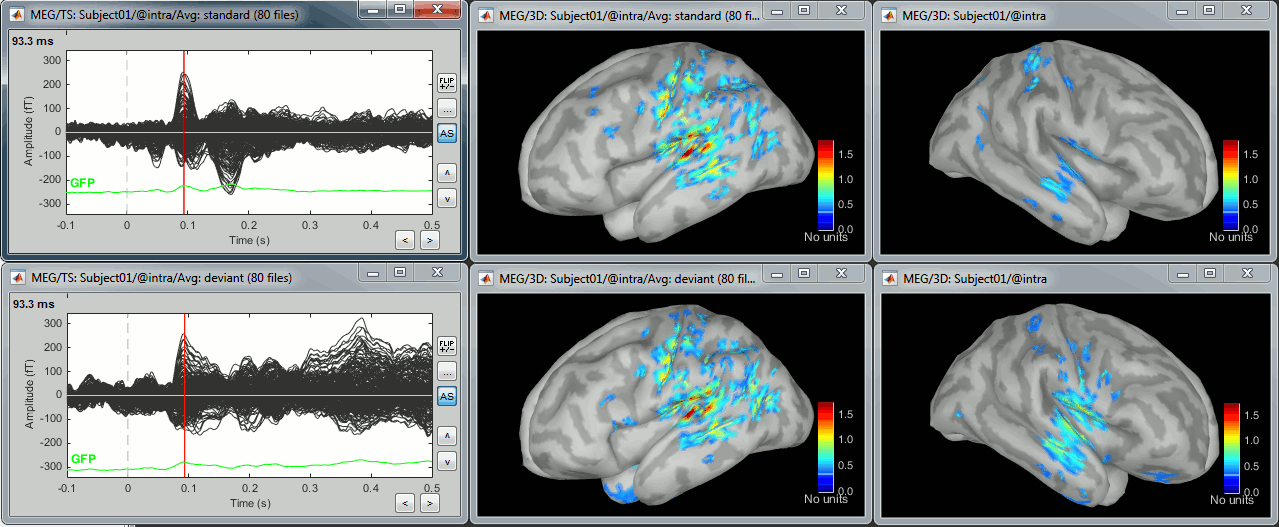
July 2014
New processes
Interface improvements
June 2014
Resting-state MEG and phase-amplitude coupling
Canolty RT, Edwards E, Dalal SS, Soltani M, Nagarajan SS, Kirsch HE, Berger MS, Barbaro NM, Knight RT,
High gamma power is phase-locked to theta oscillations in human neocortex
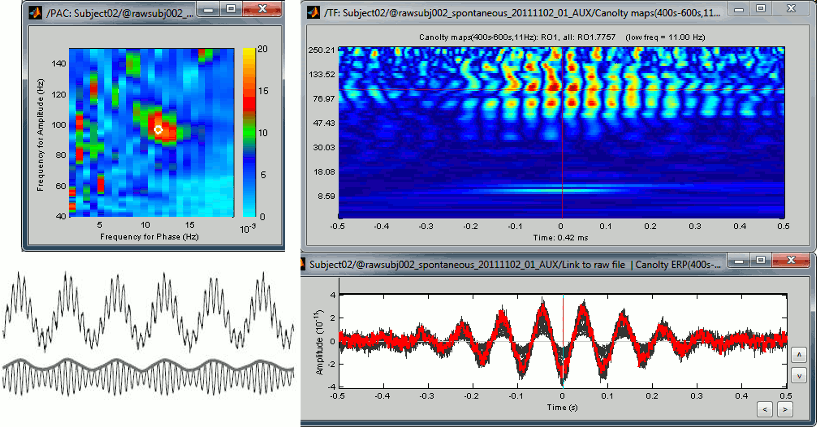
Elekta-Neuromag tutorial
May 2014
New processes
Other improvements
April 2014
Mixed head models
3D scouts
March 2014
Yokogawa tutorial
Yokogawa/KIT tutorial New processes
February 2014
EEG and epilepsy
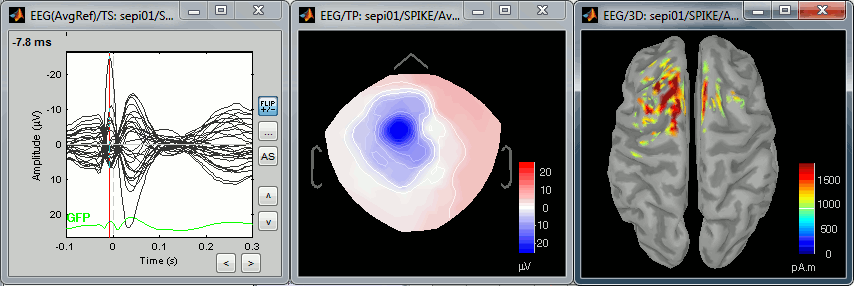
January 2014
Montage interface
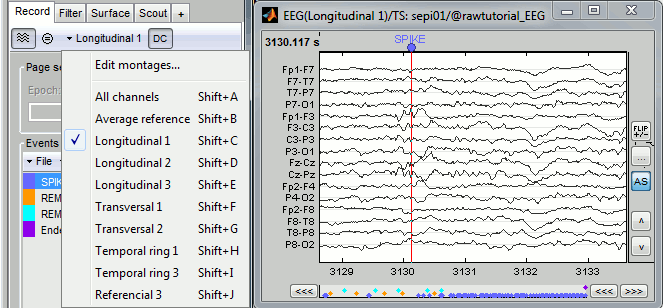
Average reference: SEEG and ECoG
The main problem with this approach is that this montage is not used during the source reconstruction procedure. When possible, always consider the second option. 
Signal viewer improvements
Flip +/- button: Exchange the direction of the Y axis, useful in clinical EEG Desktop management
The menu "Window layout options" can help you organize all the opened figures in an efficient way. There are four options for the automatic placement of the figures on the screen, and you can also save your own specific working environment with the new menu
See tutorial: Exploring the recordings 
Colormaps
See tutorial: Exploring the recordings 
December 2013
Filter files by name or comment
See tutorial: Selecting files in the database. 
New supported file formats
Other improvements
November 2013
New processes
October 2013
New tutorial: How to write your own plugins
September 2013
Find Brainstorm users next to you
Brainstorm and SPM
Export volume source maps to SPM8
Export surface source maps to SPM8/SPM12. 
August 2013
Using FreeSurfer for the subject coregistration
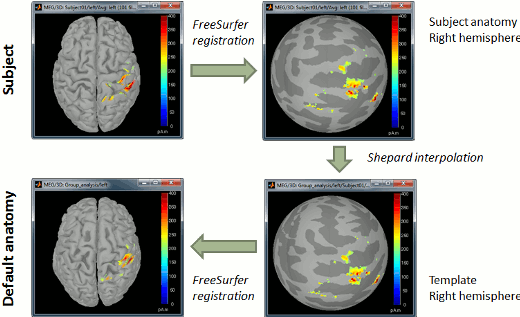
July 2013
FreeSurfer subcortical atlas and cortical maps
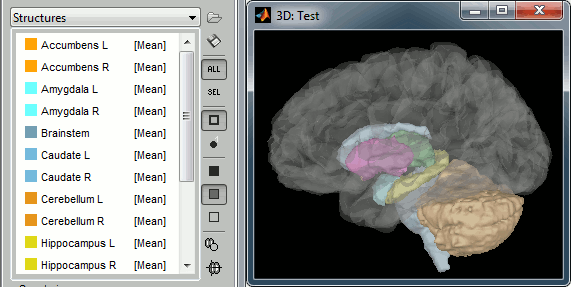
New anatomy templates
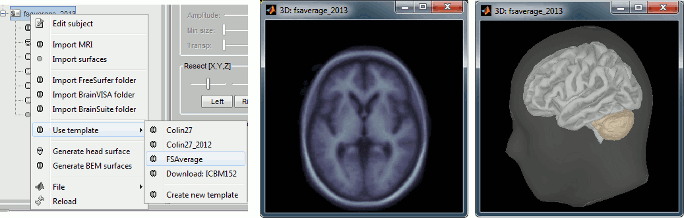
MRI segmentation: CIVET
Join the Brainstorm user community
Brainstorm movie studio
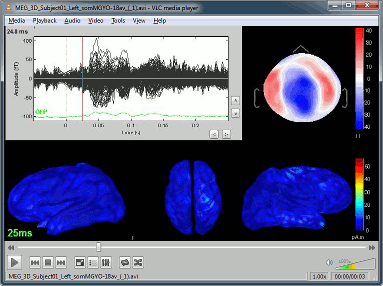
May 2013
MRI segmentation: BrainSuite support
New processes
April 2013
Event markers in the imported recordings
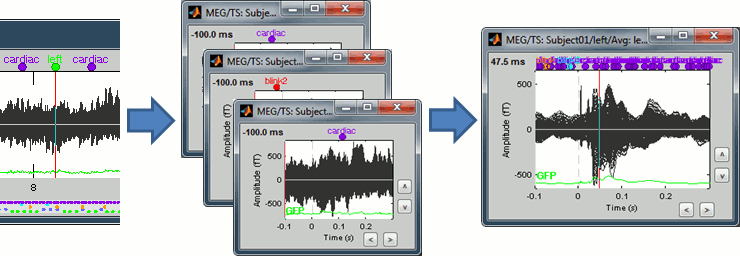
Dynamic Z-score
March 2013
Phase-amplitude coupling
"High gamma power is phase-locked to theta oscillations in human neocortex", Science, 313(5793):1626-8. 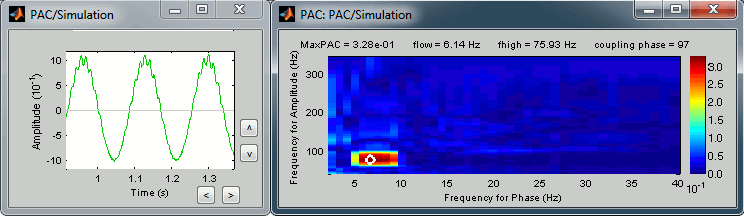
Multiple MRI volumes

Process: Run Matlab command
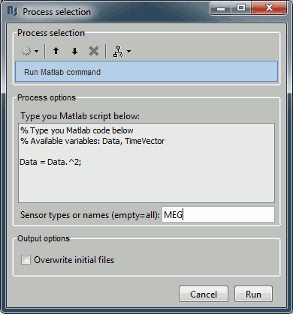
CTF/Neuromag dipole estimation
February 2013
Intra-cranial EEG
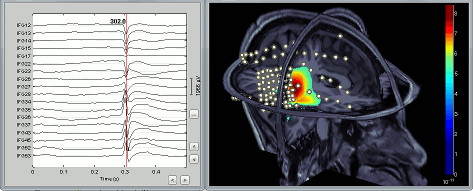
Yokogawa/KIT MEG recordings

Figure layouts
Save surface snapshot
January 2013
Documentation
Report viewer: reload a pipeline
Processing continuous FIF files
Copy of the noise covariance
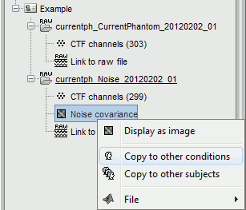
MRI registration: joining interactive and automatic methods
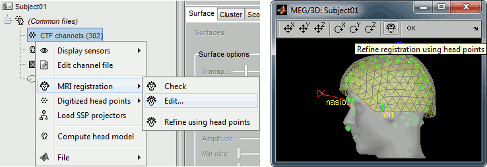
Subdivide scouts
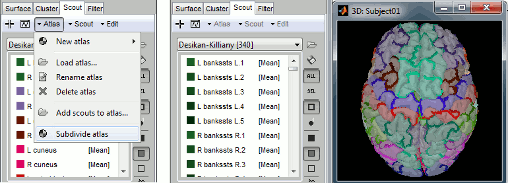
December 2012
FreeSurfer and BrainVISA
More details: Freesurfer and BrainVISA. 
Importing MRI masks
New file types supported
November 2012
Updated topography plots
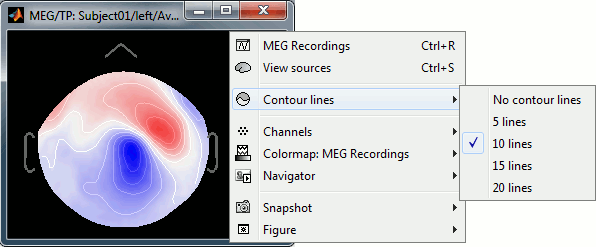
New processes
Miscelanous
October 2012
New interface for the scouts
?Tutorials/TutScouts
?Tutorials/LabelFreeSurfer 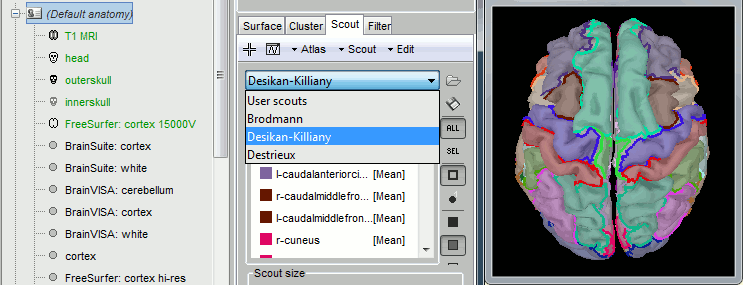
Project sources to an atlas
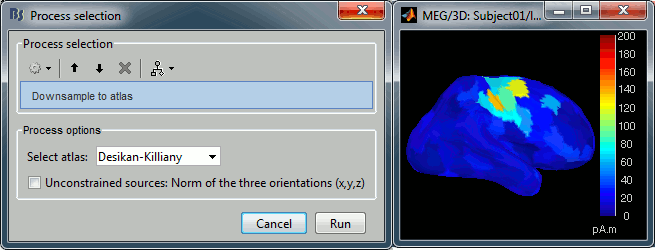
September 2012
Support for Biosemi BDF files
Support for MANSCAN files
August 2012
Drive your Polhemus from Brainstorm
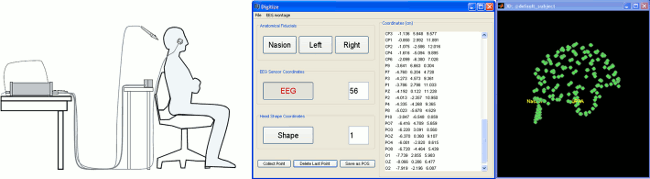
June 2012
Graphical batching interface: final version
April 2012
Matlab 2012a
New processes
Events > Combine stim/response: Create new categories of events to group the markers by pairs (stimulus / response) March 2012
Frequency analysis
Fast Fourier Transform (FFT)
Power: Most common measure to represent the power of a signal for a given frequency bin Improvements made to the continuous viewer
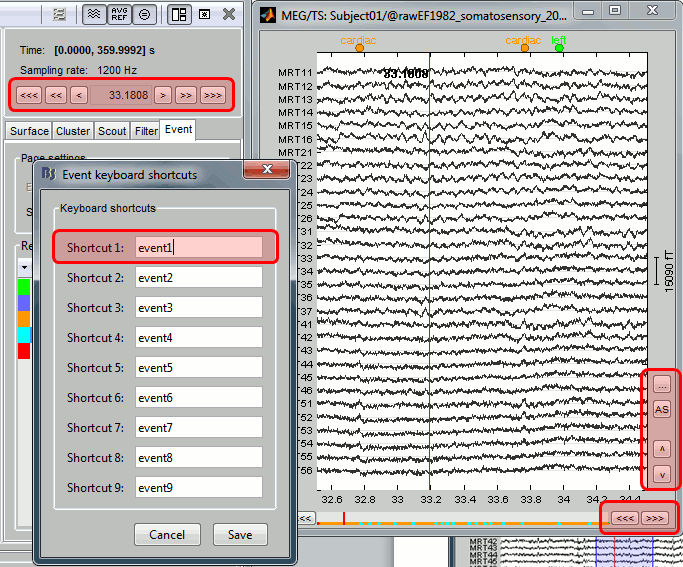
February 2012
Artifact removal with SSP
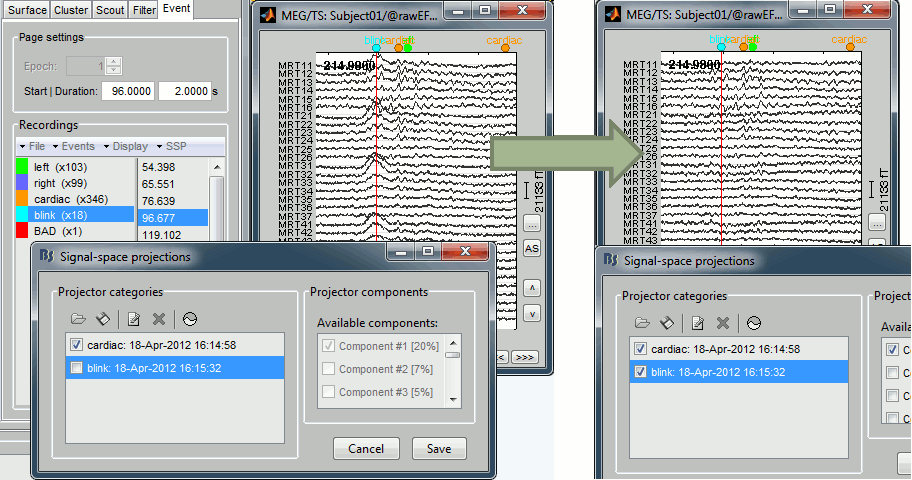
Co-registration of MEG runs
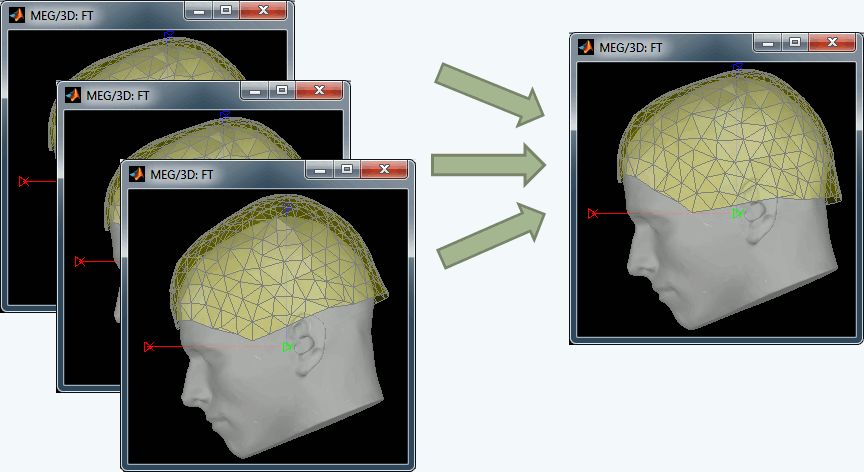
January 2012
Import FreeSurfer cortical parcellation
Import Nifti-compressed MRI images
Improved user interface for time series visualization
December 2011
Brainstorm on Facebook!

November 2011
New tools for artifact detection and correction
Stand-alone distribution for Linux and MacOSX
Brainstorm course in Montreal
May 2011
Brainstorm reference article
Improvements in navigating the database
No MRI for your participants?
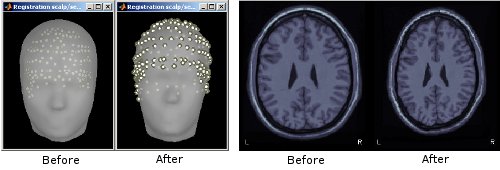
Refine MRI/MEG registration using digitized scalp points
April 2011
Realistic boundary-element-modeling (BEM) head models for EEG

Source estimation in full brain volume
March 2011
Combined MEG/EEG source reconstruction
Display of source maps in MRI volume
December 2010
Statistical inference: correction for multiple comparisons
Graphical batching interface
September 2010
Continuous/RAW file viewer and event editor
Detection of bad trials / bad channels
Estimation of the noise covariance from continuous files
Import/export protocols and subjects
June 2010
Time-frequency
Brodmann and Tzourio-Mazoyer atlases
Recordings visualization: 2D Layout
March 2010
Support for Xfit dipoles files
Minimum norm solution
Januray 2010
Project sources on default anatomy
Display channels in columns
December 2009
Automatic updates
